io6Library is an IPv6 integrated Library that can easily integrate and manage user applications that use the WIZnet Hardwired Dual TCP/IP Stack Controller ( WIZCHIP ) product family.
io6Library is implemented to manage the code dependent on the user's specific MCU so that the user does not have to perform the porting operation of the io6Library according to the user MCU. (See How to Use for more information)
io6Library can be classified into three types as follows.
-
Reigsters Defintion
- Common Registers : Defines general registers such as network information, mode, interrupt, and so on.
- Socket Registers : Define SOCKET regsiters such as socket mode, socket communication, socket interrupt, and so on.
-
Each WIZCHIP I/O Access function
- Basic I/O function : Basic unit function to access Input/Output through HOST interface (SPI, BUS, etc.) defined by WIZCHIP
- Common Register Access Functions : Function to access Common Register based on Basic I/O Function
- SOCKET Register Access Functions : Function to Access SOCKET Register based on Basic I / O Function
-
WIZCHIP control APIs for user application integration, management, and migration
- SOCKET APIs : Like as BSD SOCKET API, SOCKET APIs provide function set that can be related socket commnuincation
- Extra APIs : It provides functions to support the integration of user applications regardless of WIZCHIP specific Regiter/ Memory, Address Map, Features and so on. : It can be replaced with WIZCHIP I / O Access funcions for the small footprint of the User Application.
For more details, refer to io6Library.chm.
io6Library.chm may not be up to date, so please refer the document made by doxygen program with Doxyfile.dox project. Doxygen program can made the document to chm, html, or pdf if you want to.
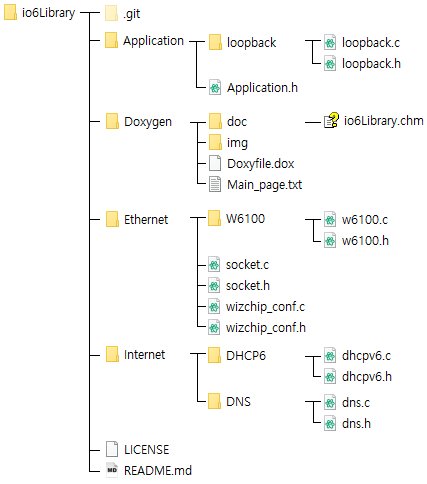
ioLibrary has the same directory structure as the above figure, and the major directory is as follows.
-
- WIZCHIP specific Directory (EX> W6100 - w6100.h, w6100.c)
- SOCKET API : socket.h, socket.c
- ioLibrary Configruation files : wizchip_conf.h, wizchip_conf.c
-
- Protcols for IP configuration (EX> DHCP, DNS)
- Some protocols will be added
-
- Application Socket Mode Definition : Application.h
- Loopback : TCP, UDP Basic Skeleton Code, loopback.h, loopback.c
io6Library users will be able to use it immediately by modifying only a few defintion in wizchip_conf.h. For more information, see How to Use.
Define the type and interface of WIZCHIP defined in wizchip_conf.h, to suit your intended usage.
-
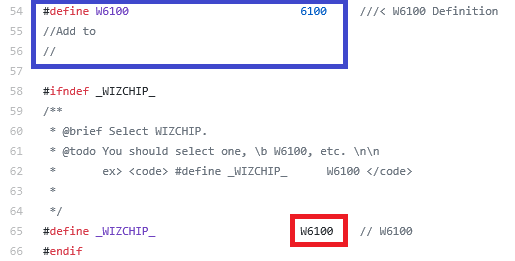
Select the Hardwired Dual TCP/IP Stack Controller to use. In the following figure, Select one of list in the blue box and define the selected it to _WIZCHIP_ like as Red Box.
-
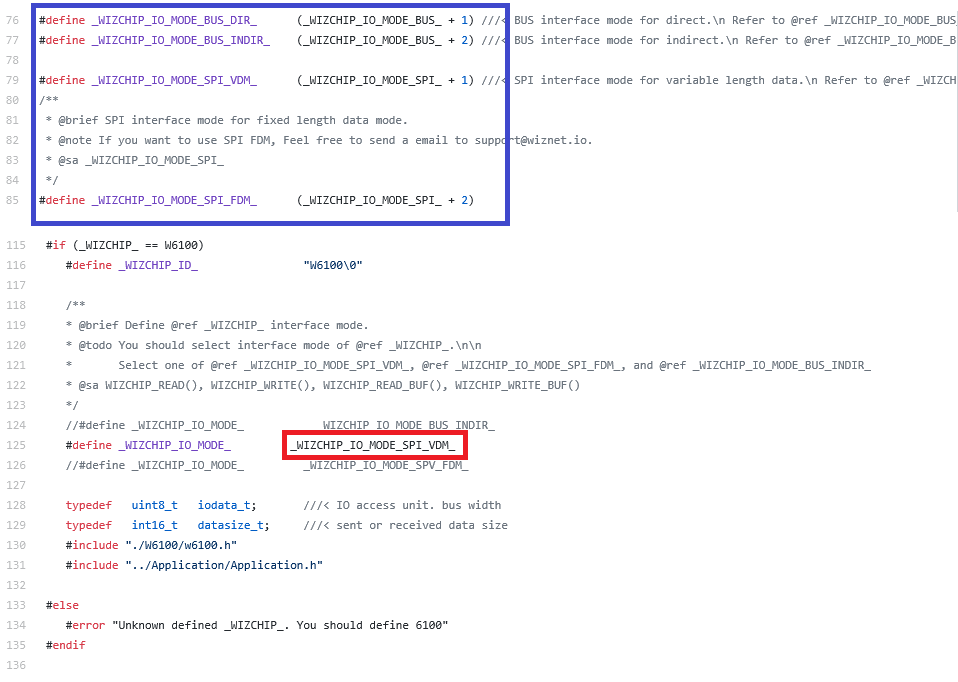
Select the HOST Interface (Parallel Bus, Serial Bus Mode, etc.) that the user will use for WIZCHIP Access. In the following figure, Select one of list in the blue box and define the selected it to _WIZCHIP_IO_MODE_ like as Red Box.
-
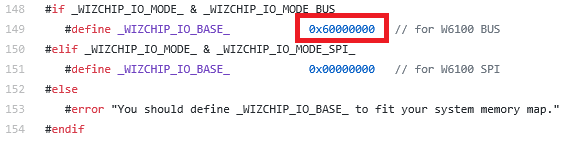
WIZCHIP PHY Access Mode Configuration Like as the following figure, Select one of the two approaches of Ethernet PHY access mode defined in blue box and define it as Red box.
- _PHY_IO_MODE_PHYCR_ : It provides simple control to Ethernet PHY of WIZCHIP thru PHY Command & Status Register such like as PHY Operation Mode and Link Status.
- _PHY__IO_MODE_MII_ : It provides direct control to Ethernet PHY Register of WIZCHIP PHY thru MDC/MDIO signal.
Make the basic Access I/O function by yourself according to your HOST interface. This is because the interface control method differs for each user HOST. So, You should make it.
For example, if you define the following and control WIZCHIP using SPI1 of STM32FXXX
#define _WIZCHIP_IO_MODE_ _WIZCHIP_IO_MODE_SPI_VDM_Create basic unit functions such as WIZCHIP select / deselect, 1byte read / write, critical section enter / exit etc. via SPI interface as follows.
Make your basic I/O access functions such as WIZCHIP select/deselect, 1byte read/write and critical section enter/exit through the SPI interface as shown belows.
- WIZCHIP select/deselect : Function to set/reset any GPIO of STM32FXXX connected with CSn Pin of WIZCHIP
void your_wizchip_enable(void)
{
/* void HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIO_TypeDef *GPIOx, uint16_t GPIO_Pin, GPIO_PinState PinState) */
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOD, GPIO_PIN_7, GPIO_PIN_RESET)
}
void your_wizchip_disable(void)
{
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOD, GPIO_PIN_7, GPIO_PIN_SET)
}- WIZCHIP 1 byte read/write : Function to read and write 1 byte through SPI interface
/* Read 1 byte thru SPI */
uint8_t your_spi_read_byte()
{
uint8_t ret;
/*HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_Receive(SPI_HandleTypeDef *hspi, uint8_t *pData, uint16_t Size, uint32_t Timeout)*/
HAL_SPI_Receive(SPI1, &ret, 1, 1000);
return ret;
}
/* Write 1 byte thru SPI */
void your_spi_wite_byte(uint8_t wd)
{
/* HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_Transmit(SPI_HandleTypeDef *hspi, uint8_t *pData, uint16_t Size, uint32_t Timeout); */
HAL_SPI_Transmit(SPI1, &wd, 1, 1000);
}- WIZCHIP Critical Section Enter/Exit : Function to protect against events such as interupts and task switching while WIZCHIP is accessing
void your_critical_enter(void)
{
__disable_irq();
}
void your_critical_exit(void)
{
__enable_irq();
}- WIZCHIP N bytes read/write Function : It is not mandatory. : But, If you want to use WIZCHIP for high speed access using a peripheral such as DMA, make it as follows. : Even if you do not, you can use N bytes read/write accesses because it is performed by repeating your 1-byte read/write function.
void your_spi_dma_write_buf(uint8_t* pbuf, iodata_t len)
{
/* HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_Transmit_DMA(SPI_HandleTypeDef *hspi, uint8_t *pData, uint16_t Size) */
HAL_SPI_Transmit_DMA(SPI1, pbuf, (uint16_t)len);
}
void your_spi_dma_read_buf(uint8_t* pbuf, iodata_t len)
{
/* HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_SPI_Receive_DMA(SPI_HandleTypeDef *hspi, uint8_t *pData, uint16_t Size) */
HAL_SPI_Receive_DMA(SPI1, pbuf, (uint16_t)len);
}Register the your defined code made in the above examples before WIZCHIP initialization as below.
#include "wizchip_conf.h" // Just only included for using ioLibrary
void main(void)
{
uint16_t chip_id;
wiz_NetTimeout tmp_timeout = 0;
/*
// Intialize your Target System such as SPI, UART, DMA, and etc.
*/
/* Register your basic access function to io6Library */
//WIZCHIP Enable/Disable
reg_wizchip_cs_cbfunc(your_wizchip_enable, your_wizchip_disable);
//WIZCHIP Critical Section
reg_wizchip_cris_cbfunc(your_critical_enter, your_critical_exit);
//WIZCHIP read/write function
reg_wizchip_spi_cbfunc(your_spi_read_byte, your_spi_write_byte, 0, 0);
// If you made DMA function for readign/writting function, you can register as following
// reg_wizchip_spi_cbfunc(your_spi_read_byte, your_spi_write_byte, your_spi_dma_read_buf, your_spi_dma_write_buf);
//
/* For io6Library Read/Write Test */
// Read Test
ctlwizchip(CW_GET_ID,&chip_id); // Check WIZCHIP ID value for read test
if(chip_id != 0x6100) printf("ERROR : HOST I/F READ\r\n") // It is just example for W6100
// Write Test
ctlwizchip(CW_PHY_RESET, 0); // Check phyically PHY Link Led to turn off and then on.
/////////////////////////////////
// Enjoy, WIZCHIP & io6Library //
// Thank you //
/////////////////////////////////
}Examples for io6Library & ioLibrary
You can refer many examples like as http, ftp, and so on related to io6Library & ioLibrary.
| Product Name | Figures |
|---|---|
| W6100-L(Q) |  |
-
WIZnet Homepage : https://www.wiznet.io/
-
WIZCHIP Set : https://www.wiznet.io/product/tcpip-chip/
-
WIZCHIP Modules : https://www.wiznet.io/product/network-module/
-
Q&A, Forum : https://forum.wiznet.io/
-
Simple IPv6 intrduction : https://maker.wiznet.io/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/WoW_part1.pdf
-
Simple W6100 Description : https://maker.wiznet.io/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/WoW_part2.pdf