DOM 模型中,提供了 N 多高度、宽度相关的属性,例如:clientHeight, scrollHeight, innerHeight, outerHeight, screen.height....
本文就来捋一捋这些繁杂的属性。
首先,分清楚 window 和 document 的区别:
window是指浏览器的窗口。document是指 HTML 文档。
首先来看 offsetHeight, MDN 上定义为:HTMLElement.offsetHeight 是一个只读属性,它的值为元素的像素高度,该高度包括元素的垂直内边距和边框。
来看两个例子:
所有的示例可见 示例
- 例子1:
<style>
#offset1 {
margin: 10px;
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 20px;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="offset1"></div>
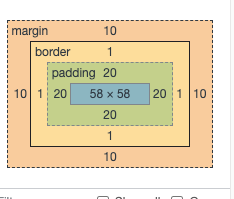
</body>此时元素 offset1.offsetHeight 为 1 2 + 20 2 + 100 = 142, 分别是上下 border, 上下 padding, 自身高度 height.
- 例子 2, border-box 的情况下:
<style>
#offset2 {
margin: 10px;
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 20px;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="offset2"></div>
</body>此时元素 offset2.offsetHeight 为 100. 这是因为 border-box 将其上下 border + 上下 padding + 自身高度 height 的和 设置成 100px, 导致自身 height 被压缩到 58px.