在上一篇文章中,简要介绍了孪生网络(siamese network)的基本原理及应用实战,这里再使用孪生网络来进行文本相似度计算。
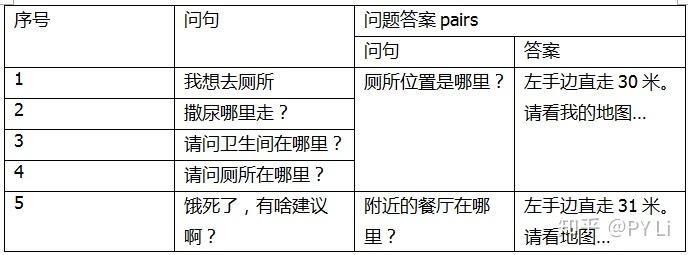
文本的相似性计算是“文本匹配”的一种特殊情况。一般来说,文本相似度计算任务的输入,是两篇文档,比如下表的前两个句子;输出是两篇文档的相似程度,通常用[0,1]区间内的小数来表示。
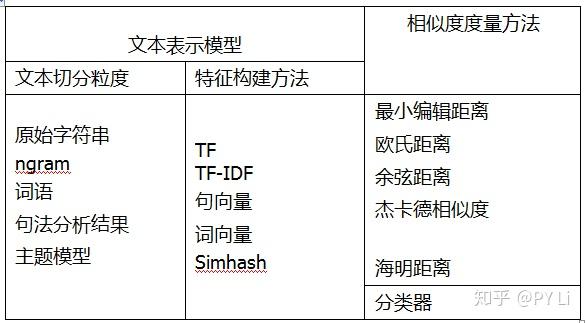
文本相似度计算在许多NLP任务中都有用到,比如问答系统,通常用户给定一个问题,需要去答案库中匹配一个答案。此时,可以直接匹配到一个答案,也可以先匹配相似的问题,再给出问题的标准答案。那么该如何计算文本相似度呢?文本相似度计算方法有2个关键组件,即文本表示模型和相似度度量方法,如下表。前者负责将文本表示为计算机可以计算的数值向量,也就是提供特征;后者负责基于前面得到的数值向量计算文本之间的相似度。从文本表示模型和相似度度量方法中选择合适的,就可以组合出一个文本相似度计算方案。
上述文本相似度计算方法都是先把给定文档通过某种向量化方法表示成文档向量,然后使用指定的相似度计算方法计算两个文本的相似度(距离)。这些方法都是无监督方法,比较简单、计算高效,不需要标注语料,特征工程或者参数估计可以使用很大的数据;很多方法对语言的依赖比较小,可以应对多语种混杂的场景;距离计算环节复杂度较低。
此外,也可以使用有监督学习方法来计算文本相似度。就是用朴素贝叶斯分类器或者神经网络模型之类的有监督模型来判断文本相似性或者计算相似度。这类方法要求有一定数量的标注语料,构建的代价比较高;由于训练语料通常无法做得很大,模型的泛化性不够,实际用起来会有点麻烦;距离计算环节的复杂度会比较高。
这里只是简要介绍下文本相似度的基本原理和方法,详细的知识可以参考这篇文章。接下来就使用孪生网络来实现文本相似度算法。
数据使用的是拍拍贷智慧金融研究院主办的第三届“魔镜杯”中的数据,拍拍贷提供智能客服聊天机器人真实数据,以自然语言处理和文本挖掘技术为主要探索对象,希望比赛选手能利用这些资源开发一种算法,提高智能客服的识别能力和服务质量。
本次比赛使用了脱敏数据,所有原始文本信息都被编码成单字ID序列和词语ID序列,并提供由google word2vec训练的300维的word_embedding和char_embedding。训练数据包含3列,label, q1, q2,其中q1和q2表示要判断的两个问题,label=1表示是相同的问题,label=0表示不同的问题。比赛要求参赛选手预测测试数据中的每一对问题是否是同一个意思。
具体数据请查看第三届魔镜杯大赛数据介绍
训练数据 测试数据 问题 预训练的字符向量 预训练的词向量把数据处理成训练需要的格式
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import os
import math
def sentences_to_indices(X, word_to_index, max_len):
"""
把字符串数组转换为字符数值索引数组
:param X:string 数组
:param word_to_index:
:param max_len:最长的序列长度
:return:
"""
m = X.shape[0]
X_indices = np.zeros((m, max_len))
for i in range(m):
# split字符串
sentence_words = X[i].split(" ")
for j, w in enumerate(sentence_words):
if j >= max_len:
break
X_indices[i, j] = word_to_index[w]
return X_indices
def load_dataset(data_dir, max_seq_len, embed_dim, word_level=True):
"""
读取数据,对数据进行预处理,并生成embed_matrix
:param data_dir:数据目录
:param max_seq_len:
:param embed_dim:词向量维度
:param word_level:
:return:
"""
question_path = os.path.join(data_dir, "question.csv")
train_path = os.path.join(data_dir, "train.csv")
if word_level:
embed_path = os.path.join(data_dir, "word_embed.txt") # 词向量
else:
embed_path = os.path.join(data_dir, "char_embed.txt") # 字符向量
# 读取数据
question = pd.read_csv(question_path)
train = pd.read_csv(train_path)
# 把train里面的问题id匹配到句子
train = pd.merge(train, question, left_on=["q1"], right_on=["qid"], how="left") # 匹配第一个问题
train = pd.merge(train, question, left_on=["q2"], right_on=["qid"], how="left") # 匹配第二个问题
if word_level:
train = train[["label", "words_x", "words_y"]]
else:
train = train[["label", "chars_x", "chars_y"]]
train.columns = ["label", "q1", "q2"]
word_to_vec_map = pd.read_csv(embed_path, sep=" ", header=None, index_col=0)
word = word_to_vec_map.index.values
# word2id,id2word
word_to_index = dict([(word[i], i+1) for i in range(len(word))])
index_to_word = dict([(i+1, word[i]) for i in range(len(word))])
train_q1_indices = sentences_to_indices(train.q1.values, word_to_index, max_seq_len)
train_q2_indices = sentences_to_indices(train.q2.values, word_to_index, max_seq_len)
label = train.label.values
vocab_len = len(word_to_index)+1
embed_matrix = np.zeros((vocab_len, embed_dim))
for word, index in word_to_index.items():
embed_matrix[index, :] = word_to_vec_map.loc[word].values
return train_q1_indices, train_q2_indices, label, embed_matrix, word_to_index, index_to_word
def load_test_data(data_dir, max_seq_len, word_level=True):
"""
读取测试数据
:param max_seq_len:
:param word_level:
:return:
"""
question_path = os.path.join(data_dir, "question.csv")
test_path = os.path.join(data_dir, "test.csv")
if word_level:
embed_path = os.path.join(data_dir, "word_embed.txt")
else:
embed_path = os.path.join(data_dir, "char_embed.txt")
# 读取数据
question = pd.read_csv(question_path)
test = pd.read_csv(test_path)
test = pd.merge(test, question, left_on=["q1"], right_on=["qid"], how="left")
test = pd.merge(test, question, left_on=["q2"], right_on=["qid"], how="left")
if word_level:
test = test[["words_x", "words_y"]]
else:
test = test[["chars_x", "chars_y"]]
test.columns = ["q1", "q2"]
word_to_vec_map = pd.read_csv(embed_path, sep=" ", header=None, index_col=0)
word = word_to_vec_map.index.values
# word2id,id2word
word_to_index = dict([(word[i], i+1) for i in range(len(word))])
index_to_word = dict([(i+1, word[i]) for i in range(len(word))])
test_q1_indices = sentences_to_indices(test.q1.values, word_to_index, max_seq_len)
test_q2_indices = sentences_to_indices(test.q2.values, word_to_index, max_seq_len)
return test_q1_indices, test_q2_indices使用LSTM作为基础网络组件
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
np.random.seed(0)
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Embedding, GaussianNoise, \
Input, Dropout, LSTM, Activation, BatchNormalization, concatenate, Subtract, Dot, Multiply, Bidirectional, Lambda
from tensorflow.keras.initializers import glorot_uniform
from tensorflow.keras import optimizers
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow.keras.callbacks as kcallbacks
np.random.seed(1)
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
MAX_SEQUENCE_LENGTH = 15 # 20 for character level and 15 for word level
EMBEDDING_DIM = 300
lstm_num = 64
lstm_drop = 0.5
BATCH_SIZE = 100
def trainLSTM(train_q1, train_q2, train_label, embed_matrix):
question1 = Input(shape=(MAX_SEQUENCE_LENGTH,), batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
question2 = Input(shape=(MAX_SEQUENCE_LENGTH,), batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
embed_layer = Embedding(embed_matrix.shape[0], EMBEDDING_DIM,weights=[embed_matrix]) #
q1_embed = embed_layer(question1)
q2_embed = embed_layer(question2)
shared_lstm1 = LSTM(lstm_num, return_sequences=True)
shared_lstm2 = LSTM(lstm_num)
q1 = shared_lstm1(q1_embed)
q1 = Dropout(lstm_drop)(q1)
q1 = BatchNormalization()(q1)
q1 = shared_lstm2(q1)
q2 = shared_lstm1(q2_embed)
q2 = Dropout(lstm_drop)(q2)
q2 = BatchNormalization()(q2)
q2 = shared_lstm2(q2)
# 求distance (batch_size,lstm_num)
d = Subtract()([q1, q2])
distance = Multiply()([d, d])
# 求angle (batch_size,lstm_num)
angle = Multiply()([q1, q2])
merged = concatenate([distance, angle])
merged = Dropout(0.3)(merged)
merged = BatchNormalization()(merged)
merged = Dense(256, activation="relu")(merged)
merged = Dropout(0.3)(merged)
merged = BatchNormalization()(merged)
merged = Dense(64, activation="relu")(merged)
merged = Dropout(0.3)(merged)
merged = BatchNormalization()(merged)
res = Dense(1, activation="sigmoid")(merged)
model = Model(inputs=[question1, question2], outputs=res)
model.compile(loss=keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(), optimizer="adam", metrics=["accuracy"])
model.summary()
hist = model.fit([train_q1, train_q2],train_label,epochs=30, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, validation_split=0.2,shuffle=True)train_q1_indices, train_q2_indices, train_label, embed_matrix, word_to_index, index_to_word = load_dataset("/content/drive/My Drive/data/text_similarity/data", MAX_SEQUENCE_LENGTH, EMBEDDING_DIM, False)
print('train_q1: ', train_q1_indices.shape)
print('train_q2: ', train_q2_indices.shape)
print('train_label: ', tf.one_hot(train_label,depth=2).shape)
print('embed_matrix: ', embed_matrix.shape)
# 加载test 数据
test_q1, test_q2 = load_test_data("/content/drive/My Drive/data/text_similarity/data", MAX_SEQUENCE_LENGTH, word_level=False)
print('test_q1: ', test_q1.shape)
print('test_q2: ', test_q2.shape)
print("word_to_index len:",len(word_to_index))trainLSTM(train_q1_indices[:243000], train_q2_indices[:243000], train_label[:243000], embed_matrix) #我这里使用的Colab,数据数量无法整除BATCH_SIZE时会报错参考:
[1] https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/88938220