-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 82
OLED Status Display (Optional)
You can optionally attach an OLED display to monitor the status of RaSCSI. This can be especially useful when running "headless" (without a monitor). The RaSCSI board (akuker version) has the I2C bus available on a header, as well as 3.3v power and ground.

Currently the following OLEDs are known to work:
- MakerFocus SSD1306 128x32 OLED
- MakerFocus SSD1306 128x64 OLED
- AZDelivery 0.91 inch OLED I2C display 128 x 32 pixels
For example, here is the display when RaSCSI is configured with two devices on SCSI ID 1 and 6. This shows when there is no CD-ROM in the virtual drive.
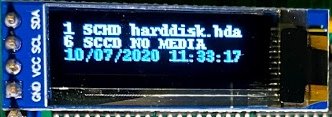
By executing the following command, the ISO image will on the display...
rasctl -i 6 -c insert -f /home/pi/marathon.iso

Ensure that your display matches the pinout on the RaSCSI board:
| Pin | Signal |
| 1 | 5v (not used) |
| 2 | Ground |
| 3 | 3.3v |
| 4 | I2C Clock (SCL) |
| 5 | I2C Data (SDA) |
Important: The Raspberry Pi I2C bus is designed to operate at 3.3v levels. Do not use a 5v OLED and expect it to work!
You will need to solder a pin header on your OLED board (if it didn't come with one). Then, plug it into J4 on the RaSCSI board.
If you're really brave, you could solder the OLED board directly to the RaSCSI board.
You can use the easyinstall.sh script to automatically install the OLED Display software.
Below follows the manual steps to install it. This example uses the system Python3, and not the virtualized venv Python environment (unlike what easyinstall.sh does.)
- Install required packages
sudo apt install python3-pip python3-pil python3-venv libjpeg-dev libpng-dev libopenjp2-7-dev i2c-tools -y
- Enable i2c
sudo raspi-config Select 3 “Interfacing Options” Highlight the “I2C” option and activate “<Select>” reboot
- Verify your screen is connected
i2cdetect -y 1
you should see your module at address 0x3c; if not check your cabling:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f
00: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
10: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
20: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
30: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 3c -- -- --
40: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
50: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
70: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
- Install python libraries
sudo pip3 install adafruit-circuitpython-ssd1306
- Clone the RaSCSI git repository and install RaSCSI (if you haven't already, follow the setup instructions)
- Try running it to verify it works. (You will need the OLED connected and RaSCSI running for this to work)
cd ~/RASCSI/oled_monitor python3 rascsi_oled_monitor.py
- Or, so start with the display rotated 0 degrees and 64px vertical resolution:
python3 rascsi_oled_monitor.py 0 64
Note: The script takes exactly two positional parameters: Rotation and vertical resolution. Rotation can be one of 0 or 180 degrees. Vertical resolution can be one of 32 or 64 pixels. You have to pass both to take effect. Without parameters, the script will default to 180 degrees rotation and 32px vertical resolution.
Copy the systemd service description file using the following command:
sudo cp ~/RASCSI/src/oled_monitor/monitor_rascsi.service /etc/systemd/system/
After you've installed the monitor_rascsi.service file, you'll need to enable it with the following command:
sudo systemctl enable monitor_rascsi.service
Note: If you modify the monitor_rascsi.service file later, you will need to run "sudo systemctl daemon-reload"
You can start the service (without rebooting) using the following command:
sudo systemctl start monitor_rascsi.service
When you run 'systemctl status monitor_rascsi.service', it should be reported that the RaSCSI Monitor is Loaded and Active:
pi@rascsi:~/RASCSI/src/oled_monitor $ sudo systemctl status monitor_rascsi.service
● monitor_rascsi.service - Monitor RaSCSI service
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/monitor_rascsi.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2020-07-10 12:21:08 CDT; 3s ago
Main PID: 14017 (rascsi_oled_mon)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 4915)
Memory: 5.5M
CGroup: /system.slice/monitor_rascsi.service
14017 /usr/bin/python /usr/local/bin/rascsi_oled_monitor.py
Jul 10 12:21:08 rascsi systemd[1]: Started Monitor RaSCSI service.
- Adafruit introduction to SSD1306 OLED displays: https://learn.adafruit.com/ssd1306-oled-displays-with-raspberry-pi-and-beaglebone-black
- Adafruit library used for this python script: https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit_Python_SSD1306
- OLED Schematic: http://github.com/akuker/RASCSI/wiki/images/OLED_Schematic.jpg
- OLED Users Manual: https://drive.google.com/open?id=14A_luFwqvZaKu-PKTfJdWmUZ4T4Wk65
- Home
- Initial Setup
- Documentation
- Companion Apps
- Developer Notes