- README.md
- Pre-requisites
- Getting Started <- you are here
- Advanced Configuration
- Setting Up Allocations
- Setting Up Cost Models
- Tips and Tricks
- Troubleshooting
Run the following commands to clone the repository and set everything up:
git clone https://github.com/StakeSquid/graphprotocol-testnet-docker
cd graphprotocol-testnet-docker
git submodule init
git submodule update
git config --global user.email "[email protected]"
git config --global user.name "Example User"
git branch --set-upstream-to=origin
To enable SSL on your host you should get a domain.
You can use any domain and any regsitrar that allowes you to edit DNS records to point subdomains to your IP address.
For a free option go to myFreenom and find a free domain name. Create a account and complete the registration.
In the last step choose "use dns" and enter the IP address of your server. You can choose up to 12 months for free.
Under "Service > My Domains > Manage Domain > Manage Freenom DNS" you can add more subdomains later.
Create 2 subdomains, named as follows:
index.sld.tld
grafana.sld.tld
Optional, create an additional subdomain for the Indexer Agent GUI:
agent.sld.tld
You need a wallet with a seed phrase that is registered as your operator wallet. This wallet will be the one that makes transactions on behalf of your main wallet (which holds and stakes the GRT).
The operator wallet has limited functionality, and it's recommended to be used for security reasons.
You need a 12-word, or 15-word mnemonic phrase in order for it to work.
To make yourself a mnemonic eth wallet you can go to this website, select ETH from the dropdown and press generate.
You get a seed phrase in the input field labeled BIP39 Mnemonic.
You can find your address, public key and private key in the first row of the table if you scroll down the page in the section with the heading "Derived Addresses".
Make sure you save the mnemonic, private key and the wallet address somewhere safe.
If you need, you can import the wallet using the private key into Metamask
Edit the file called .env and add your values to the following envs:
[email protected]
INDEX_HOST=index.sld.tld
GRAFANA_HOST=grafana.sld.tld
AGENT_GUI_HOST=agent.sld.tld
ADMIN_USER=your_user
ADMIN_PASSWORD=your_password
DB_USER=your_db_user
DB_PASS=your_db_password
GRAPH_NODE_DB_NAME=your_graphnode_db_name
AGENT_DB_NAME=your_agent_db_name
CHAIN_0_NAME="network-name"
CHAIN_0_RPC="http://ip:port"
TXN_RPC="http://ip:port"
OPERATOR_SEED_PHRASE="12 or 15 word mnemonic"
STAKING_WALLET_ADDRESS=0xAdDreSs
GEO_COORDINATES='69.420 69.420'
INDEXER_AGENT_OFFCHAIN_SUBGRAPHS=""
#Optional env vars depending on which services you use:
###Indexer agent GUI:
#AGENT_GUI_HOST=agent.sld.tld
#NEXTAUTH_SECRET=$(openssl rand -base64 32)
Required env vars:
EMAIL- only used as contact to create SSL certificates. Usually it doesn't receive any emails but is required by the certificate issuer.INDEX_HOST- your indexer public endpoint. The gateway will be sending queries to this endpoint.GRAFANA_HOST- your Grafana dashboard for indexer stack monitoring.ADMIN_USERandADMIN_PASSWORD- will be used by Grafana, Prometheus and AlertManager.DB_USERandDB_PASS- will be used for initializing the PostgreSQL Databases (both index/query DB and indexer agent/service DB).GRAPH_NODE_DB_NAME- the name of the database used by the Index/Query nodes.AGENT_DB_NAME- the name of the database used by the Indexer agent/service nodes.CHAIN_0_NAME- the name of the network that you want to indexCHAIN_0_RPC- your RPCs (archive nodes) used by the index nodes.TXN_RPC- your Goerli ETH RPC used by Indexer agent/service nodes. This can be a fast/full/archive node, up to you! Please note that using Erigon as the TXN_RPC has proven unreliable by some indexers.OPERATOR_SEED_PHRASE- the 12/15 word mnemonic that you generated earlier. Will be used by the Agent/Service to send transactions (open/close allocations, etc)STAKING_WALLET_ADDRESS- the address (0x...) that you staked your GRT with, ideally living on an entirely different mnemonic phrase than your Operator Wallet.GEO_COORDINATESof your server - you can search for an ip location website and check your server exact coordinates.
Optional env vars:
AGENT_GUI_HOST- your Agent GUI endpoint for controlling the Agent and allocations remotelyNEXTAUTH_SECRET- used by the Agent GUI to salt your password
Note: If you want to use any of the optional env vars, you need to copy the line that you want to enable above the last line, and uncomment it.
To add support for multiple chains, you need to edit the config.tmpl file yourself.
For each chain you wish to support, you need to add the corresponding provider line.
Example:
By default, we only support one chain:
[chains.${CHAIN_0_NAME}]
shard = "primary"
provider = [ { label = "${CHAIN_0_NAME}", url = "${CHAIN_0_RPC}", features = ["archive", "traces"] } ]To add another one, simply duplicate this, and increment the chain number:
[chains.${CHAIN_0_NAME}]
shard = "primary"
provider = [ { label = "${CHAIN_0_NAME}", url = "${CHAIN_0_RPC}", features = ["archive", "traces"] } ]
[chains.${CHAIN_1_NAME}]
shard = "primary"
provider = [ { label = "${CHAIN_1_NAME}", url = "${CHAIN_1_RPC}", features = ["archive", "traces"] } ]After this, all you have to do is to include in the .env file your new environment variables.
Example:
CHAIN_0_NAME="gnosis"
CHAIN_0_RPC="http://ip:port"
CHAIN_1_NAME="matic"
CHAIN_1_RPC="http://ip:port"
Additional configs and details:
- Agent/Service - networks.md
- Graph-Node - environment-variables.md
Graphnode Stack:
- Index Node
- Query Node
- Postgres Database for the Graphnode Stack
Indexer Stack:
- Indexer Agent
- Indexer Service
- Indexer CLI
- Nginx Proxy
- Nginx SSL
- Posgres Database for the Indexer Stack
Autoagora Stack:
- Indexer Service
- Rabbitmq
- Autoagora Processor
- Autoagora
- Nginx Proxy
- Nginx SSL
- Posgres Database for the Indexer Stack
- Posgres Database for the Autoagora Stack
Monitoring Stack:
- Prometheus
- Grafana
- Alertmanager
- Node exporter
- Cadvisor
- Pushgateway
- Nginx Proxy
- Nginx SSL
Optional Stack:
- Poifier client
- Indexer Agent GUI
- Nginx Proxy
- Nginx SSL
Start by picking up the right stack that you want to spin up.
There are several start files used to spin up different components.
I would recommend to start with:
bash start-essential
Be aware that initially it takes several minutes to download and run all the containers (especially the cli container, that one takes a while to build), so be patient. :)
Subsequent restarts will be much faster.
In case something goes wrong, find the problem, edit the variables, and add --force-recreate at the end of the command, plus the container you want to recreate:
bash start-essential --force-recreate <container_name>
Or to recreate the entire stack:
bash start-essential --force-recreate
start-essential - starts up the graphnode, indexer and monitoring stack - all you need to get up and running on the network
start-optional - starts up the optional stack (for components, read above)
start-autoagora - starts up the autoagora stack (for components, read above)
start-all - starts up the entire stack
To verify that everything is up and running, you need to:
docker ps
And look for containers that are crash looping - you will notice restarting and a countdown - that means those containers are not working properly.
To further debug, try looking for the container logs and see what they say. More information in the troubleshooting section.
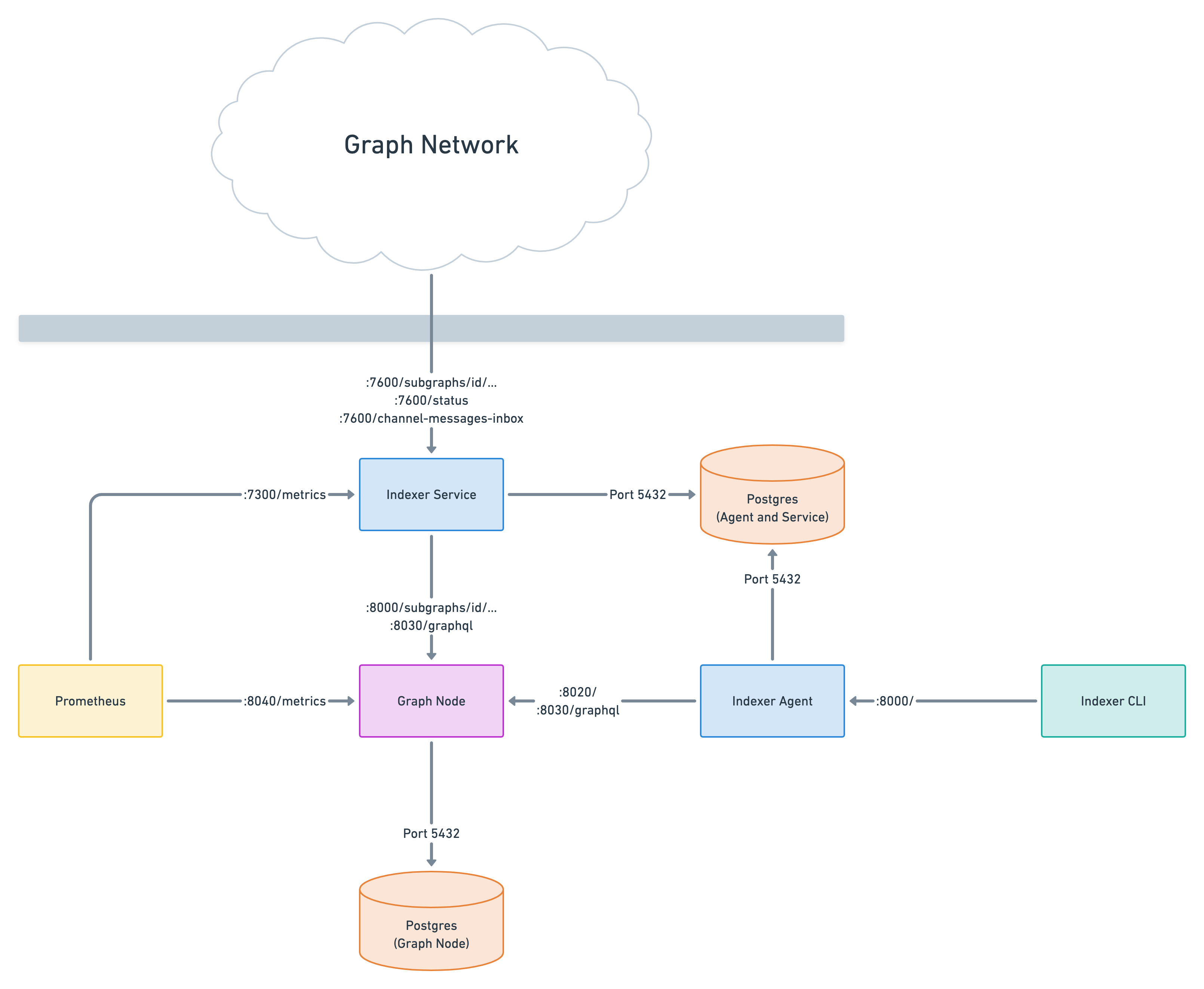
The following ports are being used by all components by default. Also listed are the CLI flags and environment variables that can be used to change the ports.
| Port | Purpose | Routes | CLI argument | Environment variable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8000 | GraphQL HTTP server (for subgraph queries) | /subgraphs/id/... subgraphs/name/.../... |
--http-port |
- |
| 8001 | GraphQL WS (for subgraph subscriptions) | /subgraphs/id/... subgraphs/name/.../... |
--ws-port |
- |
| 8020 | JSON-RPC (for managing deployments) | / |
--admin-port |
- |
| 8030 | Subgraph indexing status API | /graphql |
--index-node-port |
- |
| 8040 | Prometheus metrics | /metrics |
--metrics-port |
- |
| Port | Purpose | Routes | CLI argument | Environment variable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7600 | GraphQL HTTP server (for paid subgraph queries) | /subgraphs/id/... /status |
--port |
INDEXER_SERVICE_PORT |
| 7300 | Prometheus metrics | /metrics |
- | - |
| Port | Purpose | Routes | CLI argument | Environment variable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8000 | Indexer management API (for graph indexer) |
/ |
--indexer-management-port |
INDEXER_AGENT_INDEXER_MANAGEMENT_PORT |
To update those repos to the latest version just do the following command occasionally.
git submodule update
To use qlog or agora execute the runqlog or runagora scripts in the root of the repository.
./runagora --help
./runqlog --help
This will use the compiled qlog tool and extract queries since yesterday or 5 hours ago and store them to the query-logs folder.
./extract_queries_since yesterday
./extract_queries_since "5 hours ago"
To make journald logs persistent across restarts you need to create a folder for the logs to store in like this:
mkdir -p /var/log/journal
The general procedure is the following:
cd <project-folder>
git fetch
git pull
This will update the scripts from the repository.
To upgrade the containers:
bash start --force-recreate
To update Agora or Qlog repos to the latest version just do the following command occasionally:
git submodule update
To use qlog or agora execute the runqlog or runagora scripts in the root of the repository.
./runagora --help
./runqlog --help