链表相关的核心点
- null/nil 异常处理
- dummy node 哑巴节点
- 快慢指针
- 插入一个节点到排序链表
- 从一个链表中移除一个节点
- 翻转链表
- 合并两个链表
- 找到链表的中间节点
给定一个排序链表,删除所有重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次。
//非递归
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *cur = head;
while(cur != NULL && cur->next != NULL){
if(cur->val == cur->next->val){
cur->next = cur->next->next;
}else{
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return head;
}
};
//递归
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head;
head->next = deleteDuplicates(head->next);
return head->val == head->next->val ? head->next : head;
}
};
给定一个排序链表,删除所有含有重复数字的节点,只保留原始链表中 没有重复出现的数字。
思路:链表头结点可能被删除,所以用 dummy node 辅助删除
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head;
ListNode *dump = new ListNode(-1);
dump->next = head;
head = dump;
int temp;
while(head->next != NULL && head->next->next != NULL){
if(head->next->val == head->next->next->val){
temp = head->next->val;
while(head->next != NULL && head->next->val == temp){
head->next = head->next->next;
}
}else{
head = head->next;
}
}
return dump->next;
}
};注意点
- A->B->C 删除 B,A.next = C
- 删除用一个 Dummy Node 节点辅助(允许头节点可变)
- 访问 X.next 、X.value 一定要保证 X != nil
反转一个单链表。
思路:用一个 prev 节点保存向前指针,temp 保存向后的临时指针
//迭代
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* pre = NULL;
ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur != NULL)
{
ListNode *lat = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = lat;
}
return pre;
}
//递归
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL){
return head;
}else{
ListNode *h = reverseList(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = NULL;
return h;
}
}反转从位置 m 到 n 的链表。请使用一趟扫描完成反转。
思路:先遍历到 m 处,翻转,再拼接后续,注意指针处理
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) {
if(head == NULL) return head;
ListNode *dummp = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode *pre = dummp;
dummp->next = head;
for(int i = 0; i < m - 1; i++){
pre = pre->next;
}
//pre->next <=> pre->next->next
ListNode *cur = pre->next;
for(int i = m; i < n; i++){
ListNode *temp = cur->next;
cur->next = temp->next;
temp->next = pre->next;
pre->next = temp;
}
return dummp->next;
}
};将两个升序链表合并为一个新的升序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
思路:通过 dummy node 链表,连接各个元素
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
if(l1 == nullptr) return l2;
if(l2 == nullptr) return l1;
if(l1->val <= l2->val){
l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next, l2);
return l1;
}else{
l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2->next);
return l2;
}
}
};给定一个链表和一个特定值 x,对链表进行分隔,使得所有小于 x 的节点都在大于或等于 x 的节点之前。
思路:将大于 x 的节点,放到另外一个链表,最后连接这两个链表
ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {
if(!head) return head;
ListNode *beforeNode = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode *before = beforeNode;
ListNode *afterNode = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode *after = afterNode;
while(head != NULL){
if(head->val < x){
before->next = head;
before = before->next;
}else{
after->next = head;
after = after->next;
}
head = head->next;
}
after->next = NULL;
before->next = afterNode->next;
return beforeNode->next;
}哑巴节点使用场景
当头节点不确定的时候,使用哑巴节点
在 O(n log n) 时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序。
思路:归并排序,找中点和合并操作
//思路:归并排序,找中点和合并操作
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head;
ListNode *slow = head;
ListNode *fast = head->next;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
ListNode *middleNode = slow->next;
slow->next = NULL;
ListNode *left = sortList(head);
ListNode *right = sortList(middleNode);
return mergeSortList(left, right);
}
ListNode *mergeSortList(ListNode *left, ListNode *right){
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode *cur = dummy;
while(left != NULL && right != NULL){
if(left->val < right->val){
cur->next = left;
left = left->next;
}else{
cur->next = right;
right = right->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
while(left != NULL){
cur->next = left;
cur = cur->next;
left = left->next;
}
while(right != NULL){
cur->next = right;
cur = cur->next;
right = right->next;
}
return dummy->next;
}注意点
- 快慢指针 判断 fast 及 fast.Next 是否为 nil 值
- 递归 mergeSort 需要断开中间节点
- 递归返回条件为 head 为 nil 或者 head.Next 为 nil
给定一个单链表 L:L→L→…→L__n→L 将其重新排列后变为: L→L__n→L→L__n→L→L__n→…
思路:找到中点断开,翻转后面部分,然后合并前后两个链表
// 思路:找到中点断开,翻转后面部分,然后合并前后两个链表
void reorderList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr) return;
ListNode *slow = head;
ListNode *fast = head->next;
while(fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
ListNode *middle = slow->next;
ListNode *right = reverseList(slow->next);
slow->next = nullptr;
head = mergeTwoList(head, right);
}
ListNode *mergeTwoList(ListNode *left, ListNode *right){
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode *cur = dummy;
bool flag = true;
while(left != nullptr && right != nullptr){
if(flag){
cur->next = left;
left = left->next;
}else{
cur->next = right;
right = right->next;
}
flag = !flag;
cur = cur->next;
}
while(left != nullptr){
cur->next = left;
cur = cur->next;
left = left->next;
}
while(right != nullptr){
cur->next = right;
cur = cur->next;
right = right->next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
ListNode *reverseList(ListNode *root){
ListNode *pre = nullptr;
ListNode *cur = root;
while(cur != nullptr){
ListNode *temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
思路:快慢指针,快慢指针相同则有环,证明:如果有环每走一步快慢指针距离会减 1
// 思路:快慢指针 快慢指针相同则有环,证明:如果有环每走一步快慢指针距离会减1
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(head == NULL) return false;
ListNode *slow = head;
ListNode *fast = head->next;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){
if(fast == slow) return true;
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return false;
}给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回
null。
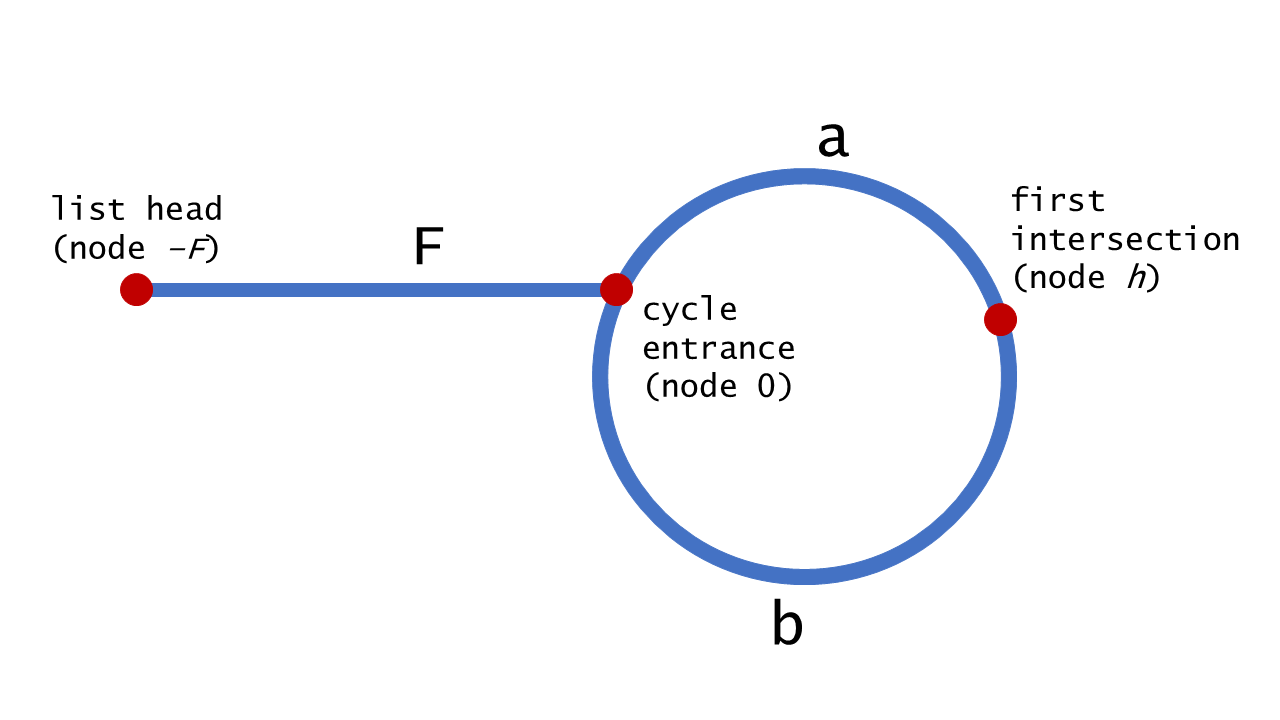
思路:快慢指针,快慢相遇之后,慢指针回到头,快慢指针步调一致一起移动,相遇点即为入环点
// 思路:快慢指针,快慢相遇之后,慢指针回到头,快慢指针步调一致一起移动,相遇点即为入环点
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(head == NULL) return head;
ListNode *fast = head->next;
ListNode *slow = head;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){
if(fast == slow){ // 第一次相遇,slow回到head, fast从相遇点下一个节点开始走
slow = head;
fast = fast->next;
while(fast != slow){ // 第二次相遇的地方就是环的入口
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return NULL;
} 坑点
- 指针比较时直接比较对象,不要用值比较,链表中有可能存在重复值情况
- 第一次相交后,快指针需要从下一个节点开始和头指针一起匀速移动
另外一种方式是 fast=head,slow=head
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(head == NULL) return head;
ListNode *fast = head;
ListNode *slow = head;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(fast == slow){ // 指针重新从头开始移动
fast = head;
while(fast != slow){ // 第二次相遇的地方就是环的入口
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return NULL;
}这两种方式不同点在于,一般用 fast=head.Next 较多,因为这样可以知道中点的上一个节点,可以用来删除等操作。
- fast 如果初始化为 head.Next 则中点在 slow.Next
- fast 初始化为 head,则中点在 slow
请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL) return true;
// fast如果初始化为head.Next则中点在slow.Next
// fast初始化为head,则中点在slow
ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head->next;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
ListNode *tail = reverseList(slow->next);
// 断开两个链表(需要用到中点前一个节点)
slow->next = NULL;
while(head != NULL && tail != NULL){
if(head->val != tail->val) return false;
head = head->next;
tail = tail->next;
}
return true;
}
ListNode *reverseList(ListNode *head){
if(head == NULL) return head;
ListNode *pre = NULL;
while(head != NULL){
ListNode *temp = head->next;
head->next = pre;
pre = head;
head = temp;
}
return pre;
}给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。 要求返回这个链表的 深拷贝。
思路:1、hash 表存储指针,2、复制节点跟在原节点后面
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if(head == NULL) return head;
// 复制节点,紧挨到到后面
// 1->2->3 ==> 1->1'->2->2'->3->3'
Node *cur = head;
while(cur != NULL){
Node *clone = new Node(cur->val);
clone->next = cur->next;
cur->next = clone;
cur = clone->next;
}
// 处理random指针
cur = head;
while(cur != NULL){
cur->next->random = (cur->random != NULL) ? cur->random->next : NULL;
cur = cur->next->next;
}
// 分离两个链表
cur = head;
Node *cloneRandom = cur->next;
while(cur != NULL && cur->next != NULL){
Node *temp = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
cur = temp;
}
// 原始链表头:head 1->2->3
// 克隆的链表头:cloneHead 1'->2'->3'
return cloneRandom;
}链表必须要掌握的一些点,通过下面练习题,基本大部分的链表类的题目都是手到擒来~
- null/nil 异常处理
- dummy node 哑巴节点
- 快慢指针
- 插入一个节点到排序链表
- 从一个链表中移除一个节点
- 翻转链表
- 合并两个链表
- 找到链表的中间节点