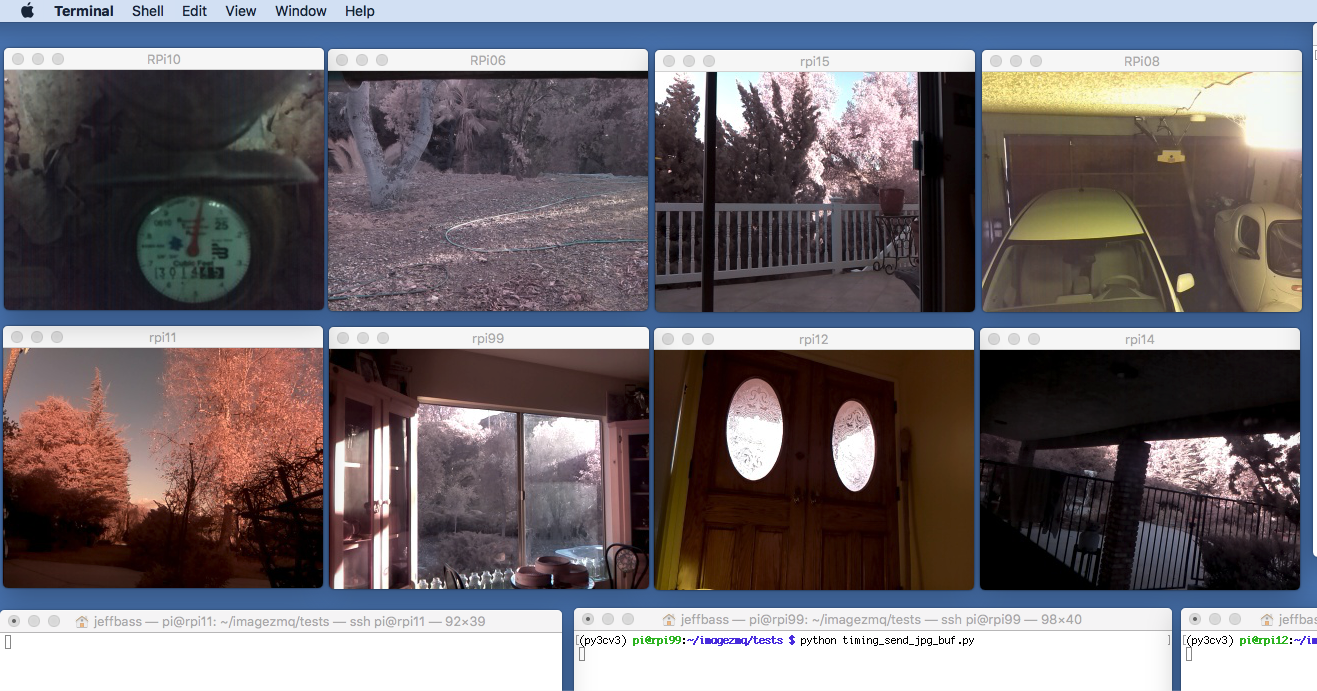
imagezmq is a set of Python classes that transport OpenCV images from one computer to another using PyZMQ messaging. For example, here is a screen on a Mac computer showing simultaneous video streams from 8 Raspberry Pi cameras:
Using imagezmq, this is possible with 11 lines of Python on each Raspberry Pi and with 8 lines of Python on the Mac.
First, run this code on the Mac (or other display computer):
1 # run this program on the Mac to display image streams from multiple RPis
2 import cv2
3 import imagezmq
4 image_hub = imagezmq.ImageHub()
5 while True: # show streamed images until Ctrl-C
6 rpi_name, image = image_hub.recv_image()
7 cv2.imshow(rpi_name, image) # 1 window for each RPi
8 cv2.waitKey(1)
9 image_hub.send_reply(b'OK')Then, on each Raspberry Pi, run:
1 # run this program on each RPi to send a labelled image stream
2 import socket
3 import time
4 from imutils.video import VideoStream
5 import imagezmq
6
7 sender = imagezmq.ImageSender(connect_to='tcp://jeff-macbook:5555')
8
9 rpi_name = socket.gethostname() # send RPi hostname with each image
10 picam = VideoStream(usePiCamera=True).start()
11 time.sleep(2.0) # allow camera sensor to warm up
12 while True: # send images as stream until Ctrl-C
13 image = picam.read()
14 sender.send_image(rpi_name, image)Wow! A video surveillance system with 8 (or more!) Raspberry Pi cameras in 19 lines of Python.
imagezmq is an easy to use image transport mechanism for a distributed image processing network. For example, a network of a dozen Raspberry Pis with cameras can send images to a more powerful central computer. The Raspberry Pis perform image capture and simple image processing like flipping, blurring and motion detection. Then the images are passed via imagezmq to the central computer for more complex image processing like image tagging, text extraction, feature recognition, etc.
- Sends OpenCV images from one computer to another using ZMQ.
- Can send jpeg compressed OpenCV images, to lighten network loads.
- Uses the powerful ZMQ messaging library through PyZMQ bindings.
- Allows a choice of 2 different ZMQ messaging patterns (REQ/REP or PUB/SUB).
- Enables the image hub to receive and process images from multiple image senders simultaneously.
There are a number of high quality and well maintained messaging protocols for passing messages between computers. I looked at MQTT, RabbitMQ, AMQP and ROS as alternatives. I chose ZMQ and its Python PyZMQ bindings for several reasons:
- ZMQ does not require a message broker. It is a peer to peer protocol that does not need to pass an image first to a message broker and then to the imagehub. This means fewer running processes and less “double handling” of images. OpenCV images are large compared to simple text messages, so the absence of a message broker is important.
- ZMQ is very fast for passing OpenCV images. It enables high throughput between image senders and image hubs.
- ZMQ and its PyZMQ bindings are easy to install.
imagezmq has been transporting images from a dozen Raspberry Pi computers scattered around my farm to 2 linux image hub servers for over 2 years. The RPi's capture and send dozens to thousands of frames frames a day. imagezmq has worked very reliably and is very fast. You can learn more about my "science experiment urban permaculture farm" project at Yin Yang Ranch project overview.
ZMQ allows many different messaging patterns. Two are implemented in imagezmq:
- REQ/REP: Each RPi sends an image and waits for a REPLY from the central image hub. The RPi sends a new image only when the REPLY is received. In the REQ/REP messaging pattern, each image sender must await a REPLY before continuing. It is a "blocking" pattern for the sender.
- PUB/SUB: Each RPi sends an image, but does not expect a REPLY from the central image hub. It can continue sending images without awaiting any acknowledgement from the image hub. The image hub provides no REPLY. It is a "non-blocking" pattern for the sender.
There are advantages and disadvantages for each pattern. REQ/REP is the default. See the documentation (link below) for more details.
imagezmq has been tested with:
- Python 3.5, 3.6, 3.7 and 3.8
- PyZMQ 16.0 and 17.1
- Numpy 1.13 and 1.16
- OpenCV 3.3 and 4.0
- Raspbian Buster, Raspbian Stretch and Raspbian Jessie
- picamera 1.13 (used to capture images for the tests)
- imutils 0.4.6 and 0.5.2 (used to capture images from PiCamera)
Install OpenCV, including Numpy, into a Python Virtual Environment. Then be sure to install imagezmq into the same virtual environment. For example, if the virtual environment is named py3cv3, you would install imagezmq using pip like this:
workon py3cv3 # use your virtual environment name
pip install imagezmqimagezmq has a directory of tests organized into sender and receiver pairs. You will get all the source code for imagezmq including all the test programs by cloning the GitHub repository:
git clone https://github.com/jeffbass/imagezmq.gitimagezmq is open source. The source code, tests and documentation are at Imagezmq on GitHub. The documentation, including links to application examples, starts from the table of contents in the README.