| comments | difficulty | edit_url |
|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
给定一个有环链表,实现一个算法返回环路的开头节点。
有环链表的定义:在链表中某个节点的next元素指向在它前面出现过的节点,则表明该链表存在环路。
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:tail connects to node index 1
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:tail connects to node index 0
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:no cycle
解释:链表中没有环。
进阶:
你是否可以不用额外空间解决此题?
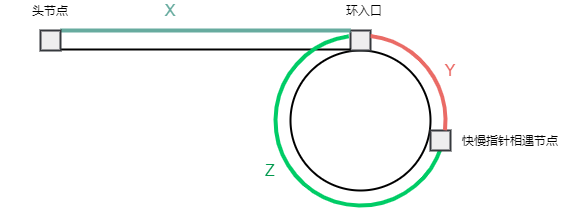
我们先利用快慢指针判断链表是否有环,如果有环的话,快慢指针一定会相遇,且相遇的节点一定在环中。
如果没有环,快指针会先到达链表尾部,直接返回 null 即可。
如果有环,我们再定义一个答案指针
为什么这样能找到环的入口节点呢?
我们不妨假设链表头节点到环入口的距离为
由于快指针速度是慢指针的
也即是说,如果我们定义一个答案指针
时间复杂度
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def detectCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
fast = slow = head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if slow == fast:
ans = head
while ans != slow:
ans = ans.next
slow = slow.next
return ans/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
ListNode ans = head;
while (ans != slow) {
ans = ans.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return ans;
}
}
return null;
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* detectCycle(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while (fast && fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast) {
ListNode* ans = head;
while (ans != slow) {
ans = ans->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return ans;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func detectCycle(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
fast, slow := head, head
for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
slow = slow.Next
fast = fast.Next.Next
if slow == fast {
ans := head
for ans != slow {
ans = ans.Next
slow = slow.Next
}
return ans
}
}
return nil
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function detectCycle(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
let [slow, fast] = [head, head];
while (fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow === fast) {
let ans = head;
while (ans !== slow) {
ans = ans.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return ans;
}
}
return null;
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var detectCycle = function (head) {
let [slow, fast] = [head, head];
while (fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow === fast) {
let ans = head;
while (ans !== slow) {
ans = ans.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return ans;
}
}
return null;
};/*
* public class ListNode {
* var val: Int
* var next: ListNode?
* init(_ x: Int) {
* self.val = x
* self.next = nil
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
func detectCycle(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
var slow = head
var fast = head
while fast != nil && fast?.next != nil {
slow = slow?.next
fast = fast?.next?.next
if slow === fast {
var ans = head
while ans !== slow {
ans = ans?.next
slow = slow?.next
}
return ans
}
}
return nil
}
}