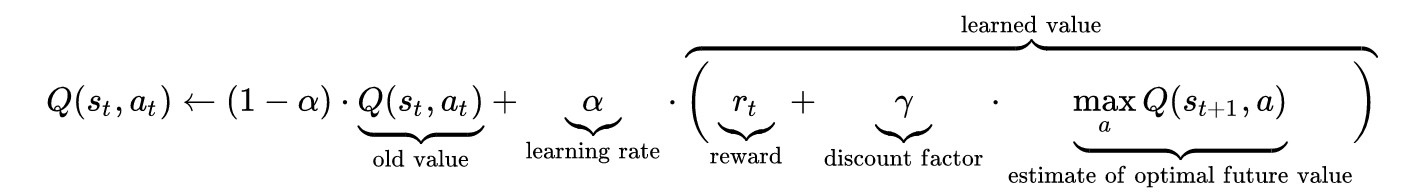This guide deals deep Q-Learning after a certain point and so the python codes are written assuming that anyone following this is familiar with basic python programming, how to develop models, and matrices manipulation, etc. If you are not upto date on the concepts, please refresh them before jumping in the code. The README, on the other hand, is written very thorougly, explaining all concepts from beginning, and can be easily followed by anyone.
For any query, please reach us at [email protected] or create a discussion!!!
This is a guide to help users get started with reinforcement learning. It will cover the following topics :
The ability of a machine to learn and improve from experience rather than explicit programming is termed as machine learning.
Types of machine learning :
✳️ Supervised
✳️ Unsupervised
✳️ Reinforcement
Reinforcement means encouraging a pattern or behaviour. This form of ML is a hit and trial method, because the model is new to the surroundings. The only way to learn is to experience and then, learn from that experience.
The main idea is to learn through a "Reward and Punishment" system. For every correct move, there is a reward, for every wrong one, there is a punishment. The model tries to maximise the reward.
It is to be noted that 'training' datasets are not present here. Neither the fed data is classified or labled. The model needs to figure out the path and the best approach to perform a certain task. The environment is also unknown to the agent.
Let's suppose a baby is learning to walk towards a box of chocolates. The box acts as reward. 2 things can happen here.
First, the baby starts walking and makes it to the box. This result is positive since the goal is achived, and hence the baby is rewarded.
Second, it starts walking but falls due to some obstacle. This is a negative result. Not only the goal isn't achieved, but the baby also got hurt. Hence, we can say that baby is punished.
There are 2 main components of the process, the learing agent, and the environment. The environment, just like in the real world, determines all parameters of larning. In programming, we call that algorithm.
The process starts when environment sends a state to the agent. The agent then takes an action on it. Based on the action taken by the agent, the environment sends the next state and the respective reward to the agent. The agent then updates its knowledge based on the reward and evalutes its previous action on it.
This goes on and on till the environment sends a terminal state.
⚛️ Reward Maximisation : The agent must be trained in a way, that it takes the best action in order to maximise the reward
⚛️ Exploration and Exploitation : The agent explores and captures more information about the environment, and then uses that information to highten the rewards
This process is a mathematical approach for mapping a solution in reinforcement learning. It can be assumed that, the purpose of reinforcement learning is to solve a Markov decision process. There are a certain number of parameters to get to the solution. They include :
- Set of actions (A)
- Set of states (S)
- Reward (R)
- Policy used to approach the problem (pi)
- Value (V)
The series of actions taken by the agent throughout the process, defines the policy. And the collection of rewards recieved defines the value. The goal is to maximise the rewards by choosing the optimum policy.
The idea of Q-learning, is to have "Q-values" for every action that a model takes, given a state. These values need to be updated overtime in such a way, that after a course of actions, good result is produced. It is done by "Rewarding" the agent.
Q-Learning is also known as "Model free learning" because the learning algorithm we write is applicable to any environment.
The Q-learning formula :
The codes of Q-learning are in continuation. Please proceed serial wise to understand everything, else, it will be very confusing as to why we are doing a certain step. For running the environment, we need a library called gym.
Installing gym -
sudo pip install gym
Or -
sudo python3 -m pip install gym
sudo pip install pyglet --upgrade
If, however, your machine does not have pyglet installed, please install the latest version for python3 -
sudo pip install pyglet
Or -
sudo python3 -m pip install pyglet
An example models directory and a logs directory has been attached for reference.
Now, you should go and check the following directories for programs based on reinforcement learning. All programs are daisy chained, so please go through them in sequence :
This tutorial is complete. Be sure to check out other ones too. Enjoy!!!