Social Login
2 - Partiendo del ejercicio anterior... realizaremos un nuevo formulario que nos permita registrarnos usando nuestra cuenta de Github.
Objetivos:
-
Comprobar si ese mismo usuario ya esta registrado, para evitar multiples inscripciones.
-
Incluiremos en la página los usuarios que se van sumando.
4 - Desarrolla una versión mejorada de MovieFire (JS puro) incluyendo llamadas AJAX a la base de datos de IMBD para enriquecer los datos, usando OMDb API.
-
Seguridad:
- Necesario SSL
- HTTPS
- Confirmación del usuario
- Necesario SSL
-
Precisión:
- Wi-fi (MAC)
- Ethernet (IP)
- Triangulación (3G y 4G)
- GPS (máxima precisión, pero tardará más en cargar)
-
Métodos de geolocation
- getCurrentPosition():
// Posición Actual navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition();
- watchPosition():
// Seguimiento como un GPS navigator.geolocation.watchPosition();
- clearWatch():
// Para el seguimiento navigator.geolocation.clearWatch();
-
Propiedades de geolocation
- Latitud (en base 10):
console.info(position.coords.latitude);
- Longitud (en base 10):
console.info(position.coords.longitude);
- Precisión en posicionamiento:
console.info(position.coords.accuracy);
- Altitud (metros por encima del nivel del mar):
console.info(position.coords.altitude);
- Precisión de altitud:
console.info(position.coords.altitudeAccuracy);
- Rumbo (Grados respectos al norte):
console.info(position.coords.heading);
- Velocidad (m/s):
console.info(position.coords.speed);
- Timestamp:
console.info(position.timestamp);
-
Ajustes de geolocation
-
enableHighAccuracy:
- Mejora los datos para conexiones no GPS, pero aumenta drásticamente el consumo de batería del dispositivo.
- False por defecto
-
timeout:
- Tiempo (ms) de espera antes de lanzar el error.
- 0 por defecto
-
maximumAge:
- Tiempo (ms) para el almacenamiento en memoria cache de la posición actual
- 0 por defecto
-
Ejemplo:
var opciones = { enableHighAccuracy: true, maximumAge: 1000, // 1s timeout: 2000 // 2s }
-
-
Trabajando con geolocation
- Comprobando la compatibildiad de geolocation
if ("geolocation" in navigator) { console.info("Podemos usar Geolocation! :-) "); } else { console.warn("Geolocation no soportado :-( "); }
- Probando la geolocalización:
if ("geolocation" in navigator) { navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(function(position) { // Consola console.info("Latitud: " + position.coords.latitude + "\nLongitud: "+ position.coords.longitude); // HTML var datos = "<h1>Te pille!</h1>" datos += "Latitud: " + position.coords.latitude.toFixed(4) + "<br>" datos += "Longitud: "+ position.coords.longitude.toFixed(4) document.body.innerHTML = datos; }); } else { console.warn("Geolocation no soportado :-( "); }
- Mostrar la localización en una imagen estatica usando Gogole Maps:
if ("geolocation" in navigator) { navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(function(position) { var latlon = position.coords.latitude + "," + position.coords.longitude; var img_url = "http://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/staticmap?center="+latlon+"&zoom=14&size=400x300&sensor=false"; document.body.innerHTML = "<img src='"+img_url+"'>"; }); } else { console.warn("Geolocation no soportado :-( "); }
- Gestionar los Errores y rechazos:
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(geo_success, geo_error); function geo_success(position) { console.info(position.coords.latitude+","+ position.coords.longitude); } function geo_error(error) { switch(error.code) { case error.PERMISSION_DENIED: document.body.innerHTML = "El usuario ha rechazado la petición."; console.warn(error); break; case error.POSITION_UNAVAILABLE: document.body.innerHTML = "La posición de usuario no es correcta."; console.warn(error); break; case error.TIMEOUT: document.body.innerHTML = "No hay respuesta en el tiempo limite previsto."; console.warn(error); break; case error.UNKNOWN_ERROR: document.body.innerHTML = "Error Desconocido"; console.warn(error); break; } }
- Trabajando con ajustes personalizados:
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(geo_exito, geo_error, opciones); var opciones = { enableHighAccuracy: true, maximumAge: 1000, // 1s timeout: 2000 // 2s } function geo_exito(position) { console.info(position.coords.latitude+","+ position.coords.longitude); } function geo_error(error) { console.warn("Error! - "+error); }
- Convirtiendo las coordenadas a hexadecimal:
/** * From Isabel Castillo * http://isabelcastillo.com/convert-latitude-longitude-decimal-degrees * Convert longitude/latitude decimal degrees to degrees and minutes * DDD to DMS, no seconds * @param lat, latitude degrees decimal * @param lng, longitude degrees decimal */ function convertDMS( lat, lng ) { var convertLat = Math.abs(lat); var LatDeg = Math.floor(convertLat); var LatSec = (Math.floor((convertLat - LatDeg) * 60)); var LatCardinal = ((lat > 0) ? "n" : "s"); var convertLng = Math.abs(lng); var LngDeg = Math.floor(convertLng); var LngSec = (Math.floor((convertLng - LngDeg) * 60)); var LngCardinal = ((lng > 0) ? "e" : "w"); return LatDeg + LatCardinal + LatSec + "<br />" + LngDeg + LngCardinal + LngSec; }
- Sigue a un usuario:
navigator.geolocation.watchPosition(geo_exito, geo_error); function geo_exito(position) { console.info(position.coords.latitude +", "+ position.coords.longitude); } function geo_error(error) { console.warn("Error! - "+error); }
Google Maps
- Librería
<script type='text/javascript' src="http://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js?sensor=false&extension=.js&output=embed"></script>- Centrar el mapa
function initMap() {
var map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById('map'), {
zoom: 8,
center: {lat: -3.8199647, lng: 40.4381307}
});
}- Markers ( Demo )
// In the following example, markers appear when the user clicks on the map.
// Each marker is labeled with a single alphabetical character.
var labels = 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ';
var labelIndex = 0;
function initialize() {
var bangalore = { lat: 12.97, lng: 77.59 };
var map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById('map'), {
zoom: 12,
center: bangalore
});
// This event listener calls addMarker() when the map is clicked.
google.maps.event.addListener(map, 'click', function(event) {
addMarker(event.latLng, map);
});
// Add a marker at the center of the map.
addMarker(bangalore, map);
}
// Adds a marker to the map.
function addMarker(location, map) {
// Add the marker at the clicked location, and add the next-available label
// from the array of alphabetical characters.
var marker = new google.maps.Marker({
position: location,
label: labels[labelIndex++ % labels.length],
map: map
});
}
google.maps.event.addDomListener(window, 'load', initialize);- Markers Personalizados ( Demo )
// This example adds a marker to indicate the position of Bondi Beach in Sydney,
// Australia.
function initMap() {
var map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById('map'), {
zoom: 4,
center: {lat: -33, lng: 151}
});
var image = 'images/beachflag.png';
var beachMarker = new google.maps.Marker({
position: {lat: -33.890, lng: 151.274},
map: map,
icon: image
});
}- InfoWindows ( Demo )
// This example displays a marker at the center of Australia.
// When the user clicks the marker, an info window opens.
function initMap() {
var uluru = {lat: -25.363, lng: 131.044};
var map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById('map'), {
zoom: 4,
center: uluru
});
var contentString = '<div id="content">'+
'<div id="siteNotice">'+
'</div>'+
'<h1 id="firstHeading" class="firstHeading">Uluru</h1>'+
'<div id="bodyContent">'+
'<p><b>Uluru</b>, also referred to as <b>Ayers Rock</b>, is a large ' +
'sandstone rock formation in the southern part of the '+
'Northern Territory, central Australia. It lies 335 km (208 mi) '+
'south west of the nearest large town, Alice Springs; 450 km '+
'(280 mi) by road. Kata Tjuta and Uluru are the two major '+
'features of the Uluru - Kata Tjuta National Park. Uluru is '+
'sacred to the Pitjantjatjara and Yankunytjatjara, the '+
'Aboriginal people of the area. It has many springs, waterholes, '+
'rock caves and ancient paintings. Uluru is listed as a World '+
'Heritage Site.</p>'+
'<p>Attribution: Uluru, <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Uluru&oldid=297882194">'+
'https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Uluru</a> '+
'(last visited June 22, 2009).</p>'+
'</div>'+
'</div>';
var infowindow = new google.maps.InfoWindow({
content: contentString
});
var marker = new google.maps.Marker({
position: uluru,
map: map,
title: 'Uluru (Ayers Rock)'
});
marker.addListener('click', function() {
infowindow.open(map, marker);
});
}- Notas sobre GMaps:
Ejercicios:
1 - Utiliza Google Maps para posicionar al usuario.
2 - Utiliza Ajax para posicionar al usuario y las estaciones de BiciMad en un mapa:
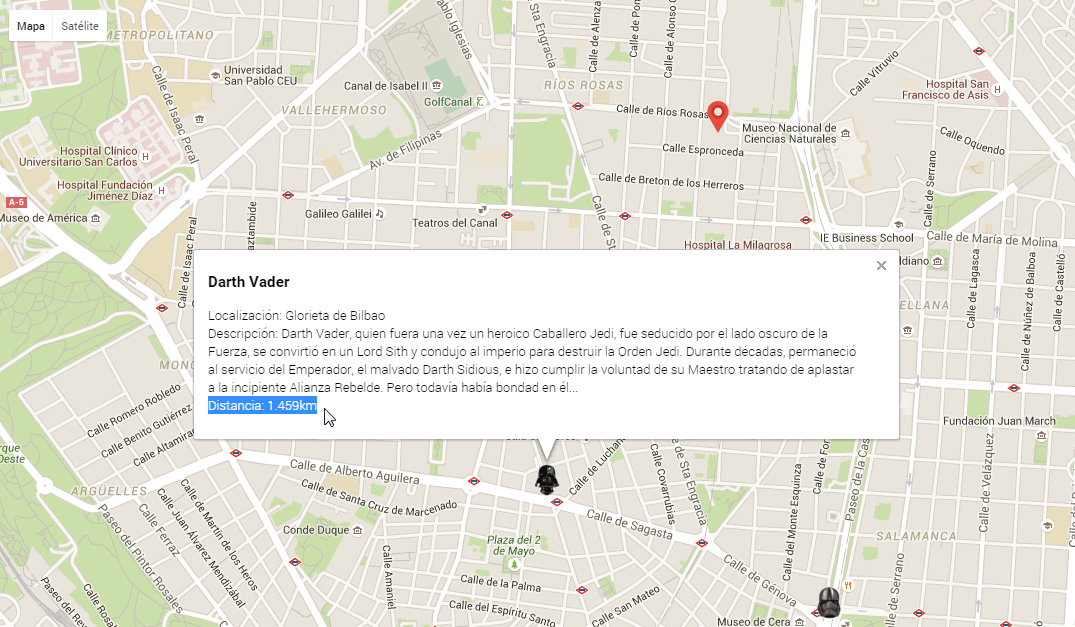
3 - Utiliza esta librería para posicionar al usuario, los cascos de StarWars con sus característicos iconos y la distancia estimada
-
Nota:
-
Podemos escuchar eventos y enlazar funciones (event handler)
-
Propagación:
- Capturing desde document hasta el elemento
- Target impacta el elemento
- Bubbling sube desde el elemento hasta document
-
Usando Eventos (Tradicional)
- Solo una función por evento
<button onclick="cambiarFondo()">Cambia el fondo</button>
function cambiarFondo() { // color = 'rgb(0-255,0-255,0-255' var color = 'rgb(' + Math.floor((Math.random() * 255))+ ','; color += Math.floor((Math.random() * 255)) + ','; color += Math.floor((Math.random() * 255)) + ')'; document.body.style.backgroundColor= color; }
-
Usando Eventos (Callbacks)
- Multiples funciones por evento
- Necesidad de compatibilizar para IE8
// Callback - Manejador de Eventos function manejadorEventos(elEvento) { // Compatibilizar el evento var evento = elEvento || window.event; // Imprimir detalles console.log("-----------------------------") console.log("Type: "+evento.type); // Tipo console.log("Bubbles: "+evento.bubbles); console.log("Cancelable: "+evento.cancelable); console.log("CurrentTarget: ", evento.currentTarget); console.log("DefaultPrevented: "+evento.defaultPrevented); console.log("EventPhase: "+evento.eventPhase); console.log("Target: ", evento.target); console.log("TimeStamp: "+evento.timeStamp); console.log("IsTrusted: "+evento.isTrusted); // true - Usuario o false - Script console.log("=============================") // Desactivamos if (document.removeEventListener){ document.removeEventListener('click', manejadorEventos, false); console.info("Listener quitado con exito"); } else { // IE8 document.detachEvent('onclick', manejadorEventos); console.info("Listener quitado con exito"); } } // Añadimos Listener if (document.addEventListener){ document.addEventListener('click', manejadorEventos, false); console.info("Listener añadido con exito"); } else if (document.attachEvent){ // IE8 document.attachEvent('onclick', manejadorEventos); console.info("Listener añadido con exito"); } else { document.onclick = manejadorEventos; console.info("Listener añadido con exito"); }
-
Deteniendo el flujo
- .preventDefault() evita el comportamiento por defecto (ex: Link -> nueva URL)
- .stopPropagation() evita la propagación por el DOM (bubble) pero permite la acción por defecto.
-
Gestión vs. Delegación de eventos
- Gestión (asociar un evento por elemento)
<ul id="miNav"> <li><a href="#nosotros">¿Quienes Somos?</a></li> <li><a href="#objetivos">Los objetivos</a></li> <li><a href="#equipo">Nuestro Equipo</a></li> <li><a href="#detalles">Más detalles</a></li> <li><a href="#contacta">Contactanos</a></li> </ul>
var miNav = document.getElementById("miNav"); var miNavLinks = miNav.getElementsByTagName("a"); for (var i = 0; i < miNavLinks.length; i++) { miNavLinks[i].onclick = function(){ console.info(this.innerHTML); } }
- Delegación (asociar un único evento al padre de los elementos)
<ul id="miNav"> <li><a href="#nosotros">¿Quienes Somos?</a></li> <li><a href="#objetivos">Los objetivos</a></li> <li><a href="#equipo">Nuestro Equipo</a></li> <li><a href="#detalles">Más detalles</a></li> <li><a href="#contacta">Contactanos</a></li> </ul>
var miNav = document.getElementById("miNav"); miNav.onclick = function(evento){ var evento = evento || window.event; var elemento = evento.target || evento.srcElement; console.info(elemento.innerHTML); }
-
Convencional:
- getElementById():
// <tag id = x > document.getElementById("id");
- getElementsByName():
// <tag name = x > document.getElementsByName("fname");
- getElementsByTagName():
// <tag > document.getElementsByTagName("input");
-
Selectores CSS3:
- URL que empieza con "javascript:"
a[href^="javascript:"] {color:blue;}
- URL que contiene "google.es"
a[href*="google.es"] {color:orange;}
- URL que termina con ".pdf"
a[href$=".pdf"] {color:red;}
-
Comprobando disponibilidad del API:
// op.1 - Positivo
if( document.querySelector && document.querySelectorAll ){
console.info("querySelector() y querySelectorAll() estan soportados!!")
} else {
console.warn("querySelector() y querySelectorAll() no estan soportados!!")
}
// op.2 - Negativo
if( typeof document.querySelector !== "function" && typeof document.querySelectorAll !== "function" ){
console.warn("querySelector() y querySelectorAll() no estan soportados!!")
} else {
console.info("querySelector() y querySelectorAll() estan soportados!!")
}- querySelector(): Devuelve el primer elemento que coincida con el selector
<div id="miDiv">
<span id="miId5" class="miClase" title="cinco"></span>
<span id="miId4" class="miClase" title="cuatro"></span>
<span id="miId3" class="miClase" title="tres"></span>
<span id="miId2" class="miClase" title="dos"></span>
<span id="miId1" class="miClase" title="uno"></span>
</div> document.getElementById('miId1').title // uno
document.querySelector('#miDiv .miClase').title // cinco
document.querySelector('#miDiv #miId1.miClase').title // uno
document.querySelector('#miDiv .inventado').title // ERROR -> undefined
document.querySelector('#miDiv .miClase[title^=u]').title // uno- querySelectorAll(): Devuelve todos los elementos que coincida con el selector en un array
document.querySelectorAll('#miDiv .miClase') // [<span id="miId5" ... ]
document.querySelectorAll('p') // todos los parrafos
document.querySelectorAll('div, img') // todos los divs e imágenes
document.querySelectorAll('a > img') // todos las imágenes contenidas en enlaces