- Change invalid CSS to valid CSS
Open 'CSS_Debrief/css-essentials-css-issue-bot-9000'
- Open index.html in your browser. Notice how our styles don't look quite right?
- Open css/style.css in your text editor.
- Visit the W3C CSS validator http://jigsaw.w3.org/css-validator/#validate_by_input. If not already selected, click on the tab labeled "By direct input".
- Copy the code from css/style.css and paste it into the text area. Click the "Check" button.
- Use the error messages to correct the CSS.
- Repeat steps 3-5 until your readout states "Congratulations! No Error Found.".
Remember to check your progress in index.html in your browser and Add, Commit and Push your changes to GitHub regularly
- Link an external CSS file
- Write CSS rules to style HTML
Open 'CSS_Debrief/css-fundamentals'
Link the 'style.css' file to the 'index.html' file. Refer to the 'completed_example' to complete the below tasks
-
Update the header: the text is a little wonky being aligned on the left like that. Provide a property that aligns it in the center instead.
-
Center our image: We only have one image on the page and we would like it centered!
-
Jazz up our navigation links: Let's center all of our nav links as well. Give all of the
<a>tags within our navbar padding of 10px on their left and right sides. In addition, change their background color to something of your choosing. We chose grey! -
Our image caption needs work: Let's shrink that font size down and make sure it is centered.
-
Update the text block: Wouldn't it look nicer if our text was centered as well? Our image is about 900px wide, so let's give all our
<p>s within#featured-propertya hard width of 800px and center the text in there. Be sure to keep a little vertical space around the<p>s. -
Make our
#detailssection horizontal: The details section could go nicely as a footer to the page, instead of a vertical list. To do this, make each of the<div>sfloatto theleft. -
As a finishing touch: Let's clean up the
<div>s at the bottom of the page. All of them should have the same background color, centered text, and occupy 25% of thewidthof the bottom row (since we have 4 divs).
- Review HTML basics
- Review CSS basics
- Specify hexadecimal color values with CSS
Open 'CSS_Debrief/css-rainbow'
In the directory, you'll see two files: index.html, main.css, and this
file. Open index.html.
If everything is working correctly, you should see a white page.
Good job!
To get ROYGBIV onto our rainbow we'll need seven hex colors. Red: #f00;
Orange: #ffa500; Yellow: #ff0; Green: #00bc3f; Blue: #06f; Indigo:
#8a2be2; Violet: #d300c9
All we have to do next is select each div individually and apply each of those colors. That is a perfect use for ids since they're meant to style one specific element only. We need to add an id for each div so a logical name for each div would be the color that they have to be. It could be something random, but good names make for semantic code. So let's give the outermost div the id red.
<div id="red">...</div>To give that id some CSS attributes we'll go into main.css, select the id, and
mark its color as red.
#red {
/* this selects any elements with the red id */
border-top-color: #f00;
}To make sure the rainbow isn't so monochromatic you now need to repeat the above steps with the final six colors, and when you do you should have a complete, colorful rainbow.
- Position elements absolutely
- Practice using CSS selectors
Oh no! All of our kittens have escaped from the wheelbarrow and we need to get them back in. Help collect all the kittens and put them into the wheelbarrow using CSS selectors and absolute positioning.
Open 'CSS_Debrief/css-kittens'
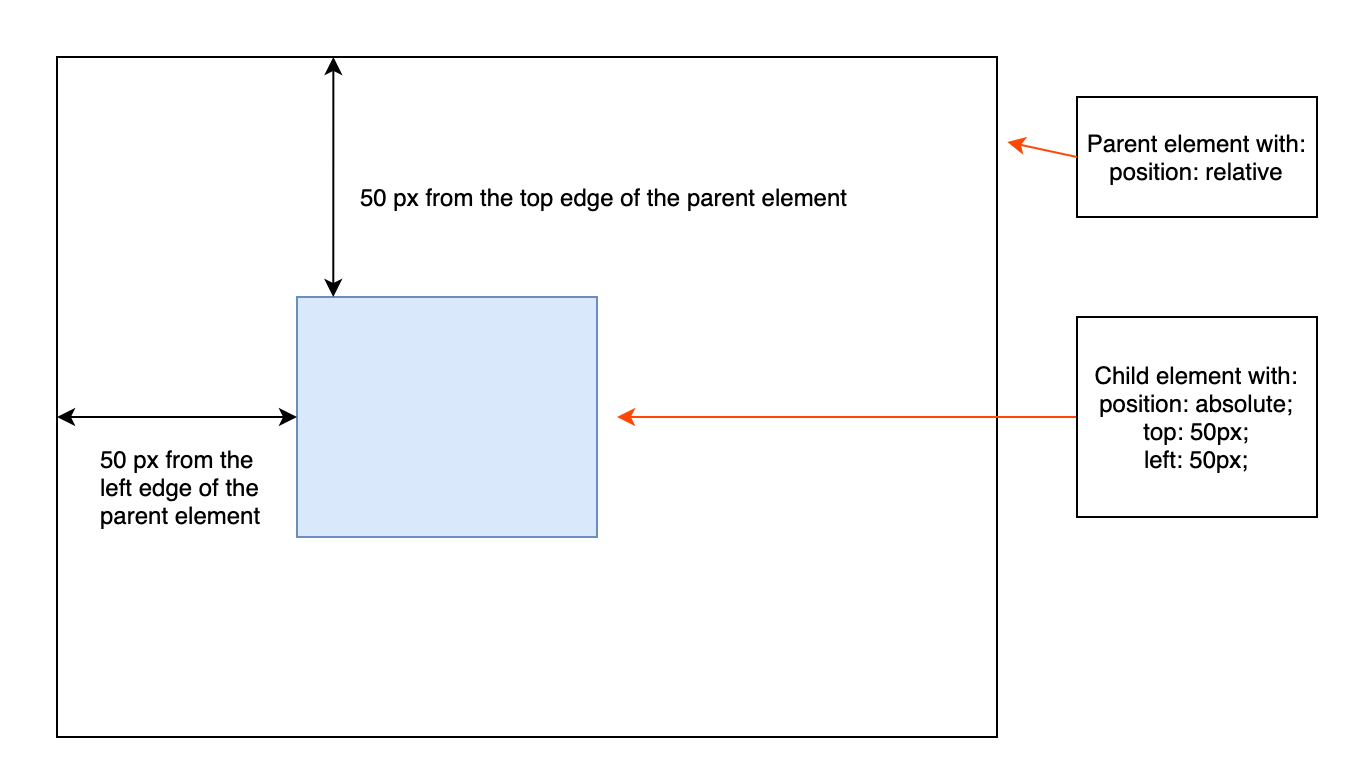
There are a few different ways we can use CSS to position elements in our web pages. Absolute positioning means placing the element in its containing element in a certain location that will stay the same no matter where other elements are placed. We can use absolute positioning to specify exactly where in the document layout we want an element to be placed:
Here's an example of what absolute positioning looks like in CSS:
.parent-element {
position: relative;
}
.child-element {
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
}Note When using
position: absolute, the browser calculates the position using top/left from the closest parent element that has a position specified — that's why in the example, we're specifyingposition: relativefor the parent element. Check out the resources on positioning for more info on this if you're interested!
The work of calculating the absolute positions and creating CSS rules for a bunch of different kitten image elements has been done already. It's your job to use CSS selectors to apply the correct positioning to each of these elements.
Use the
comments in css/place-kitty.css to write the correct selectors to move each
kitty into the wheelbarrow.
- Use the browser developer tools
- Override existing styles
Imagine that you are walking down the street, and you notice that there's a mural that has been painted over with various graffiti tags. In reality, cleaning this up could be a challenging feat; however, in CSS, you have the power to manipulate the DOM with just a line or two of code and to restore the mural to its original look! In this lab, we've created a virtual wall. Using only CSS, how can you remove the tags?
Open 'CSS_Debrief/css-graffiti'
Assuming you have opened the index file in Chrome, Inspect the elements of the graffiti wall in the dev tools by hovering over and clicking on nested elements. Take a close look at what's made available to you in the dev tools pane. You can see which style sheets specific style declarations live in, as well as create new styles on the fly.
Now, make note of the CSS styles used to add graffiti tags (as background images) to the wall.
In the file css/cleanup.css, write selectors that have more specificity
(authority) than those that are showing the graffiti tags.
To remove the tags, use the CSS declaration display:none;. It will change the
elements' previous display property value from display: block to
display: none, which will hide that graffiti.
For example, for "tag-1" the developer tools reveal that the style applying the graffiti here is:
.tag-1 {
background: url(../images/tag-1.png) no-repeat;
z-index: 7;
display: block;
}You'll need to override this by setting its display to display: none; instead.
We can do this by writing a selector statement that is more specific such as:
#wall .tag-1 {
display: none;
}This selects elements with a class of "tag-1" that happen to also be inside an element with an id of "wall". This is more specific, and therefore will override the previous statement and hide the graffiti. For more info on how specificity in CSS works take a look at: [Smashing Magazines What You Need to Know About CSS Specificity][smash]. You can also take advantage of a [Specificity Calculator][spec-calc] to assist with finding and understanding options for overriding styles.
Do not use the CSS !important value!
- Create a responsive web layout
- Make use of the CSS Flex box
Open 'CSS_Debrief/css-responsive-layout'
The Exceptional Realty Group have decided to move into the 21st century and have realised that "mobile-first" development is correct way to develop a website. They have come crawling back to you to develop a simple, responsive, mobile-first website. (dont stress!)
Using @media queries and CSS Flex boxes create a responsive website for mobile users and desktop users. If you want to stretch yourself, try creating one for mobile, tablet, laptop and desktop users if you have time.