solve!
BMI.finalize# Ribasim.config — Module.
module configRibasim.config is a submodule of Ribasim to handle the configuration of a Ribasim model. It is implemented using the Configurations package. A full configuration is represented by Config, which is the main API. Ribasim.config is a submodule mainly to avoid name clashes between the configuration sections and the rest of Ribasim.
# Ribasim.AllocationModel — Type.
Store information for a subnetwork used for allocation.
objectivetype: The name of the type of objective used allocationnetworkid: The ID of this allocation network capacity: The capacity per edge of the allocation graph, as constrained by nodes that have a maxflowrate problem: The JuMP.jl model for solving the allocation problem Δtallocation: The time interval between consecutive allocation solves
-
+
# Ribasim.AllocationModel — Method.
Construct the JuMP.jl problem for allocation.
Inputs
config: The model configuration with allocation configuration in config.allocation p: Ribasim problem parameters Δt_allocation: The timestep between successive allocation solves
Outputs
An AllocationModel object.
-
+
# Ribasim.Basin — Type.
Requirements:
@@ -292,22 +292,22 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.DiscreteControl — Type.
nodeid: node ID of the DiscreteControl node; these are not unique but repeated by the amount of conditions of this DiscreteControl node listennodeid: the ID of the node being condition on variable: the name of the variable in the condition greaterthan: The threshold value in the condition conditionvalue: The current value of each condition controlstate: Dictionary: node ID => (control state, control state start) logic_mapping: Dictionary: (control node ID, truth state) => control state record: Namedtuple with discrete control information for results
-
+
# Ribasim.EdgeMetadata — Type.
Type for storing metadata of edges in the graph: id: ID of the edge (only used for labeling flow output) type: type of the edge allocationnetworkidsource: ID of allocation network where this edge is a source (0 if not a source) fromid: the node ID of the source node toid: the node ID of the destination node allocationflow: whether this edge has a flow in an allocation graph
-
+
# Ribasim.FlatVector — Type.
struct FlatVector{T} <: AbstractVector{T}
A FlatVector is an AbstractVector that iterates the T of a Vector{Vector{T}}.
Each inner vector is assumed to be of equal length.
It is similar to Iterators.flatten, though that doesn’t work with the Tables.Column interface, which needs length and getindex support.
-
+
# Ribasim.FlowBoundary — Type.
nodeid: node ID of the FlowBoundary node active: whether this node is active and thus contributes flow flowrate: target flow rate
-
+
# Ribasim.FractionalFlow — Type.
Requirements:
@@ -316,13 +316,13 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.InNeighbors — Type.
Iterate over incoming neighbors of a given label in a MetaGraph, only for edges of edge_type
-
+
# Ribasim.LevelBoundary — Type.
node_id: node ID of the LevelBoundary node active: whether this node is active level: the fixed level of this ‘infinitely big basin’
-
+
# Ribasim.LinearResistance — Type.
Requirements:
@@ -330,7 +330,7 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.ManningResistance — Type.
This is a simple Manning-Gauckler reach connection.
@@ -360,48 +360,48 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.Model — Type.
Model(config_path::AbstractString)
Model(config::Config)
Initialize a Model.
The Model struct is an initialized model, combined with the Config used to create it and saved results. The Basic Model Interface (BMI) is implemented on the Model. A Model can be created from the path to a TOML configuration file, or a Config object.
-
+
# Ribasim.NodeMetadata — Type.
Type for storing metadata of nodes in the graph type: type of the node allocationnetworkid: Allocation network ID (0 if not in subnetwork)
-
+
# Ribasim.OutNeighbors — Type.
Iterate over outgoing neighbors of a given label in a MetaGraph, only for edges of edge_type
-
+
# Ribasim.Outlet — Type.
nodeid: node ID of the Outlet node active: whether this node is active and thus contributes flow flowrate: target flow rate minflowrate: The minimal flow rate of the outlet maxflowrate: The maximum flow rate of the outlet controlmapping: dictionary from (nodeid, controlstate) to target flow rate ispid_controlled: whether the flow rate of this outlet is governed by PID control
-
+
# Ribasim.PidControl — Type.
PID control currently only supports regulating basin levels.
nodeid: node ID of the PidControl node active: whether this node is active and thus sets flow rates listennodeid: the id of the basin being controlled pidparams: a vector interpolation for parameters changing over time. The parameters are respectively target, proportional, integral, derivative, where the last three are the coefficients for the PID equation. error: the current error; basintarget - currentlevel
-
+
# Ribasim.Pump — Type.
nodeid: node ID of the Pump node active: whether this node is active and thus contributes flow flowrate: target flow rate minflowrate: The minimal flow rate of the pump maxflowrate: The maximum flow rate of the pump controlmapping: dictionary from (nodeid, controlstate) to target flow rate ispid_controlled: whether the flow rate of this pump is governed by PID control
-
+
# Ribasim.Subgrid — Type.
Subgrid linearly interpolates basin levels.
-
+
# Ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve — Type.
struct TabulatedRatingCurve{C}
Rating curve from level to discharge. The rating curve is a lookup table with linear interpolation in between. Relation can be updated in time, which is done by moving data from the time field into the tables, which is done in the update_tabulated_rating_curve callback.
Type parameter C indicates the content backing the StructVector, which can be a NamedTuple of Vectors or Arrow Primitives, and is added to avoid type instabilities.
nodeid: node ID of the TabulatedRatingCurve node active: whether this node is active and thus contributes flows tables: The current Q(h) relationships time: The time table used for updating the tables controlmapping: dictionary from (nodeid, controlstate) to Q(h) and/or active state
-
+
# Ribasim.Terminal — Type.
node_id: node ID of the Terminal node
-
+
# Ribasim.User — Type.
demand: water flux demand of user per priority over time active: whether this node is active and thus demands water allocated: water flux currently allocated to user per priority returnfactor: the factor in [0,1] of how much of the abstracted water is given back to the system minlevel: The level of the source basin below which the user does not abstract priorities: All used priority values. Each user has a demand for all these priorities, which is 0.0 if it is not provided explicitly. record: Collected data of allocation optimizations for output file.
-
+
# Ribasim.config.Config — Method.
Config(config_path::AbstractString; kwargs...)
Parse a TOML file to a Config. Keys can be overruled using keyword arguments. To overrule keys from a subsection, e.g. dt from the solver section, use underscores: solver_dt.
-
+
@@ -410,157 +410,157 @@ # BasicModelInterface.finalize — Method.
BMI.finalize(model::Model)::Model
Write all results to the configured files.
-
+
# BasicModelInterface.initialize — Method.
BMI.initialize(T::Type{Model}, config_path::AbstractString)::Model
Initialize a Model from the path to the TOML configuration file.
-
+
# BasicModelInterface.initialize — Method.
BMI.initialize(T::Type{Model}, config::Config)::Model
Initialize a Model from a Config.
-
+
# CommonSolve.solve! — Method.
solve!(model::Model)::ODESolution
Solve a Model until the configured endtime.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_absolute_value! — Method.
Minimizing |expr| can be achieved by introducing a new variable exprabs and posing the following constraints: exprabs >= expr expr_abs >= -expr
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_capacity! — Method.
Add the flow capacity constraints to the allocation problem. Only finite capacities get a constraint. The constraint indices are (edgesourceid, edgedstid).
Constraint: flow over edge <= edge capacity
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_flow_conservation! — Method.
Add the flow conservation constraints to the allocation problem. The constraint indices are user node IDs.
Constraint: sum(flows out of node node) <= flows into node + flow from storage and vertical fluxes
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_source! — Method.
Add the source constraints to the allocation problem. The actual threshold values will be set before each allocation solve. The constraint indices are (edgesourceid, edgedstid).
Constraint: flow over source edge <= source flow in subnetwork
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_user_returnflow! — Method.
Add the user returnflow constraints to the allocation problem. The constraint indices are user node IDs.
Constraint: outflow from user <= return factor * inflow to user
-
+
# Ribasim.add_flow! — Method.
Add the given flow q to the flow over the edge on the horizontal (self-loop) edge from id to id.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_flow! — Method.
Add the given flow q to the existing flow over the edge between the given nodes.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_variables_absolute_value! — Method.
Certain allocation distribution types use absolute values in the objective function. Since most optimization packages do not support the absolute value function directly, New variables are introduced that act as the absolute value of an expression by posing the appropriate constraints.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_variables_flow! — Method.
Add the flow variables F to the allocation problem. The variable indices are (edgesourceid, edgedstid). Non-negativivity constraints are also immediately added to the flow variables.
-
+
# Ribasim.adjust_edge_capacities! — Method.
Set the values of the edge capacities. 2 cases:
- Before the first allocation solve, set the edge capacities to their full capacity;
- Before an allocation solve, subtract the flow used by allocation for the previous priority from the edge capacities.
-
+
# Ribasim.adjust_source_flows! — Method.
Adjust the source flows.
-
+
# Ribasim.all_neighbor_labels_type — Method.
Get the in- and outneighbor node IDs of the given node ID (label) over the given edge type in the graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocate! — Method.
Update the allocation optimization problem for the given subnetwork with the problem state and flows, solve the allocation problem and assign the results to the users.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_graph — Method.
Build the graph used for the allocation problem.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_graph_used_nodes! — Method.
Find all nodes in the subnetwork which will be used in the allocation network. Some nodes are skipped to optimize allocation optimization.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_path_exists_in_graph — Method.
Find out whether a path exists between a start node and end node in the given allocation graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_problem — Method.
Construct the allocation problem for the current subnetwork as a JuMP.jl model.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_table — Method.
Create an allocation result table for the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.assign_allocations! — Method.
Assign the allocations to the users as determined by the solution of the allocation problem.
-
+
# Ribasim.avoid_using_own_returnflow! — Method.
Remove allocation user return flow edges that are upstream of the user itself.
-
+
# Ribasim.basin_bottom — Method.
Return the bottom elevation of the basin with index i, or nothing if it doesn’t exist
-
+
# Ribasim.basin_bottoms — Method.
Get the bottom on both ends of a node. If only one has a bottom, use that for both.
-
+
# Ribasim.basin_table — Method.
Create the basin result table from the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.create_callbacks — Method.
Create the different callbacks that are used to store results and feed the simulation with new data. The different callbacks are combined to a CallbackSet that goes to the integrator. Returns the CallbackSet and the SavedValues for flow.
-
+
# Ribasim.create_graph — Method.
Return a directed metagraph with data of nodes (NodeMetadata): NodeMetadata
and data of edges (EdgeMetadata): EdgeMetadata
-
+
# Ribasim.create_storage_tables — Method.
Read the Basin / profile table and return all area and level and computed storage values
-
+
# Ribasim.datetime_since — Method.
datetime_since(t::Real, t0::DateTime)::DateTime
Convert a Real that represents the seconds passed since the simulation start to the nearest DateTime. This is used to convert between the solver’s inner float time, and the calendar.
-
+
# Ribasim.datetimes — Method.
Get all saved times as a Vector{DateTime}
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_affect! — Method.
Change parameters based on the control logic.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_affect_downcrossing! — Method.
An downcrossing means that a condition (always greater than) becomes false.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_affect_upcrossing! — Method.
An upcrossing means that a condition (always greater than) becomes true.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_condition — Method.
Listens for changes in condition truths.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_table — Method.
Create a discrete control result table from the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.expand_logic_mapping — Method.
Replace the truth states in the logic mapping which contain wildcards with all possible explicit truth states.
-
+
# Ribasim.find_allocation_graph_edges! — Method.
This loop finds allocation graph edges in several ways:
- Between allocation graph nodes whose equivalent in the subnetwork are directly connected
- Between allocation graph nodes whose equivalent in the subnetwork are connected with one or more allocation graph nodes in between
-
+
# Ribasim.findlastgroup — Method.
For an element id and a vector of elements ids, get the range of indices of the last consecutive block of id. Returns the empty range 1:0 if id is not in ids.
# 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Ribasim.findlastgroup(2, [5,4,2,2,5,2,2,2,1])
# output
6:8
-
+
# Ribasim.findsorted — Method.
Find the index of element x in a sorted collection a. Returns the index of x if it exists, or nothing if it doesn’t. If x occurs more than once, throw an error.
-
+
# Ribasim.flow_table — Method.
Create a flow result table from the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.formulate_basins! — Method.
Smoothly let the evaporation flux go to 0 when at small water depths Currently at less than 0.1 m.
-
+
# Ribasim.formulate_flow! — Method.
Directed graph: outflow is positive!
-
+
# Ribasim.formulate_flow! — Method.
Conservation of energy for two basins, a and b:
h_a + v_a^2 / (2 * g) = h_b + v_b^2 / (2 * g) + S_f * L + C / 2 * g * (v_b^2 - v_a^2)
@@ -588,116 +588,116 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.formulate_flow! — Method.
Directed graph: outflow is positive!
-
+
# Ribasim.get_area_and_level — Method.
Compute the area and level of a basin given its storage. Also returns darea/dlevel as it is needed for the Jacobian.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_chunk_sizes — Method.
Get the chunk sizes for DiffCache; differentiation w.r.t. u and t (the latter only if a Rosenbrock algorithm is used).
-
+
# Ribasim.get_compressor — Method.
Get the compressor based on the Results section
-
+
# Ribasim.get_flow — Method.
Get the flow over the given horizontal (selfloop) edge (val is needed for get_tmp from ForwardDiff.jl).
-
+
# Ribasim.get_flow — Method.
Get the flow over the given edge (val is needed for get_tmp from ForwardDiff.jl).
-
+
# Ribasim.get_fractional_flow_connected_basins — Method.
Get the node type specific indices of the fractional flows and basins, that are consecutively connected to a node of given id.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_jac_prototype — Method.
Get a sparse matrix whose sparsity matches the sparsity of the Jacobian of the ODE problem. All nodes are taken into consideration, also the ones that are inactive.
In Ribasim the Jacobian is typically sparse because each state only depends on a small number of other states.
Note: the name ‘prototype’ does not mean this code is a prototype, it comes from the naming convention of this sparsity structure in the differentialequations.jl docs.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_level — Method.
Get the current water level of a node ID. The ID can belong to either a Basin or a LevelBoundary. storage: tells ForwardDiff whether this call is for differentiation or not
-
+
# Ribasim.get_scalar_interpolation — Method.
Linear interpolation of a scalar with constant extrapolation.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_storage_from_level — Method.
Get the storage of a basin from its level.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_storages_and_levels — Method.
Get the storage and level of all basins as matrices of nbasin × ntime
-
+
# Ribasim.get_storages_from_levels — Method.
Compute the storages of the basins based on the water level of the basins.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_tstops — Method.
From an iterable of DateTimes, find the times the solver needs to stop
-
+
# Ribasim.get_value — Method.
Get a value for a condition. Currently supports getting levels from basins and flows from flow boundaries.
-
+
# Ribasim.id_index — Method.
Get the index of an ID in a set of indices.
-
+
# Ribasim.indicate_allocation_flow! — Method.
Add to the edge metadata that the given edge is used for allocation flow. If the edge does not exist, it is created.
-
+
# Ribasim.inflow_id — Method.
Get the unique inneighbor over a flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.inflow_ids — Method.
Get the inneighbors over flow edges.
-
+
# Ribasim.inflow_ids_allocation — Method.
Get the inneighbors of the given ID such that the connecting edge is an allocation flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.inneighbor_labels_type — Method.
Get the inneighbor node IDs of the given node ID (label) over the given edge type in the graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.inoutflow_ids — Method.
Get the in- and outneighbors over flow edges.
-
+
# Ribasim.is_allocation_source — Method.
Find out whether the given edge is a source for an allocation network.
-
+
# Ribasim.is_flow_constraining — Method.
Whether the given node node is flow constraining by having a maximum flow rate.
-
+
# Ribasim.is_flow_direction_constraining — Method.
Whether the given node is flow direction constraining (only in direction of edges).
-
+
# Ribasim.load_data — Method.
load_data(db::DB, config::Config, nodetype::Symbol, kind::Symbol)::Union{Table, Query, Nothing}
Load data from Arrow files if available, otherwise the database. Returns either an Arrow.Table, SQLite.Query or nothing if the data is not present.
-
+
# Ribasim.load_structvector — Method.
load_structvector(db::DB, config::Config, ::Type{T})::StructVector{T}
Load data from Arrow files if available, otherwise the database. Always returns a StructVector of the given struct type T, which is empty if the table is not found. This function validates the schema, and enforces the required sort order.
-
+
# Ribasim.metadata_from_edge — Method.
Get the metadata of an edge in the graph from an edge of the underlying DiGraph.
-
+
# Ribasim.nodefields — Method.
Get all node fieldnames of the parameter object.
-
+
# Ribasim.nodetype — Method.
From a SchemaVersion(“ribasim.flowboundary.static”, 1) return (:FlowBoundary, :static)
-
+
# Ribasim.outflow_id — Method.
Get the unique outneighbor over a flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.outflow_ids — Method.
Get the outneighbors over flow edges.
-
+
# Ribasim.outflow_ids_allocation — Method.
Get the outneighbors of the given ID such that the connecting edge is an allocation flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.outneighbor_labels_type — Method.
Get the outneighbor node IDs of the given node ID (label) over the given edge type in the graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.parse_static_and_time — Method.
Process the data in the static and time tables for a given node type. The ‘defaults’ named tuple dictates how missing data is filled in. ‘time_interpolatables’ is a vector of Symbols of parameter names for which a time interpolation (linear) object must be constructed. The control mapping for DiscreteControl is also constructed in this function. This function currently does not support node states that are defined by more than one row in a table, as is the case for TabulatedRatingCurve.
-
+
# Ribasim.process_allocation_graph_edges! — Method.
For the composite allocation graph edges:
@@ -705,83 +705,83 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.profile_storage — Method.
Calculate a profile storage by integrating the areas over the levels
-
+
# Ribasim.qh_interpolation — Method.
From a table with columns nodeid, discharge (Q) and level (h), create a LinearInterpolation from level to discharge for a given nodeid.
-
+
# Ribasim.reduction_factor — Method.
Function that goes smoothly from 0 to 1 in the interval [0,threshold], and is constant outside this interval.
-
+
# Ribasim.run — Method.
run(config_file::AbstractString)::Model
run(config::Config)::Model
Run a Model, given a path to a TOML configuration file, or a Config object. Running a model includes initialization, solving to the end with [solve!](@ref) and writing results with BMI.finalize.
-
+
# Ribasim.save_flow — Method.
Copy the current flow to the SavedValues
-
+
# Ribasim.save_subgrid_level — Method.
Interpolate the levels and save them to SavedValues
-
+
# Ribasim.scalar_interpolation_derivative — Method.
Derivative of scalar interpolation.
-
+
# Ribasim.seconds_since — Method.
seconds_since(t::DateTime, t0::DateTime)::Float64
Convert a DateTime to a float that is the number of seconds since the start of the simulation. This is used to convert between the solver’s inner float time, and the calendar.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_current_value! — Method.
From a timeseries table time, load the most recent applicable data into table. table must be a NamedTuple of vectors with all variables that must be loaded. The most recent applicable data is non-NaN data for a given ID that is on or before t.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_flow! — Method.
Set the given flow q on the horizontal (self-loop) edge from id to id.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_flow! — Method.
Set the given flow q over the edge between the given nodes.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_initial_discrete_controlled_parameters! — Method.
Set parameters of nodes that are controlled by DiscreteControl to the values corresponding to the initial state of the model.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_objective_priority! — Method.
Set the objective for the given priority. For an objective with absolute values this also involves adjusting constraints.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_static_value! — Method.
Load data from a source table static into a destination table. Data is matched based on the node_id, which is sorted.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_table_row! — Method.
Update table at row index i, with the values of a given row. table must be a NamedTuple of vectors with all variables that must be loaded. The row must contain all the column names that are present in the table. If a value is NaN, it is not set.
-
+
# Ribasim.sorted_table! — Method.
Depending on if a table can be sorted, either sort it or assert that it is sorted.
Tables loaded from the database into memory can be sorted. Tables loaded from Arrow files are memory mapped and can therefore not be sorted.
-
+
# Ribasim.timesteps — Method.
Get all saved times in seconds since start
-
+
# Ribasim.update_allocation! — Method.
Solve the allocation problem for all users and assign allocated abstractions to user nodes.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_basin — Method.
Load updates from ‘Basin / time’ into the parameters
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
Method for nodes that do not contribute to the Jacobian
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
The controlled basin affects itself and the basins upstream and downstream of the controlled pump affect eachother if there is a basin upstream of the pump. The state for the integral term and the controlled basin affect eachother, and the same for the integral state and the basin upstream of the pump if it is indeed a basin.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
If both the unique node upstream and the unique node downstream of these nodes are basins, then these directly depend on eachother and affect the Jacobian 2x Basins always depend on themselves.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
If both the unique node upstream and the nodes down stream (or one node further if a fractional flow is in between) are basins, then the downstream basin depends on the upstream basin(s) and affect the Jacobian as many times as there are downstream basins Upstream basins always depend on themselves.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_tabulated_rating_curve! — Method.
Load updates from ‘TabulatedRatingCurve / time’ into the parameters
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_discrete_control — Method.
Check:
@@ -789,50 +789,50 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.valid_edge_types — Method.
Check that only supported edge types are declared.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_edges — Method.
Test for each node given its node type whether the nodes that
are downstream (‘down-edge’) of this node are of an allowed type
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_flow_rates — Method.
Test whether static or discrete controlled flow rates are indeed non-negative.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_fractional_flow — Method.
Check that nodes that have fractional flow outneighbors do not have any other type of outneighbor, that the fractions leaving a node add up to ≈1 and that the fractions are non-negative.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_n_neighbors — Method.
Test for each node given its node type whether it has an allowed number of flow/control inneighbors and outneighbors
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_profiles — Method.
Check whether the profile data has no repeats in the levels and the areas start positive.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_sources — Method.
The source nodes must only have one allocation outneighbor and no allocation inneighbors.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_subgrid — Method.
Validate the entries for a single subgrid element.
-
+
# Ribasim.water_balance! — Method.
The right hand side function of the system of ODEs set up by Ribasim.
-
+
# Ribasim.write_arrow — Method.
Write a result table to disk as an Arrow file
-
+
# Ribasim.config.algorithm — Method.
Create an OrdinaryDiffEqAlgorithm from solver config
-
+
# Ribasim.config.input_path — Method.
Construct a path relative to both the TOML directory and the optional input_dir
-
+
# Ribasim.config.results_path — Method.
Construct a path relative to both the TOML directory and the optional results_dir
-
+
# Ribasim.config.snake_case — Method.
Convert a string from CamelCase to snake_case.
-
+
@@ -853,7 +853,7 @@ source
+
@@ -861,10 +861,10 @@ 1.5 Macros
# Ribasim.config.@addfields — Macro.
Add fieldnames with Union{String, Nothing} type to struct expression. Requires (option?) use before it.
-
+
# Ribasim.config.@addnodetypes — Macro.
Add all TableOption subtypes as fields to struct expression. Requires (option?) use before it.
-
+
@@ -898,8 +898,8 @@ Ribasim.User
Ribasim.config.ConfigBasicModelInterface.finalizeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeCommonSolve.solve!Ribasim.add_constraints_absolute_value!Ribasim.add_constraints_capacity!Ribasim.scalar_interpolation_derivative
Ribasim.seconds_sinceRibasim.set_current_value!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_initial_discrete_controlled_parameters!Ribasim.set_objective_priority!Ribasim.set_static_value!Ribasim.timesteps
Ribasim.update_allocation!Ribasim.update_basinRibasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_tabulated_rating_curve!Ribasim.valid_discrete_controlRibasim.valid_edge_types2 Update the basi
ax = df_flow.pivot_table(index="time", columns="edge", values="flow_m3d").plot()
ax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title="Edge")
-<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f1a7c921550>
+<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f7014656f50>

@@ -1021,7 +1021,7 @@ 4 Model with PID
<Axes: >
-
+
Write the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:
diff --git a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png
index 33e8abbcf..f5f6a2b5b 100644
Binary files a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png and b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png differ
diff --git a/qgis/index.html b/qgis/index.html
index 0980ee3b0..df224853e 100644
--- a/qgis/index.html
+++ b/qgis/index.html
@@ -20,40 +20,6 @@
margin: 0 0.8em 0.2em -1em; /* quarto-specific, see https://github.com/quarto-dev/quarto-cli/issues/4556 */
vertical-align: middle;
}
-/* CSS for syntax highlighting */
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre; position: relative; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { display: inline-block; line-height: 1.25; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span:empty { height: 1.2em; }
-.sourceCode { overflow: visible; }
-code.sourceCode > span { color: inherit; text-decoration: inherit; }
-div.sourceCode { margin: 1em 0; }
-pre.sourceCode { margin: 0; }
-@media screen {
-div.sourceCode { overflow: auto; }
-}
-@media print {
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre-wrap; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { text-indent: -5em; padding-left: 5em; }
-}
-pre.numberSource code
- { counter-reset: source-line 0; }
-pre.numberSource code > span
- { position: relative; left: -4em; counter-increment: source-line; }
-pre.numberSource code > span > a:first-child::before
- { content: counter(source-line);
- position: relative; left: -1em; text-align: right; vertical-align: baseline;
- border: none; display: inline-block;
- -webkit-touch-callout: none; -webkit-user-select: none;
- -khtml-user-select: none; -moz-user-select: none;
- -ms-user-select: none; user-select: none;
- padding: 0 4px; width: 4em;
- }
-pre.numberSource { margin-left: 3em; padding-left: 4px; }
-div.sourceCode
- { }
-@media screen {
-pre > code.sourceCode > span > a:first-child::before { text-decoration: underline; }
-}
@@ -180,11 +146,7 @@ On this page
- 1.3.2 Create connecting edges
- 1.4 Run a model
- - 1.5 Inspect results
-
+ - 1.5 Inspect results
@@ -362,18 +324,6 @@
1.4 Run a model
-- Open a text editor and create an empty file next to your database, with the
.toml extension.
-- Add the following content to the TOML file:
-
-
-
-ribasim.toml
-
-starttime = 2020-01-01 00:00:00
-endtime = 2021-01-01 00:00:00
-database = "database.gpkg"
-
-
- Unzip the Ribasim command line interface,
ribasim_cli.zip
- Open your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run
path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.
- In your model directory there is now a
results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files.
@@ -381,43 +331,21 @@
1.5 Inspect results
-
-1.5.1 Associate results to iMOD time series window
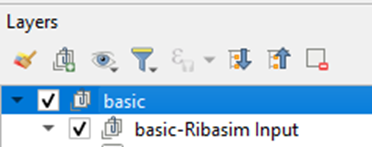
-In QGIS select the model group.
-
-
-
-
-
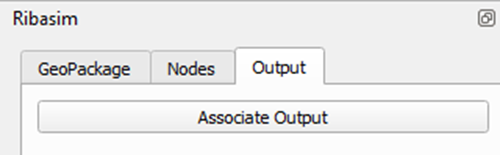
-In the Ribasim plugin widget, select the Results tab and click “Associate Results”.
-
-
-
-
-
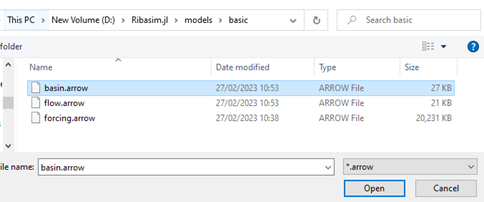
-Select results/basin.arrow.
-
-
-
-
-
-This adds metadata to the model that the iMOD plugin can use to find the timeseries data that is associated to the model nodes.
-
-
-1.5.2 Plot time series
+Before trying to inspect the results, verify that the run was successful and the output files are there.
Click the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.

+Select the layer that you wish to plot. From the “Node” layer you can plot level or storage on Basin nodes. From the “Edge” layer you can plot flow over flow edges. Note that before switching between these, you typically have to click “Clear” to clear the selection. If you run a simulation with the model open in QGIS, you have to close and re-open the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel for the new results to be loaded.
Select the variables that you want to plot.
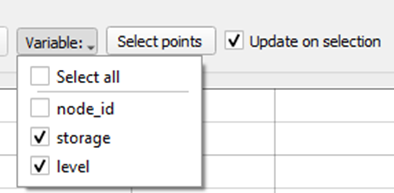
-Click “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes. Currently only the Basin nodes can be plotted.
+Click “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes.
@@ -429,9 +357,9 @@ 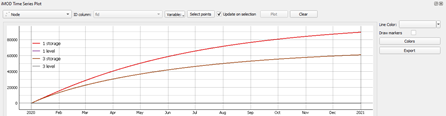
+Only the “basin.arrow” and “flow.arrow” can be inspected with the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel. All Arrow files can be loaded as a layer by dragging the files onto QGIS. Right click the layer and select “Open Attribute Table” to view the contents.
-
diff --git a/search.json b/search.json
index 4fab5eb10..635269b00 100644
--- a/search.json
+++ b/search.json
@@ -396,14 +396,14 @@
"href": "python/examples.html",
"title": "Examples",
"section": "",
- "text": "1 Basic model with static forcing\n\nfrom pathlib import Path\n\nimport geopandas as gpd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1, 3, 3, 6, 6, 9, 9],\n \"area\": [0.01, 1000.0] * 4,\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0] * 4,\n }\n)\n\n# Convert steady forcing to m/s\n# 2 mm/d precipitation, 1 mm/d evaporation\nseconds_in_day = 24 * 3600\nprecipitation = 0.002 / seconds_in_day\nevaporation = 0.001 / seconds_in_day\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [0],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [evaporation],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [precipitation],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\nstatic = static.iloc[[0, 0, 0, 0]]\nstatic[\"node_id\"] = [1, 3, 6, 9]\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static)\n\nSetup linear resistance:\n\nlinear_resistance = ribasim.LinearResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [10, 12], \"resistance\": [5e3, (3600.0 * 24) / 100.0]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup Manning resistance:\n\nmanning_resistance = ribasim.ManningResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"length\": [900.0],\n \"manning_n\": [0.04],\n \"profile_width\": [6.0],\n \"profile_slope\": [3.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up a rating curve node:\n\n# Discharge: lose 1% of storage volume per day at storage = 1000.0.\nq1000 = 1000.0 * 0.01 / seconds_in_day\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4, 4],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n \"discharge\": [0.0, q1000],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup fractional flows:\n\nfractional_flow = ribasim.FractionalFlow(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [5, 8, 13],\n \"fraction\": [0.3, 0.6, 0.1],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [7],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.5 / 3600],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [11, 17],\n \"level\": [0.5, 1.5],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [15, 16],\n \"flow_rate\": [1e-4, 1e-4],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [14],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin,\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: ManningResistance\n (2.0, 0.0), # 3: Basin\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (3.0, 1.0), # 5: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, 2.0), # 6: Basin\n (4.0, 1.0), # 7: Pump\n (4.0, 0.0), # 8: FractionalFlow\n (5.0, 0.0), # 9: Basin\n (6.0, 0.0), # 10: LinearResistance\n (2.0, 2.0), # 11: LevelBoundary\n (2.0, 1.0), # 12: LinearResistance\n (3.0, -1.0), # 13: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, -2.0), # 14: Terminal\n (3.0, 3.0), # 15: FlowBoundary\n (0.0, 1.0), # 16: FlowBoundary\n (6.0, 1.0), # 17: LevelBoundary\n ]\n)\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_id, node_type = ribasim.Node.node_ids_and_types(\n basin,\n manning_resistance,\n rating_curve,\n pump,\n fractional_flow,\n linear_resistance,\n level_boundary,\n flow_boundary,\n terminal,\n)\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(node_id, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array(\n [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 8, 7, 9, 11, 12, 4, 13, 15, 16, 10], dtype=np.int64\n)\nto_id = np.array(\n [2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 6, 7, 9, 9, 10, 12, 3, 13, 14, 6, 1, 17], dtype=np.int64\n)\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": len(from_id) * [\"flow\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n linear_resistance=linear_resistance,\n manning_resistance=manning_resistance,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n fractional_flow=fractional_flow,\n terminal=terminal,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic/ribasim.toml')\n\n\n\n\n2 Update the basic model with transient forcing\nThis assumes you have already created the basic model with static forcing.\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\nimport xarray as xr\n\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(filepath=datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\n\ntime = pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime)\nday_of_year = time.day_of_year.to_numpy()\nseconds_per_day = 24 * 60 * 60\nevaporation = (\n (-1.0 * np.cos(day_of_year / 365.0 * 2 * np.pi) + 1.0) * 0.0025 / seconds_per_day\n)\nrng = np.random.default_rng(seed=0)\nprecipitation = (\n rng.lognormal(mean=-1.0, sigma=1.7, size=time.size) * 0.001 / seconds_per_day\n)\n\nWe’ll use xarray to easily broadcast the values.\n\ntimeseries = (\n pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 1,\n \"time\": pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime),\n \"drainage\": 0.0,\n \"potential_evaporation\": evaporation,\n \"infiltration\": 0.0,\n \"precipitation\": precipitation,\n \"urban_runoff\": 0.0,\n }\n )\n .set_index(\"time\")\n .to_xarray()\n)\n\nbasin_ids = model.basin.static.df[\"node_id\"].to_numpy()\nbasin_nodes = xr.DataArray(\n np.ones(len(basin_ids)), coords={\"node_id\": basin_ids}, dims=[\"node_id\"]\n)\nforcing = (timeseries * basin_nodes).to_dataframe().reset_index()\n\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": basin_ids,\n \"level\": 1.4,\n \"concentration\": 0.0,\n }\n)\n\n\nmodel.basin.time.df = forcing\nmodel.basin.state.df = state\n\n\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic_transient/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic_transient/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim basic-transient/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\ndf_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\n<Axes: xlabel='time'>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ndf_flow = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/flow.arrow\")\ndf_flow[\"edge\"] = list(zip(df_flow.from_node_id, df_flow.to_node_id))\ndf_flow[\"flow_m3d\"] = df_flow.flow * 86400\nax = df_flow.pivot_table(index=\"time\", columns=\"edge\", values=\"flow_m3d\").plot()\nax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title=\"Edge\")\n\n<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f1a7c921550>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ntype(df_flow)\n\npandas.core.frame.DataFrame\n\n\n\n\n3 Model with discrete control\nThe model constructed below consists of a single basin which slowly drains trough a TabulatedRatingCurve, but is held within a range around a target level (setpoint) by two connected pumps. These two pumps behave like a reversible pump. When pumping can be done in only one direction, and the other direction is only possible under gravity, use an Outlet for that direction.\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin\n (1.0, 1.0), # 2: Pump\n (1.0, -1.0), # 3: Pump\n (2.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (-1.0, 0.0), # 5: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (-2.0, 0.0), # 6: Terminal\n (1.0, 0.0), # 7: DiscreteControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"TabulatedRatingCurve\",\n \"Terminal\",\n \"DiscreteControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 7, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 6, 2, 3], dtype=np.int64)\n\nedge_type = 6 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"]\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"from_node_id\": from_id, \"to_node_id\": to_id, \"edge_type\": edge_type},\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1],\n \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n }\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"level\": [20.0]})\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the discrete control:\n\ncondition = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [7],\n \"listen_feature_id\": 3 * [1],\n \"variable\": 3 * [\"level\"],\n \"greater_than\": [5.0, 10.0, 15.0], # min, setpoint, max\n }\n)\n\nlogic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 5 * [7],\n \"truth_state\": [\"FFF\", \"U**\", \"T*F\", \"**D\", \"TTT\"],\n \"control_state\": [\"in\", \"in\", \"none\", \"out\", \"out\"],\n }\n)\n\ndiscrete_control = ribasim.DiscreteControl(condition=condition, logic=logic)\n\nThe above control logic can be summarized as follows: - If the level gets above the maximum, activate the control state “out” until the setpoint is reached; - If the level gets below the minimum, active the control state “in” until the setpoint is reached; - Otherwise activate the control state “none”.\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [2] + 3 * [3],\n \"control_state\": 2 * [\"none\", \"in\", \"out\"],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0, 2e-3, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2e-3],\n }\n )\n)\n\nThe pump data defines the following:\n\n\n\nControl state\nPump #2 flow rate (m/s)\nPump #3 flow rate (m/s)\n\n\n\n\n“none”\n0.0\n0.0\n\n\n“in”\n2e-3\n0.0\n\n\n“out”\n0.0\n2e-3\n\n\n\nSetup the level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [4], \"level\": [10.0]})\n)\n\nSetup the rating curve:\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": 2 * [5], \"level\": [2.0, 15.0], \"discharge\": [0.0, 1e-3]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup the terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [6]}))\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n pump=pump,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n terminal=terminal,\n discrete_control=discrete_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nListen edges are plotted with a dashed line since they are not present in the “Edge / static” schema but only in the “Control / condition” schema.\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\n\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\ngreater_than = model.discrete_control.condition.df.greater_than\n\nax.hlines(\n greater_than,\n df_basin.time[0],\n df_basin.time.max(),\n lw=1,\n ls=\"--\",\n color=\"k\",\n)\n\ndf_control = pd.read_feather(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\ny_min, y_max = ax.get_ybound()\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[:2], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[2:4], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\n\nax.set_xticks(\n date2num(df_control.time).tolist(),\n df_control.control_state.tolist(),\n rotation=50,\n)\n\nax.set_yticks(greater_than, [\"min\", \"setpoint\", \"max\"])\nax.set_ylabel(\"level\")\nplt.show()\n\n\n\n\nThe highlighted regions show where a pump is active.\nLet’s print an overview of what happened with control:\n\nmodel.print_discrete_control_record(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\n0. At 2020-01-01 00:00:00 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTT:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"out\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n\n1. At 2020-02-08 19:02:21.861000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n2. At 2020-07-05 08:56:10.319000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state FFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"in\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n3. At 2020-08-11 06:05:15.592000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n\n\nNote that crossing direction specific truth states (containing “U”, “D”) are not present in this overview even though they are part of the control logic. This is because in the control logic for this model these truth states are only used to sustain control states, while the overview only shows changes in control states.\n\n\n4 Model with PID control\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: FlowBoundary\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: Basin\n (2.0, 0.5), # 3: Pump\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (1.5, 1.0), # 5: PidControl\n (2.0, -0.5), # 6: outlet\n (1.5, -1.0), # 7: PidControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"FlowBoundary\",\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"PidControl\",\n \"Outlet\",\n \"PidControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 5, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([2, 3, 4, 6, 2, 3, 6], dtype=np.int64)\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": 5 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [2, 2], \"level\": [0.0, 1.0], \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0]}\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"level\": [6.0],\n }\n)\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [3],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup the outlet:\n\noutlet = ribasim.Outlet(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [6],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"flow_rate\": [1e-3]})\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4],\n \"level\": [1.0], # Not relevant\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup PID control:\n\npid_control = ribasim.PidControl(\n time=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 4 * [5, 7],\n \"time\": [\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n ],\n \"listen_node_id\": 4 * [2, 2],\n \"target\": [5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5],\n \"proportional\": 4 * [-1e-3, 1e-3],\n \"integral\": 4 * [-1e-7, 1e-7],\n \"derivative\": 4 * [0.0, 0.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nNote that the coefficients for the pump and the outlet are equal in magnitude but opposite in sign. This way the pump and the outlet equally work towards the same goal, while having opposite effects on the controlled basin due to their connectivity to this basin.\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n outlet=outlet,\n pid_control=pid_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"pid_control/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/pid_control/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim pid_control/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"pid_control/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\nax.set_ylabel(\"level [m]\")\n\n# Plot target level\ntarget_levels = model.pid_control.time.df.target.to_numpy()[:4]\ntimes = date2num(model.pid_control.time.df.time)[:4]\nax.plot(times, target_levels, color=\"k\", ls=\":\", label=\"target level\")\npass"
+ "text": "1 Basic model with static forcing\n\nfrom pathlib import Path\n\nimport geopandas as gpd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1, 3, 3, 6, 6, 9, 9],\n \"area\": [0.01, 1000.0] * 4,\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0] * 4,\n }\n)\n\n# Convert steady forcing to m/s\n# 2 mm/d precipitation, 1 mm/d evaporation\nseconds_in_day = 24 * 3600\nprecipitation = 0.002 / seconds_in_day\nevaporation = 0.001 / seconds_in_day\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [0],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [evaporation],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [precipitation],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\nstatic = static.iloc[[0, 0, 0, 0]]\nstatic[\"node_id\"] = [1, 3, 6, 9]\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static)\n\nSetup linear resistance:\n\nlinear_resistance = ribasim.LinearResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [10, 12], \"resistance\": [5e3, (3600.0 * 24) / 100.0]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup Manning resistance:\n\nmanning_resistance = ribasim.ManningResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"length\": [900.0],\n \"manning_n\": [0.04],\n \"profile_width\": [6.0],\n \"profile_slope\": [3.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up a rating curve node:\n\n# Discharge: lose 1% of storage volume per day at storage = 1000.0.\nq1000 = 1000.0 * 0.01 / seconds_in_day\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4, 4],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n \"discharge\": [0.0, q1000],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup fractional flows:\n\nfractional_flow = ribasim.FractionalFlow(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [5, 8, 13],\n \"fraction\": [0.3, 0.6, 0.1],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [7],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.5 / 3600],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [11, 17],\n \"level\": [0.5, 1.5],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [15, 16],\n \"flow_rate\": [1e-4, 1e-4],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [14],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin,\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: ManningResistance\n (2.0, 0.0), # 3: Basin\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (3.0, 1.0), # 5: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, 2.0), # 6: Basin\n (4.0, 1.0), # 7: Pump\n (4.0, 0.0), # 8: FractionalFlow\n (5.0, 0.0), # 9: Basin\n (6.0, 0.0), # 10: LinearResistance\n (2.0, 2.0), # 11: LevelBoundary\n (2.0, 1.0), # 12: LinearResistance\n (3.0, -1.0), # 13: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, -2.0), # 14: Terminal\n (3.0, 3.0), # 15: FlowBoundary\n (0.0, 1.0), # 16: FlowBoundary\n (6.0, 1.0), # 17: LevelBoundary\n ]\n)\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_id, node_type = ribasim.Node.node_ids_and_types(\n basin,\n manning_resistance,\n rating_curve,\n pump,\n fractional_flow,\n linear_resistance,\n level_boundary,\n flow_boundary,\n terminal,\n)\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(node_id, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array(\n [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 8, 7, 9, 11, 12, 4, 13, 15, 16, 10], dtype=np.int64\n)\nto_id = np.array(\n [2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 6, 7, 9, 9, 10, 12, 3, 13, 14, 6, 1, 17], dtype=np.int64\n)\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": len(from_id) * [\"flow\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n linear_resistance=linear_resistance,\n manning_resistance=manning_resistance,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n fractional_flow=fractional_flow,\n terminal=terminal,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic/ribasim.toml')\n\n\n\n\n2 Update the basic model with transient forcing\nThis assumes you have already created the basic model with static forcing.\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\nimport xarray as xr\n\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(filepath=datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\n\ntime = pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime)\nday_of_year = time.day_of_year.to_numpy()\nseconds_per_day = 24 * 60 * 60\nevaporation = (\n (-1.0 * np.cos(day_of_year / 365.0 * 2 * np.pi) + 1.0) * 0.0025 / seconds_per_day\n)\nrng = np.random.default_rng(seed=0)\nprecipitation = (\n rng.lognormal(mean=-1.0, sigma=1.7, size=time.size) * 0.001 / seconds_per_day\n)\n\nWe’ll use xarray to easily broadcast the values.\n\ntimeseries = (\n pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 1,\n \"time\": pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime),\n \"drainage\": 0.0,\n \"potential_evaporation\": evaporation,\n \"infiltration\": 0.0,\n \"precipitation\": precipitation,\n \"urban_runoff\": 0.0,\n }\n )\n .set_index(\"time\")\n .to_xarray()\n)\n\nbasin_ids = model.basin.static.df[\"node_id\"].to_numpy()\nbasin_nodes = xr.DataArray(\n np.ones(len(basin_ids)), coords={\"node_id\": basin_ids}, dims=[\"node_id\"]\n)\nforcing = (timeseries * basin_nodes).to_dataframe().reset_index()\n\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": basin_ids,\n \"level\": 1.4,\n \"concentration\": 0.0,\n }\n)\n\n\nmodel.basin.time.df = forcing\nmodel.basin.state.df = state\n\n\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic_transient/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic_transient/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim basic-transient/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\ndf_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\n<Axes: xlabel='time'>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ndf_flow = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/flow.arrow\")\ndf_flow[\"edge\"] = list(zip(df_flow.from_node_id, df_flow.to_node_id))\ndf_flow[\"flow_m3d\"] = df_flow.flow * 86400\nax = df_flow.pivot_table(index=\"time\", columns=\"edge\", values=\"flow_m3d\").plot()\nax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title=\"Edge\")\n\n<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f7014656f50>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ntype(df_flow)\n\npandas.core.frame.DataFrame\n\n\n\n\n3 Model with discrete control\nThe model constructed below consists of a single basin which slowly drains trough a TabulatedRatingCurve, but is held within a range around a target level (setpoint) by two connected pumps. These two pumps behave like a reversible pump. When pumping can be done in only one direction, and the other direction is only possible under gravity, use an Outlet for that direction.\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin\n (1.0, 1.0), # 2: Pump\n (1.0, -1.0), # 3: Pump\n (2.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (-1.0, 0.0), # 5: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (-2.0, 0.0), # 6: Terminal\n (1.0, 0.0), # 7: DiscreteControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"TabulatedRatingCurve\",\n \"Terminal\",\n \"DiscreteControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 7, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 6, 2, 3], dtype=np.int64)\n\nedge_type = 6 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"]\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"from_node_id\": from_id, \"to_node_id\": to_id, \"edge_type\": edge_type},\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1],\n \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n }\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"level\": [20.0]})\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the discrete control:\n\ncondition = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [7],\n \"listen_feature_id\": 3 * [1],\n \"variable\": 3 * [\"level\"],\n \"greater_than\": [5.0, 10.0, 15.0], # min, setpoint, max\n }\n)\n\nlogic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 5 * [7],\n \"truth_state\": [\"FFF\", \"U**\", \"T*F\", \"**D\", \"TTT\"],\n \"control_state\": [\"in\", \"in\", \"none\", \"out\", \"out\"],\n }\n)\n\ndiscrete_control = ribasim.DiscreteControl(condition=condition, logic=logic)\n\nThe above control logic can be summarized as follows: - If the level gets above the maximum, activate the control state “out” until the setpoint is reached; - If the level gets below the minimum, active the control state “in” until the setpoint is reached; - Otherwise activate the control state “none”.\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [2] + 3 * [3],\n \"control_state\": 2 * [\"none\", \"in\", \"out\"],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0, 2e-3, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2e-3],\n }\n )\n)\n\nThe pump data defines the following:\n\n\n\nControl state\nPump #2 flow rate (m/s)\nPump #3 flow rate (m/s)\n\n\n\n\n“none”\n0.0\n0.0\n\n\n“in”\n2e-3\n0.0\n\n\n“out”\n0.0\n2e-3\n\n\n\nSetup the level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [4], \"level\": [10.0]})\n)\n\nSetup the rating curve:\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": 2 * [5], \"level\": [2.0, 15.0], \"discharge\": [0.0, 1e-3]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup the terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [6]}))\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n pump=pump,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n terminal=terminal,\n discrete_control=discrete_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nListen edges are plotted with a dashed line since they are not present in the “Edge / static” schema but only in the “Control / condition” schema.\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\n\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\ngreater_than = model.discrete_control.condition.df.greater_than\n\nax.hlines(\n greater_than,\n df_basin.time[0],\n df_basin.time.max(),\n lw=1,\n ls=\"--\",\n color=\"k\",\n)\n\ndf_control = pd.read_feather(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\ny_min, y_max = ax.get_ybound()\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[:2], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[2:4], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\n\nax.set_xticks(\n date2num(df_control.time).tolist(),\n df_control.control_state.tolist(),\n rotation=50,\n)\n\nax.set_yticks(greater_than, [\"min\", \"setpoint\", \"max\"])\nax.set_ylabel(\"level\")\nplt.show()\n\n\n\n\nThe highlighted regions show where a pump is active.\nLet’s print an overview of what happened with control:\n\nmodel.print_discrete_control_record(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\n0. At 2020-01-01 00:00:00 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTT:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"out\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n\n1. At 2020-02-08 19:02:21.861000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n2. At 2020-07-05 08:56:10.319000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state FFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"in\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n3. At 2020-08-11 06:05:15.592000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n\n\nNote that crossing direction specific truth states (containing “U”, “D”) are not present in this overview even though they are part of the control logic. This is because in the control logic for this model these truth states are only used to sustain control states, while the overview only shows changes in control states.\n\n\n4 Model with PID control\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: FlowBoundary\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: Basin\n (2.0, 0.5), # 3: Pump\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (1.5, 1.0), # 5: PidControl\n (2.0, -0.5), # 6: outlet\n (1.5, -1.0), # 7: PidControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"FlowBoundary\",\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"PidControl\",\n \"Outlet\",\n \"PidControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 5, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([2, 3, 4, 6, 2, 3, 6], dtype=np.int64)\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": 5 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [2, 2], \"level\": [0.0, 1.0], \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0]}\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"level\": [6.0],\n }\n)\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [3],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup the outlet:\n\noutlet = ribasim.Outlet(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [6],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"flow_rate\": [1e-3]})\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4],\n \"level\": [1.0], # Not relevant\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup PID control:\n\npid_control = ribasim.PidControl(\n time=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 4 * [5, 7],\n \"time\": [\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n ],\n \"listen_node_id\": 4 * [2, 2],\n \"target\": [5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5],\n \"proportional\": 4 * [-1e-3, 1e-3],\n \"integral\": 4 * [-1e-7, 1e-7],\n \"derivative\": 4 * [0.0, 0.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nNote that the coefficients for the pump and the outlet are equal in magnitude but opposite in sign. This way the pump and the outlet equally work towards the same goal, while having opposite effects on the controlled basin due to their connectivity to this basin.\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n outlet=outlet,\n pid_control=pid_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"pid_control/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/pid_control/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim pid_control/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"pid_control/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\nax.set_ylabel(\"level [m]\")\n\n# Plot target level\ntarget_levels = model.pid_control.time.df.target.to_numpy()[:4]\ntimes = date2num(model.pid_control.time.df.time)[:4]\nax.plot(times, target_levels, color=\"k\", ls=\":\", label=\"target level\")\npass"
},
{
"objectID": "qgis/index.html",
"href": "qgis/index.html",
"title": "QGIS plugin",
"section": "",
- "text": "Install QGIS version 3.28 or higher.\n\n\nDownload ribasim_qgis.zip, see the download section.\nPlugins menu > Manage and Install Plugins…\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Install from ZIP”:\n\nBrowse to the ribasim_qgis.zip file containing the plugin that was downloaded earlier\nClick “Install Plugin”\n\n\n\n\n\n\nStart the Ribasim plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nIn QGIS, navigate to “Plugins > Manage and Install Plugins > All”. In the search bar, type: “iMOD”. Select the iMOD plugin, and click “Install”.\nAt least version 0.4.0 of the iMOD plugin is required.\nThe Time Series widget from the iMOD plugin is used for visualizing Ribasim results, which is described in Section 1.5. Documentation on the Time Series widget can be found in the iMOD documentation.\n\n\n\nOpen an existing model or create a new model. As an example of an existing model, you can use the “basic” model from generated_testmodels.zip, see the download section.\n\n\n\n\n\nCheck if your coordinate reference system (CRS) is set correctly.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are working with an unknown CRS, right click the model database group in Layers, and click “Set Group CRS…”.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are modeling the Netherlands, select “Amersfoort / RD New” (EPSG:28992).\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Node layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn on the edit mode to be able to add nodes on the map.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdd nodes to the map with a left click and select the node type.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn the edit mode off and save the edits to the Nodes layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nRight click a layer and select “Open Attribute Table”.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick the yellow pencil icon on the top left to enable editing, and copy and paste a record. A record can be selected by clicking on the row number.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdjust the content. If you prefer, it also works to copy data with the same columns from Excel. Turn off edit mode and save changes to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nMake sure the Snapping Toolbar is visible, by going to the View > Toolbars menu. Turn on snapping mode by clicking the magnet and set the snapping distance to 25 pixels.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Edge layer and turn on the edit mode.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Add line feature”.\n\n\n\n\n\nCreate a connection by left clicking a source node and right clicking the destination node.\n\n\n\n\n\nNow leave the edit mode and save the results to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nOpen a text editor and create an empty file next to your database, with the .toml extension.\nAdd the following content to the TOML file:\n\n\n\nribasim.toml\n\nstarttime = 2020-01-01 00:00:00\nendtime = 2021-01-01 00:00:00\ndatabase = \"database.gpkg\"\n\n\nUnzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files.\n\n\n\n\n\n\nIn QGIS select the model group.\n\n\n\n\n\nIn the Ribasim plugin widget, select the Results tab and click “Associate Results”.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect results/basin.arrow.\n\n\n\n\n\nThis adds metadata to the model that the iMOD plugin can use to find the timeseries data that is associated to the model nodes.\n\n\n\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes. Currently only the Basin nodes can be plotted.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph."
+ "text": "Install QGIS version 3.28 or higher.\n\n\nDownload ribasim_qgis.zip, see the download section.\nPlugins menu > Manage and Install Plugins…\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Install from ZIP”:\n\nBrowse to the ribasim_qgis.zip file containing the plugin that was downloaded earlier\nClick “Install Plugin”\n\n\n\n\n\n\nStart the Ribasim plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nIn QGIS, navigate to “Plugins > Manage and Install Plugins > All”. In the search bar, type: “iMOD”. Select the iMOD plugin, and click “Install”.\nAt least version 0.4.0 of the iMOD plugin is required.\nThe Time Series widget from the iMOD plugin is used for visualizing Ribasim results, which is described in Section 1.5. Documentation on the Time Series widget can be found in the iMOD documentation.\n\n\n\nOpen an existing model or create a new model. As an example of an existing model, you can use the “basic” model from generated_testmodels.zip, see the download section.\n\n\n\n\n\nCheck if your coordinate reference system (CRS) is set correctly.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are working with an unknown CRS, right click the model database group in Layers, and click “Set Group CRS…”.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are modeling the Netherlands, select “Amersfoort / RD New” (EPSG:28992).\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Node layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn on the edit mode to be able to add nodes on the map.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdd nodes to the map with a left click and select the node type.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn the edit mode off and save the edits to the Nodes layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nRight click a layer and select “Open Attribute Table”.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick the yellow pencil icon on the top left to enable editing, and copy and paste a record. A record can be selected by clicking on the row number.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdjust the content. If you prefer, it also works to copy data with the same columns from Excel. Turn off edit mode and save changes to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nMake sure the Snapping Toolbar is visible, by going to the View > Toolbars menu. Turn on snapping mode by clicking the magnet and set the snapping distance to 25 pixels.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Edge layer and turn on the edit mode.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Add line feature”.\n\n\n\n\n\nCreate a connection by left clicking a source node and right clicking the destination node.\n\n\n\n\n\nNow leave the edit mode and save the results to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nUnzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files.\n\n\n\n\nBefore trying to inspect the results, verify that the run was successful and the output files are there.\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the layer that you wish to plot. From the “Node” layer you can plot level or storage on Basin nodes. From the “Edge” layer you can plot flow over flow edges. Note that before switching between these, you typically have to click “Clear” to clear the selection. If you run a simulation with the model open in QGIS, you have to close and re-open the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel for the new results to be loaded.\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph.\n\n\n\n\n\nOnly the “basin.arrow” and “flow.arrow” can be inspected with the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel. All Arrow files can be loaded as a layer by dragging the files onto QGIS. Right click the layer and select “Open Attribute Table” to view the contents."
},
{
"objectID": "qgis/index.html#start",
@@ -431,14 +431,14 @@
"href": "qgis/index.html#run-a-model",
"title": "QGIS plugin",
"section": "",
- "text": "Open a text editor and create an empty file next to your database, with the .toml extension.\nAdd the following content to the TOML file:\n\n\n\nribasim.toml\n\nstarttime = 2020-01-01 00:00:00\nendtime = 2021-01-01 00:00:00\ndatabase = \"database.gpkg\"\n\n\nUnzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files."
+ "text": "Unzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files."
},
{
"objectID": "qgis/index.html#sec-results",
"href": "qgis/index.html#sec-results",
"title": "QGIS plugin",
"section": "",
- "text": "In QGIS select the model group.\n\n\n\n\n\nIn the Ribasim plugin widget, select the Results tab and click “Associate Results”.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect results/basin.arrow.\n\n\n\n\n\nThis adds metadata to the model that the iMOD plugin can use to find the timeseries data that is associated to the model nodes.\n\n\n\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes. Currently only the Basin nodes can be plotted.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph."
+ "text": "Before trying to inspect the results, verify that the run was successful and the output files are there.\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the layer that you wish to plot. From the “Node” layer you can plot level or storage on Basin nodes. From the “Edge” layer you can plot flow over flow edges. Note that before switching between these, you typically have to click “Clear” to clear the selection. If you run a simulation with the model open in QGIS, you have to close and re-open the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel for the new results to be loaded.\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph.\n\n\n\n\n\nOnly the “basin.arrow” and “flow.arrow” can be inspected with the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel. All Arrow files can be loaded as a layer by dragging the files onto QGIS. Right click the layer and select “Open Attribute Table” to view the contents."
},
{
"objectID": "couple/modflow-demo.html",
Ribasim.AllocationModel — Method.Ribasim.Basin — Type.source
+
# Ribasim.DiscreteControl — Type.
nodeid: node ID of the DiscreteControl node; these are not unique but repeated by the amount of conditions of this DiscreteControl node listennodeid: the ID of the node being condition on variable: the name of the variable in the condition greaterthan: The threshold value in the condition conditionvalue: The current value of each condition controlstate: Dictionary: node ID => (control state, control state start) logic_mapping: Dictionary: (control node ID, truth state) => control state record: Namedtuple with discrete control information for results
-
+
# Ribasim.EdgeMetadata — Type.
Type for storing metadata of edges in the graph: id: ID of the edge (only used for labeling flow output) type: type of the edge allocationnetworkidsource: ID of allocation network where this edge is a source (0 if not a source) fromid: the node ID of the source node toid: the node ID of the destination node allocationflow: whether this edge has a flow in an allocation graph
-
+
# Ribasim.FlatVector — Type.
struct FlatVector{T} <: AbstractVector{T}
A FlatVector is an AbstractVector that iterates the T of a Vector{Vector{T}}.
Each inner vector is assumed to be of equal length.
It is similar to Iterators.flatten, though that doesn’t work with the Tables.Column interface, which needs length and getindex support.
-
+
# Ribasim.FlowBoundary — Type.
nodeid: node ID of the FlowBoundary node active: whether this node is active and thus contributes flow flowrate: target flow rate
-
+
# Ribasim.FractionalFlow — Type.
Requirements:
@@ -316,13 +316,13 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.InNeighbors — Type.
Iterate over incoming neighbors of a given label in a MetaGraph, only for edges of edge_type
-
+
# Ribasim.LevelBoundary — Type.
node_id: node ID of the LevelBoundary node active: whether this node is active level: the fixed level of this ‘infinitely big basin’
-
+
# Ribasim.LinearResistance — Type.
Requirements:
@@ -330,7 +330,7 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.ManningResistance — Type.
This is a simple Manning-Gauckler reach connection.
@@ -360,48 +360,48 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.Model — Type.
Model(config_path::AbstractString)
Model(config::Config)
Initialize a Model.
The Model struct is an initialized model, combined with the Config used to create it and saved results. The Basic Model Interface (BMI) is implemented on the Model. A Model can be created from the path to a TOML configuration file, or a Config object.
-
+
# Ribasim.NodeMetadata — Type.
Type for storing metadata of nodes in the graph type: type of the node allocationnetworkid: Allocation network ID (0 if not in subnetwork)
-
+
# Ribasim.OutNeighbors — Type.
Iterate over outgoing neighbors of a given label in a MetaGraph, only for edges of edge_type
-
+
# Ribasim.Outlet — Type.
nodeid: node ID of the Outlet node active: whether this node is active and thus contributes flow flowrate: target flow rate minflowrate: The minimal flow rate of the outlet maxflowrate: The maximum flow rate of the outlet controlmapping: dictionary from (nodeid, controlstate) to target flow rate ispid_controlled: whether the flow rate of this outlet is governed by PID control
-
+
# Ribasim.PidControl — Type.
PID control currently only supports regulating basin levels.
nodeid: node ID of the PidControl node active: whether this node is active and thus sets flow rates listennodeid: the id of the basin being controlled pidparams: a vector interpolation for parameters changing over time. The parameters are respectively target, proportional, integral, derivative, where the last three are the coefficients for the PID equation. error: the current error; basintarget - currentlevel
-
+
# Ribasim.Pump — Type.
nodeid: node ID of the Pump node active: whether this node is active and thus contributes flow flowrate: target flow rate minflowrate: The minimal flow rate of the pump maxflowrate: The maximum flow rate of the pump controlmapping: dictionary from (nodeid, controlstate) to target flow rate ispid_controlled: whether the flow rate of this pump is governed by PID control
-
+
# Ribasim.Subgrid — Type.
Subgrid linearly interpolates basin levels.
-
+
# Ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve — Type.
struct TabulatedRatingCurve{C}
Rating curve from level to discharge. The rating curve is a lookup table with linear interpolation in between. Relation can be updated in time, which is done by moving data from the time field into the tables, which is done in the update_tabulated_rating_curve callback.
Type parameter C indicates the content backing the StructVector, which can be a NamedTuple of Vectors or Arrow Primitives, and is added to avoid type instabilities.
nodeid: node ID of the TabulatedRatingCurve node active: whether this node is active and thus contributes flows tables: The current Q(h) relationships time: The time table used for updating the tables controlmapping: dictionary from (nodeid, controlstate) to Q(h) and/or active state
-
+
# Ribasim.Terminal — Type.
node_id: node ID of the Terminal node
-
+
# Ribasim.User — Type.
demand: water flux demand of user per priority over time active: whether this node is active and thus demands water allocated: water flux currently allocated to user per priority returnfactor: the factor in [0,1] of how much of the abstracted water is given back to the system minlevel: The level of the source basin below which the user does not abstract priorities: All used priority values. Each user has a demand for all these priorities, which is 0.0 if it is not provided explicitly. record: Collected data of allocation optimizations for output file.
-
+
# Ribasim.config.Config — Method.
Config(config_path::AbstractString; kwargs...)
Parse a TOML file to a Config. Keys can be overruled using keyword arguments. To overrule keys from a subsection, e.g. dt from the solver section, use underscores: solver_dt.
-
+
@@ -410,157 +410,157 @@ # BasicModelInterface.finalize — Method.
BMI.finalize(model::Model)::Model
Write all results to the configured files.
-
+
# BasicModelInterface.initialize — Method.
BMI.initialize(T::Type{Model}, config_path::AbstractString)::Model
Initialize a Model from the path to the TOML configuration file.
-
+
# BasicModelInterface.initialize — Method.
BMI.initialize(T::Type{Model}, config::Config)::Model
Initialize a Model from a Config.
-
+
# CommonSolve.solve! — Method.
solve!(model::Model)::ODESolution
Solve a Model until the configured endtime.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_absolute_value! — Method.
Minimizing |expr| can be achieved by introducing a new variable exprabs and posing the following constraints: exprabs >= expr expr_abs >= -expr
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_capacity! — Method.
Add the flow capacity constraints to the allocation problem. Only finite capacities get a constraint. The constraint indices are (edgesourceid, edgedstid).
Constraint: flow over edge <= edge capacity
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_flow_conservation! — Method.
Add the flow conservation constraints to the allocation problem. The constraint indices are user node IDs.
Constraint: sum(flows out of node node) <= flows into node + flow from storage and vertical fluxes
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_source! — Method.
Add the source constraints to the allocation problem. The actual threshold values will be set before each allocation solve. The constraint indices are (edgesourceid, edgedstid).
Constraint: flow over source edge <= source flow in subnetwork
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_user_returnflow! — Method.
Add the user returnflow constraints to the allocation problem. The constraint indices are user node IDs.
Constraint: outflow from user <= return factor * inflow to user
-
+
# Ribasim.add_flow! — Method.
Add the given flow q to the flow over the edge on the horizontal (self-loop) edge from id to id.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_flow! — Method.
Add the given flow q to the existing flow over the edge between the given nodes.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_variables_absolute_value! — Method.
Certain allocation distribution types use absolute values in the objective function. Since most optimization packages do not support the absolute value function directly, New variables are introduced that act as the absolute value of an expression by posing the appropriate constraints.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_variables_flow! — Method.
Add the flow variables F to the allocation problem. The variable indices are (edgesourceid, edgedstid). Non-negativivity constraints are also immediately added to the flow variables.
-
+
# Ribasim.adjust_edge_capacities! — Method.
Set the values of the edge capacities. 2 cases:
- Before the first allocation solve, set the edge capacities to their full capacity;
- Before an allocation solve, subtract the flow used by allocation for the previous priority from the edge capacities.
-
+
# Ribasim.adjust_source_flows! — Method.
Adjust the source flows.
-
+
# Ribasim.all_neighbor_labels_type — Method.
Get the in- and outneighbor node IDs of the given node ID (label) over the given edge type in the graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocate! — Method.
Update the allocation optimization problem for the given subnetwork with the problem state and flows, solve the allocation problem and assign the results to the users.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_graph — Method.
Build the graph used for the allocation problem.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_graph_used_nodes! — Method.
Find all nodes in the subnetwork which will be used in the allocation network. Some nodes are skipped to optimize allocation optimization.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_path_exists_in_graph — Method.
Find out whether a path exists between a start node and end node in the given allocation graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_problem — Method.
Construct the allocation problem for the current subnetwork as a JuMP.jl model.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_table — Method.
Create an allocation result table for the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.assign_allocations! — Method.
Assign the allocations to the users as determined by the solution of the allocation problem.
-
+
# Ribasim.avoid_using_own_returnflow! — Method.
Remove allocation user return flow edges that are upstream of the user itself.
-
+
# Ribasim.basin_bottom — Method.
Return the bottom elevation of the basin with index i, or nothing if it doesn’t exist
-
+
# Ribasim.basin_bottoms — Method.
Get the bottom on both ends of a node. If only one has a bottom, use that for both.
-
+
# Ribasim.basin_table — Method.
Create the basin result table from the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.create_callbacks — Method.
Create the different callbacks that are used to store results and feed the simulation with new data. The different callbacks are combined to a CallbackSet that goes to the integrator. Returns the CallbackSet and the SavedValues for flow.
-
+
# Ribasim.create_graph — Method.
Return a directed metagraph with data of nodes (NodeMetadata): NodeMetadata
and data of edges (EdgeMetadata): EdgeMetadata
-
+
# Ribasim.create_storage_tables — Method.
Read the Basin / profile table and return all area and level and computed storage values
-
+
# Ribasim.datetime_since — Method.
datetime_since(t::Real, t0::DateTime)::DateTime
Convert a Real that represents the seconds passed since the simulation start to the nearest DateTime. This is used to convert between the solver’s inner float time, and the calendar.
-
+
# Ribasim.datetimes — Method.
Get all saved times as a Vector{DateTime}
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_affect! — Method.
Change parameters based on the control logic.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_affect_downcrossing! — Method.
An downcrossing means that a condition (always greater than) becomes false.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_affect_upcrossing! — Method.
An upcrossing means that a condition (always greater than) becomes true.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_condition — Method.
Listens for changes in condition truths.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_table — Method.
Create a discrete control result table from the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.expand_logic_mapping — Method.
Replace the truth states in the logic mapping which contain wildcards with all possible explicit truth states.
-
+
# Ribasim.find_allocation_graph_edges! — Method.
This loop finds allocation graph edges in several ways:
- Between allocation graph nodes whose equivalent in the subnetwork are directly connected
- Between allocation graph nodes whose equivalent in the subnetwork are connected with one or more allocation graph nodes in between
-
+
# Ribasim.findlastgroup — Method.
For an element id and a vector of elements ids, get the range of indices of the last consecutive block of id. Returns the empty range 1:0 if id is not in ids.
# 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Ribasim.findlastgroup(2, [5,4,2,2,5,2,2,2,1])
# output
6:8
-
+
# Ribasim.findsorted — Method.
Find the index of element x in a sorted collection a. Returns the index of x if it exists, or nothing if it doesn’t. If x occurs more than once, throw an error.
-
+
# Ribasim.flow_table — Method.
Create a flow result table from the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.formulate_basins! — Method.
Smoothly let the evaporation flux go to 0 when at small water depths Currently at less than 0.1 m.
-
+
# Ribasim.formulate_flow! — Method.
Directed graph: outflow is positive!
-
+
# Ribasim.formulate_flow! — Method.
Conservation of energy for two basins, a and b:
h_a + v_a^2 / (2 * g) = h_b + v_b^2 / (2 * g) + S_f * L + C / 2 * g * (v_b^2 - v_a^2)
@@ -588,116 +588,116 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.formulate_flow! — Method.
Directed graph: outflow is positive!
-
+
# Ribasim.get_area_and_level — Method.
Compute the area and level of a basin given its storage. Also returns darea/dlevel as it is needed for the Jacobian.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_chunk_sizes — Method.
Get the chunk sizes for DiffCache; differentiation w.r.t. u and t (the latter only if a Rosenbrock algorithm is used).
-
+
# Ribasim.get_compressor — Method.
Get the compressor based on the Results section
-
+
# Ribasim.get_flow — Method.
Get the flow over the given horizontal (selfloop) edge (val is needed for get_tmp from ForwardDiff.jl).
-
+
# Ribasim.get_flow — Method.
Get the flow over the given edge (val is needed for get_tmp from ForwardDiff.jl).
-
+
# Ribasim.get_fractional_flow_connected_basins — Method.
Get the node type specific indices of the fractional flows and basins, that are consecutively connected to a node of given id.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_jac_prototype — Method.
Get a sparse matrix whose sparsity matches the sparsity of the Jacobian of the ODE problem. All nodes are taken into consideration, also the ones that are inactive.
In Ribasim the Jacobian is typically sparse because each state only depends on a small number of other states.
Note: the name ‘prototype’ does not mean this code is a prototype, it comes from the naming convention of this sparsity structure in the differentialequations.jl docs.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_level — Method.
Get the current water level of a node ID. The ID can belong to either a Basin or a LevelBoundary. storage: tells ForwardDiff whether this call is for differentiation or not
-
+
# Ribasim.get_scalar_interpolation — Method.
Linear interpolation of a scalar with constant extrapolation.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_storage_from_level — Method.
Get the storage of a basin from its level.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_storages_and_levels — Method.
Get the storage and level of all basins as matrices of nbasin × ntime
-
+
# Ribasim.get_storages_from_levels — Method.
Compute the storages of the basins based on the water level of the basins.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_tstops — Method.
From an iterable of DateTimes, find the times the solver needs to stop
-
+
# Ribasim.get_value — Method.
Get a value for a condition. Currently supports getting levels from basins and flows from flow boundaries.
-
+
# Ribasim.id_index — Method.
Get the index of an ID in a set of indices.
-
+
# Ribasim.indicate_allocation_flow! — Method.
Add to the edge metadata that the given edge is used for allocation flow. If the edge does not exist, it is created.
-
+
# Ribasim.inflow_id — Method.
Get the unique inneighbor over a flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.inflow_ids — Method.
Get the inneighbors over flow edges.
-
+
# Ribasim.inflow_ids_allocation — Method.
Get the inneighbors of the given ID such that the connecting edge is an allocation flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.inneighbor_labels_type — Method.
Get the inneighbor node IDs of the given node ID (label) over the given edge type in the graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.inoutflow_ids — Method.
Get the in- and outneighbors over flow edges.
-
+
# Ribasim.is_allocation_source — Method.
Find out whether the given edge is a source for an allocation network.
-
+
# Ribasim.is_flow_constraining — Method.
Whether the given node node is flow constraining by having a maximum flow rate.
-
+
# Ribasim.is_flow_direction_constraining — Method.
Whether the given node is flow direction constraining (only in direction of edges).
-
+
# Ribasim.load_data — Method.
load_data(db::DB, config::Config, nodetype::Symbol, kind::Symbol)::Union{Table, Query, Nothing}
Load data from Arrow files if available, otherwise the database. Returns either an Arrow.Table, SQLite.Query or nothing if the data is not present.
-
+
# Ribasim.load_structvector — Method.
load_structvector(db::DB, config::Config, ::Type{T})::StructVector{T}
Load data from Arrow files if available, otherwise the database. Always returns a StructVector of the given struct type T, which is empty if the table is not found. This function validates the schema, and enforces the required sort order.
-
+
# Ribasim.metadata_from_edge — Method.
Get the metadata of an edge in the graph from an edge of the underlying DiGraph.
-
+
# Ribasim.nodefields — Method.
Get all node fieldnames of the parameter object.
-
+
# Ribasim.nodetype — Method.
From a SchemaVersion(“ribasim.flowboundary.static”, 1) return (:FlowBoundary, :static)
-
+
# Ribasim.outflow_id — Method.
Get the unique outneighbor over a flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.outflow_ids — Method.
Get the outneighbors over flow edges.
-
+
# Ribasim.outflow_ids_allocation — Method.
Get the outneighbors of the given ID such that the connecting edge is an allocation flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.outneighbor_labels_type — Method.
Get the outneighbor node IDs of the given node ID (label) over the given edge type in the graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.parse_static_and_time — Method.
Process the data in the static and time tables for a given node type. The ‘defaults’ named tuple dictates how missing data is filled in. ‘time_interpolatables’ is a vector of Symbols of parameter names for which a time interpolation (linear) object must be constructed. The control mapping for DiscreteControl is also constructed in this function. This function currently does not support node states that are defined by more than one row in a table, as is the case for TabulatedRatingCurve.
-
+
# Ribasim.process_allocation_graph_edges! — Method.
For the composite allocation graph edges:
@@ -705,83 +705,83 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.profile_storage — Method.
Calculate a profile storage by integrating the areas over the levels
-
+
# Ribasim.qh_interpolation — Method.
From a table with columns nodeid, discharge (Q) and level (h), create a LinearInterpolation from level to discharge for a given nodeid.
-
+
# Ribasim.reduction_factor — Method.
Function that goes smoothly from 0 to 1 in the interval [0,threshold], and is constant outside this interval.
-
+
# Ribasim.run — Method.
run(config_file::AbstractString)::Model
run(config::Config)::Model
Run a Model, given a path to a TOML configuration file, or a Config object. Running a model includes initialization, solving to the end with [solve!](@ref) and writing results with BMI.finalize.
-
+
# Ribasim.save_flow — Method.
Copy the current flow to the SavedValues
-
+
# Ribasim.save_subgrid_level — Method.
Interpolate the levels and save them to SavedValues
-
+
# Ribasim.scalar_interpolation_derivative — Method.
Derivative of scalar interpolation.
-
+
# Ribasim.seconds_since — Method.
seconds_since(t::DateTime, t0::DateTime)::Float64
Convert a DateTime to a float that is the number of seconds since the start of the simulation. This is used to convert between the solver’s inner float time, and the calendar.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_current_value! — Method.
From a timeseries table time, load the most recent applicable data into table. table must be a NamedTuple of vectors with all variables that must be loaded. The most recent applicable data is non-NaN data for a given ID that is on or before t.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_flow! — Method.
Set the given flow q on the horizontal (self-loop) edge from id to id.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_flow! — Method.
Set the given flow q over the edge between the given nodes.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_initial_discrete_controlled_parameters! — Method.
Set parameters of nodes that are controlled by DiscreteControl to the values corresponding to the initial state of the model.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_objective_priority! — Method.
Set the objective for the given priority. For an objective with absolute values this also involves adjusting constraints.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_static_value! — Method.
Load data from a source table static into a destination table. Data is matched based on the node_id, which is sorted.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_table_row! — Method.
Update table at row index i, with the values of a given row. table must be a NamedTuple of vectors with all variables that must be loaded. The row must contain all the column names that are present in the table. If a value is NaN, it is not set.
-
+
# Ribasim.sorted_table! — Method.
Depending on if a table can be sorted, either sort it or assert that it is sorted.
Tables loaded from the database into memory can be sorted. Tables loaded from Arrow files are memory mapped and can therefore not be sorted.
-
+
# Ribasim.timesteps — Method.
Get all saved times in seconds since start
-
+
# Ribasim.update_allocation! — Method.
Solve the allocation problem for all users and assign allocated abstractions to user nodes.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_basin — Method.
Load updates from ‘Basin / time’ into the parameters
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
Method for nodes that do not contribute to the Jacobian
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
The controlled basin affects itself and the basins upstream and downstream of the controlled pump affect eachother if there is a basin upstream of the pump. The state for the integral term and the controlled basin affect eachother, and the same for the integral state and the basin upstream of the pump if it is indeed a basin.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
If both the unique node upstream and the unique node downstream of these nodes are basins, then these directly depend on eachother and affect the Jacobian 2x Basins always depend on themselves.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
If both the unique node upstream and the nodes down stream (or one node further if a fractional flow is in between) are basins, then the downstream basin depends on the upstream basin(s) and affect the Jacobian as many times as there are downstream basins Upstream basins always depend on themselves.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_tabulated_rating_curve! — Method.
Load updates from ‘TabulatedRatingCurve / time’ into the parameters
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_discrete_control — Method.
Check:
@@ -789,50 +789,50 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.valid_edge_types — Method.
Check that only supported edge types are declared.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_edges — Method.
Test for each node given its node type whether the nodes that
are downstream (‘down-edge’) of this node are of an allowed type
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_flow_rates — Method.
Test whether static or discrete controlled flow rates are indeed non-negative.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_fractional_flow — Method.
Check that nodes that have fractional flow outneighbors do not have any other type of outneighbor, that the fractions leaving a node add up to ≈1 and that the fractions are non-negative.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_n_neighbors — Method.
Test for each node given its node type whether it has an allowed number of flow/control inneighbors and outneighbors
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_profiles — Method.
Check whether the profile data has no repeats in the levels and the areas start positive.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_sources — Method.
The source nodes must only have one allocation outneighbor and no allocation inneighbors.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_subgrid — Method.
Validate the entries for a single subgrid element.
-
+
# Ribasim.water_balance! — Method.
The right hand side function of the system of ODEs set up by Ribasim.
-
+
# Ribasim.write_arrow — Method.
Write a result table to disk as an Arrow file
-
+
# Ribasim.config.algorithm — Method.
Create an OrdinaryDiffEqAlgorithm from solver config
-
+
# Ribasim.config.input_path — Method.
Construct a path relative to both the TOML directory and the optional input_dir
-
+
# Ribasim.config.results_path — Method.
Construct a path relative to both the TOML directory and the optional results_dir
-
+
# Ribasim.config.snake_case — Method.
Convert a string from CamelCase to snake_case.
-
+
@@ -853,7 +853,7 @@ source
+
@@ -861,10 +861,10 @@ 1.5 Macros
# Ribasim.config.@addfields — Macro.
Add fieldnames with Union{String, Nothing} type to struct expression. Requires (option?) use before it.
-
+
# Ribasim.config.@addnodetypes — Macro.
Add all TableOption subtypes as fields to struct expression. Requires (option?) use before it.
-
+
@@ -898,8 +898,8 @@ Ribasim.User
Ribasim.config.ConfigBasicModelInterface.finalizeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeCommonSolve.solve!Ribasim.add_constraints_absolute_value!Ribasim.add_constraints_capacity!Ribasim.scalar_interpolation_derivative
Ribasim.seconds_sinceRibasim.set_current_value!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_initial_discrete_controlled_parameters!Ribasim.set_objective_priority!Ribasim.set_static_value!Ribasim.timesteps
Ribasim.update_allocation!Ribasim.update_basinRibasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_tabulated_rating_curve!Ribasim.valid_discrete_controlRibasim.valid_edge_types2 Update the basi
ax = df_flow.pivot_table(index="time", columns="edge", values="flow_m3d").plot()
ax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title="Edge")
-<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f1a7c921550>
+<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f7014656f50>

@@ -1021,7 +1021,7 @@ 4 Model with PID
<Axes: >
-
+
Write the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:
diff --git a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png
index 33e8abbcf..f5f6a2b5b 100644
Binary files a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png and b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png differ
diff --git a/qgis/index.html b/qgis/index.html
index 0980ee3b0..df224853e 100644
--- a/qgis/index.html
+++ b/qgis/index.html
@@ -20,40 +20,6 @@
margin: 0 0.8em 0.2em -1em; /* quarto-specific, see https://github.com/quarto-dev/quarto-cli/issues/4556 */
vertical-align: middle;
}
-/* CSS for syntax highlighting */
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre; position: relative; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { display: inline-block; line-height: 1.25; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span:empty { height: 1.2em; }
-.sourceCode { overflow: visible; }
-code.sourceCode > span { color: inherit; text-decoration: inherit; }
-div.sourceCode { margin: 1em 0; }
-pre.sourceCode { margin: 0; }
-@media screen {
-div.sourceCode { overflow: auto; }
-}
-@media print {
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre-wrap; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { text-indent: -5em; padding-left: 5em; }
-}
-pre.numberSource code
- { counter-reset: source-line 0; }
-pre.numberSource code > span
- { position: relative; left: -4em; counter-increment: source-line; }
-pre.numberSource code > span > a:first-child::before
- { content: counter(source-line);
- position: relative; left: -1em; text-align: right; vertical-align: baseline;
- border: none; display: inline-block;
- -webkit-touch-callout: none; -webkit-user-select: none;
- -khtml-user-select: none; -moz-user-select: none;
- -ms-user-select: none; user-select: none;
- padding: 0 4px; width: 4em;
- }
-pre.numberSource { margin-left: 3em; padding-left: 4px; }
-div.sourceCode
- { }
-@media screen {
-pre > code.sourceCode > span > a:first-child::before { text-decoration: underline; }
-}
@@ -180,11 +146,7 @@ On this page
- 1.3.2 Create connecting edges
- 1.4 Run a model
- - 1.5 Inspect results
-
+ - 1.5 Inspect results
@@ -362,18 +324,6 @@
1.4 Run a model
-- Open a text editor and create an empty file next to your database, with the
.toml extension.
-- Add the following content to the TOML file:
-
-
-
-ribasim.toml
-
-starttime = 2020-01-01 00:00:00
-endtime = 2021-01-01 00:00:00
-database = "database.gpkg"
-
-
- Unzip the Ribasim command line interface,
ribasim_cli.zip
- Open your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run
path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.
- In your model directory there is now a
results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files.
@@ -381,43 +331,21 @@
1.5 Inspect results
-
-1.5.1 Associate results to iMOD time series window
-In QGIS select the model group.
-
-
-
-
-
-In the Ribasim plugin widget, select the Results tab and click “Associate Results”.
-
-
-
-
-
-Select results/basin.arrow.
-
-
-
-
-
-This adds metadata to the model that the iMOD plugin can use to find the timeseries data that is associated to the model nodes.
-
-
-1.5.2 Plot time series
+Before trying to inspect the results, verify that the run was successful and the output files are there.
Click the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.

+Select the layer that you wish to plot. From the “Node” layer you can plot level or storage on Basin nodes. From the “Edge” layer you can plot flow over flow edges. Note that before switching between these, you typically have to click “Clear” to clear the selection. If you run a simulation with the model open in QGIS, you have to close and re-open the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel for the new results to be loaded.
Select the variables that you want to plot.

-Click “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes. Currently only the Basin nodes can be plotted.
+Click “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes.

@@ -429,9 +357,9 @@ 
+Only the “basin.arrow” and “flow.arrow” can be inspected with the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel. All Arrow files can be loaded as a layer by dragging the files onto QGIS. Right click the layer and select “Open Attribute Table” to view the contents.
-
diff --git a/search.json b/search.json
index 4fab5eb10..635269b00 100644
--- a/search.json
+++ b/search.json
@@ -396,14 +396,14 @@
"href": "python/examples.html",
"title": "Examples",
"section": "",
- "text": "1 Basic model with static forcing\n\nfrom pathlib import Path\n\nimport geopandas as gpd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1, 3, 3, 6, 6, 9, 9],\n \"area\": [0.01, 1000.0] * 4,\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0] * 4,\n }\n)\n\n# Convert steady forcing to m/s\n# 2 mm/d precipitation, 1 mm/d evaporation\nseconds_in_day = 24 * 3600\nprecipitation = 0.002 / seconds_in_day\nevaporation = 0.001 / seconds_in_day\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [0],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [evaporation],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [precipitation],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\nstatic = static.iloc[[0, 0, 0, 0]]\nstatic[\"node_id\"] = [1, 3, 6, 9]\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static)\n\nSetup linear resistance:\n\nlinear_resistance = ribasim.LinearResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [10, 12], \"resistance\": [5e3, (3600.0 * 24) / 100.0]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup Manning resistance:\n\nmanning_resistance = ribasim.ManningResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"length\": [900.0],\n \"manning_n\": [0.04],\n \"profile_width\": [6.0],\n \"profile_slope\": [3.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up a rating curve node:\n\n# Discharge: lose 1% of storage volume per day at storage = 1000.0.\nq1000 = 1000.0 * 0.01 / seconds_in_day\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4, 4],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n \"discharge\": [0.0, q1000],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup fractional flows:\n\nfractional_flow = ribasim.FractionalFlow(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [5, 8, 13],\n \"fraction\": [0.3, 0.6, 0.1],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [7],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.5 / 3600],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [11, 17],\n \"level\": [0.5, 1.5],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [15, 16],\n \"flow_rate\": [1e-4, 1e-4],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [14],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin,\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: ManningResistance\n (2.0, 0.0), # 3: Basin\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (3.0, 1.0), # 5: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, 2.0), # 6: Basin\n (4.0, 1.0), # 7: Pump\n (4.0, 0.0), # 8: FractionalFlow\n (5.0, 0.0), # 9: Basin\n (6.0, 0.0), # 10: LinearResistance\n (2.0, 2.0), # 11: LevelBoundary\n (2.0, 1.0), # 12: LinearResistance\n (3.0, -1.0), # 13: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, -2.0), # 14: Terminal\n (3.0, 3.0), # 15: FlowBoundary\n (0.0, 1.0), # 16: FlowBoundary\n (6.0, 1.0), # 17: LevelBoundary\n ]\n)\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_id, node_type = ribasim.Node.node_ids_and_types(\n basin,\n manning_resistance,\n rating_curve,\n pump,\n fractional_flow,\n linear_resistance,\n level_boundary,\n flow_boundary,\n terminal,\n)\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(node_id, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array(\n [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 8, 7, 9, 11, 12, 4, 13, 15, 16, 10], dtype=np.int64\n)\nto_id = np.array(\n [2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 6, 7, 9, 9, 10, 12, 3, 13, 14, 6, 1, 17], dtype=np.int64\n)\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": len(from_id) * [\"flow\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n linear_resistance=linear_resistance,\n manning_resistance=manning_resistance,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n fractional_flow=fractional_flow,\n terminal=terminal,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic/ribasim.toml')\n\n\n\n\n2 Update the basic model with transient forcing\nThis assumes you have already created the basic model with static forcing.\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\nimport xarray as xr\n\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(filepath=datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\n\ntime = pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime)\nday_of_year = time.day_of_year.to_numpy()\nseconds_per_day = 24 * 60 * 60\nevaporation = (\n (-1.0 * np.cos(day_of_year / 365.0 * 2 * np.pi) + 1.0) * 0.0025 / seconds_per_day\n)\nrng = np.random.default_rng(seed=0)\nprecipitation = (\n rng.lognormal(mean=-1.0, sigma=1.7, size=time.size) * 0.001 / seconds_per_day\n)\n\nWe’ll use xarray to easily broadcast the values.\n\ntimeseries = (\n pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 1,\n \"time\": pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime),\n \"drainage\": 0.0,\n \"potential_evaporation\": evaporation,\n \"infiltration\": 0.0,\n \"precipitation\": precipitation,\n \"urban_runoff\": 0.0,\n }\n )\n .set_index(\"time\")\n .to_xarray()\n)\n\nbasin_ids = model.basin.static.df[\"node_id\"].to_numpy()\nbasin_nodes = xr.DataArray(\n np.ones(len(basin_ids)), coords={\"node_id\": basin_ids}, dims=[\"node_id\"]\n)\nforcing = (timeseries * basin_nodes).to_dataframe().reset_index()\n\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": basin_ids,\n \"level\": 1.4,\n \"concentration\": 0.0,\n }\n)\n\n\nmodel.basin.time.df = forcing\nmodel.basin.state.df = state\n\n\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic_transient/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic_transient/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim basic-transient/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\ndf_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\n<Axes: xlabel='time'>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ndf_flow = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/flow.arrow\")\ndf_flow[\"edge\"] = list(zip(df_flow.from_node_id, df_flow.to_node_id))\ndf_flow[\"flow_m3d\"] = df_flow.flow * 86400\nax = df_flow.pivot_table(index=\"time\", columns=\"edge\", values=\"flow_m3d\").plot()\nax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title=\"Edge\")\n\n<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f1a7c921550>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ntype(df_flow)\n\npandas.core.frame.DataFrame\n\n\n\n\n3 Model with discrete control\nThe model constructed below consists of a single basin which slowly drains trough a TabulatedRatingCurve, but is held within a range around a target level (setpoint) by two connected pumps. These two pumps behave like a reversible pump. When pumping can be done in only one direction, and the other direction is only possible under gravity, use an Outlet for that direction.\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin\n (1.0, 1.0), # 2: Pump\n (1.0, -1.0), # 3: Pump\n (2.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (-1.0, 0.0), # 5: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (-2.0, 0.0), # 6: Terminal\n (1.0, 0.0), # 7: DiscreteControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"TabulatedRatingCurve\",\n \"Terminal\",\n \"DiscreteControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 7, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 6, 2, 3], dtype=np.int64)\n\nedge_type = 6 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"]\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"from_node_id\": from_id, \"to_node_id\": to_id, \"edge_type\": edge_type},\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1],\n \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n }\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"level\": [20.0]})\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the discrete control:\n\ncondition = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [7],\n \"listen_feature_id\": 3 * [1],\n \"variable\": 3 * [\"level\"],\n \"greater_than\": [5.0, 10.0, 15.0], # min, setpoint, max\n }\n)\n\nlogic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 5 * [7],\n \"truth_state\": [\"FFF\", \"U**\", \"T*F\", \"**D\", \"TTT\"],\n \"control_state\": [\"in\", \"in\", \"none\", \"out\", \"out\"],\n }\n)\n\ndiscrete_control = ribasim.DiscreteControl(condition=condition, logic=logic)\n\nThe above control logic can be summarized as follows: - If the level gets above the maximum, activate the control state “out” until the setpoint is reached; - If the level gets below the minimum, active the control state “in” until the setpoint is reached; - Otherwise activate the control state “none”.\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [2] + 3 * [3],\n \"control_state\": 2 * [\"none\", \"in\", \"out\"],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0, 2e-3, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2e-3],\n }\n )\n)\n\nThe pump data defines the following:\n\n\n\nControl state\nPump #2 flow rate (m/s)\nPump #3 flow rate (m/s)\n\n\n\n\n“none”\n0.0\n0.0\n\n\n“in”\n2e-3\n0.0\n\n\n“out”\n0.0\n2e-3\n\n\n\nSetup the level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [4], \"level\": [10.0]})\n)\n\nSetup the rating curve:\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": 2 * [5], \"level\": [2.0, 15.0], \"discharge\": [0.0, 1e-3]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup the terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [6]}))\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n pump=pump,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n terminal=terminal,\n discrete_control=discrete_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nListen edges are plotted with a dashed line since they are not present in the “Edge / static” schema but only in the “Control / condition” schema.\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\n\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\ngreater_than = model.discrete_control.condition.df.greater_than\n\nax.hlines(\n greater_than,\n df_basin.time[0],\n df_basin.time.max(),\n lw=1,\n ls=\"--\",\n color=\"k\",\n)\n\ndf_control = pd.read_feather(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\ny_min, y_max = ax.get_ybound()\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[:2], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[2:4], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\n\nax.set_xticks(\n date2num(df_control.time).tolist(),\n df_control.control_state.tolist(),\n rotation=50,\n)\n\nax.set_yticks(greater_than, [\"min\", \"setpoint\", \"max\"])\nax.set_ylabel(\"level\")\nplt.show()\n\n\n\n\nThe highlighted regions show where a pump is active.\nLet’s print an overview of what happened with control:\n\nmodel.print_discrete_control_record(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\n0. At 2020-01-01 00:00:00 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTT:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"out\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n\n1. At 2020-02-08 19:02:21.861000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n2. At 2020-07-05 08:56:10.319000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state FFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"in\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n3. At 2020-08-11 06:05:15.592000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n\n\nNote that crossing direction specific truth states (containing “U”, “D”) are not present in this overview even though they are part of the control logic. This is because in the control logic for this model these truth states are only used to sustain control states, while the overview only shows changes in control states.\n\n\n4 Model with PID control\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: FlowBoundary\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: Basin\n (2.0, 0.5), # 3: Pump\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (1.5, 1.0), # 5: PidControl\n (2.0, -0.5), # 6: outlet\n (1.5, -1.0), # 7: PidControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"FlowBoundary\",\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"PidControl\",\n \"Outlet\",\n \"PidControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 5, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([2, 3, 4, 6, 2, 3, 6], dtype=np.int64)\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": 5 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [2, 2], \"level\": [0.0, 1.0], \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0]}\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"level\": [6.0],\n }\n)\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [3],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup the outlet:\n\noutlet = ribasim.Outlet(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [6],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"flow_rate\": [1e-3]})\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4],\n \"level\": [1.0], # Not relevant\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup PID control:\n\npid_control = ribasim.PidControl(\n time=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 4 * [5, 7],\n \"time\": [\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n ],\n \"listen_node_id\": 4 * [2, 2],\n \"target\": [5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5],\n \"proportional\": 4 * [-1e-3, 1e-3],\n \"integral\": 4 * [-1e-7, 1e-7],\n \"derivative\": 4 * [0.0, 0.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nNote that the coefficients for the pump and the outlet are equal in magnitude but opposite in sign. This way the pump and the outlet equally work towards the same goal, while having opposite effects on the controlled basin due to their connectivity to this basin.\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n outlet=outlet,\n pid_control=pid_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"pid_control/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/pid_control/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim pid_control/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"pid_control/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\nax.set_ylabel(\"level [m]\")\n\n# Plot target level\ntarget_levels = model.pid_control.time.df.target.to_numpy()[:4]\ntimes = date2num(model.pid_control.time.df.time)[:4]\nax.plot(times, target_levels, color=\"k\", ls=\":\", label=\"target level\")\npass"
+ "text": "1 Basic model with static forcing\n\nfrom pathlib import Path\n\nimport geopandas as gpd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1, 3, 3, 6, 6, 9, 9],\n \"area\": [0.01, 1000.0] * 4,\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0] * 4,\n }\n)\n\n# Convert steady forcing to m/s\n# 2 mm/d precipitation, 1 mm/d evaporation\nseconds_in_day = 24 * 3600\nprecipitation = 0.002 / seconds_in_day\nevaporation = 0.001 / seconds_in_day\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [0],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [evaporation],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [precipitation],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\nstatic = static.iloc[[0, 0, 0, 0]]\nstatic[\"node_id\"] = [1, 3, 6, 9]\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static)\n\nSetup linear resistance:\n\nlinear_resistance = ribasim.LinearResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [10, 12], \"resistance\": [5e3, (3600.0 * 24) / 100.0]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup Manning resistance:\n\nmanning_resistance = ribasim.ManningResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"length\": [900.0],\n \"manning_n\": [0.04],\n \"profile_width\": [6.0],\n \"profile_slope\": [3.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up a rating curve node:\n\n# Discharge: lose 1% of storage volume per day at storage = 1000.0.\nq1000 = 1000.0 * 0.01 / seconds_in_day\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4, 4],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n \"discharge\": [0.0, q1000],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup fractional flows:\n\nfractional_flow = ribasim.FractionalFlow(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [5, 8, 13],\n \"fraction\": [0.3, 0.6, 0.1],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [7],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.5 / 3600],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [11, 17],\n \"level\": [0.5, 1.5],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [15, 16],\n \"flow_rate\": [1e-4, 1e-4],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [14],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin,\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: ManningResistance\n (2.0, 0.0), # 3: Basin\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (3.0, 1.0), # 5: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, 2.0), # 6: Basin\n (4.0, 1.0), # 7: Pump\n (4.0, 0.0), # 8: FractionalFlow\n (5.0, 0.0), # 9: Basin\n (6.0, 0.0), # 10: LinearResistance\n (2.0, 2.0), # 11: LevelBoundary\n (2.0, 1.0), # 12: LinearResistance\n (3.0, -1.0), # 13: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, -2.0), # 14: Terminal\n (3.0, 3.0), # 15: FlowBoundary\n (0.0, 1.0), # 16: FlowBoundary\n (6.0, 1.0), # 17: LevelBoundary\n ]\n)\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_id, node_type = ribasim.Node.node_ids_and_types(\n basin,\n manning_resistance,\n rating_curve,\n pump,\n fractional_flow,\n linear_resistance,\n level_boundary,\n flow_boundary,\n terminal,\n)\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(node_id, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array(\n [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 8, 7, 9, 11, 12, 4, 13, 15, 16, 10], dtype=np.int64\n)\nto_id = np.array(\n [2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 6, 7, 9, 9, 10, 12, 3, 13, 14, 6, 1, 17], dtype=np.int64\n)\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": len(from_id) * [\"flow\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n linear_resistance=linear_resistance,\n manning_resistance=manning_resistance,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n fractional_flow=fractional_flow,\n terminal=terminal,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic/ribasim.toml')\n\n\n\n\n2 Update the basic model with transient forcing\nThis assumes you have already created the basic model with static forcing.\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\nimport xarray as xr\n\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(filepath=datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\n\ntime = pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime)\nday_of_year = time.day_of_year.to_numpy()\nseconds_per_day = 24 * 60 * 60\nevaporation = (\n (-1.0 * np.cos(day_of_year / 365.0 * 2 * np.pi) + 1.0) * 0.0025 / seconds_per_day\n)\nrng = np.random.default_rng(seed=0)\nprecipitation = (\n rng.lognormal(mean=-1.0, sigma=1.7, size=time.size) * 0.001 / seconds_per_day\n)\n\nWe’ll use xarray to easily broadcast the values.\n\ntimeseries = (\n pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 1,\n \"time\": pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime),\n \"drainage\": 0.0,\n \"potential_evaporation\": evaporation,\n \"infiltration\": 0.0,\n \"precipitation\": precipitation,\n \"urban_runoff\": 0.0,\n }\n )\n .set_index(\"time\")\n .to_xarray()\n)\n\nbasin_ids = model.basin.static.df[\"node_id\"].to_numpy()\nbasin_nodes = xr.DataArray(\n np.ones(len(basin_ids)), coords={\"node_id\": basin_ids}, dims=[\"node_id\"]\n)\nforcing = (timeseries * basin_nodes).to_dataframe().reset_index()\n\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": basin_ids,\n \"level\": 1.4,\n \"concentration\": 0.0,\n }\n)\n\n\nmodel.basin.time.df = forcing\nmodel.basin.state.df = state\n\n\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic_transient/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic_transient/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim basic-transient/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\ndf_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\n<Axes: xlabel='time'>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ndf_flow = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/flow.arrow\")\ndf_flow[\"edge\"] = list(zip(df_flow.from_node_id, df_flow.to_node_id))\ndf_flow[\"flow_m3d\"] = df_flow.flow * 86400\nax = df_flow.pivot_table(index=\"time\", columns=\"edge\", values=\"flow_m3d\").plot()\nax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title=\"Edge\")\n\n<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f7014656f50>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ntype(df_flow)\n\npandas.core.frame.DataFrame\n\n\n\n\n3 Model with discrete control\nThe model constructed below consists of a single basin which slowly drains trough a TabulatedRatingCurve, but is held within a range around a target level (setpoint) by two connected pumps. These two pumps behave like a reversible pump. When pumping can be done in only one direction, and the other direction is only possible under gravity, use an Outlet for that direction.\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin\n (1.0, 1.0), # 2: Pump\n (1.0, -1.0), # 3: Pump\n (2.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (-1.0, 0.0), # 5: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (-2.0, 0.0), # 6: Terminal\n (1.0, 0.0), # 7: DiscreteControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"TabulatedRatingCurve\",\n \"Terminal\",\n \"DiscreteControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 7, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 6, 2, 3], dtype=np.int64)\n\nedge_type = 6 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"]\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"from_node_id\": from_id, \"to_node_id\": to_id, \"edge_type\": edge_type},\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1],\n \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n }\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"level\": [20.0]})\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the discrete control:\n\ncondition = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [7],\n \"listen_feature_id\": 3 * [1],\n \"variable\": 3 * [\"level\"],\n \"greater_than\": [5.0, 10.0, 15.0], # min, setpoint, max\n }\n)\n\nlogic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 5 * [7],\n \"truth_state\": [\"FFF\", \"U**\", \"T*F\", \"**D\", \"TTT\"],\n \"control_state\": [\"in\", \"in\", \"none\", \"out\", \"out\"],\n }\n)\n\ndiscrete_control = ribasim.DiscreteControl(condition=condition, logic=logic)\n\nThe above control logic can be summarized as follows: - If the level gets above the maximum, activate the control state “out” until the setpoint is reached; - If the level gets below the minimum, active the control state “in” until the setpoint is reached; - Otherwise activate the control state “none”.\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [2] + 3 * [3],\n \"control_state\": 2 * [\"none\", \"in\", \"out\"],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0, 2e-3, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2e-3],\n }\n )\n)\n\nThe pump data defines the following:\n\n\n\nControl state\nPump #2 flow rate (m/s)\nPump #3 flow rate (m/s)\n\n\n\n\n“none”\n0.0\n0.0\n\n\n“in”\n2e-3\n0.0\n\n\n“out”\n0.0\n2e-3\n\n\n\nSetup the level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [4], \"level\": [10.0]})\n)\n\nSetup the rating curve:\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": 2 * [5], \"level\": [2.0, 15.0], \"discharge\": [0.0, 1e-3]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup the terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [6]}))\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n pump=pump,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n terminal=terminal,\n discrete_control=discrete_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nListen edges are plotted with a dashed line since they are not present in the “Edge / static” schema but only in the “Control / condition” schema.\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\n\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\ngreater_than = model.discrete_control.condition.df.greater_than\n\nax.hlines(\n greater_than,\n df_basin.time[0],\n df_basin.time.max(),\n lw=1,\n ls=\"--\",\n color=\"k\",\n)\n\ndf_control = pd.read_feather(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\ny_min, y_max = ax.get_ybound()\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[:2], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[2:4], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\n\nax.set_xticks(\n date2num(df_control.time).tolist(),\n df_control.control_state.tolist(),\n rotation=50,\n)\n\nax.set_yticks(greater_than, [\"min\", \"setpoint\", \"max\"])\nax.set_ylabel(\"level\")\nplt.show()\n\n\n\n\nThe highlighted regions show where a pump is active.\nLet’s print an overview of what happened with control:\n\nmodel.print_discrete_control_record(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\n0. At 2020-01-01 00:00:00 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTT:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"out\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n\n1. At 2020-02-08 19:02:21.861000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n2. At 2020-07-05 08:56:10.319000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state FFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"in\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n3. At 2020-08-11 06:05:15.592000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n\n\nNote that crossing direction specific truth states (containing “U”, “D”) are not present in this overview even though they are part of the control logic. This is because in the control logic for this model these truth states are only used to sustain control states, while the overview only shows changes in control states.\n\n\n4 Model with PID control\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: FlowBoundary\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: Basin\n (2.0, 0.5), # 3: Pump\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (1.5, 1.0), # 5: PidControl\n (2.0, -0.5), # 6: outlet\n (1.5, -1.0), # 7: PidControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"FlowBoundary\",\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"PidControl\",\n \"Outlet\",\n \"PidControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 5, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([2, 3, 4, 6, 2, 3, 6], dtype=np.int64)\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": 5 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [2, 2], \"level\": [0.0, 1.0], \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0]}\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"level\": [6.0],\n }\n)\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [3],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup the outlet:\n\noutlet = ribasim.Outlet(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [6],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"flow_rate\": [1e-3]})\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4],\n \"level\": [1.0], # Not relevant\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup PID control:\n\npid_control = ribasim.PidControl(\n time=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 4 * [5, 7],\n \"time\": [\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n ],\n \"listen_node_id\": 4 * [2, 2],\n \"target\": [5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5],\n \"proportional\": 4 * [-1e-3, 1e-3],\n \"integral\": 4 * [-1e-7, 1e-7],\n \"derivative\": 4 * [0.0, 0.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nNote that the coefficients for the pump and the outlet are equal in magnitude but opposite in sign. This way the pump and the outlet equally work towards the same goal, while having opposite effects on the controlled basin due to their connectivity to this basin.\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n outlet=outlet,\n pid_control=pid_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"pid_control/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/pid_control/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim pid_control/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"pid_control/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\nax.set_ylabel(\"level [m]\")\n\n# Plot target level\ntarget_levels = model.pid_control.time.df.target.to_numpy()[:4]\ntimes = date2num(model.pid_control.time.df.time)[:4]\nax.plot(times, target_levels, color=\"k\", ls=\":\", label=\"target level\")\npass"
},
{
"objectID": "qgis/index.html",
"href": "qgis/index.html",
"title": "QGIS plugin",
"section": "",
- "text": "Install QGIS version 3.28 or higher.\n\n\nDownload ribasim_qgis.zip, see the download section.\nPlugins menu > Manage and Install Plugins…\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Install from ZIP”:\n\nBrowse to the ribasim_qgis.zip file containing the plugin that was downloaded earlier\nClick “Install Plugin”\n\n\n\n\n\n\nStart the Ribasim plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nIn QGIS, navigate to “Plugins > Manage and Install Plugins > All”. In the search bar, type: “iMOD”. Select the iMOD plugin, and click “Install”.\nAt least version 0.4.0 of the iMOD plugin is required.\nThe Time Series widget from the iMOD plugin is used for visualizing Ribasim results, which is described in Section 1.5. Documentation on the Time Series widget can be found in the iMOD documentation.\n\n\n\nOpen an existing model or create a new model. As an example of an existing model, you can use the “basic” model from generated_testmodels.zip, see the download section.\n\n\n\n\n\nCheck if your coordinate reference system (CRS) is set correctly.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are working with an unknown CRS, right click the model database group in Layers, and click “Set Group CRS…”.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are modeling the Netherlands, select “Amersfoort / RD New” (EPSG:28992).\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Node layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn on the edit mode to be able to add nodes on the map.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdd nodes to the map with a left click and select the node type.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn the edit mode off and save the edits to the Nodes layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nRight click a layer and select “Open Attribute Table”.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick the yellow pencil icon on the top left to enable editing, and copy and paste a record. A record can be selected by clicking on the row number.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdjust the content. If you prefer, it also works to copy data with the same columns from Excel. Turn off edit mode and save changes to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nMake sure the Snapping Toolbar is visible, by going to the View > Toolbars menu. Turn on snapping mode by clicking the magnet and set the snapping distance to 25 pixels.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Edge layer and turn on the edit mode.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Add line feature”.\n\n\n\n\n\nCreate a connection by left clicking a source node and right clicking the destination node.\n\n\n\n\n\nNow leave the edit mode and save the results to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nOpen a text editor and create an empty file next to your database, with the .toml extension.\nAdd the following content to the TOML file:\n\n\n\nribasim.toml\n\nstarttime = 2020-01-01 00:00:00\nendtime = 2021-01-01 00:00:00\ndatabase = \"database.gpkg\"\n\n\nUnzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files.\n\n\n\n\n\n\nIn QGIS select the model group.\n\n\n\n\n\nIn the Ribasim plugin widget, select the Results tab and click “Associate Results”.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect results/basin.arrow.\n\n\n\n\n\nThis adds metadata to the model that the iMOD plugin can use to find the timeseries data that is associated to the model nodes.\n\n\n\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes. Currently only the Basin nodes can be plotted.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph."
+ "text": "Install QGIS version 3.28 or higher.\n\n\nDownload ribasim_qgis.zip, see the download section.\nPlugins menu > Manage and Install Plugins…\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Install from ZIP”:\n\nBrowse to the ribasim_qgis.zip file containing the plugin that was downloaded earlier\nClick “Install Plugin”\n\n\n\n\n\n\nStart the Ribasim plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nIn QGIS, navigate to “Plugins > Manage and Install Plugins > All”. In the search bar, type: “iMOD”. Select the iMOD plugin, and click “Install”.\nAt least version 0.4.0 of the iMOD plugin is required.\nThe Time Series widget from the iMOD plugin is used for visualizing Ribasim results, which is described in Section 1.5. Documentation on the Time Series widget can be found in the iMOD documentation.\n\n\n\nOpen an existing model or create a new model. As an example of an existing model, you can use the “basic” model from generated_testmodels.zip, see the download section.\n\n\n\n\n\nCheck if your coordinate reference system (CRS) is set correctly.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are working with an unknown CRS, right click the model database group in Layers, and click “Set Group CRS…”.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are modeling the Netherlands, select “Amersfoort / RD New” (EPSG:28992).\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Node layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn on the edit mode to be able to add nodes on the map.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdd nodes to the map with a left click and select the node type.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn the edit mode off and save the edits to the Nodes layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nRight click a layer and select “Open Attribute Table”.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick the yellow pencil icon on the top left to enable editing, and copy and paste a record. A record can be selected by clicking on the row number.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdjust the content. If you prefer, it also works to copy data with the same columns from Excel. Turn off edit mode and save changes to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nMake sure the Snapping Toolbar is visible, by going to the View > Toolbars menu. Turn on snapping mode by clicking the magnet and set the snapping distance to 25 pixels.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Edge layer and turn on the edit mode.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Add line feature”.\n\n\n\n\n\nCreate a connection by left clicking a source node and right clicking the destination node.\n\n\n\n\n\nNow leave the edit mode and save the results to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nUnzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files.\n\n\n\n\nBefore trying to inspect the results, verify that the run was successful and the output files are there.\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the layer that you wish to plot. From the “Node” layer you can plot level or storage on Basin nodes. From the “Edge” layer you can plot flow over flow edges. Note that before switching between these, you typically have to click “Clear” to clear the selection. If you run a simulation with the model open in QGIS, you have to close and re-open the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel for the new results to be loaded.\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph.\n\n\n\n\n\nOnly the “basin.arrow” and “flow.arrow” can be inspected with the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel. All Arrow files can be loaded as a layer by dragging the files onto QGIS. Right click the layer and select “Open Attribute Table” to view the contents."
},
{
"objectID": "qgis/index.html#start",
@@ -431,14 +431,14 @@
"href": "qgis/index.html#run-a-model",
"title": "QGIS plugin",
"section": "",
- "text": "Open a text editor and create an empty file next to your database, with the .toml extension.\nAdd the following content to the TOML file:\n\n\n\nribasim.toml\n\nstarttime = 2020-01-01 00:00:00\nendtime = 2021-01-01 00:00:00\ndatabase = \"database.gpkg\"\n\n\nUnzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files."
+ "text": "Unzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files."
},
{
"objectID": "qgis/index.html#sec-results",
"href": "qgis/index.html#sec-results",
"title": "QGIS plugin",
"section": "",
- "text": "In QGIS select the model group.\n\n\n\n\n\nIn the Ribasim plugin widget, select the Results tab and click “Associate Results”.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect results/basin.arrow.\n\n\n\n\n\nThis adds metadata to the model that the iMOD plugin can use to find the timeseries data that is associated to the model nodes.\n\n\n\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes. Currently only the Basin nodes can be plotted.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph."
+ "text": "Before trying to inspect the results, verify that the run was successful and the output files are there.\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the layer that you wish to plot. From the “Node” layer you can plot level or storage on Basin nodes. From the “Edge” layer you can plot flow over flow edges. Note that before switching between these, you typically have to click “Clear” to clear the selection. If you run a simulation with the model open in QGIS, you have to close and re-open the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel for the new results to be loaded.\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph.\n\n\n\n\n\nOnly the “basin.arrow” and “flow.arrow” can be inspected with the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel. All Arrow files can be loaded as a layer by dragging the files onto QGIS. Right click the layer and select “Open Attribute Table” to view the contents."
},
{
"objectID": "couple/modflow-demo.html",
Ribasim.DiscreteControl — Type.Ribasim.EdgeMetadata — Type.Ribasim.FlatVector — Type.struct FlatVector{T} <: AbstractVector{T}Vector{Vector{T}}.Iterators.flatten, though that doesn’t work with the Tables.Column interface, which needs length and getindex support.Ribasim.FlowBoundary — Type.Ribasim.FractionalFlow — Type.source
+
# Ribasim.InNeighbors — Type.
Iterate over incoming neighbors of a given label in a MetaGraph, only for edges of edge_type
-
+
# Ribasim.LevelBoundary — Type.
node_id: node ID of the LevelBoundary node active: whether this node is active level: the fixed level of this ‘infinitely big basin’
-
+
# Ribasim.LinearResistance — Type.
Requirements:
@@ -330,7 +330,7 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.ManningResistance — Type.
This is a simple Manning-Gauckler reach connection.
@@ -360,48 +360,48 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.Model — Type.
Model(config_path::AbstractString)
Model(config::Config)
Initialize a Model.
The Model struct is an initialized model, combined with the Config used to create it and saved results. The Basic Model Interface (BMI) is implemented on the Model. A Model can be created from the path to a TOML configuration file, or a Config object.
-
+
# Ribasim.NodeMetadata — Type.
Type for storing metadata of nodes in the graph type: type of the node allocationnetworkid: Allocation network ID (0 if not in subnetwork)
-
+
# Ribasim.OutNeighbors — Type.
Iterate over outgoing neighbors of a given label in a MetaGraph, only for edges of edge_type
-
+
# Ribasim.Outlet — Type.
nodeid: node ID of the Outlet node active: whether this node is active and thus contributes flow flowrate: target flow rate minflowrate: The minimal flow rate of the outlet maxflowrate: The maximum flow rate of the outlet controlmapping: dictionary from (nodeid, controlstate) to target flow rate ispid_controlled: whether the flow rate of this outlet is governed by PID control
-
+
# Ribasim.PidControl — Type.
PID control currently only supports regulating basin levels.
nodeid: node ID of the PidControl node active: whether this node is active and thus sets flow rates listennodeid: the id of the basin being controlled pidparams: a vector interpolation for parameters changing over time. The parameters are respectively target, proportional, integral, derivative, where the last three are the coefficients for the PID equation. error: the current error; basintarget - currentlevel
-
+
# Ribasim.Pump — Type.
nodeid: node ID of the Pump node active: whether this node is active and thus contributes flow flowrate: target flow rate minflowrate: The minimal flow rate of the pump maxflowrate: The maximum flow rate of the pump controlmapping: dictionary from (nodeid, controlstate) to target flow rate ispid_controlled: whether the flow rate of this pump is governed by PID control
-
+
# Ribasim.Subgrid — Type.
Subgrid linearly interpolates basin levels.
-
+
# Ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve — Type.
struct TabulatedRatingCurve{C}
Rating curve from level to discharge. The rating curve is a lookup table with linear interpolation in between. Relation can be updated in time, which is done by moving data from the time field into the tables, which is done in the update_tabulated_rating_curve callback.
Type parameter C indicates the content backing the StructVector, which can be a NamedTuple of Vectors or Arrow Primitives, and is added to avoid type instabilities.
nodeid: node ID of the TabulatedRatingCurve node active: whether this node is active and thus contributes flows tables: The current Q(h) relationships time: The time table used for updating the tables controlmapping: dictionary from (nodeid, controlstate) to Q(h) and/or active state
-
+
# Ribasim.Terminal — Type.
node_id: node ID of the Terminal node
-
+
# Ribasim.User — Type.
demand: water flux demand of user per priority over time active: whether this node is active and thus demands water allocated: water flux currently allocated to user per priority returnfactor: the factor in [0,1] of how much of the abstracted water is given back to the system minlevel: The level of the source basin below which the user does not abstract priorities: All used priority values. Each user has a demand for all these priorities, which is 0.0 if it is not provided explicitly. record: Collected data of allocation optimizations for output file.
-
+
# Ribasim.config.Config — Method.
Config(config_path::AbstractString; kwargs...)
Parse a TOML file to a Config. Keys can be overruled using keyword arguments. To overrule keys from a subsection, e.g. dt from the solver section, use underscores: solver_dt.
-
+
@@ -410,157 +410,157 @@ # BasicModelInterface.finalize — Method.
BMI.finalize(model::Model)::Model
Write all results to the configured files.
-
+
# BasicModelInterface.initialize — Method.
BMI.initialize(T::Type{Model}, config_path::AbstractString)::Model
Initialize a Model from the path to the TOML configuration file.
-
+
# BasicModelInterface.initialize — Method.
BMI.initialize(T::Type{Model}, config::Config)::Model
Initialize a Model from a Config.
-
+
# CommonSolve.solve! — Method.
solve!(model::Model)::ODESolution
Solve a Model until the configured endtime.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_absolute_value! — Method.
Minimizing |expr| can be achieved by introducing a new variable exprabs and posing the following constraints: exprabs >= expr expr_abs >= -expr
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_capacity! — Method.
Add the flow capacity constraints to the allocation problem. Only finite capacities get a constraint. The constraint indices are (edgesourceid, edgedstid).
Constraint: flow over edge <= edge capacity
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_flow_conservation! — Method.
Add the flow conservation constraints to the allocation problem. The constraint indices are user node IDs.
Constraint: sum(flows out of node node) <= flows into node + flow from storage and vertical fluxes
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_source! — Method.
Add the source constraints to the allocation problem. The actual threshold values will be set before each allocation solve. The constraint indices are (edgesourceid, edgedstid).
Constraint: flow over source edge <= source flow in subnetwork
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_user_returnflow! — Method.
Add the user returnflow constraints to the allocation problem. The constraint indices are user node IDs.
Constraint: outflow from user <= return factor * inflow to user
-
+
# Ribasim.add_flow! — Method.
Add the given flow q to the flow over the edge on the horizontal (self-loop) edge from id to id.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_flow! — Method.
Add the given flow q to the existing flow over the edge between the given nodes.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_variables_absolute_value! — Method.
Certain allocation distribution types use absolute values in the objective function. Since most optimization packages do not support the absolute value function directly, New variables are introduced that act as the absolute value of an expression by posing the appropriate constraints.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_variables_flow! — Method.
Add the flow variables F to the allocation problem. The variable indices are (edgesourceid, edgedstid). Non-negativivity constraints are also immediately added to the flow variables.
-
+
# Ribasim.adjust_edge_capacities! — Method.
Set the values of the edge capacities. 2 cases:
- Before the first allocation solve, set the edge capacities to their full capacity;
- Before an allocation solve, subtract the flow used by allocation for the previous priority from the edge capacities.
-
+
# Ribasim.adjust_source_flows! — Method.
Adjust the source flows.
-
+
# Ribasim.all_neighbor_labels_type — Method.
Get the in- and outneighbor node IDs of the given node ID (label) over the given edge type in the graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocate! — Method.
Update the allocation optimization problem for the given subnetwork with the problem state and flows, solve the allocation problem and assign the results to the users.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_graph — Method.
Build the graph used for the allocation problem.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_graph_used_nodes! — Method.
Find all nodes in the subnetwork which will be used in the allocation network. Some nodes are skipped to optimize allocation optimization.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_path_exists_in_graph — Method.
Find out whether a path exists between a start node and end node in the given allocation graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_problem — Method.
Construct the allocation problem for the current subnetwork as a JuMP.jl model.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_table — Method.
Create an allocation result table for the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.assign_allocations! — Method.
Assign the allocations to the users as determined by the solution of the allocation problem.
-
+
# Ribasim.avoid_using_own_returnflow! — Method.
Remove allocation user return flow edges that are upstream of the user itself.
-
+
# Ribasim.basin_bottom — Method.
Return the bottom elevation of the basin with index i, or nothing if it doesn’t exist
-
+
# Ribasim.basin_bottoms — Method.
Get the bottom on both ends of a node. If only one has a bottom, use that for both.
-
+
# Ribasim.basin_table — Method.
Create the basin result table from the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.create_callbacks — Method.
Create the different callbacks that are used to store results and feed the simulation with new data. The different callbacks are combined to a CallbackSet that goes to the integrator. Returns the CallbackSet and the SavedValues for flow.
-
+
# Ribasim.create_graph — Method.
Return a directed metagraph with data of nodes (NodeMetadata): NodeMetadata
and data of edges (EdgeMetadata): EdgeMetadata
-
+
# Ribasim.create_storage_tables — Method.
Read the Basin / profile table and return all area and level and computed storage values
-
+
# Ribasim.datetime_since — Method.
datetime_since(t::Real, t0::DateTime)::DateTime
Convert a Real that represents the seconds passed since the simulation start to the nearest DateTime. This is used to convert between the solver’s inner float time, and the calendar.
-
+
# Ribasim.datetimes — Method.
Get all saved times as a Vector{DateTime}
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_affect! — Method.
Change parameters based on the control logic.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_affect_downcrossing! — Method.
An downcrossing means that a condition (always greater than) becomes false.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_affect_upcrossing! — Method.
An upcrossing means that a condition (always greater than) becomes true.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_condition — Method.
Listens for changes in condition truths.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_table — Method.
Create a discrete control result table from the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.expand_logic_mapping — Method.
Replace the truth states in the logic mapping which contain wildcards with all possible explicit truth states.
-
+
# Ribasim.find_allocation_graph_edges! — Method.
This loop finds allocation graph edges in several ways:
- Between allocation graph nodes whose equivalent in the subnetwork are directly connected
- Between allocation graph nodes whose equivalent in the subnetwork are connected with one or more allocation graph nodes in between
-
+
# Ribasim.findlastgroup — Method.
For an element id and a vector of elements ids, get the range of indices of the last consecutive block of id. Returns the empty range 1:0 if id is not in ids.
# 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Ribasim.findlastgroup(2, [5,4,2,2,5,2,2,2,1])
# output
6:8
-
+
# Ribasim.findsorted — Method.
Find the index of element x in a sorted collection a. Returns the index of x if it exists, or nothing if it doesn’t. If x occurs more than once, throw an error.
-
+
# Ribasim.flow_table — Method.
Create a flow result table from the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.formulate_basins! — Method.
Smoothly let the evaporation flux go to 0 when at small water depths Currently at less than 0.1 m.
-
+
# Ribasim.formulate_flow! — Method.
Directed graph: outflow is positive!
-
+
# Ribasim.formulate_flow! — Method.
Conservation of energy for two basins, a and b:
h_a + v_a^2 / (2 * g) = h_b + v_b^2 / (2 * g) + S_f * L + C / 2 * g * (v_b^2 - v_a^2)
@@ -588,116 +588,116 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.formulate_flow! — Method.
Directed graph: outflow is positive!
-
+
# Ribasim.get_area_and_level — Method.
Compute the area and level of a basin given its storage. Also returns darea/dlevel as it is needed for the Jacobian.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_chunk_sizes — Method.
Get the chunk sizes for DiffCache; differentiation w.r.t. u and t (the latter only if a Rosenbrock algorithm is used).
-
+
# Ribasim.get_compressor — Method.
Get the compressor based on the Results section
-
+
# Ribasim.get_flow — Method.
Get the flow over the given horizontal (selfloop) edge (val is needed for get_tmp from ForwardDiff.jl).
-
+
# Ribasim.get_flow — Method.
Get the flow over the given edge (val is needed for get_tmp from ForwardDiff.jl).
-
+
# Ribasim.get_fractional_flow_connected_basins — Method.
Get the node type specific indices of the fractional flows and basins, that are consecutively connected to a node of given id.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_jac_prototype — Method.
Get a sparse matrix whose sparsity matches the sparsity of the Jacobian of the ODE problem. All nodes are taken into consideration, also the ones that are inactive.
In Ribasim the Jacobian is typically sparse because each state only depends on a small number of other states.
Note: the name ‘prototype’ does not mean this code is a prototype, it comes from the naming convention of this sparsity structure in the differentialequations.jl docs.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_level — Method.
Get the current water level of a node ID. The ID can belong to either a Basin or a LevelBoundary. storage: tells ForwardDiff whether this call is for differentiation or not
-
+
# Ribasim.get_scalar_interpolation — Method.
Linear interpolation of a scalar with constant extrapolation.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_storage_from_level — Method.
Get the storage of a basin from its level.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_storages_and_levels — Method.
Get the storage and level of all basins as matrices of nbasin × ntime
-
+
# Ribasim.get_storages_from_levels — Method.
Compute the storages of the basins based on the water level of the basins.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_tstops — Method.
From an iterable of DateTimes, find the times the solver needs to stop
-
+
# Ribasim.get_value — Method.
Get a value for a condition. Currently supports getting levels from basins and flows from flow boundaries.
-
+
# Ribasim.id_index — Method.
Get the index of an ID in a set of indices.
-
+
# Ribasim.indicate_allocation_flow! — Method.
Add to the edge metadata that the given edge is used for allocation flow. If the edge does not exist, it is created.
-
+
# Ribasim.inflow_id — Method.
Get the unique inneighbor over a flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.inflow_ids — Method.
Get the inneighbors over flow edges.
-
+
# Ribasim.inflow_ids_allocation — Method.
Get the inneighbors of the given ID such that the connecting edge is an allocation flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.inneighbor_labels_type — Method.
Get the inneighbor node IDs of the given node ID (label) over the given edge type in the graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.inoutflow_ids — Method.
Get the in- and outneighbors over flow edges.
-
+
# Ribasim.is_allocation_source — Method.
Find out whether the given edge is a source for an allocation network.
-
+
# Ribasim.is_flow_constraining — Method.
Whether the given node node is flow constraining by having a maximum flow rate.
-
+
# Ribasim.is_flow_direction_constraining — Method.
Whether the given node is flow direction constraining (only in direction of edges).
-
+
# Ribasim.load_data — Method.
load_data(db::DB, config::Config, nodetype::Symbol, kind::Symbol)::Union{Table, Query, Nothing}
Load data from Arrow files if available, otherwise the database. Returns either an Arrow.Table, SQLite.Query or nothing if the data is not present.
-
+
# Ribasim.load_structvector — Method.
load_structvector(db::DB, config::Config, ::Type{T})::StructVector{T}
Load data from Arrow files if available, otherwise the database. Always returns a StructVector of the given struct type T, which is empty if the table is not found. This function validates the schema, and enforces the required sort order.
-
+
# Ribasim.metadata_from_edge — Method.
Get the metadata of an edge in the graph from an edge of the underlying DiGraph.
-
+
# Ribasim.nodefields — Method.
Get all node fieldnames of the parameter object.
-
+
# Ribasim.nodetype — Method.
From a SchemaVersion(“ribasim.flowboundary.static”, 1) return (:FlowBoundary, :static)
-
+
# Ribasim.outflow_id — Method.
Get the unique outneighbor over a flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.outflow_ids — Method.
Get the outneighbors over flow edges.
-
+
# Ribasim.outflow_ids_allocation — Method.
Get the outneighbors of the given ID such that the connecting edge is an allocation flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.outneighbor_labels_type — Method.
Get the outneighbor node IDs of the given node ID (label) over the given edge type in the graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.parse_static_and_time — Method.
Process the data in the static and time tables for a given node type. The ‘defaults’ named tuple dictates how missing data is filled in. ‘time_interpolatables’ is a vector of Symbols of parameter names for which a time interpolation (linear) object must be constructed. The control mapping for DiscreteControl is also constructed in this function. This function currently does not support node states that are defined by more than one row in a table, as is the case for TabulatedRatingCurve.
-
+
# Ribasim.process_allocation_graph_edges! — Method.
For the composite allocation graph edges:
@@ -705,83 +705,83 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.profile_storage — Method.
Calculate a profile storage by integrating the areas over the levels
-
+
# Ribasim.qh_interpolation — Method.
From a table with columns nodeid, discharge (Q) and level (h), create a LinearInterpolation from level to discharge for a given nodeid.
-
+
# Ribasim.reduction_factor — Method.
Function that goes smoothly from 0 to 1 in the interval [0,threshold], and is constant outside this interval.
-
+
# Ribasim.run — Method.
run(config_file::AbstractString)::Model
run(config::Config)::Model
Run a Model, given a path to a TOML configuration file, or a Config object. Running a model includes initialization, solving to the end with [solve!](@ref) and writing results with BMI.finalize.
-
+
# Ribasim.save_flow — Method.
Copy the current flow to the SavedValues
-
+
# Ribasim.save_subgrid_level — Method.
Interpolate the levels and save them to SavedValues
-
+
# Ribasim.scalar_interpolation_derivative — Method.
Derivative of scalar interpolation.
-
+
# Ribasim.seconds_since — Method.
seconds_since(t::DateTime, t0::DateTime)::Float64
Convert a DateTime to a float that is the number of seconds since the start of the simulation. This is used to convert between the solver’s inner float time, and the calendar.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_current_value! — Method.
From a timeseries table time, load the most recent applicable data into table. table must be a NamedTuple of vectors with all variables that must be loaded. The most recent applicable data is non-NaN data for a given ID that is on or before t.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_flow! — Method.
Set the given flow q on the horizontal (self-loop) edge from id to id.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_flow! — Method.
Set the given flow q over the edge between the given nodes.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_initial_discrete_controlled_parameters! — Method.
Set parameters of nodes that are controlled by DiscreteControl to the values corresponding to the initial state of the model.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_objective_priority! — Method.
Set the objective for the given priority. For an objective with absolute values this also involves adjusting constraints.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_static_value! — Method.
Load data from a source table static into a destination table. Data is matched based on the node_id, which is sorted.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_table_row! — Method.
Update table at row index i, with the values of a given row. table must be a NamedTuple of vectors with all variables that must be loaded. The row must contain all the column names that are present in the table. If a value is NaN, it is not set.
-
+
# Ribasim.sorted_table! — Method.
Depending on if a table can be sorted, either sort it or assert that it is sorted.
Tables loaded from the database into memory can be sorted. Tables loaded from Arrow files are memory mapped and can therefore not be sorted.
-
+
# Ribasim.timesteps — Method.
Get all saved times in seconds since start
-
+
# Ribasim.update_allocation! — Method.
Solve the allocation problem for all users and assign allocated abstractions to user nodes.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_basin — Method.
Load updates from ‘Basin / time’ into the parameters
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
Method for nodes that do not contribute to the Jacobian
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
The controlled basin affects itself and the basins upstream and downstream of the controlled pump affect eachother if there is a basin upstream of the pump. The state for the integral term and the controlled basin affect eachother, and the same for the integral state and the basin upstream of the pump if it is indeed a basin.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
If both the unique node upstream and the unique node downstream of these nodes are basins, then these directly depend on eachother and affect the Jacobian 2x Basins always depend on themselves.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
If both the unique node upstream and the nodes down stream (or one node further if a fractional flow is in between) are basins, then the downstream basin depends on the upstream basin(s) and affect the Jacobian as many times as there are downstream basins Upstream basins always depend on themselves.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_tabulated_rating_curve! — Method.
Load updates from ‘TabulatedRatingCurve / time’ into the parameters
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_discrete_control — Method.
Check:
@@ -789,50 +789,50 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.valid_edge_types — Method.
Check that only supported edge types are declared.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_edges — Method.
Test for each node given its node type whether the nodes that
are downstream (‘down-edge’) of this node are of an allowed type
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_flow_rates — Method.
Test whether static or discrete controlled flow rates are indeed non-negative.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_fractional_flow — Method.
Check that nodes that have fractional flow outneighbors do not have any other type of outneighbor, that the fractions leaving a node add up to ≈1 and that the fractions are non-negative.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_n_neighbors — Method.
Test for each node given its node type whether it has an allowed number of flow/control inneighbors and outneighbors
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_profiles — Method.
Check whether the profile data has no repeats in the levels and the areas start positive.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_sources — Method.
The source nodes must only have one allocation outneighbor and no allocation inneighbors.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_subgrid — Method.
Validate the entries for a single subgrid element.
-
+
# Ribasim.water_balance! — Method.
The right hand side function of the system of ODEs set up by Ribasim.
-
+
# Ribasim.write_arrow — Method.
Write a result table to disk as an Arrow file
-
+
# Ribasim.config.algorithm — Method.
Create an OrdinaryDiffEqAlgorithm from solver config
-
+
# Ribasim.config.input_path — Method.
Construct a path relative to both the TOML directory and the optional input_dir
-
+
# Ribasim.config.results_path — Method.
Construct a path relative to both the TOML directory and the optional results_dir
-
+
# Ribasim.config.snake_case — Method.
Convert a string from CamelCase to snake_case.
-
+
@@ -853,7 +853,7 @@ source
+
@@ -861,10 +861,10 @@ 1.5 Macros
# Ribasim.config.@addfields — Macro.
Add fieldnames with Union{String, Nothing} type to struct expression. Requires (option?) use before it.
-
+
# Ribasim.config.@addnodetypes — Macro.
Add all TableOption subtypes as fields to struct expression. Requires (option?) use before it.
-
+
@@ -898,8 +898,8 @@ Ribasim.User
Ribasim.config.ConfigBasicModelInterface.finalizeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeCommonSolve.solve!Ribasim.add_constraints_absolute_value!Ribasim.add_constraints_capacity!Ribasim.scalar_interpolation_derivative
Ribasim.seconds_sinceRibasim.set_current_value!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_initial_discrete_controlled_parameters!Ribasim.set_objective_priority!Ribasim.set_static_value!Ribasim.timesteps
Ribasim.update_allocation!Ribasim.update_basinRibasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_tabulated_rating_curve!Ribasim.valid_discrete_controlRibasim.valid_edge_types2 Update the basi
ax = df_flow.pivot_table(index="time", columns="edge", values="flow_m3d").plot()
ax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title="Edge")
-<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f1a7c921550>
+<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f7014656f50>

@@ -1021,7 +1021,7 @@ 4 Model with PID
<Axes: >
-
+
Write the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:
diff --git a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png
index 33e8abbcf..f5f6a2b5b 100644
Binary files a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png and b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png differ
diff --git a/qgis/index.html b/qgis/index.html
index 0980ee3b0..df224853e 100644
--- a/qgis/index.html
+++ b/qgis/index.html
@@ -20,40 +20,6 @@
margin: 0 0.8em 0.2em -1em; /* quarto-specific, see https://github.com/quarto-dev/quarto-cli/issues/4556 */
vertical-align: middle;
}
-/* CSS for syntax highlighting */
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre; position: relative; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { display: inline-block; line-height: 1.25; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span:empty { height: 1.2em; }
-.sourceCode { overflow: visible; }
-code.sourceCode > span { color: inherit; text-decoration: inherit; }
-div.sourceCode { margin: 1em 0; }
-pre.sourceCode { margin: 0; }
-@media screen {
-div.sourceCode { overflow: auto; }
-}
-@media print {
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre-wrap; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { text-indent: -5em; padding-left: 5em; }
-}
-pre.numberSource code
- { counter-reset: source-line 0; }
-pre.numberSource code > span
- { position: relative; left: -4em; counter-increment: source-line; }
-pre.numberSource code > span > a:first-child::before
- { content: counter(source-line);
- position: relative; left: -1em; text-align: right; vertical-align: baseline;
- border: none; display: inline-block;
- -webkit-touch-callout: none; -webkit-user-select: none;
- -khtml-user-select: none; -moz-user-select: none;
- -ms-user-select: none; user-select: none;
- padding: 0 4px; width: 4em;
- }
-pre.numberSource { margin-left: 3em; padding-left: 4px; }
-div.sourceCode
- { }
-@media screen {
-pre > code.sourceCode > span > a:first-child::before { text-decoration: underline; }
-}
@@ -180,11 +146,7 @@ On this page
- 1.3.2 Create connecting edges
- 1.4 Run a model
- - 1.5 Inspect results
-
+ - 1.5 Inspect results
@@ -362,18 +324,6 @@
1.4 Run a model
-- Open a text editor and create an empty file next to your database, with the
.toml extension.
-- Add the following content to the TOML file:
-
-
-
-ribasim.toml
-
-starttime = 2020-01-01 00:00:00
-endtime = 2021-01-01 00:00:00
-database = "database.gpkg"
-
-
- Unzip the Ribasim command line interface,
ribasim_cli.zip
- Open your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run
path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.
- In your model directory there is now a
results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files.
@@ -381,43 +331,21 @@
1.5 Inspect results
-
-1.5.1 Associate results to iMOD time series window
-In QGIS select the model group.
-
-
-
-
-
-In the Ribasim plugin widget, select the Results tab and click “Associate Results”.
-
-
-
-
-
-Select results/basin.arrow.
-
-
-
-
-
-This adds metadata to the model that the iMOD plugin can use to find the timeseries data that is associated to the model nodes.
-
-
-1.5.2 Plot time series
+Before trying to inspect the results, verify that the run was successful and the output files are there.
Click the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.

+Select the layer that you wish to plot. From the “Node” layer you can plot level or storage on Basin nodes. From the “Edge” layer you can plot flow over flow edges. Note that before switching between these, you typically have to click “Clear” to clear the selection. If you run a simulation with the model open in QGIS, you have to close and re-open the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel for the new results to be loaded.
Select the variables that you want to plot.

-Click “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes. Currently only the Basin nodes can be plotted.
+Click “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes.

@@ -429,9 +357,9 @@ 
+Only the “basin.arrow” and “flow.arrow” can be inspected with the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel. All Arrow files can be loaded as a layer by dragging the files onto QGIS. Right click the layer and select “Open Attribute Table” to view the contents.
-
diff --git a/search.json b/search.json
index 4fab5eb10..635269b00 100644
--- a/search.json
+++ b/search.json
@@ -396,14 +396,14 @@
"href": "python/examples.html",
"title": "Examples",
"section": "",
- "text": "1 Basic model with static forcing\n\nfrom pathlib import Path\n\nimport geopandas as gpd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1, 3, 3, 6, 6, 9, 9],\n \"area\": [0.01, 1000.0] * 4,\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0] * 4,\n }\n)\n\n# Convert steady forcing to m/s\n# 2 mm/d precipitation, 1 mm/d evaporation\nseconds_in_day = 24 * 3600\nprecipitation = 0.002 / seconds_in_day\nevaporation = 0.001 / seconds_in_day\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [0],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [evaporation],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [precipitation],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\nstatic = static.iloc[[0, 0, 0, 0]]\nstatic[\"node_id\"] = [1, 3, 6, 9]\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static)\n\nSetup linear resistance:\n\nlinear_resistance = ribasim.LinearResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [10, 12], \"resistance\": [5e3, (3600.0 * 24) / 100.0]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup Manning resistance:\n\nmanning_resistance = ribasim.ManningResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"length\": [900.0],\n \"manning_n\": [0.04],\n \"profile_width\": [6.0],\n \"profile_slope\": [3.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up a rating curve node:\n\n# Discharge: lose 1% of storage volume per day at storage = 1000.0.\nq1000 = 1000.0 * 0.01 / seconds_in_day\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4, 4],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n \"discharge\": [0.0, q1000],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup fractional flows:\n\nfractional_flow = ribasim.FractionalFlow(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [5, 8, 13],\n \"fraction\": [0.3, 0.6, 0.1],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [7],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.5 / 3600],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [11, 17],\n \"level\": [0.5, 1.5],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [15, 16],\n \"flow_rate\": [1e-4, 1e-4],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [14],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin,\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: ManningResistance\n (2.0, 0.0), # 3: Basin\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (3.0, 1.0), # 5: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, 2.0), # 6: Basin\n (4.0, 1.0), # 7: Pump\n (4.0, 0.0), # 8: FractionalFlow\n (5.0, 0.0), # 9: Basin\n (6.0, 0.0), # 10: LinearResistance\n (2.0, 2.0), # 11: LevelBoundary\n (2.0, 1.0), # 12: LinearResistance\n (3.0, -1.0), # 13: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, -2.0), # 14: Terminal\n (3.0, 3.0), # 15: FlowBoundary\n (0.0, 1.0), # 16: FlowBoundary\n (6.0, 1.0), # 17: LevelBoundary\n ]\n)\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_id, node_type = ribasim.Node.node_ids_and_types(\n basin,\n manning_resistance,\n rating_curve,\n pump,\n fractional_flow,\n linear_resistance,\n level_boundary,\n flow_boundary,\n terminal,\n)\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(node_id, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array(\n [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 8, 7, 9, 11, 12, 4, 13, 15, 16, 10], dtype=np.int64\n)\nto_id = np.array(\n [2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 6, 7, 9, 9, 10, 12, 3, 13, 14, 6, 1, 17], dtype=np.int64\n)\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": len(from_id) * [\"flow\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n linear_resistance=linear_resistance,\n manning_resistance=manning_resistance,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n fractional_flow=fractional_flow,\n terminal=terminal,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic/ribasim.toml')\n\n\n\n\n2 Update the basic model with transient forcing\nThis assumes you have already created the basic model with static forcing.\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\nimport xarray as xr\n\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(filepath=datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\n\ntime = pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime)\nday_of_year = time.day_of_year.to_numpy()\nseconds_per_day = 24 * 60 * 60\nevaporation = (\n (-1.0 * np.cos(day_of_year / 365.0 * 2 * np.pi) + 1.0) * 0.0025 / seconds_per_day\n)\nrng = np.random.default_rng(seed=0)\nprecipitation = (\n rng.lognormal(mean=-1.0, sigma=1.7, size=time.size) * 0.001 / seconds_per_day\n)\n\nWe’ll use xarray to easily broadcast the values.\n\ntimeseries = (\n pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 1,\n \"time\": pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime),\n \"drainage\": 0.0,\n \"potential_evaporation\": evaporation,\n \"infiltration\": 0.0,\n \"precipitation\": precipitation,\n \"urban_runoff\": 0.0,\n }\n )\n .set_index(\"time\")\n .to_xarray()\n)\n\nbasin_ids = model.basin.static.df[\"node_id\"].to_numpy()\nbasin_nodes = xr.DataArray(\n np.ones(len(basin_ids)), coords={\"node_id\": basin_ids}, dims=[\"node_id\"]\n)\nforcing = (timeseries * basin_nodes).to_dataframe().reset_index()\n\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": basin_ids,\n \"level\": 1.4,\n \"concentration\": 0.0,\n }\n)\n\n\nmodel.basin.time.df = forcing\nmodel.basin.state.df = state\n\n\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic_transient/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic_transient/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim basic-transient/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\ndf_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\n<Axes: xlabel='time'>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ndf_flow = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/flow.arrow\")\ndf_flow[\"edge\"] = list(zip(df_flow.from_node_id, df_flow.to_node_id))\ndf_flow[\"flow_m3d\"] = df_flow.flow * 86400\nax = df_flow.pivot_table(index=\"time\", columns=\"edge\", values=\"flow_m3d\").plot()\nax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title=\"Edge\")\n\n<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f1a7c921550>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ntype(df_flow)\n\npandas.core.frame.DataFrame\n\n\n\n\n3 Model with discrete control\nThe model constructed below consists of a single basin which slowly drains trough a TabulatedRatingCurve, but is held within a range around a target level (setpoint) by two connected pumps. These two pumps behave like a reversible pump. When pumping can be done in only one direction, and the other direction is only possible under gravity, use an Outlet for that direction.\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin\n (1.0, 1.0), # 2: Pump\n (1.0, -1.0), # 3: Pump\n (2.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (-1.0, 0.0), # 5: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (-2.0, 0.0), # 6: Terminal\n (1.0, 0.0), # 7: DiscreteControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"TabulatedRatingCurve\",\n \"Terminal\",\n \"DiscreteControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 7, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 6, 2, 3], dtype=np.int64)\n\nedge_type = 6 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"]\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"from_node_id\": from_id, \"to_node_id\": to_id, \"edge_type\": edge_type},\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1],\n \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n }\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"level\": [20.0]})\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the discrete control:\n\ncondition = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [7],\n \"listen_feature_id\": 3 * [1],\n \"variable\": 3 * [\"level\"],\n \"greater_than\": [5.0, 10.0, 15.0], # min, setpoint, max\n }\n)\n\nlogic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 5 * [7],\n \"truth_state\": [\"FFF\", \"U**\", \"T*F\", \"**D\", \"TTT\"],\n \"control_state\": [\"in\", \"in\", \"none\", \"out\", \"out\"],\n }\n)\n\ndiscrete_control = ribasim.DiscreteControl(condition=condition, logic=logic)\n\nThe above control logic can be summarized as follows: - If the level gets above the maximum, activate the control state “out” until the setpoint is reached; - If the level gets below the minimum, active the control state “in” until the setpoint is reached; - Otherwise activate the control state “none”.\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [2] + 3 * [3],\n \"control_state\": 2 * [\"none\", \"in\", \"out\"],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0, 2e-3, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2e-3],\n }\n )\n)\n\nThe pump data defines the following:\n\n\n\nControl state\nPump #2 flow rate (m/s)\nPump #3 flow rate (m/s)\n\n\n\n\n“none”\n0.0\n0.0\n\n\n“in”\n2e-3\n0.0\n\n\n“out”\n0.0\n2e-3\n\n\n\nSetup the level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [4], \"level\": [10.0]})\n)\n\nSetup the rating curve:\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": 2 * [5], \"level\": [2.0, 15.0], \"discharge\": [0.0, 1e-3]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup the terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [6]}))\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n pump=pump,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n terminal=terminal,\n discrete_control=discrete_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nListen edges are plotted with a dashed line since they are not present in the “Edge / static” schema but only in the “Control / condition” schema.\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\n\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\ngreater_than = model.discrete_control.condition.df.greater_than\n\nax.hlines(\n greater_than,\n df_basin.time[0],\n df_basin.time.max(),\n lw=1,\n ls=\"--\",\n color=\"k\",\n)\n\ndf_control = pd.read_feather(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\ny_min, y_max = ax.get_ybound()\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[:2], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[2:4], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\n\nax.set_xticks(\n date2num(df_control.time).tolist(),\n df_control.control_state.tolist(),\n rotation=50,\n)\n\nax.set_yticks(greater_than, [\"min\", \"setpoint\", \"max\"])\nax.set_ylabel(\"level\")\nplt.show()\n\n\n\n\nThe highlighted regions show where a pump is active.\nLet’s print an overview of what happened with control:\n\nmodel.print_discrete_control_record(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\n0. At 2020-01-01 00:00:00 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTT:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"out\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n\n1. At 2020-02-08 19:02:21.861000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n2. At 2020-07-05 08:56:10.319000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state FFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"in\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n3. At 2020-08-11 06:05:15.592000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n\n\nNote that crossing direction specific truth states (containing “U”, “D”) are not present in this overview even though they are part of the control logic. This is because in the control logic for this model these truth states are only used to sustain control states, while the overview only shows changes in control states.\n\n\n4 Model with PID control\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: FlowBoundary\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: Basin\n (2.0, 0.5), # 3: Pump\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (1.5, 1.0), # 5: PidControl\n (2.0, -0.5), # 6: outlet\n (1.5, -1.0), # 7: PidControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"FlowBoundary\",\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"PidControl\",\n \"Outlet\",\n \"PidControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 5, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([2, 3, 4, 6, 2, 3, 6], dtype=np.int64)\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": 5 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [2, 2], \"level\": [0.0, 1.0], \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0]}\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"level\": [6.0],\n }\n)\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [3],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup the outlet:\n\noutlet = ribasim.Outlet(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [6],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"flow_rate\": [1e-3]})\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4],\n \"level\": [1.0], # Not relevant\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup PID control:\n\npid_control = ribasim.PidControl(\n time=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 4 * [5, 7],\n \"time\": [\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n ],\n \"listen_node_id\": 4 * [2, 2],\n \"target\": [5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5],\n \"proportional\": 4 * [-1e-3, 1e-3],\n \"integral\": 4 * [-1e-7, 1e-7],\n \"derivative\": 4 * [0.0, 0.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nNote that the coefficients for the pump and the outlet are equal in magnitude but opposite in sign. This way the pump and the outlet equally work towards the same goal, while having opposite effects on the controlled basin due to their connectivity to this basin.\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n outlet=outlet,\n pid_control=pid_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"pid_control/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/pid_control/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim pid_control/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"pid_control/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\nax.set_ylabel(\"level [m]\")\n\n# Plot target level\ntarget_levels = model.pid_control.time.df.target.to_numpy()[:4]\ntimes = date2num(model.pid_control.time.df.time)[:4]\nax.plot(times, target_levels, color=\"k\", ls=\":\", label=\"target level\")\npass"
+ "text": "1 Basic model with static forcing\n\nfrom pathlib import Path\n\nimport geopandas as gpd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1, 3, 3, 6, 6, 9, 9],\n \"area\": [0.01, 1000.0] * 4,\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0] * 4,\n }\n)\n\n# Convert steady forcing to m/s\n# 2 mm/d precipitation, 1 mm/d evaporation\nseconds_in_day = 24 * 3600\nprecipitation = 0.002 / seconds_in_day\nevaporation = 0.001 / seconds_in_day\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [0],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [evaporation],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [precipitation],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\nstatic = static.iloc[[0, 0, 0, 0]]\nstatic[\"node_id\"] = [1, 3, 6, 9]\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static)\n\nSetup linear resistance:\n\nlinear_resistance = ribasim.LinearResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [10, 12], \"resistance\": [5e3, (3600.0 * 24) / 100.0]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup Manning resistance:\n\nmanning_resistance = ribasim.ManningResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"length\": [900.0],\n \"manning_n\": [0.04],\n \"profile_width\": [6.0],\n \"profile_slope\": [3.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up a rating curve node:\n\n# Discharge: lose 1% of storage volume per day at storage = 1000.0.\nq1000 = 1000.0 * 0.01 / seconds_in_day\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4, 4],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n \"discharge\": [0.0, q1000],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup fractional flows:\n\nfractional_flow = ribasim.FractionalFlow(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [5, 8, 13],\n \"fraction\": [0.3, 0.6, 0.1],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [7],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.5 / 3600],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [11, 17],\n \"level\": [0.5, 1.5],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [15, 16],\n \"flow_rate\": [1e-4, 1e-4],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [14],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin,\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: ManningResistance\n (2.0, 0.0), # 3: Basin\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (3.0, 1.0), # 5: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, 2.0), # 6: Basin\n (4.0, 1.0), # 7: Pump\n (4.0, 0.0), # 8: FractionalFlow\n (5.0, 0.0), # 9: Basin\n (6.0, 0.0), # 10: LinearResistance\n (2.0, 2.0), # 11: LevelBoundary\n (2.0, 1.0), # 12: LinearResistance\n (3.0, -1.0), # 13: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, -2.0), # 14: Terminal\n (3.0, 3.0), # 15: FlowBoundary\n (0.0, 1.0), # 16: FlowBoundary\n (6.0, 1.0), # 17: LevelBoundary\n ]\n)\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_id, node_type = ribasim.Node.node_ids_and_types(\n basin,\n manning_resistance,\n rating_curve,\n pump,\n fractional_flow,\n linear_resistance,\n level_boundary,\n flow_boundary,\n terminal,\n)\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(node_id, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array(\n [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 8, 7, 9, 11, 12, 4, 13, 15, 16, 10], dtype=np.int64\n)\nto_id = np.array(\n [2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 6, 7, 9, 9, 10, 12, 3, 13, 14, 6, 1, 17], dtype=np.int64\n)\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": len(from_id) * [\"flow\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n linear_resistance=linear_resistance,\n manning_resistance=manning_resistance,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n fractional_flow=fractional_flow,\n terminal=terminal,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic/ribasim.toml')\n\n\n\n\n2 Update the basic model with transient forcing\nThis assumes you have already created the basic model with static forcing.\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\nimport xarray as xr\n\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(filepath=datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\n\ntime = pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime)\nday_of_year = time.day_of_year.to_numpy()\nseconds_per_day = 24 * 60 * 60\nevaporation = (\n (-1.0 * np.cos(day_of_year / 365.0 * 2 * np.pi) + 1.0) * 0.0025 / seconds_per_day\n)\nrng = np.random.default_rng(seed=0)\nprecipitation = (\n rng.lognormal(mean=-1.0, sigma=1.7, size=time.size) * 0.001 / seconds_per_day\n)\n\nWe’ll use xarray to easily broadcast the values.\n\ntimeseries = (\n pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 1,\n \"time\": pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime),\n \"drainage\": 0.0,\n \"potential_evaporation\": evaporation,\n \"infiltration\": 0.0,\n \"precipitation\": precipitation,\n \"urban_runoff\": 0.0,\n }\n )\n .set_index(\"time\")\n .to_xarray()\n)\n\nbasin_ids = model.basin.static.df[\"node_id\"].to_numpy()\nbasin_nodes = xr.DataArray(\n np.ones(len(basin_ids)), coords={\"node_id\": basin_ids}, dims=[\"node_id\"]\n)\nforcing = (timeseries * basin_nodes).to_dataframe().reset_index()\n\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": basin_ids,\n \"level\": 1.4,\n \"concentration\": 0.0,\n }\n)\n\n\nmodel.basin.time.df = forcing\nmodel.basin.state.df = state\n\n\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic_transient/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic_transient/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim basic-transient/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\ndf_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\n<Axes: xlabel='time'>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ndf_flow = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/flow.arrow\")\ndf_flow[\"edge\"] = list(zip(df_flow.from_node_id, df_flow.to_node_id))\ndf_flow[\"flow_m3d\"] = df_flow.flow * 86400\nax = df_flow.pivot_table(index=\"time\", columns=\"edge\", values=\"flow_m3d\").plot()\nax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title=\"Edge\")\n\n<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f7014656f50>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ntype(df_flow)\n\npandas.core.frame.DataFrame\n\n\n\n\n3 Model with discrete control\nThe model constructed below consists of a single basin which slowly drains trough a TabulatedRatingCurve, but is held within a range around a target level (setpoint) by two connected pumps. These two pumps behave like a reversible pump. When pumping can be done in only one direction, and the other direction is only possible under gravity, use an Outlet for that direction.\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin\n (1.0, 1.0), # 2: Pump\n (1.0, -1.0), # 3: Pump\n (2.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (-1.0, 0.0), # 5: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (-2.0, 0.0), # 6: Terminal\n (1.0, 0.0), # 7: DiscreteControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"TabulatedRatingCurve\",\n \"Terminal\",\n \"DiscreteControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 7, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 6, 2, 3], dtype=np.int64)\n\nedge_type = 6 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"]\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"from_node_id\": from_id, \"to_node_id\": to_id, \"edge_type\": edge_type},\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1],\n \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n }\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"level\": [20.0]})\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the discrete control:\n\ncondition = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [7],\n \"listen_feature_id\": 3 * [1],\n \"variable\": 3 * [\"level\"],\n \"greater_than\": [5.0, 10.0, 15.0], # min, setpoint, max\n }\n)\n\nlogic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 5 * [7],\n \"truth_state\": [\"FFF\", \"U**\", \"T*F\", \"**D\", \"TTT\"],\n \"control_state\": [\"in\", \"in\", \"none\", \"out\", \"out\"],\n }\n)\n\ndiscrete_control = ribasim.DiscreteControl(condition=condition, logic=logic)\n\nThe above control logic can be summarized as follows: - If the level gets above the maximum, activate the control state “out” until the setpoint is reached; - If the level gets below the minimum, active the control state “in” until the setpoint is reached; - Otherwise activate the control state “none”.\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [2] + 3 * [3],\n \"control_state\": 2 * [\"none\", \"in\", \"out\"],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0, 2e-3, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2e-3],\n }\n )\n)\n\nThe pump data defines the following:\n\n\n\nControl state\nPump #2 flow rate (m/s)\nPump #3 flow rate (m/s)\n\n\n\n\n“none”\n0.0\n0.0\n\n\n“in”\n2e-3\n0.0\n\n\n“out”\n0.0\n2e-3\n\n\n\nSetup the level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [4], \"level\": [10.0]})\n)\n\nSetup the rating curve:\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": 2 * [5], \"level\": [2.0, 15.0], \"discharge\": [0.0, 1e-3]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup the terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [6]}))\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n pump=pump,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n terminal=terminal,\n discrete_control=discrete_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nListen edges are plotted with a dashed line since they are not present in the “Edge / static” schema but only in the “Control / condition” schema.\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\n\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\ngreater_than = model.discrete_control.condition.df.greater_than\n\nax.hlines(\n greater_than,\n df_basin.time[0],\n df_basin.time.max(),\n lw=1,\n ls=\"--\",\n color=\"k\",\n)\n\ndf_control = pd.read_feather(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\ny_min, y_max = ax.get_ybound()\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[:2], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[2:4], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\n\nax.set_xticks(\n date2num(df_control.time).tolist(),\n df_control.control_state.tolist(),\n rotation=50,\n)\n\nax.set_yticks(greater_than, [\"min\", \"setpoint\", \"max\"])\nax.set_ylabel(\"level\")\nplt.show()\n\n\n\n\nThe highlighted regions show where a pump is active.\nLet’s print an overview of what happened with control:\n\nmodel.print_discrete_control_record(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\n0. At 2020-01-01 00:00:00 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTT:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"out\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n\n1. At 2020-02-08 19:02:21.861000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n2. At 2020-07-05 08:56:10.319000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state FFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"in\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n3. At 2020-08-11 06:05:15.592000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n\n\nNote that crossing direction specific truth states (containing “U”, “D”) are not present in this overview even though they are part of the control logic. This is because in the control logic for this model these truth states are only used to sustain control states, while the overview only shows changes in control states.\n\n\n4 Model with PID control\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: FlowBoundary\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: Basin\n (2.0, 0.5), # 3: Pump\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (1.5, 1.0), # 5: PidControl\n (2.0, -0.5), # 6: outlet\n (1.5, -1.0), # 7: PidControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"FlowBoundary\",\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"PidControl\",\n \"Outlet\",\n \"PidControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 5, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([2, 3, 4, 6, 2, 3, 6], dtype=np.int64)\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": 5 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [2, 2], \"level\": [0.0, 1.0], \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0]}\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"level\": [6.0],\n }\n)\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [3],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup the outlet:\n\noutlet = ribasim.Outlet(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [6],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"flow_rate\": [1e-3]})\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4],\n \"level\": [1.0], # Not relevant\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup PID control:\n\npid_control = ribasim.PidControl(\n time=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 4 * [5, 7],\n \"time\": [\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n ],\n \"listen_node_id\": 4 * [2, 2],\n \"target\": [5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5],\n \"proportional\": 4 * [-1e-3, 1e-3],\n \"integral\": 4 * [-1e-7, 1e-7],\n \"derivative\": 4 * [0.0, 0.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nNote that the coefficients for the pump and the outlet are equal in magnitude but opposite in sign. This way the pump and the outlet equally work towards the same goal, while having opposite effects on the controlled basin due to their connectivity to this basin.\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n outlet=outlet,\n pid_control=pid_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"pid_control/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/pid_control/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim pid_control/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"pid_control/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\nax.set_ylabel(\"level [m]\")\n\n# Plot target level\ntarget_levels = model.pid_control.time.df.target.to_numpy()[:4]\ntimes = date2num(model.pid_control.time.df.time)[:4]\nax.plot(times, target_levels, color=\"k\", ls=\":\", label=\"target level\")\npass"
},
{
"objectID": "qgis/index.html",
"href": "qgis/index.html",
"title": "QGIS plugin",
"section": "",
- "text": "Install QGIS version 3.28 or higher.\n\n\nDownload ribasim_qgis.zip, see the download section.\nPlugins menu > Manage and Install Plugins…\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Install from ZIP”:\n\nBrowse to the ribasim_qgis.zip file containing the plugin that was downloaded earlier\nClick “Install Plugin”\n\n\n\n\n\n\nStart the Ribasim plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nIn QGIS, navigate to “Plugins > Manage and Install Plugins > All”. In the search bar, type: “iMOD”. Select the iMOD plugin, and click “Install”.\nAt least version 0.4.0 of the iMOD plugin is required.\nThe Time Series widget from the iMOD plugin is used for visualizing Ribasim results, which is described in Section 1.5. Documentation on the Time Series widget can be found in the iMOD documentation.\n\n\n\nOpen an existing model or create a new model. As an example of an existing model, you can use the “basic” model from generated_testmodels.zip, see the download section.\n\n\n\n\n\nCheck if your coordinate reference system (CRS) is set correctly.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are working with an unknown CRS, right click the model database group in Layers, and click “Set Group CRS…”.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are modeling the Netherlands, select “Amersfoort / RD New” (EPSG:28992).\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Node layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn on the edit mode to be able to add nodes on the map.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdd nodes to the map with a left click and select the node type.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn the edit mode off and save the edits to the Nodes layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nRight click a layer and select “Open Attribute Table”.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick the yellow pencil icon on the top left to enable editing, and copy and paste a record. A record can be selected by clicking on the row number.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdjust the content. If you prefer, it also works to copy data with the same columns from Excel. Turn off edit mode and save changes to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nMake sure the Snapping Toolbar is visible, by going to the View > Toolbars menu. Turn on snapping mode by clicking the magnet and set the snapping distance to 25 pixels.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Edge layer and turn on the edit mode.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Add line feature”.\n\n\n\n\n\nCreate a connection by left clicking a source node and right clicking the destination node.\n\n\n\n\n\nNow leave the edit mode and save the results to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nOpen a text editor and create an empty file next to your database, with the .toml extension.\nAdd the following content to the TOML file:\n\n\n\nribasim.toml\n\nstarttime = 2020-01-01 00:00:00\nendtime = 2021-01-01 00:00:00\ndatabase = \"database.gpkg\"\n\n\nUnzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files.\n\n\n\n\n\n\nIn QGIS select the model group.\n\n\n\n\n\nIn the Ribasim plugin widget, select the Results tab and click “Associate Results”.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect results/basin.arrow.\n\n\n\n\n\nThis adds metadata to the model that the iMOD plugin can use to find the timeseries data that is associated to the model nodes.\n\n\n\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes. Currently only the Basin nodes can be plotted.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph."
+ "text": "Install QGIS version 3.28 or higher.\n\n\nDownload ribasim_qgis.zip, see the download section.\nPlugins menu > Manage and Install Plugins…\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Install from ZIP”:\n\nBrowse to the ribasim_qgis.zip file containing the plugin that was downloaded earlier\nClick “Install Plugin”\n\n\n\n\n\n\nStart the Ribasim plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nIn QGIS, navigate to “Plugins > Manage and Install Plugins > All”. In the search bar, type: “iMOD”. Select the iMOD plugin, and click “Install”.\nAt least version 0.4.0 of the iMOD plugin is required.\nThe Time Series widget from the iMOD plugin is used for visualizing Ribasim results, which is described in Section 1.5. Documentation on the Time Series widget can be found in the iMOD documentation.\n\n\n\nOpen an existing model or create a new model. As an example of an existing model, you can use the “basic” model from generated_testmodels.zip, see the download section.\n\n\n\n\n\nCheck if your coordinate reference system (CRS) is set correctly.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are working with an unknown CRS, right click the model database group in Layers, and click “Set Group CRS…”.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are modeling the Netherlands, select “Amersfoort / RD New” (EPSG:28992).\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Node layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn on the edit mode to be able to add nodes on the map.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdd nodes to the map with a left click and select the node type.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn the edit mode off and save the edits to the Nodes layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nRight click a layer and select “Open Attribute Table”.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick the yellow pencil icon on the top left to enable editing, and copy and paste a record. A record can be selected by clicking on the row number.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdjust the content. If you prefer, it also works to copy data with the same columns from Excel. Turn off edit mode and save changes to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nMake sure the Snapping Toolbar is visible, by going to the View > Toolbars menu. Turn on snapping mode by clicking the magnet and set the snapping distance to 25 pixels.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Edge layer and turn on the edit mode.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Add line feature”.\n\n\n\n\n\nCreate a connection by left clicking a source node and right clicking the destination node.\n\n\n\n\n\nNow leave the edit mode and save the results to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nUnzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files.\n\n\n\n\nBefore trying to inspect the results, verify that the run was successful and the output files are there.\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the layer that you wish to plot. From the “Node” layer you can plot level or storage on Basin nodes. From the “Edge” layer you can plot flow over flow edges. Note that before switching between these, you typically have to click “Clear” to clear the selection. If you run a simulation with the model open in QGIS, you have to close and re-open the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel for the new results to be loaded.\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph.\n\n\n\n\n\nOnly the “basin.arrow” and “flow.arrow” can be inspected with the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel. All Arrow files can be loaded as a layer by dragging the files onto QGIS. Right click the layer and select “Open Attribute Table” to view the contents."
},
{
"objectID": "qgis/index.html#start",
@@ -431,14 +431,14 @@
"href": "qgis/index.html#run-a-model",
"title": "QGIS plugin",
"section": "",
- "text": "Open a text editor and create an empty file next to your database, with the .toml extension.\nAdd the following content to the TOML file:\n\n\n\nribasim.toml\n\nstarttime = 2020-01-01 00:00:00\nendtime = 2021-01-01 00:00:00\ndatabase = \"database.gpkg\"\n\n\nUnzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files."
+ "text": "Unzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files."
},
{
"objectID": "qgis/index.html#sec-results",
"href": "qgis/index.html#sec-results",
"title": "QGIS plugin",
"section": "",
- "text": "In QGIS select the model group.\n\n\n\n\n\nIn the Ribasim plugin widget, select the Results tab and click “Associate Results”.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect results/basin.arrow.\n\n\n\n\n\nThis adds metadata to the model that the iMOD plugin can use to find the timeseries data that is associated to the model nodes.\n\n\n\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes. Currently only the Basin nodes can be plotted.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph."
+ "text": "Before trying to inspect the results, verify that the run was successful and the output files are there.\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the layer that you wish to plot. From the “Node” layer you can plot level or storage on Basin nodes. From the “Edge” layer you can plot flow over flow edges. Note that before switching between these, you typically have to click “Clear” to clear the selection. If you run a simulation with the model open in QGIS, you have to close and re-open the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel for the new results to be loaded.\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph.\n\n\n\n\n\nOnly the “basin.arrow” and “flow.arrow” can be inspected with the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel. All Arrow files can be loaded as a layer by dragging the files onto QGIS. Right click the layer and select “Open Attribute Table” to view the contents."
},
{
"objectID": "couple/modflow-demo.html",
Ribasim.InNeighbors — Type.Ribasim.LevelBoundary — Type.Ribasim.LinearResistance — Type.source
+
# Ribasim.ManningResistance — Type.
This is a simple Manning-Gauckler reach connection.
@@ -360,48 +360,48 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.Model — Type.
Model(config_path::AbstractString)
Model(config::Config)
Initialize a Model.
The Model struct is an initialized model, combined with the Config used to create it and saved results. The Basic Model Interface (BMI) is implemented on the Model. A Model can be created from the path to a TOML configuration file, or a Config object.
-
+
# Ribasim.NodeMetadata — Type.
Type for storing metadata of nodes in the graph type: type of the node allocationnetworkid: Allocation network ID (0 if not in subnetwork)
-
+
# Ribasim.OutNeighbors — Type.
Iterate over outgoing neighbors of a given label in a MetaGraph, only for edges of edge_type
-
+
# Ribasim.Outlet — Type.
nodeid: node ID of the Outlet node active: whether this node is active and thus contributes flow flowrate: target flow rate minflowrate: The minimal flow rate of the outlet maxflowrate: The maximum flow rate of the outlet controlmapping: dictionary from (nodeid, controlstate) to target flow rate ispid_controlled: whether the flow rate of this outlet is governed by PID control
-
+
# Ribasim.PidControl — Type.
PID control currently only supports regulating basin levels.
nodeid: node ID of the PidControl node active: whether this node is active and thus sets flow rates listennodeid: the id of the basin being controlled pidparams: a vector interpolation for parameters changing over time. The parameters are respectively target, proportional, integral, derivative, where the last three are the coefficients for the PID equation. error: the current error; basintarget - currentlevel
-
+
# Ribasim.Pump — Type.
nodeid: node ID of the Pump node active: whether this node is active and thus contributes flow flowrate: target flow rate minflowrate: The minimal flow rate of the pump maxflowrate: The maximum flow rate of the pump controlmapping: dictionary from (nodeid, controlstate) to target flow rate ispid_controlled: whether the flow rate of this pump is governed by PID control
-
+
# Ribasim.Subgrid — Type.
Subgrid linearly interpolates basin levels.
-
+
# Ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve — Type.
struct TabulatedRatingCurve{C}
Rating curve from level to discharge. The rating curve is a lookup table with linear interpolation in between. Relation can be updated in time, which is done by moving data from the time field into the tables, which is done in the update_tabulated_rating_curve callback.
Type parameter C indicates the content backing the StructVector, which can be a NamedTuple of Vectors or Arrow Primitives, and is added to avoid type instabilities.
nodeid: node ID of the TabulatedRatingCurve node active: whether this node is active and thus contributes flows tables: The current Q(h) relationships time: The time table used for updating the tables controlmapping: dictionary from (nodeid, controlstate) to Q(h) and/or active state
-
+
# Ribasim.Terminal — Type.
node_id: node ID of the Terminal node
-
+
# Ribasim.User — Type.
demand: water flux demand of user per priority over time active: whether this node is active and thus demands water allocated: water flux currently allocated to user per priority returnfactor: the factor in [0,1] of how much of the abstracted water is given back to the system minlevel: The level of the source basin below which the user does not abstract priorities: All used priority values. Each user has a demand for all these priorities, which is 0.0 if it is not provided explicitly. record: Collected data of allocation optimizations for output file.
-
+
# Ribasim.config.Config — Method.
Config(config_path::AbstractString; kwargs...)
Parse a TOML file to a Config. Keys can be overruled using keyword arguments. To overrule keys from a subsection, e.g. dt from the solver section, use underscores: solver_dt.
-
+
@@ -410,157 +410,157 @@ # BasicModelInterface.finalize — Method.
BMI.finalize(model::Model)::Model
Write all results to the configured files.
-
+
# BasicModelInterface.initialize — Method.
BMI.initialize(T::Type{Model}, config_path::AbstractString)::Model
Initialize a Model from the path to the TOML configuration file.
-
+
# BasicModelInterface.initialize — Method.
BMI.initialize(T::Type{Model}, config::Config)::Model
Initialize a Model from a Config.
-
+
# CommonSolve.solve! — Method.
solve!(model::Model)::ODESolution
Solve a Model until the configured endtime.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_absolute_value! — Method.
Minimizing |expr| can be achieved by introducing a new variable exprabs and posing the following constraints: exprabs >= expr expr_abs >= -expr
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_capacity! — Method.
Add the flow capacity constraints to the allocation problem. Only finite capacities get a constraint. The constraint indices are (edgesourceid, edgedstid).
Constraint: flow over edge <= edge capacity
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_flow_conservation! — Method.
Add the flow conservation constraints to the allocation problem. The constraint indices are user node IDs.
Constraint: sum(flows out of node node) <= flows into node + flow from storage and vertical fluxes
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_source! — Method.
Add the source constraints to the allocation problem. The actual threshold values will be set before each allocation solve. The constraint indices are (edgesourceid, edgedstid).
Constraint: flow over source edge <= source flow in subnetwork
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_user_returnflow! — Method.
Add the user returnflow constraints to the allocation problem. The constraint indices are user node IDs.
Constraint: outflow from user <= return factor * inflow to user
-
+
# Ribasim.add_flow! — Method.
Add the given flow q to the flow over the edge on the horizontal (self-loop) edge from id to id.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_flow! — Method.
Add the given flow q to the existing flow over the edge between the given nodes.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_variables_absolute_value! — Method.
Certain allocation distribution types use absolute values in the objective function. Since most optimization packages do not support the absolute value function directly, New variables are introduced that act as the absolute value of an expression by posing the appropriate constraints.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_variables_flow! — Method.
Add the flow variables F to the allocation problem. The variable indices are (edgesourceid, edgedstid). Non-negativivity constraints are also immediately added to the flow variables.
-
+
# Ribasim.adjust_edge_capacities! — Method.
Set the values of the edge capacities. 2 cases:
- Before the first allocation solve, set the edge capacities to their full capacity;
- Before an allocation solve, subtract the flow used by allocation for the previous priority from the edge capacities.
-
+
# Ribasim.adjust_source_flows! — Method.
Adjust the source flows.
-
+
# Ribasim.all_neighbor_labels_type — Method.
Get the in- and outneighbor node IDs of the given node ID (label) over the given edge type in the graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocate! — Method.
Update the allocation optimization problem for the given subnetwork with the problem state and flows, solve the allocation problem and assign the results to the users.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_graph — Method.
Build the graph used for the allocation problem.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_graph_used_nodes! — Method.
Find all nodes in the subnetwork which will be used in the allocation network. Some nodes are skipped to optimize allocation optimization.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_path_exists_in_graph — Method.
Find out whether a path exists between a start node and end node in the given allocation graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_problem — Method.
Construct the allocation problem for the current subnetwork as a JuMP.jl model.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_table — Method.
Create an allocation result table for the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.assign_allocations! — Method.
Assign the allocations to the users as determined by the solution of the allocation problem.
-
+
# Ribasim.avoid_using_own_returnflow! — Method.
Remove allocation user return flow edges that are upstream of the user itself.
-
+
# Ribasim.basin_bottom — Method.
Return the bottom elevation of the basin with index i, or nothing if it doesn’t exist
-
+
# Ribasim.basin_bottoms — Method.
Get the bottom on both ends of a node. If only one has a bottom, use that for both.
-
+
# Ribasim.basin_table — Method.
Create the basin result table from the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.create_callbacks — Method.
Create the different callbacks that are used to store results and feed the simulation with new data. The different callbacks are combined to a CallbackSet that goes to the integrator. Returns the CallbackSet and the SavedValues for flow.
-
+
# Ribasim.create_graph — Method.
Return a directed metagraph with data of nodes (NodeMetadata): NodeMetadata
and data of edges (EdgeMetadata): EdgeMetadata
-
+
# Ribasim.create_storage_tables — Method.
Read the Basin / profile table and return all area and level and computed storage values
-
+
# Ribasim.datetime_since — Method.
datetime_since(t::Real, t0::DateTime)::DateTime
Convert a Real that represents the seconds passed since the simulation start to the nearest DateTime. This is used to convert between the solver’s inner float time, and the calendar.
-
+
# Ribasim.datetimes — Method.
Get all saved times as a Vector{DateTime}
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_affect! — Method.
Change parameters based on the control logic.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_affect_downcrossing! — Method.
An downcrossing means that a condition (always greater than) becomes false.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_affect_upcrossing! — Method.
An upcrossing means that a condition (always greater than) becomes true.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_condition — Method.
Listens for changes in condition truths.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_table — Method.
Create a discrete control result table from the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.expand_logic_mapping — Method.
Replace the truth states in the logic mapping which contain wildcards with all possible explicit truth states.
-
+
# Ribasim.find_allocation_graph_edges! — Method.
This loop finds allocation graph edges in several ways:
- Between allocation graph nodes whose equivalent in the subnetwork are directly connected
- Between allocation graph nodes whose equivalent in the subnetwork are connected with one or more allocation graph nodes in between
-
+
# Ribasim.findlastgroup — Method.
For an element id and a vector of elements ids, get the range of indices of the last consecutive block of id. Returns the empty range 1:0 if id is not in ids.
# 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Ribasim.findlastgroup(2, [5,4,2,2,5,2,2,2,1])
# output
6:8
-
+
# Ribasim.findsorted — Method.
Find the index of element x in a sorted collection a. Returns the index of x if it exists, or nothing if it doesn’t. If x occurs more than once, throw an error.
-
+
# Ribasim.flow_table — Method.
Create a flow result table from the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.formulate_basins! — Method.
Smoothly let the evaporation flux go to 0 when at small water depths Currently at less than 0.1 m.
-
+
# Ribasim.formulate_flow! — Method.
Directed graph: outflow is positive!
-
+
# Ribasim.formulate_flow! — Method.
Conservation of energy for two basins, a and b:
h_a + v_a^2 / (2 * g) = h_b + v_b^2 / (2 * g) + S_f * L + C / 2 * g * (v_b^2 - v_a^2)
@@ -588,116 +588,116 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.formulate_flow! — Method.
Directed graph: outflow is positive!
-
+
# Ribasim.get_area_and_level — Method.
Compute the area and level of a basin given its storage. Also returns darea/dlevel as it is needed for the Jacobian.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_chunk_sizes — Method.
Get the chunk sizes for DiffCache; differentiation w.r.t. u and t (the latter only if a Rosenbrock algorithm is used).
-
+
# Ribasim.get_compressor — Method.
Get the compressor based on the Results section
-
+
# Ribasim.get_flow — Method.
Get the flow over the given horizontal (selfloop) edge (val is needed for get_tmp from ForwardDiff.jl).
-
+
# Ribasim.get_flow — Method.
Get the flow over the given edge (val is needed for get_tmp from ForwardDiff.jl).
-
+
# Ribasim.get_fractional_flow_connected_basins — Method.
Get the node type specific indices of the fractional flows and basins, that are consecutively connected to a node of given id.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_jac_prototype — Method.
Get a sparse matrix whose sparsity matches the sparsity of the Jacobian of the ODE problem. All nodes are taken into consideration, also the ones that are inactive.
In Ribasim the Jacobian is typically sparse because each state only depends on a small number of other states.
Note: the name ‘prototype’ does not mean this code is a prototype, it comes from the naming convention of this sparsity structure in the differentialequations.jl docs.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_level — Method.
Get the current water level of a node ID. The ID can belong to either a Basin or a LevelBoundary. storage: tells ForwardDiff whether this call is for differentiation or not
-
+
# Ribasim.get_scalar_interpolation — Method.
Linear interpolation of a scalar with constant extrapolation.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_storage_from_level — Method.
Get the storage of a basin from its level.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_storages_and_levels — Method.
Get the storage and level of all basins as matrices of nbasin × ntime
-
+
# Ribasim.get_storages_from_levels — Method.
Compute the storages of the basins based on the water level of the basins.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_tstops — Method.
From an iterable of DateTimes, find the times the solver needs to stop
-
+
# Ribasim.get_value — Method.
Get a value for a condition. Currently supports getting levels from basins and flows from flow boundaries.
-
+
# Ribasim.id_index — Method.
Get the index of an ID in a set of indices.
-
+
# Ribasim.indicate_allocation_flow! — Method.
Add to the edge metadata that the given edge is used for allocation flow. If the edge does not exist, it is created.
-
+
# Ribasim.inflow_id — Method.
Get the unique inneighbor over a flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.inflow_ids — Method.
Get the inneighbors over flow edges.
-
+
# Ribasim.inflow_ids_allocation — Method.
Get the inneighbors of the given ID such that the connecting edge is an allocation flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.inneighbor_labels_type — Method.
Get the inneighbor node IDs of the given node ID (label) over the given edge type in the graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.inoutflow_ids — Method.
Get the in- and outneighbors over flow edges.
-
+
# Ribasim.is_allocation_source — Method.
Find out whether the given edge is a source for an allocation network.
-
+
# Ribasim.is_flow_constraining — Method.
Whether the given node node is flow constraining by having a maximum flow rate.
-
+
# Ribasim.is_flow_direction_constraining — Method.
Whether the given node is flow direction constraining (only in direction of edges).
-
+
# Ribasim.load_data — Method.
load_data(db::DB, config::Config, nodetype::Symbol, kind::Symbol)::Union{Table, Query, Nothing}
Load data from Arrow files if available, otherwise the database. Returns either an Arrow.Table, SQLite.Query or nothing if the data is not present.
-
+
# Ribasim.load_structvector — Method.
load_structvector(db::DB, config::Config, ::Type{T})::StructVector{T}
Load data from Arrow files if available, otherwise the database. Always returns a StructVector of the given struct type T, which is empty if the table is not found. This function validates the schema, and enforces the required sort order.
-
+
# Ribasim.metadata_from_edge — Method.
Get the metadata of an edge in the graph from an edge of the underlying DiGraph.
-
+
# Ribasim.nodefields — Method.
Get all node fieldnames of the parameter object.
-
+
# Ribasim.nodetype — Method.
From a SchemaVersion(“ribasim.flowboundary.static”, 1) return (:FlowBoundary, :static)
-
+
# Ribasim.outflow_id — Method.
Get the unique outneighbor over a flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.outflow_ids — Method.
Get the outneighbors over flow edges.
-
+
# Ribasim.outflow_ids_allocation — Method.
Get the outneighbors of the given ID such that the connecting edge is an allocation flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.outneighbor_labels_type — Method.
Get the outneighbor node IDs of the given node ID (label) over the given edge type in the graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.parse_static_and_time — Method.
Process the data in the static and time tables for a given node type. The ‘defaults’ named tuple dictates how missing data is filled in. ‘time_interpolatables’ is a vector of Symbols of parameter names for which a time interpolation (linear) object must be constructed. The control mapping for DiscreteControl is also constructed in this function. This function currently does not support node states that are defined by more than one row in a table, as is the case for TabulatedRatingCurve.
-
+
# Ribasim.process_allocation_graph_edges! — Method.
For the composite allocation graph edges:
@@ -705,83 +705,83 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.profile_storage — Method.
Calculate a profile storage by integrating the areas over the levels
-
+
# Ribasim.qh_interpolation — Method.
From a table with columns nodeid, discharge (Q) and level (h), create a LinearInterpolation from level to discharge for a given nodeid.
-
+
# Ribasim.reduction_factor — Method.
Function that goes smoothly from 0 to 1 in the interval [0,threshold], and is constant outside this interval.
-
+
# Ribasim.run — Method.
run(config_file::AbstractString)::Model
run(config::Config)::Model
Run a Model, given a path to a TOML configuration file, or a Config object. Running a model includes initialization, solving to the end with [solve!](@ref) and writing results with BMI.finalize.
-
+
# Ribasim.save_flow — Method.
Copy the current flow to the SavedValues
-
+
# Ribasim.save_subgrid_level — Method.
Interpolate the levels and save them to SavedValues
-
+
# Ribasim.scalar_interpolation_derivative — Method.
Derivative of scalar interpolation.
-
+
# Ribasim.seconds_since — Method.
seconds_since(t::DateTime, t0::DateTime)::Float64
Convert a DateTime to a float that is the number of seconds since the start of the simulation. This is used to convert between the solver’s inner float time, and the calendar.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_current_value! — Method.
From a timeseries table time, load the most recent applicable data into table. table must be a NamedTuple of vectors with all variables that must be loaded. The most recent applicable data is non-NaN data for a given ID that is on or before t.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_flow! — Method.
Set the given flow q on the horizontal (self-loop) edge from id to id.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_flow! — Method.
Set the given flow q over the edge between the given nodes.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_initial_discrete_controlled_parameters! — Method.
Set parameters of nodes that are controlled by DiscreteControl to the values corresponding to the initial state of the model.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_objective_priority! — Method.
Set the objective for the given priority. For an objective with absolute values this also involves adjusting constraints.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_static_value! — Method.
Load data from a source table static into a destination table. Data is matched based on the node_id, which is sorted.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_table_row! — Method.
Update table at row index i, with the values of a given row. table must be a NamedTuple of vectors with all variables that must be loaded. The row must contain all the column names that are present in the table. If a value is NaN, it is not set.
-
+
# Ribasim.sorted_table! — Method.
Depending on if a table can be sorted, either sort it or assert that it is sorted.
Tables loaded from the database into memory can be sorted. Tables loaded from Arrow files are memory mapped and can therefore not be sorted.
-
+
# Ribasim.timesteps — Method.
Get all saved times in seconds since start
-
+
# Ribasim.update_allocation! — Method.
Solve the allocation problem for all users and assign allocated abstractions to user nodes.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_basin — Method.
Load updates from ‘Basin / time’ into the parameters
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
Method for nodes that do not contribute to the Jacobian
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
The controlled basin affects itself and the basins upstream and downstream of the controlled pump affect eachother if there is a basin upstream of the pump. The state for the integral term and the controlled basin affect eachother, and the same for the integral state and the basin upstream of the pump if it is indeed a basin.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
If both the unique node upstream and the unique node downstream of these nodes are basins, then these directly depend on eachother and affect the Jacobian 2x Basins always depend on themselves.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
If both the unique node upstream and the nodes down stream (or one node further if a fractional flow is in between) are basins, then the downstream basin depends on the upstream basin(s) and affect the Jacobian as many times as there are downstream basins Upstream basins always depend on themselves.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_tabulated_rating_curve! — Method.
Load updates from ‘TabulatedRatingCurve / time’ into the parameters
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_discrete_control — Method.
Check:
@@ -789,50 +789,50 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.valid_edge_types — Method.
Check that only supported edge types are declared.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_edges — Method.
Test for each node given its node type whether the nodes that
are downstream (‘down-edge’) of this node are of an allowed type
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_flow_rates — Method.
Test whether static or discrete controlled flow rates are indeed non-negative.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_fractional_flow — Method.
Check that nodes that have fractional flow outneighbors do not have any other type of outneighbor, that the fractions leaving a node add up to ≈1 and that the fractions are non-negative.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_n_neighbors — Method.
Test for each node given its node type whether it has an allowed number of flow/control inneighbors and outneighbors
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_profiles — Method.
Check whether the profile data has no repeats in the levels and the areas start positive.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_sources — Method.
The source nodes must only have one allocation outneighbor and no allocation inneighbors.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_subgrid — Method.
Validate the entries for a single subgrid element.
-
+
# Ribasim.water_balance! — Method.
The right hand side function of the system of ODEs set up by Ribasim.
-
+
# Ribasim.write_arrow — Method.
Write a result table to disk as an Arrow file
-
+
# Ribasim.config.algorithm — Method.
Create an OrdinaryDiffEqAlgorithm from solver config
-
+
# Ribasim.config.input_path — Method.
Construct a path relative to both the TOML directory and the optional input_dir
-
+
# Ribasim.config.results_path — Method.
Construct a path relative to both the TOML directory and the optional results_dir
-
+
# Ribasim.config.snake_case — Method.
Convert a string from CamelCase to snake_case.
-
+
@@ -853,7 +853,7 @@ source
+
@@ -861,10 +861,10 @@ 1.5 Macros
# Ribasim.config.@addfields — Macro.
Add fieldnames with Union{String, Nothing} type to struct expression. Requires (option?) use before it.
-
+
# Ribasim.config.@addnodetypes — Macro.
Add all TableOption subtypes as fields to struct expression. Requires (option?) use before it.
-
+
@@ -898,8 +898,8 @@ Ribasim.User
Ribasim.config.ConfigBasicModelInterface.finalizeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeCommonSolve.solve!Ribasim.add_constraints_absolute_value!Ribasim.add_constraints_capacity!Ribasim.scalar_interpolation_derivative
Ribasim.seconds_sinceRibasim.set_current_value!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_initial_discrete_controlled_parameters!Ribasim.set_objective_priority!Ribasim.set_static_value!Ribasim.timesteps
Ribasim.update_allocation!Ribasim.update_basinRibasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_tabulated_rating_curve!Ribasim.valid_discrete_controlRibasim.valid_edge_types2 Update the basi
ax = df_flow.pivot_table(index="time", columns="edge", values="flow_m3d").plot()
ax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title="Edge")
-<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f1a7c921550>
+<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f7014656f50>

@@ -1021,7 +1021,7 @@ 4 Model with PID
<Axes: >
-
+
Write the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:
diff --git a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png
index 33e8abbcf..f5f6a2b5b 100644
Binary files a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png and b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png differ
diff --git a/qgis/index.html b/qgis/index.html
index 0980ee3b0..df224853e 100644
--- a/qgis/index.html
+++ b/qgis/index.html
@@ -20,40 +20,6 @@
margin: 0 0.8em 0.2em -1em; /* quarto-specific, see https://github.com/quarto-dev/quarto-cli/issues/4556 */
vertical-align: middle;
}
-/* CSS for syntax highlighting */
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre; position: relative; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { display: inline-block; line-height: 1.25; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span:empty { height: 1.2em; }
-.sourceCode { overflow: visible; }
-code.sourceCode > span { color: inherit; text-decoration: inherit; }
-div.sourceCode { margin: 1em 0; }
-pre.sourceCode { margin: 0; }
-@media screen {
-div.sourceCode { overflow: auto; }
-}
-@media print {
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre-wrap; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { text-indent: -5em; padding-left: 5em; }
-}
-pre.numberSource code
- { counter-reset: source-line 0; }
-pre.numberSource code > span
- { position: relative; left: -4em; counter-increment: source-line; }
-pre.numberSource code > span > a:first-child::before
- { content: counter(source-line);
- position: relative; left: -1em; text-align: right; vertical-align: baseline;
- border: none; display: inline-block;
- -webkit-touch-callout: none; -webkit-user-select: none;
- -khtml-user-select: none; -moz-user-select: none;
- -ms-user-select: none; user-select: none;
- padding: 0 4px; width: 4em;
- }
-pre.numberSource { margin-left: 3em; padding-left: 4px; }
-div.sourceCode
- { }
-@media screen {
-pre > code.sourceCode > span > a:first-child::before { text-decoration: underline; }
-}
@@ -180,11 +146,7 @@ On this page
- 1.3.2 Create connecting edges
- 1.4 Run a model
- - 1.5 Inspect results
-
+ - 1.5 Inspect results
@@ -362,18 +324,6 @@
1.4 Run a model
-- Open a text editor and create an empty file next to your database, with the
.toml extension.
-- Add the following content to the TOML file:
-
-
-
-ribasim.toml
-
-starttime = 2020-01-01 00:00:00
-endtime = 2021-01-01 00:00:00
-database = "database.gpkg"
-
-
- Unzip the Ribasim command line interface,
ribasim_cli.zip
- Open your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run
path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.
- In your model directory there is now a
results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files.
@@ -381,43 +331,21 @@
1.5 Inspect results
-
-1.5.1 Associate results to iMOD time series window
-In QGIS select the model group.
-
-
-
-
-
-In the Ribasim plugin widget, select the Results tab and click “Associate Results”.
-
-
-
-
-
-Select results/basin.arrow.
-
-
-
-
-
-This adds metadata to the model that the iMOD plugin can use to find the timeseries data that is associated to the model nodes.
-
-
-1.5.2 Plot time series
+Before trying to inspect the results, verify that the run was successful and the output files are there.
Click the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.

+Select the layer that you wish to plot. From the “Node” layer you can plot level or storage on Basin nodes. From the “Edge” layer you can plot flow over flow edges. Note that before switching between these, you typically have to click “Clear” to clear the selection. If you run a simulation with the model open in QGIS, you have to close and re-open the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel for the new results to be loaded.
Select the variables that you want to plot.

-Click “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes. Currently only the Basin nodes can be plotted.
+Click “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes.

@@ -429,9 +357,9 @@ 
+Only the “basin.arrow” and “flow.arrow” can be inspected with the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel. All Arrow files can be loaded as a layer by dragging the files onto QGIS. Right click the layer and select “Open Attribute Table” to view the contents.
-
diff --git a/search.json b/search.json
index 4fab5eb10..635269b00 100644
--- a/search.json
+++ b/search.json
@@ -396,14 +396,14 @@
"href": "python/examples.html",
"title": "Examples",
"section": "",
- "text": "1 Basic model with static forcing\n\nfrom pathlib import Path\n\nimport geopandas as gpd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1, 3, 3, 6, 6, 9, 9],\n \"area\": [0.01, 1000.0] * 4,\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0] * 4,\n }\n)\n\n# Convert steady forcing to m/s\n# 2 mm/d precipitation, 1 mm/d evaporation\nseconds_in_day = 24 * 3600\nprecipitation = 0.002 / seconds_in_day\nevaporation = 0.001 / seconds_in_day\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [0],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [evaporation],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [precipitation],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\nstatic = static.iloc[[0, 0, 0, 0]]\nstatic[\"node_id\"] = [1, 3, 6, 9]\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static)\n\nSetup linear resistance:\n\nlinear_resistance = ribasim.LinearResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [10, 12], \"resistance\": [5e3, (3600.0 * 24) / 100.0]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup Manning resistance:\n\nmanning_resistance = ribasim.ManningResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"length\": [900.0],\n \"manning_n\": [0.04],\n \"profile_width\": [6.0],\n \"profile_slope\": [3.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up a rating curve node:\n\n# Discharge: lose 1% of storage volume per day at storage = 1000.0.\nq1000 = 1000.0 * 0.01 / seconds_in_day\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4, 4],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n \"discharge\": [0.0, q1000],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup fractional flows:\n\nfractional_flow = ribasim.FractionalFlow(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [5, 8, 13],\n \"fraction\": [0.3, 0.6, 0.1],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [7],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.5 / 3600],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [11, 17],\n \"level\": [0.5, 1.5],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [15, 16],\n \"flow_rate\": [1e-4, 1e-4],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [14],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin,\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: ManningResistance\n (2.0, 0.0), # 3: Basin\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (3.0, 1.0), # 5: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, 2.0), # 6: Basin\n (4.0, 1.0), # 7: Pump\n (4.0, 0.0), # 8: FractionalFlow\n (5.0, 0.0), # 9: Basin\n (6.0, 0.0), # 10: LinearResistance\n (2.0, 2.0), # 11: LevelBoundary\n (2.0, 1.0), # 12: LinearResistance\n (3.0, -1.0), # 13: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, -2.0), # 14: Terminal\n (3.0, 3.0), # 15: FlowBoundary\n (0.0, 1.0), # 16: FlowBoundary\n (6.0, 1.0), # 17: LevelBoundary\n ]\n)\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_id, node_type = ribasim.Node.node_ids_and_types(\n basin,\n manning_resistance,\n rating_curve,\n pump,\n fractional_flow,\n linear_resistance,\n level_boundary,\n flow_boundary,\n terminal,\n)\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(node_id, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array(\n [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 8, 7, 9, 11, 12, 4, 13, 15, 16, 10], dtype=np.int64\n)\nto_id = np.array(\n [2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 6, 7, 9, 9, 10, 12, 3, 13, 14, 6, 1, 17], dtype=np.int64\n)\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": len(from_id) * [\"flow\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n linear_resistance=linear_resistance,\n manning_resistance=manning_resistance,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n fractional_flow=fractional_flow,\n terminal=terminal,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic/ribasim.toml')\n\n\n\n\n2 Update the basic model with transient forcing\nThis assumes you have already created the basic model with static forcing.\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\nimport xarray as xr\n\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(filepath=datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\n\ntime = pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime)\nday_of_year = time.day_of_year.to_numpy()\nseconds_per_day = 24 * 60 * 60\nevaporation = (\n (-1.0 * np.cos(day_of_year / 365.0 * 2 * np.pi) + 1.0) * 0.0025 / seconds_per_day\n)\nrng = np.random.default_rng(seed=0)\nprecipitation = (\n rng.lognormal(mean=-1.0, sigma=1.7, size=time.size) * 0.001 / seconds_per_day\n)\n\nWe’ll use xarray to easily broadcast the values.\n\ntimeseries = (\n pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 1,\n \"time\": pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime),\n \"drainage\": 0.0,\n \"potential_evaporation\": evaporation,\n \"infiltration\": 0.0,\n \"precipitation\": precipitation,\n \"urban_runoff\": 0.0,\n }\n )\n .set_index(\"time\")\n .to_xarray()\n)\n\nbasin_ids = model.basin.static.df[\"node_id\"].to_numpy()\nbasin_nodes = xr.DataArray(\n np.ones(len(basin_ids)), coords={\"node_id\": basin_ids}, dims=[\"node_id\"]\n)\nforcing = (timeseries * basin_nodes).to_dataframe().reset_index()\n\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": basin_ids,\n \"level\": 1.4,\n \"concentration\": 0.0,\n }\n)\n\n\nmodel.basin.time.df = forcing\nmodel.basin.state.df = state\n\n\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic_transient/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic_transient/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim basic-transient/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\ndf_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\n<Axes: xlabel='time'>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ndf_flow = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/flow.arrow\")\ndf_flow[\"edge\"] = list(zip(df_flow.from_node_id, df_flow.to_node_id))\ndf_flow[\"flow_m3d\"] = df_flow.flow * 86400\nax = df_flow.pivot_table(index=\"time\", columns=\"edge\", values=\"flow_m3d\").plot()\nax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title=\"Edge\")\n\n<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f1a7c921550>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ntype(df_flow)\n\npandas.core.frame.DataFrame\n\n\n\n\n3 Model with discrete control\nThe model constructed below consists of a single basin which slowly drains trough a TabulatedRatingCurve, but is held within a range around a target level (setpoint) by two connected pumps. These two pumps behave like a reversible pump. When pumping can be done in only one direction, and the other direction is only possible under gravity, use an Outlet for that direction.\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin\n (1.0, 1.0), # 2: Pump\n (1.0, -1.0), # 3: Pump\n (2.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (-1.0, 0.0), # 5: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (-2.0, 0.0), # 6: Terminal\n (1.0, 0.0), # 7: DiscreteControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"TabulatedRatingCurve\",\n \"Terminal\",\n \"DiscreteControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 7, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 6, 2, 3], dtype=np.int64)\n\nedge_type = 6 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"]\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"from_node_id\": from_id, \"to_node_id\": to_id, \"edge_type\": edge_type},\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1],\n \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n }\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"level\": [20.0]})\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the discrete control:\n\ncondition = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [7],\n \"listen_feature_id\": 3 * [1],\n \"variable\": 3 * [\"level\"],\n \"greater_than\": [5.0, 10.0, 15.0], # min, setpoint, max\n }\n)\n\nlogic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 5 * [7],\n \"truth_state\": [\"FFF\", \"U**\", \"T*F\", \"**D\", \"TTT\"],\n \"control_state\": [\"in\", \"in\", \"none\", \"out\", \"out\"],\n }\n)\n\ndiscrete_control = ribasim.DiscreteControl(condition=condition, logic=logic)\n\nThe above control logic can be summarized as follows: - If the level gets above the maximum, activate the control state “out” until the setpoint is reached; - If the level gets below the minimum, active the control state “in” until the setpoint is reached; - Otherwise activate the control state “none”.\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [2] + 3 * [3],\n \"control_state\": 2 * [\"none\", \"in\", \"out\"],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0, 2e-3, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2e-3],\n }\n )\n)\n\nThe pump data defines the following:\n\n\n\nControl state\nPump #2 flow rate (m/s)\nPump #3 flow rate (m/s)\n\n\n\n\n“none”\n0.0\n0.0\n\n\n“in”\n2e-3\n0.0\n\n\n“out”\n0.0\n2e-3\n\n\n\nSetup the level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [4], \"level\": [10.0]})\n)\n\nSetup the rating curve:\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": 2 * [5], \"level\": [2.0, 15.0], \"discharge\": [0.0, 1e-3]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup the terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [6]}))\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n pump=pump,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n terminal=terminal,\n discrete_control=discrete_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nListen edges are plotted with a dashed line since they are not present in the “Edge / static” schema but only in the “Control / condition” schema.\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\n\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\ngreater_than = model.discrete_control.condition.df.greater_than\n\nax.hlines(\n greater_than,\n df_basin.time[0],\n df_basin.time.max(),\n lw=1,\n ls=\"--\",\n color=\"k\",\n)\n\ndf_control = pd.read_feather(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\ny_min, y_max = ax.get_ybound()\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[:2], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[2:4], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\n\nax.set_xticks(\n date2num(df_control.time).tolist(),\n df_control.control_state.tolist(),\n rotation=50,\n)\n\nax.set_yticks(greater_than, [\"min\", \"setpoint\", \"max\"])\nax.set_ylabel(\"level\")\nplt.show()\n\n\n\n\nThe highlighted regions show where a pump is active.\nLet’s print an overview of what happened with control:\n\nmodel.print_discrete_control_record(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\n0. At 2020-01-01 00:00:00 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTT:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"out\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n\n1. At 2020-02-08 19:02:21.861000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n2. At 2020-07-05 08:56:10.319000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state FFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"in\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n3. At 2020-08-11 06:05:15.592000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n\n\nNote that crossing direction specific truth states (containing “U”, “D”) are not present in this overview even though they are part of the control logic. This is because in the control logic for this model these truth states are only used to sustain control states, while the overview only shows changes in control states.\n\n\n4 Model with PID control\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: FlowBoundary\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: Basin\n (2.0, 0.5), # 3: Pump\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (1.5, 1.0), # 5: PidControl\n (2.0, -0.5), # 6: outlet\n (1.5, -1.0), # 7: PidControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"FlowBoundary\",\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"PidControl\",\n \"Outlet\",\n \"PidControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 5, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([2, 3, 4, 6, 2, 3, 6], dtype=np.int64)\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": 5 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [2, 2], \"level\": [0.0, 1.0], \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0]}\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"level\": [6.0],\n }\n)\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [3],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup the outlet:\n\noutlet = ribasim.Outlet(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [6],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"flow_rate\": [1e-3]})\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4],\n \"level\": [1.0], # Not relevant\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup PID control:\n\npid_control = ribasim.PidControl(\n time=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 4 * [5, 7],\n \"time\": [\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n ],\n \"listen_node_id\": 4 * [2, 2],\n \"target\": [5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5],\n \"proportional\": 4 * [-1e-3, 1e-3],\n \"integral\": 4 * [-1e-7, 1e-7],\n \"derivative\": 4 * [0.0, 0.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nNote that the coefficients for the pump and the outlet are equal in magnitude but opposite in sign. This way the pump and the outlet equally work towards the same goal, while having opposite effects on the controlled basin due to their connectivity to this basin.\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n outlet=outlet,\n pid_control=pid_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"pid_control/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/pid_control/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim pid_control/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"pid_control/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\nax.set_ylabel(\"level [m]\")\n\n# Plot target level\ntarget_levels = model.pid_control.time.df.target.to_numpy()[:4]\ntimes = date2num(model.pid_control.time.df.time)[:4]\nax.plot(times, target_levels, color=\"k\", ls=\":\", label=\"target level\")\npass"
+ "text": "1 Basic model with static forcing\n\nfrom pathlib import Path\n\nimport geopandas as gpd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1, 3, 3, 6, 6, 9, 9],\n \"area\": [0.01, 1000.0] * 4,\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0] * 4,\n }\n)\n\n# Convert steady forcing to m/s\n# 2 mm/d precipitation, 1 mm/d evaporation\nseconds_in_day = 24 * 3600\nprecipitation = 0.002 / seconds_in_day\nevaporation = 0.001 / seconds_in_day\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [0],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [evaporation],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [precipitation],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\nstatic = static.iloc[[0, 0, 0, 0]]\nstatic[\"node_id\"] = [1, 3, 6, 9]\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static)\n\nSetup linear resistance:\n\nlinear_resistance = ribasim.LinearResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [10, 12], \"resistance\": [5e3, (3600.0 * 24) / 100.0]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup Manning resistance:\n\nmanning_resistance = ribasim.ManningResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"length\": [900.0],\n \"manning_n\": [0.04],\n \"profile_width\": [6.0],\n \"profile_slope\": [3.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up a rating curve node:\n\n# Discharge: lose 1% of storage volume per day at storage = 1000.0.\nq1000 = 1000.0 * 0.01 / seconds_in_day\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4, 4],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n \"discharge\": [0.0, q1000],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup fractional flows:\n\nfractional_flow = ribasim.FractionalFlow(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [5, 8, 13],\n \"fraction\": [0.3, 0.6, 0.1],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [7],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.5 / 3600],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [11, 17],\n \"level\": [0.5, 1.5],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [15, 16],\n \"flow_rate\": [1e-4, 1e-4],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [14],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin,\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: ManningResistance\n (2.0, 0.0), # 3: Basin\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (3.0, 1.0), # 5: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, 2.0), # 6: Basin\n (4.0, 1.0), # 7: Pump\n (4.0, 0.0), # 8: FractionalFlow\n (5.0, 0.0), # 9: Basin\n (6.0, 0.0), # 10: LinearResistance\n (2.0, 2.0), # 11: LevelBoundary\n (2.0, 1.0), # 12: LinearResistance\n (3.0, -1.0), # 13: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, -2.0), # 14: Terminal\n (3.0, 3.0), # 15: FlowBoundary\n (0.0, 1.0), # 16: FlowBoundary\n (6.0, 1.0), # 17: LevelBoundary\n ]\n)\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_id, node_type = ribasim.Node.node_ids_and_types(\n basin,\n manning_resistance,\n rating_curve,\n pump,\n fractional_flow,\n linear_resistance,\n level_boundary,\n flow_boundary,\n terminal,\n)\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(node_id, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array(\n [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 8, 7, 9, 11, 12, 4, 13, 15, 16, 10], dtype=np.int64\n)\nto_id = np.array(\n [2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 6, 7, 9, 9, 10, 12, 3, 13, 14, 6, 1, 17], dtype=np.int64\n)\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": len(from_id) * [\"flow\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n linear_resistance=linear_resistance,\n manning_resistance=manning_resistance,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n fractional_flow=fractional_flow,\n terminal=terminal,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic/ribasim.toml')\n\n\n\n\n2 Update the basic model with transient forcing\nThis assumes you have already created the basic model with static forcing.\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\nimport xarray as xr\n\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(filepath=datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\n\ntime = pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime)\nday_of_year = time.day_of_year.to_numpy()\nseconds_per_day = 24 * 60 * 60\nevaporation = (\n (-1.0 * np.cos(day_of_year / 365.0 * 2 * np.pi) + 1.0) * 0.0025 / seconds_per_day\n)\nrng = np.random.default_rng(seed=0)\nprecipitation = (\n rng.lognormal(mean=-1.0, sigma=1.7, size=time.size) * 0.001 / seconds_per_day\n)\n\nWe’ll use xarray to easily broadcast the values.\n\ntimeseries = (\n pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 1,\n \"time\": pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime),\n \"drainage\": 0.0,\n \"potential_evaporation\": evaporation,\n \"infiltration\": 0.0,\n \"precipitation\": precipitation,\n \"urban_runoff\": 0.0,\n }\n )\n .set_index(\"time\")\n .to_xarray()\n)\n\nbasin_ids = model.basin.static.df[\"node_id\"].to_numpy()\nbasin_nodes = xr.DataArray(\n np.ones(len(basin_ids)), coords={\"node_id\": basin_ids}, dims=[\"node_id\"]\n)\nforcing = (timeseries * basin_nodes).to_dataframe().reset_index()\n\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": basin_ids,\n \"level\": 1.4,\n \"concentration\": 0.0,\n }\n)\n\n\nmodel.basin.time.df = forcing\nmodel.basin.state.df = state\n\n\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic_transient/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic_transient/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim basic-transient/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\ndf_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\n<Axes: xlabel='time'>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ndf_flow = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/flow.arrow\")\ndf_flow[\"edge\"] = list(zip(df_flow.from_node_id, df_flow.to_node_id))\ndf_flow[\"flow_m3d\"] = df_flow.flow * 86400\nax = df_flow.pivot_table(index=\"time\", columns=\"edge\", values=\"flow_m3d\").plot()\nax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title=\"Edge\")\n\n<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f7014656f50>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ntype(df_flow)\n\npandas.core.frame.DataFrame\n\n\n\n\n3 Model with discrete control\nThe model constructed below consists of a single basin which slowly drains trough a TabulatedRatingCurve, but is held within a range around a target level (setpoint) by two connected pumps. These two pumps behave like a reversible pump. When pumping can be done in only one direction, and the other direction is only possible under gravity, use an Outlet for that direction.\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin\n (1.0, 1.0), # 2: Pump\n (1.0, -1.0), # 3: Pump\n (2.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (-1.0, 0.0), # 5: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (-2.0, 0.0), # 6: Terminal\n (1.0, 0.0), # 7: DiscreteControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"TabulatedRatingCurve\",\n \"Terminal\",\n \"DiscreteControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 7, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 6, 2, 3], dtype=np.int64)\n\nedge_type = 6 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"]\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"from_node_id\": from_id, \"to_node_id\": to_id, \"edge_type\": edge_type},\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1],\n \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n }\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"level\": [20.0]})\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the discrete control:\n\ncondition = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [7],\n \"listen_feature_id\": 3 * [1],\n \"variable\": 3 * [\"level\"],\n \"greater_than\": [5.0, 10.0, 15.0], # min, setpoint, max\n }\n)\n\nlogic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 5 * [7],\n \"truth_state\": [\"FFF\", \"U**\", \"T*F\", \"**D\", \"TTT\"],\n \"control_state\": [\"in\", \"in\", \"none\", \"out\", \"out\"],\n }\n)\n\ndiscrete_control = ribasim.DiscreteControl(condition=condition, logic=logic)\n\nThe above control logic can be summarized as follows: - If the level gets above the maximum, activate the control state “out” until the setpoint is reached; - If the level gets below the minimum, active the control state “in” until the setpoint is reached; - Otherwise activate the control state “none”.\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [2] + 3 * [3],\n \"control_state\": 2 * [\"none\", \"in\", \"out\"],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0, 2e-3, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2e-3],\n }\n )\n)\n\nThe pump data defines the following:\n\n\n\nControl state\nPump #2 flow rate (m/s)\nPump #3 flow rate (m/s)\n\n\n\n\n“none”\n0.0\n0.0\n\n\n“in”\n2e-3\n0.0\n\n\n“out”\n0.0\n2e-3\n\n\n\nSetup the level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [4], \"level\": [10.0]})\n)\n\nSetup the rating curve:\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": 2 * [5], \"level\": [2.0, 15.0], \"discharge\": [0.0, 1e-3]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup the terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [6]}))\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n pump=pump,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n terminal=terminal,\n discrete_control=discrete_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nListen edges are plotted with a dashed line since they are not present in the “Edge / static” schema but only in the “Control / condition” schema.\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\n\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\ngreater_than = model.discrete_control.condition.df.greater_than\n\nax.hlines(\n greater_than,\n df_basin.time[0],\n df_basin.time.max(),\n lw=1,\n ls=\"--\",\n color=\"k\",\n)\n\ndf_control = pd.read_feather(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\ny_min, y_max = ax.get_ybound()\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[:2], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[2:4], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\n\nax.set_xticks(\n date2num(df_control.time).tolist(),\n df_control.control_state.tolist(),\n rotation=50,\n)\n\nax.set_yticks(greater_than, [\"min\", \"setpoint\", \"max\"])\nax.set_ylabel(\"level\")\nplt.show()\n\n\n\n\nThe highlighted regions show where a pump is active.\nLet’s print an overview of what happened with control:\n\nmodel.print_discrete_control_record(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\n0. At 2020-01-01 00:00:00 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTT:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"out\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n\n1. At 2020-02-08 19:02:21.861000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n2. At 2020-07-05 08:56:10.319000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state FFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"in\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n3. At 2020-08-11 06:05:15.592000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n\n\nNote that crossing direction specific truth states (containing “U”, “D”) are not present in this overview even though they are part of the control logic. This is because in the control logic for this model these truth states are only used to sustain control states, while the overview only shows changes in control states.\n\n\n4 Model with PID control\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: FlowBoundary\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: Basin\n (2.0, 0.5), # 3: Pump\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (1.5, 1.0), # 5: PidControl\n (2.0, -0.5), # 6: outlet\n (1.5, -1.0), # 7: PidControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"FlowBoundary\",\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"PidControl\",\n \"Outlet\",\n \"PidControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 5, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([2, 3, 4, 6, 2, 3, 6], dtype=np.int64)\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": 5 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [2, 2], \"level\": [0.0, 1.0], \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0]}\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"level\": [6.0],\n }\n)\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [3],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup the outlet:\n\noutlet = ribasim.Outlet(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [6],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"flow_rate\": [1e-3]})\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4],\n \"level\": [1.0], # Not relevant\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup PID control:\n\npid_control = ribasim.PidControl(\n time=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 4 * [5, 7],\n \"time\": [\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n ],\n \"listen_node_id\": 4 * [2, 2],\n \"target\": [5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5],\n \"proportional\": 4 * [-1e-3, 1e-3],\n \"integral\": 4 * [-1e-7, 1e-7],\n \"derivative\": 4 * [0.0, 0.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nNote that the coefficients for the pump and the outlet are equal in magnitude but opposite in sign. This way the pump and the outlet equally work towards the same goal, while having opposite effects on the controlled basin due to their connectivity to this basin.\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n outlet=outlet,\n pid_control=pid_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"pid_control/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/pid_control/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim pid_control/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"pid_control/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\nax.set_ylabel(\"level [m]\")\n\n# Plot target level\ntarget_levels = model.pid_control.time.df.target.to_numpy()[:4]\ntimes = date2num(model.pid_control.time.df.time)[:4]\nax.plot(times, target_levels, color=\"k\", ls=\":\", label=\"target level\")\npass"
},
{
"objectID": "qgis/index.html",
"href": "qgis/index.html",
"title": "QGIS plugin",
"section": "",
- "text": "Install QGIS version 3.28 or higher.\n\n\nDownload ribasim_qgis.zip, see the download section.\nPlugins menu > Manage and Install Plugins…\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Install from ZIP”:\n\nBrowse to the ribasim_qgis.zip file containing the plugin that was downloaded earlier\nClick “Install Plugin”\n\n\n\n\n\n\nStart the Ribasim plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nIn QGIS, navigate to “Plugins > Manage and Install Plugins > All”. In the search bar, type: “iMOD”. Select the iMOD plugin, and click “Install”.\nAt least version 0.4.0 of the iMOD plugin is required.\nThe Time Series widget from the iMOD plugin is used for visualizing Ribasim results, which is described in Section 1.5. Documentation on the Time Series widget can be found in the iMOD documentation.\n\n\n\nOpen an existing model or create a new model. As an example of an existing model, you can use the “basic” model from generated_testmodels.zip, see the download section.\n\n\n\n\n\nCheck if your coordinate reference system (CRS) is set correctly.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are working with an unknown CRS, right click the model database group in Layers, and click “Set Group CRS…”.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are modeling the Netherlands, select “Amersfoort / RD New” (EPSG:28992).\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Node layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn on the edit mode to be able to add nodes on the map.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdd nodes to the map with a left click and select the node type.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn the edit mode off and save the edits to the Nodes layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nRight click a layer and select “Open Attribute Table”.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick the yellow pencil icon on the top left to enable editing, and copy and paste a record. A record can be selected by clicking on the row number.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdjust the content. If you prefer, it also works to copy data with the same columns from Excel. Turn off edit mode and save changes to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nMake sure the Snapping Toolbar is visible, by going to the View > Toolbars menu. Turn on snapping mode by clicking the magnet and set the snapping distance to 25 pixels.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Edge layer and turn on the edit mode.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Add line feature”.\n\n\n\n\n\nCreate a connection by left clicking a source node and right clicking the destination node.\n\n\n\n\n\nNow leave the edit mode and save the results to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nOpen a text editor and create an empty file next to your database, with the .toml extension.\nAdd the following content to the TOML file:\n\n\n\nribasim.toml\n\nstarttime = 2020-01-01 00:00:00\nendtime = 2021-01-01 00:00:00\ndatabase = \"database.gpkg\"\n\n\nUnzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files.\n\n\n\n\n\n\nIn QGIS select the model group.\n\n\n\n\n\nIn the Ribasim plugin widget, select the Results tab and click “Associate Results”.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect results/basin.arrow.\n\n\n\n\n\nThis adds metadata to the model that the iMOD plugin can use to find the timeseries data that is associated to the model nodes.\n\n\n\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes. Currently only the Basin nodes can be plotted.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph."
+ "text": "Install QGIS version 3.28 or higher.\n\n\nDownload ribasim_qgis.zip, see the download section.\nPlugins menu > Manage and Install Plugins…\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Install from ZIP”:\n\nBrowse to the ribasim_qgis.zip file containing the plugin that was downloaded earlier\nClick “Install Plugin”\n\n\n\n\n\n\nStart the Ribasim plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nIn QGIS, navigate to “Plugins > Manage and Install Plugins > All”. In the search bar, type: “iMOD”. Select the iMOD plugin, and click “Install”.\nAt least version 0.4.0 of the iMOD plugin is required.\nThe Time Series widget from the iMOD plugin is used for visualizing Ribasim results, which is described in Section 1.5. Documentation on the Time Series widget can be found in the iMOD documentation.\n\n\n\nOpen an existing model or create a new model. As an example of an existing model, you can use the “basic” model from generated_testmodels.zip, see the download section.\n\n\n\n\n\nCheck if your coordinate reference system (CRS) is set correctly.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are working with an unknown CRS, right click the model database group in Layers, and click “Set Group CRS…”.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are modeling the Netherlands, select “Amersfoort / RD New” (EPSG:28992).\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Node layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn on the edit mode to be able to add nodes on the map.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdd nodes to the map with a left click and select the node type.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn the edit mode off and save the edits to the Nodes layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nRight click a layer and select “Open Attribute Table”.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick the yellow pencil icon on the top left to enable editing, and copy and paste a record. A record can be selected by clicking on the row number.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdjust the content. If you prefer, it also works to copy data with the same columns from Excel. Turn off edit mode and save changes to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nMake sure the Snapping Toolbar is visible, by going to the View > Toolbars menu. Turn on snapping mode by clicking the magnet and set the snapping distance to 25 pixels.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Edge layer and turn on the edit mode.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Add line feature”.\n\n\n\n\n\nCreate a connection by left clicking a source node and right clicking the destination node.\n\n\n\n\n\nNow leave the edit mode and save the results to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nUnzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files.\n\n\n\n\nBefore trying to inspect the results, verify that the run was successful and the output files are there.\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the layer that you wish to plot. From the “Node” layer you can plot level or storage on Basin nodes. From the “Edge” layer you can plot flow over flow edges. Note that before switching between these, you typically have to click “Clear” to clear the selection. If you run a simulation with the model open in QGIS, you have to close and re-open the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel for the new results to be loaded.\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph.\n\n\n\n\n\nOnly the “basin.arrow” and “flow.arrow” can be inspected with the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel. All Arrow files can be loaded as a layer by dragging the files onto QGIS. Right click the layer and select “Open Attribute Table” to view the contents."
},
{
"objectID": "qgis/index.html#start",
@@ -431,14 +431,14 @@
"href": "qgis/index.html#run-a-model",
"title": "QGIS plugin",
"section": "",
- "text": "Open a text editor and create an empty file next to your database, with the .toml extension.\nAdd the following content to the TOML file:\n\n\n\nribasim.toml\n\nstarttime = 2020-01-01 00:00:00\nendtime = 2021-01-01 00:00:00\ndatabase = \"database.gpkg\"\n\n\nUnzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files."
+ "text": "Unzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files."
},
{
"objectID": "qgis/index.html#sec-results",
"href": "qgis/index.html#sec-results",
"title": "QGIS plugin",
"section": "",
- "text": "In QGIS select the model group.\n\n\n\n\n\nIn the Ribasim plugin widget, select the Results tab and click “Associate Results”.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect results/basin.arrow.\n\n\n\n\n\nThis adds metadata to the model that the iMOD plugin can use to find the timeseries data that is associated to the model nodes.\n\n\n\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes. Currently only the Basin nodes can be plotted.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph."
+ "text": "Before trying to inspect the results, verify that the run was successful and the output files are there.\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the layer that you wish to plot. From the “Node” layer you can plot level or storage on Basin nodes. From the “Edge” layer you can plot flow over flow edges. Note that before switching between these, you typically have to click “Clear” to clear the selection. If you run a simulation with the model open in QGIS, you have to close and re-open the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel for the new results to be loaded.\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph.\n\n\n\n\n\nOnly the “basin.arrow” and “flow.arrow” can be inspected with the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel. All Arrow files can be loaded as a layer by dragging the files onto QGIS. Right click the layer and select “Open Attribute Table” to view the contents."
},
{
"objectID": "couple/modflow-demo.html",
Ribasim.ManningResistance — Type.source
+
# Ribasim.Model — Type.
Model(config_path::AbstractString)
Model(config::Config)
Initialize a Model.
The Model struct is an initialized model, combined with the Config used to create it and saved results. The Basic Model Interface (BMI) is implemented on the Model. A Model can be created from the path to a TOML configuration file, or a Config object.
-
+
# Ribasim.NodeMetadata — Type.
Type for storing metadata of nodes in the graph type: type of the node allocationnetworkid: Allocation network ID (0 if not in subnetwork)
-
+
# Ribasim.OutNeighbors — Type.
Iterate over outgoing neighbors of a given label in a MetaGraph, only for edges of edge_type
-
+
# Ribasim.Outlet — Type.
nodeid: node ID of the Outlet node active: whether this node is active and thus contributes flow flowrate: target flow rate minflowrate: The minimal flow rate of the outlet maxflowrate: The maximum flow rate of the outlet controlmapping: dictionary from (nodeid, controlstate) to target flow rate ispid_controlled: whether the flow rate of this outlet is governed by PID control
-
+
# Ribasim.PidControl — Type.
PID control currently only supports regulating basin levels.
nodeid: node ID of the PidControl node active: whether this node is active and thus sets flow rates listennodeid: the id of the basin being controlled pidparams: a vector interpolation for parameters changing over time. The parameters are respectively target, proportional, integral, derivative, where the last three are the coefficients for the PID equation. error: the current error; basintarget - currentlevel
-
+
# Ribasim.Pump — Type.
nodeid: node ID of the Pump node active: whether this node is active and thus contributes flow flowrate: target flow rate minflowrate: The minimal flow rate of the pump maxflowrate: The maximum flow rate of the pump controlmapping: dictionary from (nodeid, controlstate) to target flow rate ispid_controlled: whether the flow rate of this pump is governed by PID control
-
+
# Ribasim.Subgrid — Type.
Subgrid linearly interpolates basin levels.
-
+
# Ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve — Type.
struct TabulatedRatingCurve{C}
Rating curve from level to discharge. The rating curve is a lookup table with linear interpolation in between. Relation can be updated in time, which is done by moving data from the time field into the tables, which is done in the update_tabulated_rating_curve callback.
Type parameter C indicates the content backing the StructVector, which can be a NamedTuple of Vectors or Arrow Primitives, and is added to avoid type instabilities.
nodeid: node ID of the TabulatedRatingCurve node active: whether this node is active and thus contributes flows tables: The current Q(h) relationships time: The time table used for updating the tables controlmapping: dictionary from (nodeid, controlstate) to Q(h) and/or active state
-
+
# Ribasim.Terminal — Type.
node_id: node ID of the Terminal node
-
+
# Ribasim.User — Type.
demand: water flux demand of user per priority over time active: whether this node is active and thus demands water allocated: water flux currently allocated to user per priority returnfactor: the factor in [0,1] of how much of the abstracted water is given back to the system minlevel: The level of the source basin below which the user does not abstract priorities: All used priority values. Each user has a demand for all these priorities, which is 0.0 if it is not provided explicitly. record: Collected data of allocation optimizations for output file.
-
+
# Ribasim.config.Config — Method.
Config(config_path::AbstractString; kwargs...)
Parse a TOML file to a Config. Keys can be overruled using keyword arguments. To overrule keys from a subsection, e.g. dt from the solver section, use underscores: solver_dt.
-
+
@@ -410,157 +410,157 @@ # BasicModelInterface.finalize — Method.
BMI.finalize(model::Model)::Model
Write all results to the configured files.
-
+
# BasicModelInterface.initialize — Method.
BMI.initialize(T::Type{Model}, config_path::AbstractString)::Model
Initialize a Model from the path to the TOML configuration file.
-
+
# BasicModelInterface.initialize — Method.
BMI.initialize(T::Type{Model}, config::Config)::Model
Initialize a Model from a Config.
-
+
# CommonSolve.solve! — Method.
solve!(model::Model)::ODESolution
Solve a Model until the configured endtime.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_absolute_value! — Method.
Minimizing |expr| can be achieved by introducing a new variable exprabs and posing the following constraints: exprabs >= expr expr_abs >= -expr
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_capacity! — Method.
Add the flow capacity constraints to the allocation problem. Only finite capacities get a constraint. The constraint indices are (edgesourceid, edgedstid).
Constraint: flow over edge <= edge capacity
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_flow_conservation! — Method.
Add the flow conservation constraints to the allocation problem. The constraint indices are user node IDs.
Constraint: sum(flows out of node node) <= flows into node + flow from storage and vertical fluxes
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_source! — Method.
Add the source constraints to the allocation problem. The actual threshold values will be set before each allocation solve. The constraint indices are (edgesourceid, edgedstid).
Constraint: flow over source edge <= source flow in subnetwork
-
+
# Ribasim.add_constraints_user_returnflow! — Method.
Add the user returnflow constraints to the allocation problem. The constraint indices are user node IDs.
Constraint: outflow from user <= return factor * inflow to user
-
+
# Ribasim.add_flow! — Method.
Add the given flow q to the flow over the edge on the horizontal (self-loop) edge from id to id.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_flow! — Method.
Add the given flow q to the existing flow over the edge between the given nodes.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_variables_absolute_value! — Method.
Certain allocation distribution types use absolute values in the objective function. Since most optimization packages do not support the absolute value function directly, New variables are introduced that act as the absolute value of an expression by posing the appropriate constraints.
-
+
# Ribasim.add_variables_flow! — Method.
Add the flow variables F to the allocation problem. The variable indices are (edgesourceid, edgedstid). Non-negativivity constraints are also immediately added to the flow variables.
-
+
# Ribasim.adjust_edge_capacities! — Method.
Set the values of the edge capacities. 2 cases:
- Before the first allocation solve, set the edge capacities to their full capacity;
- Before an allocation solve, subtract the flow used by allocation for the previous priority from the edge capacities.
-
+
# Ribasim.adjust_source_flows! — Method.
Adjust the source flows.
-
+
# Ribasim.all_neighbor_labels_type — Method.
Get the in- and outneighbor node IDs of the given node ID (label) over the given edge type in the graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocate! — Method.
Update the allocation optimization problem for the given subnetwork with the problem state and flows, solve the allocation problem and assign the results to the users.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_graph — Method.
Build the graph used for the allocation problem.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_graph_used_nodes! — Method.
Find all nodes in the subnetwork which will be used in the allocation network. Some nodes are skipped to optimize allocation optimization.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_path_exists_in_graph — Method.
Find out whether a path exists between a start node and end node in the given allocation graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_problem — Method.
Construct the allocation problem for the current subnetwork as a JuMP.jl model.
-
+
# Ribasim.allocation_table — Method.
Create an allocation result table for the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.assign_allocations! — Method.
Assign the allocations to the users as determined by the solution of the allocation problem.
-
+
# Ribasim.avoid_using_own_returnflow! — Method.
Remove allocation user return flow edges that are upstream of the user itself.
-
+
# Ribasim.basin_bottom — Method.
Return the bottom elevation of the basin with index i, or nothing if it doesn’t exist
-
+
# Ribasim.basin_bottoms — Method.
Get the bottom on both ends of a node. If only one has a bottom, use that for both.
-
+
# Ribasim.basin_table — Method.
Create the basin result table from the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.create_callbacks — Method.
Create the different callbacks that are used to store results and feed the simulation with new data. The different callbacks are combined to a CallbackSet that goes to the integrator. Returns the CallbackSet and the SavedValues for flow.
-
+
# Ribasim.create_graph — Method.
Return a directed metagraph with data of nodes (NodeMetadata): NodeMetadata
and data of edges (EdgeMetadata): EdgeMetadata
-
+
# Ribasim.create_storage_tables — Method.
Read the Basin / profile table and return all area and level and computed storage values
-
+
# Ribasim.datetime_since — Method.
datetime_since(t::Real, t0::DateTime)::DateTime
Convert a Real that represents the seconds passed since the simulation start to the nearest DateTime. This is used to convert between the solver’s inner float time, and the calendar.
-
+
# Ribasim.datetimes — Method.
Get all saved times as a Vector{DateTime}
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_affect! — Method.
Change parameters based on the control logic.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_affect_downcrossing! — Method.
An downcrossing means that a condition (always greater than) becomes false.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_affect_upcrossing! — Method.
An upcrossing means that a condition (always greater than) becomes true.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_condition — Method.
Listens for changes in condition truths.
-
+
# Ribasim.discrete_control_table — Method.
Create a discrete control result table from the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.expand_logic_mapping — Method.
Replace the truth states in the logic mapping which contain wildcards with all possible explicit truth states.
-
+
# Ribasim.find_allocation_graph_edges! — Method.
This loop finds allocation graph edges in several ways:
- Between allocation graph nodes whose equivalent in the subnetwork are directly connected
- Between allocation graph nodes whose equivalent in the subnetwork are connected with one or more allocation graph nodes in between
-
+
# Ribasim.findlastgroup — Method.
For an element id and a vector of elements ids, get the range of indices of the last consecutive block of id. Returns the empty range 1:0 if id is not in ids.
# 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Ribasim.findlastgroup(2, [5,4,2,2,5,2,2,2,1])
# output
6:8
-
+
# Ribasim.findsorted — Method.
Find the index of element x in a sorted collection a. Returns the index of x if it exists, or nothing if it doesn’t. If x occurs more than once, throw an error.
-
+
# Ribasim.flow_table — Method.
Create a flow result table from the saved data
-
+
# Ribasim.formulate_basins! — Method.
Smoothly let the evaporation flux go to 0 when at small water depths Currently at less than 0.1 m.
-
+
# Ribasim.formulate_flow! — Method.
Directed graph: outflow is positive!
-
+
# Ribasim.formulate_flow! — Method.
Conservation of energy for two basins, a and b:
h_a + v_a^2 / (2 * g) = h_b + v_b^2 / (2 * g) + S_f * L + C / 2 * g * (v_b^2 - v_a^2)
@@ -588,116 +588,116 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.formulate_flow! — Method.
Directed graph: outflow is positive!
-
+
# Ribasim.get_area_and_level — Method.
Compute the area and level of a basin given its storage. Also returns darea/dlevel as it is needed for the Jacobian.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_chunk_sizes — Method.
Get the chunk sizes for DiffCache; differentiation w.r.t. u and t (the latter only if a Rosenbrock algorithm is used).
-
+
# Ribasim.get_compressor — Method.
Get the compressor based on the Results section
-
+
# Ribasim.get_flow — Method.
Get the flow over the given horizontal (selfloop) edge (val is needed for get_tmp from ForwardDiff.jl).
-
+
# Ribasim.get_flow — Method.
Get the flow over the given edge (val is needed for get_tmp from ForwardDiff.jl).
-
+
# Ribasim.get_fractional_flow_connected_basins — Method.
Get the node type specific indices of the fractional flows and basins, that are consecutively connected to a node of given id.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_jac_prototype — Method.
Get a sparse matrix whose sparsity matches the sparsity of the Jacobian of the ODE problem. All nodes are taken into consideration, also the ones that are inactive.
In Ribasim the Jacobian is typically sparse because each state only depends on a small number of other states.
Note: the name ‘prototype’ does not mean this code is a prototype, it comes from the naming convention of this sparsity structure in the differentialequations.jl docs.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_level — Method.
Get the current water level of a node ID. The ID can belong to either a Basin or a LevelBoundary. storage: tells ForwardDiff whether this call is for differentiation or not
-
+
# Ribasim.get_scalar_interpolation — Method.
Linear interpolation of a scalar with constant extrapolation.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_storage_from_level — Method.
Get the storage of a basin from its level.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_storages_and_levels — Method.
Get the storage and level of all basins as matrices of nbasin × ntime
-
+
# Ribasim.get_storages_from_levels — Method.
Compute the storages of the basins based on the water level of the basins.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_tstops — Method.
From an iterable of DateTimes, find the times the solver needs to stop
-
+
# Ribasim.get_value — Method.
Get a value for a condition. Currently supports getting levels from basins and flows from flow boundaries.
-
+
# Ribasim.id_index — Method.
Get the index of an ID in a set of indices.
-
+
# Ribasim.indicate_allocation_flow! — Method.
Add to the edge metadata that the given edge is used for allocation flow. If the edge does not exist, it is created.
-
+
# Ribasim.inflow_id — Method.
Get the unique inneighbor over a flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.inflow_ids — Method.
Get the inneighbors over flow edges.
-
+
# Ribasim.inflow_ids_allocation — Method.
Get the inneighbors of the given ID such that the connecting edge is an allocation flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.inneighbor_labels_type — Method.
Get the inneighbor node IDs of the given node ID (label) over the given edge type in the graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.inoutflow_ids — Method.
Get the in- and outneighbors over flow edges.
-
+
# Ribasim.is_allocation_source — Method.
Find out whether the given edge is a source for an allocation network.
-
+
# Ribasim.is_flow_constraining — Method.
Whether the given node node is flow constraining by having a maximum flow rate.
-
+
# Ribasim.is_flow_direction_constraining — Method.
Whether the given node is flow direction constraining (only in direction of edges).
-
+
# Ribasim.load_data — Method.
load_data(db::DB, config::Config, nodetype::Symbol, kind::Symbol)::Union{Table, Query, Nothing}
Load data from Arrow files if available, otherwise the database. Returns either an Arrow.Table, SQLite.Query or nothing if the data is not present.
-
+
# Ribasim.load_structvector — Method.
load_structvector(db::DB, config::Config, ::Type{T})::StructVector{T}
Load data from Arrow files if available, otherwise the database. Always returns a StructVector of the given struct type T, which is empty if the table is not found. This function validates the schema, and enforces the required sort order.
-
+
# Ribasim.metadata_from_edge — Method.
Get the metadata of an edge in the graph from an edge of the underlying DiGraph.
-
+
# Ribasim.nodefields — Method.
Get all node fieldnames of the parameter object.
-
+
# Ribasim.nodetype — Method.
From a SchemaVersion(“ribasim.flowboundary.static”, 1) return (:FlowBoundary, :static)
-
+
# Ribasim.outflow_id — Method.
Get the unique outneighbor over a flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.outflow_ids — Method.
Get the outneighbors over flow edges.
-
+
# Ribasim.outflow_ids_allocation — Method.
Get the outneighbors of the given ID such that the connecting edge is an allocation flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.outneighbor_labels_type — Method.
Get the outneighbor node IDs of the given node ID (label) over the given edge type in the graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.parse_static_and_time — Method.
Process the data in the static and time tables for a given node type. The ‘defaults’ named tuple dictates how missing data is filled in. ‘time_interpolatables’ is a vector of Symbols of parameter names for which a time interpolation (linear) object must be constructed. The control mapping for DiscreteControl is also constructed in this function. This function currently does not support node states that are defined by more than one row in a table, as is the case for TabulatedRatingCurve.
-
+
# Ribasim.process_allocation_graph_edges! — Method.
For the composite allocation graph edges:
@@ -705,83 +705,83 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.profile_storage — Method.
Calculate a profile storage by integrating the areas over the levels
-
+
# Ribasim.qh_interpolation — Method.
From a table with columns nodeid, discharge (Q) and level (h), create a LinearInterpolation from level to discharge for a given nodeid.
-
+
# Ribasim.reduction_factor — Method.
Function that goes smoothly from 0 to 1 in the interval [0,threshold], and is constant outside this interval.
-
+
# Ribasim.run — Method.
run(config_file::AbstractString)::Model
run(config::Config)::Model
Run a Model, given a path to a TOML configuration file, or a Config object. Running a model includes initialization, solving to the end with [solve!](@ref) and writing results with BMI.finalize.
-
+
# Ribasim.save_flow — Method.
Copy the current flow to the SavedValues
-
+
# Ribasim.save_subgrid_level — Method.
Interpolate the levels and save them to SavedValues
-
+
# Ribasim.scalar_interpolation_derivative — Method.
Derivative of scalar interpolation.
-
+
# Ribasim.seconds_since — Method.
seconds_since(t::DateTime, t0::DateTime)::Float64
Convert a DateTime to a float that is the number of seconds since the start of the simulation. This is used to convert between the solver’s inner float time, and the calendar.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_current_value! — Method.
From a timeseries table time, load the most recent applicable data into table. table must be a NamedTuple of vectors with all variables that must be loaded. The most recent applicable data is non-NaN data for a given ID that is on or before t.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_flow! — Method.
Set the given flow q on the horizontal (self-loop) edge from id to id.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_flow! — Method.
Set the given flow q over the edge between the given nodes.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_initial_discrete_controlled_parameters! — Method.
Set parameters of nodes that are controlled by DiscreteControl to the values corresponding to the initial state of the model.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_objective_priority! — Method.
Set the objective for the given priority. For an objective with absolute values this also involves adjusting constraints.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_static_value! — Method.
Load data from a source table static into a destination table. Data is matched based on the node_id, which is sorted.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_table_row! — Method.
Update table at row index i, with the values of a given row. table must be a NamedTuple of vectors with all variables that must be loaded. The row must contain all the column names that are present in the table. If a value is NaN, it is not set.
-
+
# Ribasim.sorted_table! — Method.
Depending on if a table can be sorted, either sort it or assert that it is sorted.
Tables loaded from the database into memory can be sorted. Tables loaded from Arrow files are memory mapped and can therefore not be sorted.
-
+
# Ribasim.timesteps — Method.
Get all saved times in seconds since start
-
+
# Ribasim.update_allocation! — Method.
Solve the allocation problem for all users and assign allocated abstractions to user nodes.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_basin — Method.
Load updates from ‘Basin / time’ into the parameters
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
Method for nodes that do not contribute to the Jacobian
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
The controlled basin affects itself and the basins upstream and downstream of the controlled pump affect eachother if there is a basin upstream of the pump. The state for the integral term and the controlled basin affect eachother, and the same for the integral state and the basin upstream of the pump if it is indeed a basin.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
If both the unique node upstream and the unique node downstream of these nodes are basins, then these directly depend on eachother and affect the Jacobian 2x Basins always depend on themselves.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
If both the unique node upstream and the nodes down stream (or one node further if a fractional flow is in between) are basins, then the downstream basin depends on the upstream basin(s) and affect the Jacobian as many times as there are downstream basins Upstream basins always depend on themselves.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_tabulated_rating_curve! — Method.
Load updates from ‘TabulatedRatingCurve / time’ into the parameters
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_discrete_control — Method.
Check:
@@ -789,50 +789,50 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.valid_edge_types — Method.
Check that only supported edge types are declared.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_edges — Method.
Test for each node given its node type whether the nodes that
are downstream (‘down-edge’) of this node are of an allowed type
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_flow_rates — Method.
Test whether static or discrete controlled flow rates are indeed non-negative.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_fractional_flow — Method.
Check that nodes that have fractional flow outneighbors do not have any other type of outneighbor, that the fractions leaving a node add up to ≈1 and that the fractions are non-negative.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_n_neighbors — Method.
Test for each node given its node type whether it has an allowed number of flow/control inneighbors and outneighbors
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_profiles — Method.
Check whether the profile data has no repeats in the levels and the areas start positive.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_sources — Method.
The source nodes must only have one allocation outneighbor and no allocation inneighbors.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_subgrid — Method.
Validate the entries for a single subgrid element.
-
+
# Ribasim.water_balance! — Method.
The right hand side function of the system of ODEs set up by Ribasim.
-
+
# Ribasim.write_arrow — Method.
Write a result table to disk as an Arrow file
-
+
# Ribasim.config.algorithm — Method.
Create an OrdinaryDiffEqAlgorithm from solver config
-
+
# Ribasim.config.input_path — Method.
Construct a path relative to both the TOML directory and the optional input_dir
-
+
# Ribasim.config.results_path — Method.
Construct a path relative to both the TOML directory and the optional results_dir
-
+
# Ribasim.config.snake_case — Method.
Convert a string from CamelCase to snake_case.
-
+
@@ -853,7 +853,7 @@ source
+
@@ -861,10 +861,10 @@ 1.5 Macros
# Ribasim.config.@addfields — Macro.
Add fieldnames with Union{String, Nothing} type to struct expression. Requires (option?) use before it.
-
+
# Ribasim.config.@addnodetypes — Macro.
Add all TableOption subtypes as fields to struct expression. Requires (option?) use before it.
-
+
@@ -898,8 +898,8 @@ Ribasim.User
Ribasim.config.ConfigBasicModelInterface.finalizeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeCommonSolve.solve!Ribasim.add_constraints_absolute_value!Ribasim.add_constraints_capacity!Ribasim.scalar_interpolation_derivative
Ribasim.seconds_sinceRibasim.set_current_value!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_initial_discrete_controlled_parameters!Ribasim.set_objective_priority!Ribasim.set_static_value!Ribasim.timesteps
Ribasim.update_allocation!Ribasim.update_basinRibasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_tabulated_rating_curve!Ribasim.valid_discrete_controlRibasim.valid_edge_types2 Update the basi
ax = df_flow.pivot_table(index="time", columns="edge", values="flow_m3d").plot()
ax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title="Edge")
-<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f1a7c921550>
+<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f7014656f50>

@@ -1021,7 +1021,7 @@ 4 Model with PID
<Axes: >
-
+
Write the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:
diff --git a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png
index 33e8abbcf..f5f6a2b5b 100644
Binary files a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png and b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png differ
diff --git a/qgis/index.html b/qgis/index.html
index 0980ee3b0..df224853e 100644
--- a/qgis/index.html
+++ b/qgis/index.html
@@ -20,40 +20,6 @@
margin: 0 0.8em 0.2em -1em; /* quarto-specific, see https://github.com/quarto-dev/quarto-cli/issues/4556 */
vertical-align: middle;
}
-/* CSS for syntax highlighting */
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre; position: relative; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { display: inline-block; line-height: 1.25; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span:empty { height: 1.2em; }
-.sourceCode { overflow: visible; }
-code.sourceCode > span { color: inherit; text-decoration: inherit; }
-div.sourceCode { margin: 1em 0; }
-pre.sourceCode { margin: 0; }
-@media screen {
-div.sourceCode { overflow: auto; }
-}
-@media print {
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre-wrap; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { text-indent: -5em; padding-left: 5em; }
-}
-pre.numberSource code
- { counter-reset: source-line 0; }
-pre.numberSource code > span
- { position: relative; left: -4em; counter-increment: source-line; }
-pre.numberSource code > span > a:first-child::before
- { content: counter(source-line);
- position: relative; left: -1em; text-align: right; vertical-align: baseline;
- border: none; display: inline-block;
- -webkit-touch-callout: none; -webkit-user-select: none;
- -khtml-user-select: none; -moz-user-select: none;
- -ms-user-select: none; user-select: none;
- padding: 0 4px; width: 4em;
- }
-pre.numberSource { margin-left: 3em; padding-left: 4px; }
-div.sourceCode
- { }
-@media screen {
-pre > code.sourceCode > span > a:first-child::before { text-decoration: underline; }
-}
@@ -180,11 +146,7 @@ On this page
- 1.3.2 Create connecting edges
- 1.4 Run a model
- - 1.5 Inspect results
-
+ - 1.5 Inspect results
Ribasim.Model — Type.Model(config_path::AbstractString)
Model(config::Config)Config used to create it and saved results. The Basic Model Interface (BMI) is implemented on the Model. A Model can be created from the path to a TOML configuration file, or a Config object.Ribasim.NodeMetadata — Type.Ribasim.OutNeighbors — Type.Ribasim.Outlet — Type.Ribasim.PidControl — Type.Ribasim.Pump — Type.Ribasim.Subgrid — Type.Ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve — Type.struct TabulatedRatingCurve{C}time field into the tables, which is done in the update_tabulated_rating_curve callback.Ribasim.Terminal — Type.Ribasim.User — Type.Ribasim.config.Config — Method.Config(config_path::AbstractString; kwargs...)dt from the solver section, use underscores: solver_dt.BasicModelInterface.finalize — Method.
BMI.finalize(model::Model)::ModelWrite all results to the configured files.
- +# BasicModelInterface.initialize — Method.
BMI.initialize(T::Type{Model}, config_path::AbstractString)::ModelInitialize a Model from the path to the TOML configuration file.
# BasicModelInterface.initialize — Method.
BMI.initialize(T::Type{Model}, config::Config)::ModelInitialize a Model from a Config.
# CommonSolve.solve! — Method.
solve!(model::Model)::ODESolutionSolve a Model until the configured endtime.
# Ribasim.add_constraints_absolute_value! — Method.
Minimizing |expr| can be achieved by introducing a new variable exprabs and posing the following constraints: exprabs >= expr expr_abs >= -expr
- +# Ribasim.add_constraints_capacity! — Method.
Add the flow capacity constraints to the allocation problem. Only finite capacities get a constraint. The constraint indices are (edgesourceid, edgedstid).
Constraint: flow over edge <= edge capacity
- +# Ribasim.add_constraints_flow_conservation! — Method.
Add the flow conservation constraints to the allocation problem. The constraint indices are user node IDs.
Constraint: sum(flows out of node node) <= flows into node + flow from storage and vertical fluxes
- +# Ribasim.add_constraints_source! — Method.
Add the source constraints to the allocation problem. The actual threshold values will be set before each allocation solve. The constraint indices are (edgesourceid, edgedstid).
Constraint: flow over source edge <= source flow in subnetwork
- +# Ribasim.add_constraints_user_returnflow! — Method.
Add the user returnflow constraints to the allocation problem. The constraint indices are user node IDs.
Constraint: outflow from user <= return factor * inflow to user
- +# Ribasim.add_flow! — Method.
Add the given flow q to the flow over the edge on the horizontal (self-loop) edge from id to id.
- +# Ribasim.add_flow! — Method.
Add the given flow q to the existing flow over the edge between the given nodes.
- +# Ribasim.add_variables_absolute_value! — Method.
Certain allocation distribution types use absolute values in the objective function. Since most optimization packages do not support the absolute value function directly, New variables are introduced that act as the absolute value of an expression by posing the appropriate constraints.
- +# Ribasim.add_variables_flow! — Method.
Add the flow variables F to the allocation problem. The variable indices are (edgesourceid, edgedstid). Non-negativivity constraints are also immediately added to the flow variables.
- +# Ribasim.adjust_edge_capacities! — Method.
Set the values of the edge capacities. 2 cases:
- Before the first allocation solve, set the edge capacities to their full capacity;
- Before an allocation solve, subtract the flow used by allocation for the previous priority from the edge capacities.
# Ribasim.adjust_source_flows! — Method.
Adjust the source flows.
- +# Ribasim.all_neighbor_labels_type — Method.
Get the in- and outneighbor node IDs of the given node ID (label) over the given edge type in the graph.
- +# Ribasim.allocate! — Method.
Update the allocation optimization problem for the given subnetwork with the problem state and flows, solve the allocation problem and assign the results to the users.
- +# Ribasim.allocation_graph — Method.
Build the graph used for the allocation problem.
- +# Ribasim.allocation_graph_used_nodes! — Method.
Find all nodes in the subnetwork which will be used in the allocation network. Some nodes are skipped to optimize allocation optimization.
- +# Ribasim.allocation_path_exists_in_graph — Method.
Find out whether a path exists between a start node and end node in the given allocation graph.
- +# Ribasim.allocation_problem — Method.
Construct the allocation problem for the current subnetwork as a JuMP.jl model.
- +# Ribasim.allocation_table — Method.
Create an allocation result table for the saved data
- +# Ribasim.assign_allocations! — Method.
Assign the allocations to the users as determined by the solution of the allocation problem.
- +# Ribasim.avoid_using_own_returnflow! — Method.
Remove allocation user return flow edges that are upstream of the user itself.
- +# Ribasim.basin_bottom — Method.
Return the bottom elevation of the basin with index i, or nothing if it doesn’t exist
- +# Ribasim.basin_bottoms — Method.
Get the bottom on both ends of a node. If only one has a bottom, use that for both.
- +# Ribasim.basin_table — Method.
Create the basin result table from the saved data
- +# Ribasim.create_callbacks — Method.
Create the different callbacks that are used to store results and feed the simulation with new data. The different callbacks are combined to a CallbackSet that goes to the integrator. Returns the CallbackSet and the SavedValues for flow.
- +# Ribasim.create_graph — Method.
Return a directed metagraph with data of nodes (NodeMetadata): NodeMetadata
and data of edges (EdgeMetadata): EdgeMetadata
# Ribasim.create_storage_tables — Method.
Read the Basin / profile table and return all area and level and computed storage values
- +# Ribasim.datetime_since — Method.
datetime_since(t::Real, t0::DateTime)::DateTimeConvert a Real that represents the seconds passed since the simulation start to the nearest DateTime. This is used to convert between the solver’s inner float time, and the calendar.
- +# Ribasim.datetimes — Method.
Get all saved times as a Vector{DateTime}
- +# Ribasim.discrete_control_affect! — Method.
Change parameters based on the control logic.
- +# Ribasim.discrete_control_affect_downcrossing! — Method.
An downcrossing means that a condition (always greater than) becomes false.
- +# Ribasim.discrete_control_affect_upcrossing! — Method.
An upcrossing means that a condition (always greater than) becomes true.
- +# Ribasim.discrete_control_condition — Method.
Listens for changes in condition truths.
- +# Ribasim.discrete_control_table — Method.
Create a discrete control result table from the saved data
- +# Ribasim.expand_logic_mapping — Method.
Replace the truth states in the logic mapping which contain wildcards with all possible explicit truth states.
- +# Ribasim.find_allocation_graph_edges! — Method.
This loop finds allocation graph edges in several ways:
- Between allocation graph nodes whose equivalent in the subnetwork are directly connected
- Between allocation graph nodes whose equivalent in the subnetwork are connected with one or more allocation graph nodes in between
# Ribasim.findlastgroup — Method.
For an element id and a vector of elements ids, get the range of indices of the last consecutive block of id. Returns the empty range 1:0 if id is not in ids.
# 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Ribasim.findlastgroup(2, [5,4,2,2,5,2,2,2,1])
# output
6:8# Ribasim.findsorted — Method.
Find the index of element x in a sorted collection a. Returns the index of x if it exists, or nothing if it doesn’t. If x occurs more than once, throw an error.
- +# Ribasim.flow_table — Method.
Create a flow result table from the saved data
- +# Ribasim.formulate_basins! — Method.
Smoothly let the evaporation flux go to 0 when at small water depths Currently at less than 0.1 m.
- +# Ribasim.formulate_flow! — Method.
Directed graph: outflow is positive!
- +# Ribasim.formulate_flow! — Method.
Conservation of energy for two basins, a and b:
h_a + v_a^2 / (2 * g) = h_b + v_b^2 / (2 * g) + S_f * L + C / 2 * g * (v_b^2 - v_a^2)source
+
# Ribasim.formulate_flow! — Method.
Directed graph: outflow is positive!
-
+
# Ribasim.get_area_and_level — Method.
Compute the area and level of a basin given its storage. Also returns darea/dlevel as it is needed for the Jacobian.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_chunk_sizes — Method.
Get the chunk sizes for DiffCache; differentiation w.r.t. u and t (the latter only if a Rosenbrock algorithm is used).
-
+
# Ribasim.get_compressor — Method.
Get the compressor based on the Results section
-
+
# Ribasim.get_flow — Method.
Get the flow over the given horizontal (selfloop) edge (val is needed for get_tmp from ForwardDiff.jl).
-
+
# Ribasim.get_flow — Method.
Get the flow over the given edge (val is needed for get_tmp from ForwardDiff.jl).
-
+
# Ribasim.get_fractional_flow_connected_basins — Method.
Get the node type specific indices of the fractional flows and basins, that are consecutively connected to a node of given id.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_jac_prototype — Method.
Get a sparse matrix whose sparsity matches the sparsity of the Jacobian of the ODE problem. All nodes are taken into consideration, also the ones that are inactive.
In Ribasim the Jacobian is typically sparse because each state only depends on a small number of other states.
Note: the name ‘prototype’ does not mean this code is a prototype, it comes from the naming convention of this sparsity structure in the differentialequations.jl docs.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_level — Method.
Get the current water level of a node ID. The ID can belong to either a Basin or a LevelBoundary. storage: tells ForwardDiff whether this call is for differentiation or not
-
+
# Ribasim.get_scalar_interpolation — Method.
Linear interpolation of a scalar with constant extrapolation.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_storage_from_level — Method.
Get the storage of a basin from its level.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_storages_and_levels — Method.
Get the storage and level of all basins as matrices of nbasin × ntime
-
+
# Ribasim.get_storages_from_levels — Method.
Compute the storages of the basins based on the water level of the basins.
-
+
# Ribasim.get_tstops — Method.
From an iterable of DateTimes, find the times the solver needs to stop
-
+
# Ribasim.get_value — Method.
Get a value for a condition. Currently supports getting levels from basins and flows from flow boundaries.
-
+
# Ribasim.id_index — Method.
Get the index of an ID in a set of indices.
-
+
# Ribasim.indicate_allocation_flow! — Method.
Add to the edge metadata that the given edge is used for allocation flow. If the edge does not exist, it is created.
-
+
# Ribasim.inflow_id — Method.
Get the unique inneighbor over a flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.inflow_ids — Method.
Get the inneighbors over flow edges.
-
+
# Ribasim.inflow_ids_allocation — Method.
Get the inneighbors of the given ID such that the connecting edge is an allocation flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.inneighbor_labels_type — Method.
Get the inneighbor node IDs of the given node ID (label) over the given edge type in the graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.inoutflow_ids — Method.
Get the in- and outneighbors over flow edges.
-
+
# Ribasim.is_allocation_source — Method.
Find out whether the given edge is a source for an allocation network.
-
+
# Ribasim.is_flow_constraining — Method.
Whether the given node node is flow constraining by having a maximum flow rate.
-
+
# Ribasim.is_flow_direction_constraining — Method.
Whether the given node is flow direction constraining (only in direction of edges).
-
+
# Ribasim.load_data — Method.
load_data(db::DB, config::Config, nodetype::Symbol, kind::Symbol)::Union{Table, Query, Nothing}
Load data from Arrow files if available, otherwise the database. Returns either an Arrow.Table, SQLite.Query or nothing if the data is not present.
-
+
# Ribasim.load_structvector — Method.
load_structvector(db::DB, config::Config, ::Type{T})::StructVector{T}
Load data from Arrow files if available, otherwise the database. Always returns a StructVector of the given struct type T, which is empty if the table is not found. This function validates the schema, and enforces the required sort order.
-
+
# Ribasim.metadata_from_edge — Method.
Get the metadata of an edge in the graph from an edge of the underlying DiGraph.
-
+
# Ribasim.nodefields — Method.
Get all node fieldnames of the parameter object.
-
+
# Ribasim.nodetype — Method.
From a SchemaVersion(“ribasim.flowboundary.static”, 1) return (:FlowBoundary, :static)
-
+
# Ribasim.outflow_id — Method.
Get the unique outneighbor over a flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.outflow_ids — Method.
Get the outneighbors over flow edges.
-
+
# Ribasim.outflow_ids_allocation — Method.
Get the outneighbors of the given ID such that the connecting edge is an allocation flow edge.
-
+
# Ribasim.outneighbor_labels_type — Method.
Get the outneighbor node IDs of the given node ID (label) over the given edge type in the graph.
-
+
# Ribasim.parse_static_and_time — Method.
Process the data in the static and time tables for a given node type. The ‘defaults’ named tuple dictates how missing data is filled in. ‘time_interpolatables’ is a vector of Symbols of parameter names for which a time interpolation (linear) object must be constructed. The control mapping for DiscreteControl is also constructed in this function. This function currently does not support node states that are defined by more than one row in a table, as is the case for TabulatedRatingCurve.
-
+
# Ribasim.process_allocation_graph_edges! — Method.
For the composite allocation graph edges:
@@ -705,83 +705,83 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.profile_storage — Method.
Calculate a profile storage by integrating the areas over the levels
-
+
# Ribasim.qh_interpolation — Method.
From a table with columns nodeid, discharge (Q) and level (h), create a LinearInterpolation from level to discharge for a given nodeid.
-
+
# Ribasim.reduction_factor — Method.
Function that goes smoothly from 0 to 1 in the interval [0,threshold], and is constant outside this interval.
-
+
# Ribasim.run — Method.
run(config_file::AbstractString)::Model
run(config::Config)::Model
Run a Model, given a path to a TOML configuration file, or a Config object. Running a model includes initialization, solving to the end with [solve!](@ref) and writing results with BMI.finalize.
-
+
# Ribasim.save_flow — Method.
Copy the current flow to the SavedValues
-
+
# Ribasim.save_subgrid_level — Method.
Interpolate the levels and save them to SavedValues
-
+
# Ribasim.scalar_interpolation_derivative — Method.
Derivative of scalar interpolation.
-
+
# Ribasim.seconds_since — Method.
seconds_since(t::DateTime, t0::DateTime)::Float64
Convert a DateTime to a float that is the number of seconds since the start of the simulation. This is used to convert between the solver’s inner float time, and the calendar.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_current_value! — Method.
From a timeseries table time, load the most recent applicable data into table. table must be a NamedTuple of vectors with all variables that must be loaded. The most recent applicable data is non-NaN data for a given ID that is on or before t.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_flow! — Method.
Set the given flow q on the horizontal (self-loop) edge from id to id.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_flow! — Method.
Set the given flow q over the edge between the given nodes.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_initial_discrete_controlled_parameters! — Method.
Set parameters of nodes that are controlled by DiscreteControl to the values corresponding to the initial state of the model.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_objective_priority! — Method.
Set the objective for the given priority. For an objective with absolute values this also involves adjusting constraints.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_static_value! — Method.
Load data from a source table static into a destination table. Data is matched based on the node_id, which is sorted.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_table_row! — Method.
Update table at row index i, with the values of a given row. table must be a NamedTuple of vectors with all variables that must be loaded. The row must contain all the column names that are present in the table. If a value is NaN, it is not set.
-
+
# Ribasim.sorted_table! — Method.
Depending on if a table can be sorted, either sort it or assert that it is sorted.
Tables loaded from the database into memory can be sorted. Tables loaded from Arrow files are memory mapped and can therefore not be sorted.
-
+
# Ribasim.timesteps — Method.
Get all saved times in seconds since start
-
+
# Ribasim.update_allocation! — Method.
Solve the allocation problem for all users and assign allocated abstractions to user nodes.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_basin — Method.
Load updates from ‘Basin / time’ into the parameters
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
Method for nodes that do not contribute to the Jacobian
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
The controlled basin affects itself and the basins upstream and downstream of the controlled pump affect eachother if there is a basin upstream of the pump. The state for the integral term and the controlled basin affect eachother, and the same for the integral state and the basin upstream of the pump if it is indeed a basin.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
If both the unique node upstream and the unique node downstream of these nodes are basins, then these directly depend on eachother and affect the Jacobian 2x Basins always depend on themselves.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
If both the unique node upstream and the nodes down stream (or one node further if a fractional flow is in between) are basins, then the downstream basin depends on the upstream basin(s) and affect the Jacobian as many times as there are downstream basins Upstream basins always depend on themselves.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_tabulated_rating_curve! — Method.
Load updates from ‘TabulatedRatingCurve / time’ into the parameters
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_discrete_control — Method.
Check:
@@ -789,50 +789,50 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.valid_edge_types — Method.
Check that only supported edge types are declared.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_edges — Method.
Test for each node given its node type whether the nodes that
are downstream (‘down-edge’) of this node are of an allowed type
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_flow_rates — Method.
Test whether static or discrete controlled flow rates are indeed non-negative.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_fractional_flow — Method.
Check that nodes that have fractional flow outneighbors do not have any other type of outneighbor, that the fractions leaving a node add up to ≈1 and that the fractions are non-negative.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_n_neighbors — Method.
Test for each node given its node type whether it has an allowed number of flow/control inneighbors and outneighbors
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_profiles — Method.
Check whether the profile data has no repeats in the levels and the areas start positive.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_sources — Method.
The source nodes must only have one allocation outneighbor and no allocation inneighbors.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_subgrid — Method.
Validate the entries for a single subgrid element.
-
+
# Ribasim.water_balance! — Method.
The right hand side function of the system of ODEs set up by Ribasim.
-
+
# Ribasim.write_arrow — Method.
Write a result table to disk as an Arrow file
-
+
# Ribasim.config.algorithm — Method.
Create an OrdinaryDiffEqAlgorithm from solver config
-
+
# Ribasim.config.input_path — Method.
Construct a path relative to both the TOML directory and the optional input_dir
-
+
# Ribasim.config.results_path — Method.
Construct a path relative to both the TOML directory and the optional results_dir
-
+
# Ribasim.config.snake_case — Method.
Convert a string from CamelCase to snake_case.
-
+
@@ -853,7 +853,7 @@ source
+
@@ -861,10 +861,10 @@ 1.5 Macros
# Ribasim.config.@addfields — Macro.
Add fieldnames with Union{String, Nothing} type to struct expression. Requires (option?) use before it.
-
+
# Ribasim.config.@addnodetypes — Macro.
Add all TableOption subtypes as fields to struct expression. Requires (option?) use before it.
-
+
@@ -898,8 +898,8 @@ Ribasim.User
Ribasim.config.ConfigBasicModelInterface.finalizeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeCommonSolve.solve!Ribasim.add_constraints_absolute_value!Ribasim.add_constraints_capacity!Ribasim.scalar_interpolation_derivative
Ribasim.seconds_sinceRibasim.set_current_value!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_initial_discrete_controlled_parameters!Ribasim.set_objective_priority!Ribasim.set_static_value!Ribasim.timesteps
Ribasim.update_allocation!Ribasim.update_basinRibasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_tabulated_rating_curve!Ribasim.valid_discrete_controlRibasim.valid_edge_types2 Update the basi
ax = df_flow.pivot_table(index="time", columns="edge", values="flow_m3d").plot()
ax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title="Edge")
-<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f1a7c921550>
+<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f7014656f50>

@@ -1021,7 +1021,7 @@ 4 Model with PID
<Axes: >
-
+
Write the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:
diff --git a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png
index 33e8abbcf..f5f6a2b5b 100644
Binary files a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png and b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png differ
diff --git a/qgis/index.html b/qgis/index.html
index 0980ee3b0..df224853e 100644
--- a/qgis/index.html
+++ b/qgis/index.html
@@ -20,40 +20,6 @@
margin: 0 0.8em 0.2em -1em; /* quarto-specific, see https://github.com/quarto-dev/quarto-cli/issues/4556 */
vertical-align: middle;
}
-/* CSS for syntax highlighting */
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre; position: relative; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { display: inline-block; line-height: 1.25; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span:empty { height: 1.2em; }
-.sourceCode { overflow: visible; }
-code.sourceCode > span { color: inherit; text-decoration: inherit; }
-div.sourceCode { margin: 1em 0; }
-pre.sourceCode { margin: 0; }
-@media screen {
-div.sourceCode { overflow: auto; }
-}
-@media print {
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre-wrap; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { text-indent: -5em; padding-left: 5em; }
-}
-pre.numberSource code
- { counter-reset: source-line 0; }
-pre.numberSource code > span
- { position: relative; left: -4em; counter-increment: source-line; }
-pre.numberSource code > span > a:first-child::before
- { content: counter(source-line);
- position: relative; left: -1em; text-align: right; vertical-align: baseline;
- border: none; display: inline-block;
- -webkit-touch-callout: none; -webkit-user-select: none;
- -khtml-user-select: none; -moz-user-select: none;
- -ms-user-select: none; user-select: none;
- padding: 0 4px; width: 4em;
- }
-pre.numberSource { margin-left: 3em; padding-left: 4px; }
-div.sourceCode
- { }
-@media screen {
-pre > code.sourceCode > span > a:first-child::before { text-decoration: underline; }
-}
@@ -180,11 +146,7 @@ On this page
- 1.3.2 Create connecting edges
- 1.4 Run a model
- - 1.5 Inspect results
-
+ - 1.5 Inspect results
Ribasim.formulate_flow! — Method.Ribasim.get_area_and_level — Method.Ribasim.get_chunk_sizes — Method.Ribasim.get_compressor — Method.Ribasim.get_flow — Method.Ribasim.get_flow — Method.Ribasim.get_fractional_flow_connected_basins — Method.Ribasim.get_jac_prototype — Method.Ribasim.get_level — Method.Ribasim.get_scalar_interpolation — Method.Ribasim.get_storage_from_level — Method.Ribasim.get_storages_and_levels — Method.Ribasim.get_storages_from_levels — Method.Ribasim.get_tstops — Method.Ribasim.get_value — Method.Ribasim.id_index — Method.Ribasim.indicate_allocation_flow! — Method.Ribasim.inflow_id — Method.Ribasim.inflow_ids — Method.Ribasim.inflow_ids_allocation — Method.Ribasim.inneighbor_labels_type — Method.Ribasim.inoutflow_ids — Method.Ribasim.is_allocation_source — Method.Ribasim.is_flow_constraining — Method.Ribasim.is_flow_direction_constraining — Method.Ribasim.load_data — Method.load_data(db::DB, config::Config, nodetype::Symbol, kind::Symbol)::Union{Table, Query, Nothing}Arrow.Table, SQLite.Query or nothing if the data is not present.Ribasim.load_structvector — Method.load_structvector(db::DB, config::Config, ::Type{T})::StructVector{T}Ribasim.metadata_from_edge — Method.Ribasim.nodefields — Method.Ribasim.nodetype — Method.Ribasim.outflow_id — Method.Ribasim.outflow_ids — Method.Ribasim.outflow_ids_allocation — Method.Ribasim.outneighbor_labels_type — Method.Ribasim.parse_static_and_time — Method.Ribasim.process_allocation_graph_edges! — Method.source
+
# Ribasim.profile_storage — Method.
Calculate a profile storage by integrating the areas over the levels
-
+
# Ribasim.qh_interpolation — Method.
From a table with columns nodeid, discharge (Q) and level (h), create a LinearInterpolation from level to discharge for a given nodeid.
-
+
# Ribasim.reduction_factor — Method.
Function that goes smoothly from 0 to 1 in the interval [0,threshold], and is constant outside this interval.
-
+
# Ribasim.run — Method.
run(config_file::AbstractString)::Model
run(config::Config)::Model
Run a Model, given a path to a TOML configuration file, or a Config object. Running a model includes initialization, solving to the end with [solve!](@ref) and writing results with BMI.finalize.
-
+
# Ribasim.save_flow — Method.
Copy the current flow to the SavedValues
-
+
# Ribasim.save_subgrid_level — Method.
Interpolate the levels and save them to SavedValues
-
+
# Ribasim.scalar_interpolation_derivative — Method.
Derivative of scalar interpolation.
-
+
# Ribasim.seconds_since — Method.
seconds_since(t::DateTime, t0::DateTime)::Float64
Convert a DateTime to a float that is the number of seconds since the start of the simulation. This is used to convert between the solver’s inner float time, and the calendar.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_current_value! — Method.
From a timeseries table time, load the most recent applicable data into table. table must be a NamedTuple of vectors with all variables that must be loaded. The most recent applicable data is non-NaN data for a given ID that is on or before t.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_flow! — Method.
Set the given flow q on the horizontal (self-loop) edge from id to id.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_flow! — Method.
Set the given flow q over the edge between the given nodes.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_initial_discrete_controlled_parameters! — Method.
Set parameters of nodes that are controlled by DiscreteControl to the values corresponding to the initial state of the model.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_objective_priority! — Method.
Set the objective for the given priority. For an objective with absolute values this also involves adjusting constraints.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_static_value! — Method.
Load data from a source table static into a destination table. Data is matched based on the node_id, which is sorted.
-
+
# Ribasim.set_table_row! — Method.
Update table at row index i, with the values of a given row. table must be a NamedTuple of vectors with all variables that must be loaded. The row must contain all the column names that are present in the table. If a value is NaN, it is not set.
-
+
# Ribasim.sorted_table! — Method.
Depending on if a table can be sorted, either sort it or assert that it is sorted.
Tables loaded from the database into memory can be sorted. Tables loaded from Arrow files are memory mapped and can therefore not be sorted.
-
+
# Ribasim.timesteps — Method.
Get all saved times in seconds since start
-
+
# Ribasim.update_allocation! — Method.
Solve the allocation problem for all users and assign allocated abstractions to user nodes.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_basin — Method.
Load updates from ‘Basin / time’ into the parameters
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
Method for nodes that do not contribute to the Jacobian
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
The controlled basin affects itself and the basins upstream and downstream of the controlled pump affect eachother if there is a basin upstream of the pump. The state for the integral term and the controlled basin affect eachother, and the same for the integral state and the basin upstream of the pump if it is indeed a basin.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
If both the unique node upstream and the unique node downstream of these nodes are basins, then these directly depend on eachother and affect the Jacobian 2x Basins always depend on themselves.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.
If both the unique node upstream and the nodes down stream (or one node further if a fractional flow is in between) are basins, then the downstream basin depends on the upstream basin(s) and affect the Jacobian as many times as there are downstream basins Upstream basins always depend on themselves.
-
+
# Ribasim.update_tabulated_rating_curve! — Method.
Load updates from ‘TabulatedRatingCurve / time’ into the parameters
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_discrete_control — Method.
Check:
@@ -789,50 +789,50 @@ source
+
# Ribasim.valid_edge_types — Method.
Check that only supported edge types are declared.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_edges — Method.
Test for each node given its node type whether the nodes that
are downstream (‘down-edge’) of this node are of an allowed type
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_flow_rates — Method.
Test whether static or discrete controlled flow rates are indeed non-negative.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_fractional_flow — Method.
Check that nodes that have fractional flow outneighbors do not have any other type of outneighbor, that the fractions leaving a node add up to ≈1 and that the fractions are non-negative.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_n_neighbors — Method.
Test for each node given its node type whether it has an allowed number of flow/control inneighbors and outneighbors
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_profiles — Method.
Check whether the profile data has no repeats in the levels and the areas start positive.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_sources — Method.
The source nodes must only have one allocation outneighbor and no allocation inneighbors.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_subgrid — Method.
Validate the entries for a single subgrid element.
-
+
# Ribasim.water_balance! — Method.
The right hand side function of the system of ODEs set up by Ribasim.
-
+
# Ribasim.write_arrow — Method.
Write a result table to disk as an Arrow file
-
+
# Ribasim.config.algorithm — Method.
Create an OrdinaryDiffEqAlgorithm from solver config
-
+
# Ribasim.config.input_path — Method.
Construct a path relative to both the TOML directory and the optional input_dir
-
+
# Ribasim.config.results_path — Method.
Construct a path relative to both the TOML directory and the optional results_dir
-
+
# Ribasim.config.snake_case — Method.
Convert a string from CamelCase to snake_case.
-
+
@@ -853,7 +853,7 @@ source
+
@@ -861,10 +861,10 @@ 1.5 Macros
# Ribasim.config.@addfields — Macro.
Add fieldnames with Union{String, Nothing} type to struct expression. Requires (option?) use before it.
-
+
# Ribasim.config.@addnodetypes — Macro.
Add all TableOption subtypes as fields to struct expression. Requires (option?) use before it.
-
+
@@ -898,8 +898,8 @@ Ribasim.User
Ribasim.config.ConfigBasicModelInterface.finalizeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeCommonSolve.solve!Ribasim.add_constraints_absolute_value!Ribasim.add_constraints_capacity!Ribasim.scalar_interpolation_derivative
Ribasim.seconds_sinceRibasim.set_current_value!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_initial_discrete_controlled_parameters!Ribasim.set_objective_priority!Ribasim.set_static_value!Ribasim.timesteps
Ribasim.update_allocation!Ribasim.update_basinRibasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_tabulated_rating_curve!Ribasim.valid_discrete_controlRibasim.valid_edge_types2 Update the basi
ax = df_flow.pivot_table(index="time", columns="edge", values="flow_m3d").plot()
ax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title="Edge")
-<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f1a7c921550>
+<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f7014656f50>

@@ -1021,7 +1021,7 @@ 4 Model with PID
<Axes: >
-
+
Write the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:
diff --git a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png
index 33e8abbcf..f5f6a2b5b 100644
Binary files a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png and b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png differ
diff --git a/qgis/index.html b/qgis/index.html
index 0980ee3b0..df224853e 100644
--- a/qgis/index.html
+++ b/qgis/index.html
@@ -20,40 +20,6 @@
margin: 0 0.8em 0.2em -1em; /* quarto-specific, see https://github.com/quarto-dev/quarto-cli/issues/4556 */
vertical-align: middle;
}
-/* CSS for syntax highlighting */
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre; position: relative; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { display: inline-block; line-height: 1.25; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span:empty { height: 1.2em; }
-.sourceCode { overflow: visible; }
-code.sourceCode > span { color: inherit; text-decoration: inherit; }
-div.sourceCode { margin: 1em 0; }
-pre.sourceCode { margin: 0; }
-@media screen {
-div.sourceCode { overflow: auto; }
-}
-@media print {
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre-wrap; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { text-indent: -5em; padding-left: 5em; }
-}
-pre.numberSource code
- { counter-reset: source-line 0; }
-pre.numberSource code > span
- { position: relative; left: -4em; counter-increment: source-line; }
-pre.numberSource code > span > a:first-child::before
- { content: counter(source-line);
- position: relative; left: -1em; text-align: right; vertical-align: baseline;
- border: none; display: inline-block;
- -webkit-touch-callout: none; -webkit-user-select: none;
- -khtml-user-select: none; -moz-user-select: none;
- -ms-user-select: none; user-select: none;
- padding: 0 4px; width: 4em;
- }
-pre.numberSource { margin-left: 3em; padding-left: 4px; }
-div.sourceCode
- { }
-@media screen {
-pre > code.sourceCode > span > a:first-child::before { text-decoration: underline; }
-}
@@ -180,11 +146,7 @@ On this page
- 1.3.2 Create connecting edges
- 1.4 Run a model
- - 1.5 Inspect results
-
+ - 1.5 Inspect results
Ribasim.profile_storage — Method.Ribasim.qh_interpolation — Method.Ribasim.reduction_factor — Method.Ribasim.run — Method.run(config_file::AbstractString)::Model
run(config::Config)::ModelModel, given a path to a TOML configuration file, or a Config object. Running a model includes initialization, solving to the end with [solve!](@ref) and writing results with BMI.finalize.Ribasim.save_flow — Method.Ribasim.save_subgrid_level — Method.Ribasim.scalar_interpolation_derivative — Method.Ribasim.seconds_since — Method.seconds_since(t::DateTime, t0::DateTime)::Float64Ribasim.set_current_value! — Method.time, load the most recent applicable data into table. table must be a NamedTuple of vectors with all variables that must be loaded. The most recent applicable data is non-NaN data for a given ID that is on or before t.Ribasim.set_flow! — Method.Ribasim.set_flow! — Method.Ribasim.set_initial_discrete_controlled_parameters! — Method.Ribasim.set_objective_priority! — Method.Ribasim.set_static_value! — Method.static into a destination table. Data is matched based on the node_id, which is sorted.Ribasim.set_table_row! — Method.table at row index i, with the values of a given row. table must be a NamedTuple of vectors with all variables that must be loaded. The row must contain all the column names that are present in the table. If a value is NaN, it is not set.Ribasim.sorted_table! — Method.Ribasim.timesteps — Method.Ribasim.update_allocation! — Method.Ribasim.update_basin — Method.Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.Ribasim.update_jac_prototype! — Method.Ribasim.update_tabulated_rating_curve! — Method.Ribasim.valid_discrete_control — Method.source
+
# Ribasim.valid_edge_types — Method.
Check that only supported edge types are declared.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_edges — Method.
Test for each node given its node type whether the nodes that
are downstream (‘down-edge’) of this node are of an allowed type
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_flow_rates — Method.
Test whether static or discrete controlled flow rates are indeed non-negative.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_fractional_flow — Method.
Check that nodes that have fractional flow outneighbors do not have any other type of outneighbor, that the fractions leaving a node add up to ≈1 and that the fractions are non-negative.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_n_neighbors — Method.
Test for each node given its node type whether it has an allowed number of flow/control inneighbors and outneighbors
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_profiles — Method.
Check whether the profile data has no repeats in the levels and the areas start positive.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_sources — Method.
The source nodes must only have one allocation outneighbor and no allocation inneighbors.
-
+
# Ribasim.valid_subgrid — Method.
Validate the entries for a single subgrid element.
-
+
# Ribasim.water_balance! — Method.
The right hand side function of the system of ODEs set up by Ribasim.
-
+
# Ribasim.write_arrow — Method.
Write a result table to disk as an Arrow file
-
+
# Ribasim.config.algorithm — Method.
Create an OrdinaryDiffEqAlgorithm from solver config
-
+
# Ribasim.config.input_path — Method.
Construct a path relative to both the TOML directory and the optional input_dir
-
+
# Ribasim.config.results_path — Method.
Construct a path relative to both the TOML directory and the optional results_dir
-
+
# Ribasim.config.snake_case — Method.
Convert a string from CamelCase to snake_case.
-
+
@@ -853,7 +853,7 @@ source
+
@@ -861,10 +861,10 @@ 1.5 Macros
# Ribasim.config.@addfields — Macro.
Add fieldnames with Union{String, Nothing} type to struct expression. Requires (option?) use before it.
-
+
# Ribasim.config.@addnodetypes — Macro.
Add all TableOption subtypes as fields to struct expression. Requires (option?) use before it.
-
+
@@ -898,8 +898,8 @@ Ribasim.User
Ribasim.config.ConfigBasicModelInterface.finalizeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeCommonSolve.solve!Ribasim.add_constraints_absolute_value!Ribasim.add_constraints_capacity!Ribasim.scalar_interpolation_derivative
Ribasim.seconds_sinceRibasim.set_current_value!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_initial_discrete_controlled_parameters!Ribasim.set_objective_priority!Ribasim.set_static_value!Ribasim.timesteps
Ribasim.update_allocation!Ribasim.update_basinRibasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_tabulated_rating_curve!Ribasim.valid_discrete_controlRibasim.valid_edge_types2 Update the basi
ax = df_flow.pivot_table(index="time", columns="edge", values="flow_m3d").plot()
ax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title="Edge")
-<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f1a7c921550>
+<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f7014656f50>

@@ -1021,7 +1021,7 @@ 4 Model with PID
<Axes: >
-
+
Write the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:
diff --git a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png
index 33e8abbcf..f5f6a2b5b 100644
Binary files a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png and b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png differ
diff --git a/qgis/index.html b/qgis/index.html
index 0980ee3b0..df224853e 100644
--- a/qgis/index.html
+++ b/qgis/index.html
@@ -20,40 +20,6 @@
margin: 0 0.8em 0.2em -1em; /* quarto-specific, see https://github.com/quarto-dev/quarto-cli/issues/4556 */
vertical-align: middle;
}
-/* CSS for syntax highlighting */
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre; position: relative; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { display: inline-block; line-height: 1.25; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span:empty { height: 1.2em; }
-.sourceCode { overflow: visible; }
-code.sourceCode > span { color: inherit; text-decoration: inherit; }
-div.sourceCode { margin: 1em 0; }
-pre.sourceCode { margin: 0; }
-@media screen {
-div.sourceCode { overflow: auto; }
-}
-@media print {
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre-wrap; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { text-indent: -5em; padding-left: 5em; }
-}
-pre.numberSource code
- { counter-reset: source-line 0; }
-pre.numberSource code > span
- { position: relative; left: -4em; counter-increment: source-line; }
-pre.numberSource code > span > a:first-child::before
- { content: counter(source-line);
- position: relative; left: -1em; text-align: right; vertical-align: baseline;
- border: none; display: inline-block;
- -webkit-touch-callout: none; -webkit-user-select: none;
- -khtml-user-select: none; -moz-user-select: none;
- -ms-user-select: none; user-select: none;
- padding: 0 4px; width: 4em;
- }
-pre.numberSource { margin-left: 3em; padding-left: 4px; }
-div.sourceCode
- { }
-@media screen {
-pre > code.sourceCode > span > a:first-child::before { text-decoration: underline; }
-}
@@ -180,11 +146,7 @@ On this page
- 1.3.2 Create connecting edges
Ribasim.valid_edge_types — Method.Ribasim.valid_edges — Method.Ribasim.valid_flow_rates — Method.Ribasim.valid_fractional_flow — Method.Ribasim.valid_n_neighbors — Method.Ribasim.valid_profiles — Method.Ribasim.valid_sources — Method.Ribasim.valid_subgrid — Method.Ribasim.water_balance! — Method.Ribasim.write_arrow — Method.Ribasim.config.algorithm — Method.Ribasim.config.input_path — Method.input_dirRibasim.config.results_path — Method.results_dirRibasim.config.snake_case — Method.+ @@ -861,10 +861,10 @@
1.5 Macros
# Ribasim.config.@addfields — Macro.
Add fieldnames with Union{String, Nothing} type to struct expression. Requires (option?) use before it.
- +# Ribasim.config.@addnodetypes — Macro.
Add all TableOption subtypes as fields to struct expression. Requires (option?) use before it.
- + @@ -898,8 +898,8 @@Ribasim.User
Ribasim.config.ConfigBasicModelInterface.finalizeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeCommonSolve.solve!Ribasim.add_constraints_absolute_value!Ribasim.add_constraints_capacity!Ribasim.scalar_interpolation_derivative
Ribasim.seconds_sinceRibasim.set_current_value!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_initial_discrete_controlled_parameters!Ribasim.set_objective_priority!Ribasim.set_static_value!Ribasim.timesteps
Ribasim.update_allocation!Ribasim.update_basinRibasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_tabulated_rating_curve!Ribasim.valid_discrete_controlRibasim.valid_edge_types2 Update the basi
ax = df_flow.pivot_table(index="time", columns="edge", values="flow_m3d").plot()
ax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title="Edge")
-<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f1a7c921550>
+<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f7014656f50>

@@ -1021,7 +1021,7 @@ 4 Model with PID
<Axes: >
-
+
Write the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:
diff --git a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png
index 33e8abbcf..f5f6a2b5b 100644
Binary files a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png and b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png differ
diff --git a/qgis/index.html b/qgis/index.html
index 0980ee3b0..df224853e 100644
--- a/qgis/index.html
+++ b/qgis/index.html
@@ -20,40 +20,6 @@
margin: 0 0.8em 0.2em -1em; /* quarto-specific, see https://github.com/quarto-dev/quarto-cli/issues/4556 */
vertical-align: middle;
}
-/* CSS for syntax highlighting */
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre; position: relative; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { display: inline-block; line-height: 1.25; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span:empty { height: 1.2em; }
-.sourceCode { overflow: visible; }
-code.sourceCode > span { color: inherit; text-decoration: inherit; }
-div.sourceCode { margin: 1em 0; }
-pre.sourceCode { margin: 0; }
-@media screen {
-div.sourceCode { overflow: auto; }
-}
-@media print {
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre-wrap; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { text-indent: -5em; padding-left: 5em; }
-}
-pre.numberSource code
- { counter-reset: source-line 0; }
-pre.numberSource code > span
- { position: relative; left: -4em; counter-increment: source-line; }
-pre.numberSource code > span > a:first-child::before
- { content: counter(source-line);
- position: relative; left: -1em; text-align: right; vertical-align: baseline;
- border: none; display: inline-block;
- -webkit-touch-callout: none; -webkit-user-select: none;
- -khtml-user-select: none; -moz-user-select: none;
- -ms-user-select: none; user-select: none;
- padding: 0 4px; width: 4em;
- }
-pre.numberSource { margin-left: 3em; padding-left: 4px; }
-div.sourceCode
- { }
-@media screen {
-pre > code.sourceCode > span > a:first-child::before { text-decoration: underline; }
-}
@@ -180,11 +146,7 @@ On this page
- 1.3.2 Create connecting edges
Ribasim.config.ConfigBasicModelInterface.finalizeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeBasicModelInterface.initializeCommonSolve.solve!Ribasim.add_constraints_absolute_value!Ribasim.add_constraints_capacity!Ribasim.scalar_interpolation_derivative
Ribasim.seconds_sinceRibasim.set_current_value!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_flow!Ribasim.set_initial_discrete_controlled_parameters!Ribasim.set_objective_priority!Ribasim.set_static_value!Ribasim.timesteps
Ribasim.update_allocation!Ribasim.update_basinRibasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_tabulated_rating_curve!Ribasim.valid_discrete_controlRibasim.valid_edge_types2 Update the basi
ax = df_flow.pivot_table(index="time", columns="edge", values="flow_m3d").plot()
ax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title="Edge")
-<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f1a7c921550>
+<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f7014656f50>

@@ -1021,7 +1021,7 @@ 4 Model with PID
<Axes: >
-
+
Write the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:
diff --git a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png
index 33e8abbcf..f5f6a2b5b 100644
Binary files a/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png and b/python/examples_files/figure-html/cell-52-output-2.png differ
diff --git a/qgis/index.html b/qgis/index.html
index 0980ee3b0..df224853e 100644
--- a/qgis/index.html
+++ b/qgis/index.html
@@ -20,40 +20,6 @@
margin: 0 0.8em 0.2em -1em; /* quarto-specific, see https://github.com/quarto-dev/quarto-cli/issues/4556 */
vertical-align: middle;
}
-/* CSS for syntax highlighting */
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre; position: relative; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { display: inline-block; line-height: 1.25; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span:empty { height: 1.2em; }
-.sourceCode { overflow: visible; }
-code.sourceCode > span { color: inherit; text-decoration: inherit; }
-div.sourceCode { margin: 1em 0; }
-pre.sourceCode { margin: 0; }
-@media screen {
-div.sourceCode { overflow: auto; }
-}
-@media print {
-pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre-wrap; }
-pre > code.sourceCode > span { text-indent: -5em; padding-left: 5em; }
-}
-pre.numberSource code
- { counter-reset: source-line 0; }
-pre.numberSource code > span
- { position: relative; left: -4em; counter-increment: source-line; }
-pre.numberSource code > span > a:first-child::before
- { content: counter(source-line);
- position: relative; left: -1em; text-align: right; vertical-align: baseline;
- border: none; display: inline-block;
- -webkit-touch-callout: none; -webkit-user-select: none;
- -khtml-user-select: none; -moz-user-select: none;
- -ms-user-select: none; user-select: none;
- padding: 0 4px; width: 4em;
- }
-pre.numberSource { margin-left: 3em; padding-left: 4px; }
-div.sourceCode
- { }
-@media screen {
-pre > code.sourceCode > span > a:first-child::before { text-decoration: underline; }
-}
@@ -180,11 +146,7 @@ On this page
- 1.3.2 Create connecting edges
Ribasim.update_allocation!Ribasim.update_basinRibasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_jac_prototype!Ribasim.update_tabulated_rating_curve!Ribasim.valid_discrete_controlRibasim.valid_edge_types<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f1a7c921550><matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f7014656f50>
4 Model with PID
<Axes: >
<Axes: >

1.4 Run a model
-
-
- Open a text editor and create an empty file next to your database, with the
.tomlextension.
- - Add the following content to the TOML file: -
ribasim.toml-
starttime = 2020-01-01 00:00:00
-endtime = 2021-01-01 00:00:00
-database = "database.gpkg"- Unzip the Ribasim command line interface,
ribasim_cli.zip - Open your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run
path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to theribasim_clifolder to where you placed it. This runs the model. - In your model directory there is now a
results/folder withbasin.arrowandflow.arrowoutput files.
@@ -381,43 +331,21 @@
1.5 Inspect results
-
-1.5.1 Associate results to iMOD time series window
-In QGIS select the model group.
-
-
-
-
-
-In the Ribasim plugin widget, select the Results tab and click “Associate Results”.
-
-
-
-
-
-Select results/basin.arrow.
-
-
-
-
-
-This adds metadata to the model that the iMOD plugin can use to find the timeseries data that is associated to the model nodes.
-
-
-1.5.2 Plot time series
+Before trying to inspect the results, verify that the run was successful and the output files are there.
Click the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.

+Select the layer that you wish to plot. From the “Node” layer you can plot level or storage on Basin nodes. From the “Edge” layer you can plot flow over flow edges. Note that before switching between these, you typically have to click “Clear” to clear the selection. If you run a simulation with the model open in QGIS, you have to close and re-open the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel for the new results to be loaded.
Select the variables that you want to plot.

-Click “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes. Currently only the Basin nodes can be plotted.
+Click “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes.

@@ -429,9 +357,9 @@ 
+Only the “basin.arrow” and “flow.arrow” can be inspected with the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel. All Arrow files can be loaded as a layer by dragging the files onto QGIS. Right click the layer and select “Open Attribute Table” to view the contents.
-
diff --git a/search.json b/search.json
index 4fab5eb10..635269b00 100644
--- a/search.json
+++ b/search.json
@@ -396,14 +396,14 @@
"href": "python/examples.html",
"title": "Examples",
"section": "",
- "text": "1 Basic model with static forcing\n\nfrom pathlib import Path\n\nimport geopandas as gpd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1, 3, 3, 6, 6, 9, 9],\n \"area\": [0.01, 1000.0] * 4,\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0] * 4,\n }\n)\n\n# Convert steady forcing to m/s\n# 2 mm/d precipitation, 1 mm/d evaporation\nseconds_in_day = 24 * 3600\nprecipitation = 0.002 / seconds_in_day\nevaporation = 0.001 / seconds_in_day\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [0],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [evaporation],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [precipitation],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\nstatic = static.iloc[[0, 0, 0, 0]]\nstatic[\"node_id\"] = [1, 3, 6, 9]\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static)\n\nSetup linear resistance:\n\nlinear_resistance = ribasim.LinearResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [10, 12], \"resistance\": [5e3, (3600.0 * 24) / 100.0]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup Manning resistance:\n\nmanning_resistance = ribasim.ManningResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"length\": [900.0],\n \"manning_n\": [0.04],\n \"profile_width\": [6.0],\n \"profile_slope\": [3.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up a rating curve node:\n\n# Discharge: lose 1% of storage volume per day at storage = 1000.0.\nq1000 = 1000.0 * 0.01 / seconds_in_day\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4, 4],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n \"discharge\": [0.0, q1000],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup fractional flows:\n\nfractional_flow = ribasim.FractionalFlow(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [5, 8, 13],\n \"fraction\": [0.3, 0.6, 0.1],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [7],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.5 / 3600],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [11, 17],\n \"level\": [0.5, 1.5],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [15, 16],\n \"flow_rate\": [1e-4, 1e-4],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [14],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin,\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: ManningResistance\n (2.0, 0.0), # 3: Basin\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (3.0, 1.0), # 5: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, 2.0), # 6: Basin\n (4.0, 1.0), # 7: Pump\n (4.0, 0.0), # 8: FractionalFlow\n (5.0, 0.0), # 9: Basin\n (6.0, 0.0), # 10: LinearResistance\n (2.0, 2.0), # 11: LevelBoundary\n (2.0, 1.0), # 12: LinearResistance\n (3.0, -1.0), # 13: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, -2.0), # 14: Terminal\n (3.0, 3.0), # 15: FlowBoundary\n (0.0, 1.0), # 16: FlowBoundary\n (6.0, 1.0), # 17: LevelBoundary\n ]\n)\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_id, node_type = ribasim.Node.node_ids_and_types(\n basin,\n manning_resistance,\n rating_curve,\n pump,\n fractional_flow,\n linear_resistance,\n level_boundary,\n flow_boundary,\n terminal,\n)\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(node_id, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array(\n [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 8, 7, 9, 11, 12, 4, 13, 15, 16, 10], dtype=np.int64\n)\nto_id = np.array(\n [2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 6, 7, 9, 9, 10, 12, 3, 13, 14, 6, 1, 17], dtype=np.int64\n)\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": len(from_id) * [\"flow\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n linear_resistance=linear_resistance,\n manning_resistance=manning_resistance,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n fractional_flow=fractional_flow,\n terminal=terminal,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic/ribasim.toml')\n\n\n\n\n2 Update the basic model with transient forcing\nThis assumes you have already created the basic model with static forcing.\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\nimport xarray as xr\n\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(filepath=datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\n\ntime = pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime)\nday_of_year = time.day_of_year.to_numpy()\nseconds_per_day = 24 * 60 * 60\nevaporation = (\n (-1.0 * np.cos(day_of_year / 365.0 * 2 * np.pi) + 1.0) * 0.0025 / seconds_per_day\n)\nrng = np.random.default_rng(seed=0)\nprecipitation = (\n rng.lognormal(mean=-1.0, sigma=1.7, size=time.size) * 0.001 / seconds_per_day\n)\n\nWe’ll use xarray to easily broadcast the values.\n\ntimeseries = (\n pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 1,\n \"time\": pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime),\n \"drainage\": 0.0,\n \"potential_evaporation\": evaporation,\n \"infiltration\": 0.0,\n \"precipitation\": precipitation,\n \"urban_runoff\": 0.0,\n }\n )\n .set_index(\"time\")\n .to_xarray()\n)\n\nbasin_ids = model.basin.static.df[\"node_id\"].to_numpy()\nbasin_nodes = xr.DataArray(\n np.ones(len(basin_ids)), coords={\"node_id\": basin_ids}, dims=[\"node_id\"]\n)\nforcing = (timeseries * basin_nodes).to_dataframe().reset_index()\n\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": basin_ids,\n \"level\": 1.4,\n \"concentration\": 0.0,\n }\n)\n\n\nmodel.basin.time.df = forcing\nmodel.basin.state.df = state\n\n\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic_transient/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic_transient/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim basic-transient/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\ndf_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\n<Axes: xlabel='time'>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ndf_flow = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/flow.arrow\")\ndf_flow[\"edge\"] = list(zip(df_flow.from_node_id, df_flow.to_node_id))\ndf_flow[\"flow_m3d\"] = df_flow.flow * 86400\nax = df_flow.pivot_table(index=\"time\", columns=\"edge\", values=\"flow_m3d\").plot()\nax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title=\"Edge\")\n\n<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f1a7c921550>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ntype(df_flow)\n\npandas.core.frame.DataFrame\n\n\n\n\n3 Model with discrete control\nThe model constructed below consists of a single basin which slowly drains trough a TabulatedRatingCurve, but is held within a range around a target level (setpoint) by two connected pumps. These two pumps behave like a reversible pump. When pumping can be done in only one direction, and the other direction is only possible under gravity, use an Outlet for that direction.\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin\n (1.0, 1.0), # 2: Pump\n (1.0, -1.0), # 3: Pump\n (2.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (-1.0, 0.0), # 5: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (-2.0, 0.0), # 6: Terminal\n (1.0, 0.0), # 7: DiscreteControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"TabulatedRatingCurve\",\n \"Terminal\",\n \"DiscreteControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 7, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 6, 2, 3], dtype=np.int64)\n\nedge_type = 6 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"]\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"from_node_id\": from_id, \"to_node_id\": to_id, \"edge_type\": edge_type},\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1],\n \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n }\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"level\": [20.0]})\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the discrete control:\n\ncondition = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [7],\n \"listen_feature_id\": 3 * [1],\n \"variable\": 3 * [\"level\"],\n \"greater_than\": [5.0, 10.0, 15.0], # min, setpoint, max\n }\n)\n\nlogic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 5 * [7],\n \"truth_state\": [\"FFF\", \"U**\", \"T*F\", \"**D\", \"TTT\"],\n \"control_state\": [\"in\", \"in\", \"none\", \"out\", \"out\"],\n }\n)\n\ndiscrete_control = ribasim.DiscreteControl(condition=condition, logic=logic)\n\nThe above control logic can be summarized as follows: - If the level gets above the maximum, activate the control state “out” until the setpoint is reached; - If the level gets below the minimum, active the control state “in” until the setpoint is reached; - Otherwise activate the control state “none”.\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [2] + 3 * [3],\n \"control_state\": 2 * [\"none\", \"in\", \"out\"],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0, 2e-3, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2e-3],\n }\n )\n)\n\nThe pump data defines the following:\n\n\n\nControl state\nPump #2 flow rate (m/s)\nPump #3 flow rate (m/s)\n\n\n\n\n“none”\n0.0\n0.0\n\n\n“in”\n2e-3\n0.0\n\n\n“out”\n0.0\n2e-3\n\n\n\nSetup the level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [4], \"level\": [10.0]})\n)\n\nSetup the rating curve:\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": 2 * [5], \"level\": [2.0, 15.0], \"discharge\": [0.0, 1e-3]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup the terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [6]}))\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n pump=pump,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n terminal=terminal,\n discrete_control=discrete_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nListen edges are plotted with a dashed line since they are not present in the “Edge / static” schema but only in the “Control / condition” schema.\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\n\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\ngreater_than = model.discrete_control.condition.df.greater_than\n\nax.hlines(\n greater_than,\n df_basin.time[0],\n df_basin.time.max(),\n lw=1,\n ls=\"--\",\n color=\"k\",\n)\n\ndf_control = pd.read_feather(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\ny_min, y_max = ax.get_ybound()\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[:2], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[2:4], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\n\nax.set_xticks(\n date2num(df_control.time).tolist(),\n df_control.control_state.tolist(),\n rotation=50,\n)\n\nax.set_yticks(greater_than, [\"min\", \"setpoint\", \"max\"])\nax.set_ylabel(\"level\")\nplt.show()\n\n\n\n\nThe highlighted regions show where a pump is active.\nLet’s print an overview of what happened with control:\n\nmodel.print_discrete_control_record(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\n0. At 2020-01-01 00:00:00 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTT:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"out\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n\n1. At 2020-02-08 19:02:21.861000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n2. At 2020-07-05 08:56:10.319000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state FFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"in\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n3. At 2020-08-11 06:05:15.592000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n\n\nNote that crossing direction specific truth states (containing “U”, “D”) are not present in this overview even though they are part of the control logic. This is because in the control logic for this model these truth states are only used to sustain control states, while the overview only shows changes in control states.\n\n\n4 Model with PID control\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: FlowBoundary\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: Basin\n (2.0, 0.5), # 3: Pump\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (1.5, 1.0), # 5: PidControl\n (2.0, -0.5), # 6: outlet\n (1.5, -1.0), # 7: PidControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"FlowBoundary\",\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"PidControl\",\n \"Outlet\",\n \"PidControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 5, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([2, 3, 4, 6, 2, 3, 6], dtype=np.int64)\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": 5 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [2, 2], \"level\": [0.0, 1.0], \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0]}\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"level\": [6.0],\n }\n)\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [3],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup the outlet:\n\noutlet = ribasim.Outlet(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [6],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"flow_rate\": [1e-3]})\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4],\n \"level\": [1.0], # Not relevant\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup PID control:\n\npid_control = ribasim.PidControl(\n time=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 4 * [5, 7],\n \"time\": [\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n ],\n \"listen_node_id\": 4 * [2, 2],\n \"target\": [5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5],\n \"proportional\": 4 * [-1e-3, 1e-3],\n \"integral\": 4 * [-1e-7, 1e-7],\n \"derivative\": 4 * [0.0, 0.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nNote that the coefficients for the pump and the outlet are equal in magnitude but opposite in sign. This way the pump and the outlet equally work towards the same goal, while having opposite effects on the controlled basin due to their connectivity to this basin.\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n outlet=outlet,\n pid_control=pid_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"pid_control/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/pid_control/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim pid_control/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"pid_control/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\nax.set_ylabel(\"level [m]\")\n\n# Plot target level\ntarget_levels = model.pid_control.time.df.target.to_numpy()[:4]\ntimes = date2num(model.pid_control.time.df.time)[:4]\nax.plot(times, target_levels, color=\"k\", ls=\":\", label=\"target level\")\npass"
+ "text": "1 Basic model with static forcing\n\nfrom pathlib import Path\n\nimport geopandas as gpd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1, 3, 3, 6, 6, 9, 9],\n \"area\": [0.01, 1000.0] * 4,\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0] * 4,\n }\n)\n\n# Convert steady forcing to m/s\n# 2 mm/d precipitation, 1 mm/d evaporation\nseconds_in_day = 24 * 3600\nprecipitation = 0.002 / seconds_in_day\nevaporation = 0.001 / seconds_in_day\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [0],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [evaporation],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [precipitation],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\nstatic = static.iloc[[0, 0, 0, 0]]\nstatic[\"node_id\"] = [1, 3, 6, 9]\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static)\n\nSetup linear resistance:\n\nlinear_resistance = ribasim.LinearResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [10, 12], \"resistance\": [5e3, (3600.0 * 24) / 100.0]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup Manning resistance:\n\nmanning_resistance = ribasim.ManningResistance(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"length\": [900.0],\n \"manning_n\": [0.04],\n \"profile_width\": [6.0],\n \"profile_slope\": [3.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up a rating curve node:\n\n# Discharge: lose 1% of storage volume per day at storage = 1000.0.\nq1000 = 1000.0 * 0.01 / seconds_in_day\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4, 4],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n \"discharge\": [0.0, q1000],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup fractional flows:\n\nfractional_flow = ribasim.FractionalFlow(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [5, 8, 13],\n \"fraction\": [0.3, 0.6, 0.1],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [7],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.5 / 3600],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [11, 17],\n \"level\": [0.5, 1.5],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [15, 16],\n \"flow_rate\": [1e-4, 1e-4],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [14],\n }\n )\n)\n\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin,\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: ManningResistance\n (2.0, 0.0), # 3: Basin\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (3.0, 1.0), # 5: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, 2.0), # 6: Basin\n (4.0, 1.0), # 7: Pump\n (4.0, 0.0), # 8: FractionalFlow\n (5.0, 0.0), # 9: Basin\n (6.0, 0.0), # 10: LinearResistance\n (2.0, 2.0), # 11: LevelBoundary\n (2.0, 1.0), # 12: LinearResistance\n (3.0, -1.0), # 13: FractionalFlow\n (3.0, -2.0), # 14: Terminal\n (3.0, 3.0), # 15: FlowBoundary\n (0.0, 1.0), # 16: FlowBoundary\n (6.0, 1.0), # 17: LevelBoundary\n ]\n)\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_id, node_type = ribasim.Node.node_ids_and_types(\n basin,\n manning_resistance,\n rating_curve,\n pump,\n fractional_flow,\n linear_resistance,\n level_boundary,\n flow_boundary,\n terminal,\n)\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(node_id, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array(\n [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 8, 7, 9, 11, 12, 4, 13, 15, 16, 10], dtype=np.int64\n)\nto_id = np.array(\n [2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 6, 7, 9, 9, 10, 12, 3, 13, 14, 6, 1, 17], dtype=np.int64\n)\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": len(from_id) * [\"flow\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n linear_resistance=linear_resistance,\n manning_resistance=manning_resistance,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n fractional_flow=fractional_flow,\n terminal=terminal,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic/ribasim.toml')\n\n\n\n\n2 Update the basic model with transient forcing\nThis assumes you have already created the basic model with static forcing.\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ribasim\nimport xarray as xr\n\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(filepath=datadir / \"basic/ribasim.toml\")\n\n\ntime = pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime)\nday_of_year = time.day_of_year.to_numpy()\nseconds_per_day = 24 * 60 * 60\nevaporation = (\n (-1.0 * np.cos(day_of_year / 365.0 * 2 * np.pi) + 1.0) * 0.0025 / seconds_per_day\n)\nrng = np.random.default_rng(seed=0)\nprecipitation = (\n rng.lognormal(mean=-1.0, sigma=1.7, size=time.size) * 0.001 / seconds_per_day\n)\n\nWe’ll use xarray to easily broadcast the values.\n\ntimeseries = (\n pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 1,\n \"time\": pd.date_range(model.starttime, model.endtime),\n \"drainage\": 0.0,\n \"potential_evaporation\": evaporation,\n \"infiltration\": 0.0,\n \"precipitation\": precipitation,\n \"urban_runoff\": 0.0,\n }\n )\n .set_index(\"time\")\n .to_xarray()\n)\n\nbasin_ids = model.basin.static.df[\"node_id\"].to_numpy()\nbasin_nodes = xr.DataArray(\n np.ones(len(basin_ids)), coords={\"node_id\": basin_ids}, dims=[\"node_id\"]\n)\nforcing = (timeseries * basin_nodes).to_dataframe().reset_index()\n\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": basin_ids,\n \"level\": 1.4,\n \"concentration\": 0.0,\n }\n)\n\n\nmodel.basin.time.df = forcing\nmodel.basin.state.df = state\n\n\nmodel.write(datadir / \"basic_transient/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/basic_transient/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim basic-transient/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\ndf_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\n<Axes: xlabel='time'>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ndf_flow = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"basic_transient/results/flow.arrow\")\ndf_flow[\"edge\"] = list(zip(df_flow.from_node_id, df_flow.to_node_id))\ndf_flow[\"flow_m3d\"] = df_flow.flow * 86400\nax = df_flow.pivot_table(index=\"time\", columns=\"edge\", values=\"flow_m3d\").plot()\nax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.3, 1), title=\"Edge\")\n\n<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f7014656f50>\n\n\n\n\n\n\ntype(df_flow)\n\npandas.core.frame.DataFrame\n\n\n\n\n3 Model with discrete control\nThe model constructed below consists of a single basin which slowly drains trough a TabulatedRatingCurve, but is held within a range around a target level (setpoint) by two connected pumps. These two pumps behave like a reversible pump. When pumping can be done in only one direction, and the other direction is only possible under gravity, use an Outlet for that direction.\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: Basin\n (1.0, 1.0), # 2: Pump\n (1.0, -1.0), # 3: Pump\n (2.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (-1.0, 0.0), # 5: TabulatedRatingCurve\n (-2.0, 0.0), # 6: Terminal\n (1.0, 0.0), # 7: DiscreteControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"TabulatedRatingCurve\",\n \"Terminal\",\n \"DiscreteControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 7, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 6, 2, 3], dtype=np.int64)\n\nedge_type = 6 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"]\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"from_node_id\": from_id, \"to_node_id\": to_id, \"edge_type\": edge_type},\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1, 1],\n \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0],\n \"level\": [0.0, 1.0],\n }\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [1],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"level\": [20.0]})\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the discrete control:\n\ncondition = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [7],\n \"listen_feature_id\": 3 * [1],\n \"variable\": 3 * [\"level\"],\n \"greater_than\": [5.0, 10.0, 15.0], # min, setpoint, max\n }\n)\n\nlogic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 5 * [7],\n \"truth_state\": [\"FFF\", \"U**\", \"T*F\", \"**D\", \"TTT\"],\n \"control_state\": [\"in\", \"in\", \"none\", \"out\", \"out\"],\n }\n)\n\ndiscrete_control = ribasim.DiscreteControl(condition=condition, logic=logic)\n\nThe above control logic can be summarized as follows: - If the level gets above the maximum, activate the control state “out” until the setpoint is reached; - If the level gets below the minimum, active the control state “in” until the setpoint is reached; - Otherwise activate the control state “none”.\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 3 * [2] + 3 * [3],\n \"control_state\": 2 * [\"none\", \"in\", \"out\"],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0, 2e-3, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2e-3],\n }\n )\n)\n\nThe pump data defines the following:\n\n\n\nControl state\nPump #2 flow rate (m/s)\nPump #3 flow rate (m/s)\n\n\n\n\n“none”\n0.0\n0.0\n\n\n“in”\n2e-3\n0.0\n\n\n“out”\n0.0\n2e-3\n\n\n\nSetup the level boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [4], \"level\": [10.0]})\n)\n\nSetup the rating curve:\n\nrating_curve = ribasim.TabulatedRatingCurve(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": 2 * [5], \"level\": [2.0, 15.0], \"discharge\": [0.0, 1e-3]}\n )\n)\n\nSetup the terminal:\n\nterminal = ribasim.Terminal(static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [6]}))\n\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n pump=pump,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n tabulated_rating_curve=rating_curve,\n terminal=terminal,\n discrete_control=discrete_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2021-01-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nListen edges are plotted with a dashed line since they are not present in the “Edge / static” schema but only in the “Control / condition” schema.\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with level_setpoint_with_minmax/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\n\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\n\ngreater_than = model.discrete_control.condition.df.greater_than\n\nax.hlines(\n greater_than,\n df_basin.time[0],\n df_basin.time.max(),\n lw=1,\n ls=\"--\",\n color=\"k\",\n)\n\ndf_control = pd.read_feather(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\ny_min, y_max = ax.get_ybound()\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[:2], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\nax.fill_between(df_control.time[2:4], 2 * [y_min], 2 * [y_max], alpha=0.2, color=\"C0\")\n\nax.set_xticks(\n date2num(df_control.time).tolist(),\n df_control.control_state.tolist(),\n rotation=50,\n)\n\nax.set_yticks(greater_than, [\"min\", \"setpoint\", \"max\"])\nax.set_ylabel(\"level\")\nplt.show()\n\n\n\n\nThe highlighted regions show where a pump is active.\nLet’s print an overview of what happened with control:\n\nmodel.print_discrete_control_record(\n datadir / \"level_setpoint_with_minmax/results/control.arrow\"\n)\n\n0. At 2020-01-01 00:00:00 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTT:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"out\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n\n1. At 2020-02-08 19:02:21.861000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n2. At 2020-07-05 08:56:10.319000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state FFF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"in\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.002\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n3. At 2020-08-11 06:05:15.592000 the control node with ID 7 reached truth state TTF:\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 5.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level > 10.0\n For node ID 1 (Basin): level < 15.0\n\n This yielded control state \"none\":\n For node ID 2 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n For node ID 3 (Pump): flow_rate = 0.0\n\n\n\nNote that crossing direction specific truth states (containing “U”, “D”) are not present in this overview even though they are part of the control logic. This is because in the control logic for this model these truth states are only used to sustain control states, while the overview only shows changes in control states.\n\n\n4 Model with PID control\nSet up the nodes:\n\nxy = np.array(\n [\n (0.0, 0.0), # 1: FlowBoundary\n (1.0, 0.0), # 2: Basin\n (2.0, 0.5), # 3: Pump\n (3.0, 0.0), # 4: LevelBoundary\n (1.5, 1.0), # 5: PidControl\n (2.0, -0.5), # 6: outlet\n (1.5, -1.0), # 7: PidControl\n ]\n)\n\nnode_xy = gpd.points_from_xy(x=xy[:, 0], y=xy[:, 1])\n\nnode_type = [\n \"FlowBoundary\",\n \"Basin\",\n \"Pump\",\n \"LevelBoundary\",\n \"PidControl\",\n \"Outlet\",\n \"PidControl\",\n]\n\n# Make sure the feature id starts at 1: explicitly give an index.\nnode = ribasim.Node(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\"type\": node_type},\n index=pd.Index(np.arange(len(xy)) + 1, name=\"fid\"),\n geometry=node_xy,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the edges:\n\nfrom_id = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 5, 7], dtype=np.int64)\nto_id = np.array([2, 3, 4, 6, 2, 3, 6], dtype=np.int64)\n\nlines = node.geometry_from_connectivity(from_id, to_id)\nedge = ribasim.Edge(\n df=gpd.GeoDataFrame(\n data={\n \"from_node_id\": from_id,\n \"to_node_id\": to_id,\n \"edge_type\": 5 * [\"flow\"] + 2 * [\"control\"],\n },\n geometry=lines,\n crs=\"EPSG:28992\",\n )\n)\n\nSetup the basins:\n\nprofile = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\"node_id\": [2, 2], \"level\": [0.0, 1.0], \"area\": [1000.0, 1000.0]}\n)\n\nstatic = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"drainage\": [0.0],\n \"potential_evaporation\": [0.0],\n \"infiltration\": [0.0],\n \"precipitation\": [0.0],\n \"urban_runoff\": [0.0],\n }\n)\n\nstate = pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [2],\n \"level\": [6.0],\n }\n)\n\nbasin = ribasim.Basin(profile=profile, static=static, state=state)\n\nSetup the pump:\n\npump = ribasim.Pump(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [3],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup the outlet:\n\noutlet = ribasim.Outlet(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [6],\n \"flow_rate\": [0.0], # Will be overwritten by PID controller\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nflow_boundary = ribasim.FlowBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(data={\"node_id\": [1], \"flow_rate\": [1e-3]})\n)\n\nSetup flow boundary:\n\nlevel_boundary = ribasim.LevelBoundary(\n static=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": [4],\n \"level\": [1.0], # Not relevant\n }\n )\n)\n\nSetup PID control:\n\npid_control = ribasim.PidControl(\n time=pd.DataFrame(\n data={\n \"node_id\": 4 * [5, 7],\n \"time\": [\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-05-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-07-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n \"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n ],\n \"listen_node_id\": 4 * [2, 2],\n \"target\": [5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 5.0, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5, 7.5],\n \"proportional\": 4 * [-1e-3, 1e-3],\n \"integral\": 4 * [-1e-7, 1e-7],\n \"derivative\": 4 * [0.0, 0.0],\n }\n )\n)\n\nNote that the coefficients for the pump and the outlet are equal in magnitude but opposite in sign. This way the pump and the outlet equally work towards the same goal, while having opposite effects on the controlled basin due to their connectivity to this basin.\nSetup a model:\n\nmodel = ribasim.Model(\n network=ribasim.Network(\n node=node,\n edge=edge,\n ),\n basin=basin,\n flow_boundary=flow_boundary,\n level_boundary=level_boundary,\n pump=pump,\n outlet=outlet,\n pid_control=pid_control,\n starttime=\"2020-01-01 00:00:00\",\n endtime=\"2020-12-01 00:00:00\",\n)\n\nLet’s take a look at the model:\n\nmodel.plot()\n\n<Axes: >\n\n\n\n\n\nWrite the model to a TOML and GeoPackage:\n\ndatadir = Path(\"data\")\nmodel.write(datadir / \"pid_control/ribasim.toml\")\n\nPosixPath('data/pid_control/ribasim.toml')\n\n\nNow run the model with ribasim pid_control/ribasim.toml. After running the model, read back the results:\n\nfrom matplotlib.dates import date2num\n\ndf_basin = pd.read_feather(datadir / \"pid_control/results/basin.arrow\")\ndf_basin_wide = df_basin.pivot_table(\n index=\"time\", columns=\"node_id\", values=[\"storage\", \"level\"]\n)\nax = df_basin_wide[\"level\"].plot()\nax.set_ylabel(\"level [m]\")\n\n# Plot target level\ntarget_levels = model.pid_control.time.df.target.to_numpy()[:4]\ntimes = date2num(model.pid_control.time.df.time)[:4]\nax.plot(times, target_levels, color=\"k\", ls=\":\", label=\"target level\")\npass"
},
{
"objectID": "qgis/index.html",
"href": "qgis/index.html",
"title": "QGIS plugin",
"section": "",
- "text": "Install QGIS version 3.28 or higher.\n\n\nDownload ribasim_qgis.zip, see the download section.\nPlugins menu > Manage and Install Plugins…\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Install from ZIP”:\n\nBrowse to the ribasim_qgis.zip file containing the plugin that was downloaded earlier\nClick “Install Plugin”\n\n\n\n\n\n\nStart the Ribasim plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nIn QGIS, navigate to “Plugins > Manage and Install Plugins > All”. In the search bar, type: “iMOD”. Select the iMOD plugin, and click “Install”.\nAt least version 0.4.0 of the iMOD plugin is required.\nThe Time Series widget from the iMOD plugin is used for visualizing Ribasim results, which is described in Section 1.5. Documentation on the Time Series widget can be found in the iMOD documentation.\n\n\n\nOpen an existing model or create a new model. As an example of an existing model, you can use the “basic” model from generated_testmodels.zip, see the download section.\n\n\n\n\n\nCheck if your coordinate reference system (CRS) is set correctly.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are working with an unknown CRS, right click the model database group in Layers, and click “Set Group CRS…”.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are modeling the Netherlands, select “Amersfoort / RD New” (EPSG:28992).\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Node layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn on the edit mode to be able to add nodes on the map.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdd nodes to the map with a left click and select the node type.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn the edit mode off and save the edits to the Nodes layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nRight click a layer and select “Open Attribute Table”.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick the yellow pencil icon on the top left to enable editing, and copy and paste a record. A record can be selected by clicking on the row number.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdjust the content. If you prefer, it also works to copy data with the same columns from Excel. Turn off edit mode and save changes to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nMake sure the Snapping Toolbar is visible, by going to the View > Toolbars menu. Turn on snapping mode by clicking the magnet and set the snapping distance to 25 pixels.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Edge layer and turn on the edit mode.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Add line feature”.\n\n\n\n\n\nCreate a connection by left clicking a source node and right clicking the destination node.\n\n\n\n\n\nNow leave the edit mode and save the results to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nOpen a text editor and create an empty file next to your database, with the .toml extension.\nAdd the following content to the TOML file:\n\n\n\nribasim.toml\n\nstarttime = 2020-01-01 00:00:00\nendtime = 2021-01-01 00:00:00\ndatabase = \"database.gpkg\"\n\n\nUnzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files.\n\n\n\n\n\n\nIn QGIS select the model group.\n\n\n\n\n\nIn the Ribasim plugin widget, select the Results tab and click “Associate Results”.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect results/basin.arrow.\n\n\n\n\n\nThis adds metadata to the model that the iMOD plugin can use to find the timeseries data that is associated to the model nodes.\n\n\n\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes. Currently only the Basin nodes can be plotted.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph."
+ "text": "Install QGIS version 3.28 or higher.\n\n\nDownload ribasim_qgis.zip, see the download section.\nPlugins menu > Manage and Install Plugins…\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Install from ZIP”:\n\nBrowse to the ribasim_qgis.zip file containing the plugin that was downloaded earlier\nClick “Install Plugin”\n\n\n\n\n\n\nStart the Ribasim plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nIn QGIS, navigate to “Plugins > Manage and Install Plugins > All”. In the search bar, type: “iMOD”. Select the iMOD plugin, and click “Install”.\nAt least version 0.4.0 of the iMOD plugin is required.\nThe Time Series widget from the iMOD plugin is used for visualizing Ribasim results, which is described in Section 1.5. Documentation on the Time Series widget can be found in the iMOD documentation.\n\n\n\nOpen an existing model or create a new model. As an example of an existing model, you can use the “basic” model from generated_testmodels.zip, see the download section.\n\n\n\n\n\nCheck if your coordinate reference system (CRS) is set correctly.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are working with an unknown CRS, right click the model database group in Layers, and click “Set Group CRS…”.\n\n\n\n\n\nIf you are modeling the Netherlands, select “Amersfoort / RD New” (EPSG:28992).\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Node layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn on the edit mode to be able to add nodes on the map.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdd nodes to the map with a left click and select the node type.\n\n\n\n\n\nTurn the edit mode off and save the edits to the Nodes layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nRight click a layer and select “Open Attribute Table”.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick the yellow pencil icon on the top left to enable editing, and copy and paste a record. A record can be selected by clicking on the row number.\n\n\n\n\n\nAdjust the content. If you prefer, it also works to copy data with the same columns from Excel. Turn off edit mode and save changes to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nMake sure the Snapping Toolbar is visible, by going to the View > Toolbars menu. Turn on snapping mode by clicking the magnet and set the snapping distance to 25 pixels.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the Edge layer and turn on the edit mode.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect “Add line feature”.\n\n\n\n\n\nCreate a connection by left clicking a source node and right clicking the destination node.\n\n\n\n\n\nNow leave the edit mode and save the results to the layer.\n\n\n\n\n\nUnzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files.\n\n\n\n\nBefore trying to inspect the results, verify that the run was successful and the output files are there.\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the layer that you wish to plot. From the “Node” layer you can plot level or storage on Basin nodes. From the “Edge” layer you can plot flow over flow edges. Note that before switching between these, you typically have to click “Clear” to clear the selection. If you run a simulation with the model open in QGIS, you have to close and re-open the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel for the new results to be loaded.\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph.\n\n\n\n\n\nOnly the “basin.arrow” and “flow.arrow” can be inspected with the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel. All Arrow files can be loaded as a layer by dragging the files onto QGIS. Right click the layer and select “Open Attribute Table” to view the contents."
},
{
"objectID": "qgis/index.html#start",
@@ -431,14 +431,14 @@
"href": "qgis/index.html#run-a-model",
"title": "QGIS plugin",
"section": "",
- "text": "Open a text editor and create an empty file next to your database, with the .toml extension.\nAdd the following content to the TOML file:\n\n\n\nribasim.toml\n\nstarttime = 2020-01-01 00:00:00\nendtime = 2021-01-01 00:00:00\ndatabase = \"database.gpkg\"\n\n\nUnzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files."
+ "text": "Unzip the Ribasim command line interface, ribasim_cli.zip\nOpen your terminal and go to the directory where your TOML is stored. Now run path/to/ribasim_cli/ribasim ribasim.toml. Adjust the path to the ribasim_cli folder to where you placed it. This runs the model.\nIn your model directory there is now a results/ folder with basin.arrow and flow.arrow output files."
},
{
"objectID": "qgis/index.html#sec-results",
"href": "qgis/index.html#sec-results",
"title": "QGIS plugin",
"section": "",
- "text": "In QGIS select the model group.\n\n\n\n\n\nIn the Ribasim plugin widget, select the Results tab and click “Associate Results”.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect results/basin.arrow.\n\n\n\n\n\nThis adds metadata to the model that the iMOD plugin can use to find the timeseries data that is associated to the model nodes.\n\n\n\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes. Currently only the Basin nodes can be plotted.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph."
+ "text": "Before trying to inspect the results, verify that the run was successful and the output files are there.\nClick the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.\n\n\n\n\n\nSelect the layer that you wish to plot. From the “Node” layer you can plot level or storage on Basin nodes. From the “Edge” layer you can plot flow over flow edges. Note that before switching between these, you typically have to click “Clear” to clear the selection. If you run a simulation with the model open in QGIS, you have to close and re-open the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel for the new results to be loaded.\nSelect the variables that you want to plot.\n\n\n\n\n\nClick “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes.\n\n\n\n\n\nThe associated time series are shown the the graph.\n\n\n\n\n\nOnly the “basin.arrow” and “flow.arrow” can be inspected with the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel. All Arrow files can be loaded as a layer by dragging the files onto QGIS. Right click the layer and select “Open Attribute Table” to view the contents."
},
{
"objectID": "couple/modflow-demo.html",
1.5 Inspect results
-1.5.1 Associate results to iMOD time series window
-In QGIS select the model group.
-
In the Ribasim plugin widget, select the Results tab and click “Associate Results”.
-
Select results/basin.arrow.

This adds metadata to the model that the iMOD plugin can use to find the timeseries data that is associated to the model nodes.
-1.5.2 Plot time series
+Before trying to inspect the results, verify that the run was successful and the output files are there.
Click the “Time Series” button of the iMOD plugin.

Select the layer that you wish to plot. From the “Node” layer you can plot level or storage on Basin nodes. From the “Edge” layer you can plot flow over flow edges. Note that before switching between these, you typically have to click “Clear” to clear the selection. If you run a simulation with the model open in QGIS, you have to close and re-open the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel for the new results to be loaded.
Select the variables that you want to plot.

Click “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes. Currently only the Basin nodes can be plotted.
+Click “Select points” and select a node by dragging a rectangle around it on the map. Hold the Ctrl key to select multiple nodes.

Only the “basin.arrow” and “flow.arrow” can be inspected with the “iMOD Time Series Plot” panel. All Arrow files can be loaded as a layer by dragging the files onto QGIS. Right click the layer and select “Open Attribute Table” to view the contents.
-