- Binary Tree Paths
简单
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-paths/
Given the root of a binary tree, return all root-to-leaf paths in any order.
A leaf is a node with no children.
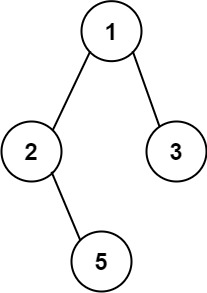
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5]
Output: ["1->2->5","1->3"]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1]
Output: ["1"]
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 100].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
相关企业
- 彭博 Bloomberg|4
- 字节跳动|3
- 谷歌 Google|2
- 亚马逊 Amazon|2
- 微软 Microsoft|2
相关标签
- Tree
- Depth-First Search
- String
- Backtracking
- Binary Tree
相似题目
- Path Sum II 中等
- Smallest String Starting From Leaf 中等
def findNodes(self, node, nodes):
if not node:
return
nodes.append(node.val)
self.findNodes(node.left, nodes)
self.findNodes(node.right, nodes)Yes.
self.findNodes(node.left, nodes)调函数进入下一层之后新的node是node.left, 但是这一行执行完成之后,node仍旧变回node自己。操作系统完成了这个回溯。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def binaryTreePaths(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[str]:
if not root:
return []
all_paths = []
self.dfs(root, [root], all_paths)
return all_paths
def dfs(self, curr_node, curr_path, all_paths):
if not curr_node.left and not curr_node.right:
all_paths.append(self.printPath(curr_path))
# this function calling can be replaced by one line:
# all_paths.append("->".join([str(node.val) for node in curr_path]))
if curr_node.left:
curr_path.append(curr_node.left)
self.dfs(curr_node.left, curr_path, all_paths)
curr_path.pop()
if curr_node.right:
curr_path.append(curr_node.right)
self.dfs(curr_node.right, curr_path, all_paths)
curr_path.pop()
def printPath(self, curr_path):
path_str = ""
for i in range(len(curr_path)-1):
path_str += str(curr_path[i].val) + "->"
path_str += str(curr_path[-1].val)
return path_str# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def binaryTreePaths(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[str]:
if not root:
return []
all_paths = []
self.dfs(root, str(root.val), all_paths)
return all_paths
def dfs(self, curr_node, curr_path_str, all_paths):
if not curr_node.left and not curr_node.right:
all_paths.append(curr_path_str)
if curr_node.left:
self.dfs(curr_node.left, curr_path_str + "->" + str(curr_node.left.val), all_paths) # big space consumption
if curr_node.right:
self.dfs(curr_node.right, curr_path_str + "->" + str(curr_node.right.val), all_paths)- 遍历法 = 一个小人拿着一个记事本走遍所有的节点
- 上面的例子是遍历法
- 通常会用到一个全局变量或者是共享参数
- 分治法 = 分配小弟去做子任务,自己进行结果汇总
- 下面的例子是分治法的解法
- 通常将利用 return value 记录子问题结果
分治法:整棵树路径 = 左子树路径 + 右子树路径
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def binaryTreePaths(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[str]:
all_paths = []
if not root: # root as curr_node
return all_paths
if not root.left and not root.right:
return [str(root.val)]
for path in self.binaryTreePaths(root.left):
all_paths.append(str(root.val) + "->" + path)
for path in self.binaryTreePaths(root.right):
all_paths.append(str(root.val) + "->" + path)
return all_paths这个题目分治法效率更低一些(因为每一次string都要复制)。但是这个思路需要掌握。