크루스칼 알고리즘은 프림 알고리즘과 마찬가지로 MST(Mininum Spannig Tree)를 만들 때 사용하는 알고리즘이다.
이 알고리즘 역시 탐욕 알고리즘(Greedy Algorithm) 의 기반을 두고 있다.
이 알고리즘은 프림 알고리즘보다 더 간단하다.
모든 간선 중에 가장 cost가 적은 것을 하나씩 고르고 그 선택된 간선에 연결된 정점들이 사이클을 이루는지만 확인해주면 된다.
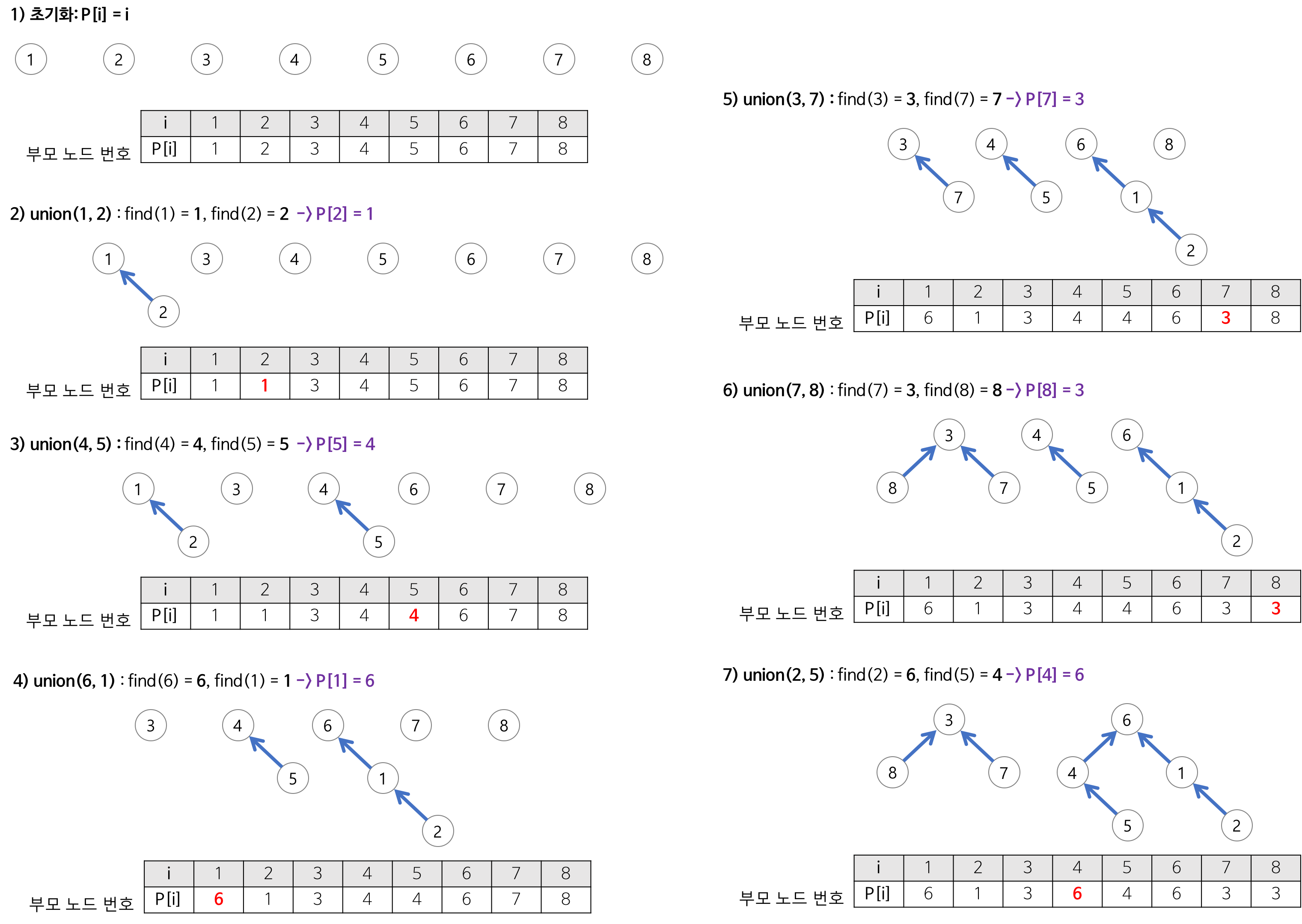
그 사이클 여부를 판단하기 위해서 사용하는 것이 Union- Find 인데 아래와 같은 알고리즘을 타게 된다.
-
모든 정점의 부모가 자기 자신이라고 초기화 한다.
-
그리고 두 정점을 union 하게 되면 한 정점의 부모가 또 다른 정점이 되게 되는 것이다.
-
find는 연결된 루트 노드의 번호를 찾게 된다.
이걸 코드로 구현하면
//두 집합을 묶는 과정
public void union(int x, int y){
int rootX = find(x); //두점의 루트를 찾는다.
int rootY = find(y);
if(rootX != rootY){ // 루트가 다르면 한 정점의 루트를 다른 정점에 연결한다.
parent[rootX] = y;
}
}
//루트를 찾는 과정
public int find(int x) {
if(x == parent[x]) // 본인이 루트이면 본인 리턴
return x;
parent[x] = find(parent[x]); //아닐 경우 루트를 재귀로 찾는다.
return parent[x];
}이 알고리즘을 이용해서 크루스칼을 구현할 수 있는데
private int[] parent;
public int solution(int n, int[][] costs) { //cost[i][0]: 시작점, cost[i][1]: 끝점, cost[i][2]: 비용
parent = new int[n]; //parent 초기화
PriorityQueue<int[]> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparing(o -> o[2])); // 비용이 가장 낮은 것을 뱉도록 만든 우선순위 큐
for(int i = 0; i< costs.length; i++) {
priorityQueue.add(costs[i]); //큐에 간선들을 넣어준다.
}
for(int i = 0; i< n; i++) {
parent[i] = i; //각 노드에 대해서 자신의 부모를 자신으로 초기화
}
int answer = 0;
for(int i = 0; i< costs.length; i++) {
int[] node = priorityQueue.poll(); //queue에서 cost 낮은 순으로 하나씩 꺼낸 후
int start = node[0];
int end = node[1];
int cost = node[2];
int rootA = find(start); // 두점의 루트를 찾는다.
int rootB = find(end);
if(rootA == rootB) continue; // 루트가 같으면 싸이클이 생기므로 pass
union(start,end); // 다르면 두개를 union해주고 answer에 코스트를 더해준다.
answer += cost;
}
return answer;
}