diff --git a/CHANGES.md b/CHANGES.md
index e516132f..4e72641d 100644
--- a/CHANGES.md
+++ b/CHANGES.md
@@ -1,8 +1,12 @@
-# unreleased
+# 6.3.0 (unreleased)
* do not use `warpedVRT` when overwriting the dataset nodata value
+* add `align_bounds_with_dataset` option in `rio_tiler.reader.part` to align input bounds with the dataset resolution
+
+  +
# 6.2.10 (2024-01-08)
* remove default Endpoint URL in AWS S3 Client for STAC Reader
@@ -88,7 +92,7 @@ This release was made while we waited on a fix for https://github.com/cogeotiff/
* add `cmocean` colormaps
-
+
# 6.2.10 (2024-01-08)
* remove default Endpoint URL in AWS S3 Client for STAC Reader
@@ -88,7 +92,7 @@ This release was made while we waited on a fix for https://github.com/cogeotiff/
* add `cmocean` colormaps
-  +
+  * allow uppercase in `cmap.get` method
diff --git a/docs/src/advanced/statistics.md b/docs/src/advanced/statistics.md
index 8209b50c..f3acc561 100644
--- a/docs/src/advanced/statistics.md
+++ b/docs/src/advanced/statistics.md
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
-### Statistics
+#### Form `Readers`
`rio-tiler`'s Readers provide simple `.statistics` method to retrieve dataset global statistics
@@ -34,83 +34,19 @@ print(stats["1"].model_dump().keys())
]
```
-### Zonal Statistics
+#### ImageData
-You can easily extend the `statistics()` method to create a `.zonal_statistics` one which will accept input features to get statistics from.
+You can get statistics from `ImageData` objects which are returned by all rio-tiler reader methods (e.g. `.tile()`, `.preview()`, `.part()`, ...)
```python
-
-import attr
-from typing import Any, Union, Optional, List, Dict
-
-from rio_tiler import io
-from rio_tiler.models import BandStatistics
-
-from geojson_pydantic.features import Feature, FeatureCollection
-from geojson_pydantic.geometries import Polygon
-
-class Reader(io.Reader):
- """Custom Reader with zonal_statistics method."""
-
- def zonal_statistics(
- self,
- geojson: Union[FeatureCollection, Feature],
- categorical: bool = False,
- categories: Optional[List[float]] = None,
- percentiles: Optional[List[int]] = None,
- hist_options: Optional[Dict] = None,
- max_size: int = None,
- **kwargs: Any,
- ) -> Union[FeatureCollection, Feature]:
- """Return statistics from GeoJSON features.
-
- Args:
- geojson (Feature or FeatureCollection): a GeoJSON Feature or FeatureCollection.
- categorical (bool): treat input data as categorical data. Defaults to False.
- categories (list of numbers, optional): list of categories to return value for.
- percentiles (list of numbers, optional): list of percentile values to calculate. Defaults to `[2, 98]`.
- hist_options (dict, optional): Options to forward to numpy.histogram function.
- max_size (int, optional): Limit the size of the longest dimension of the dataset read, respecting bounds X/Y aspect ratio. Defaults to None.
- kwargs (optional): Options to forward to `self.preview`.
-
- Returns:
- Feature or FeatureCollection
-
- """
- kwargs = {**self.options, **kwargs}
-
- hist_options = hist_options or {}
-
- fc = geojson
- # We transform the input Feature to a FeatureCollection
- if isinstance(fc, Feature):
- fc = FeatureCollection(type="FeatureCollection", features=[geojson])
-
- for feature in fc:
- # Get data overlapping with the feature (using Reader.feature method)
- data = self.feature(
- feature.model_dump(exclude_none=True),
- max_size=max_size,
- **kwargs,
- )
- stats = data.statistics(
- categorical=categorical,
- categories=categories,
- percentiles=percentiles,
- hist_options=hist_options,
- )
-
- # Update input feature properties and add the statistics
- feature.properties = feature.properties or {}
- feature.properties.update({"statistics": stats})
-
- return fc.features[0] if isinstance(geojson, Feature) else fc
+with Reader("cog.tif") as src:
+ image = src.preview()
+ stats = image.statistics()
```
-
### Area Weighted Statistics
-When getting statistics from `feature`, you may want to calculate values from the pixels which intersect with the geometry but also take the pixel intersection percentage into account. Starting with rio-tiler `6.2.0`, we've added a `coverage` option to the `statistics` utility which enable the user to pass an array representing the coverage percentage such as:
+When getting statistics from a `feature`, you may want to calculate values from the pixels which intersect with the geometry but also take the pixel intersection percentage into account. Starting with rio-tiler `6.2.0`, we've added a `coverage` option to the `statistics` utility which enable the user to pass an array representing the coverage percentage such as:
```python
import numpy
@@ -133,34 +69,110 @@ assert stats[0]["mean"] == 1.125 # (1 * 0.5 + 2 * 0.0 + 3 * 1.0 + 4 * 0.25) / 4
assert stats[0]["count"] == 1.75 # (0.5 + 0 + 1 + 0.25) sum of the coverage array
```
-When using with a `feature`, your code might look something like:
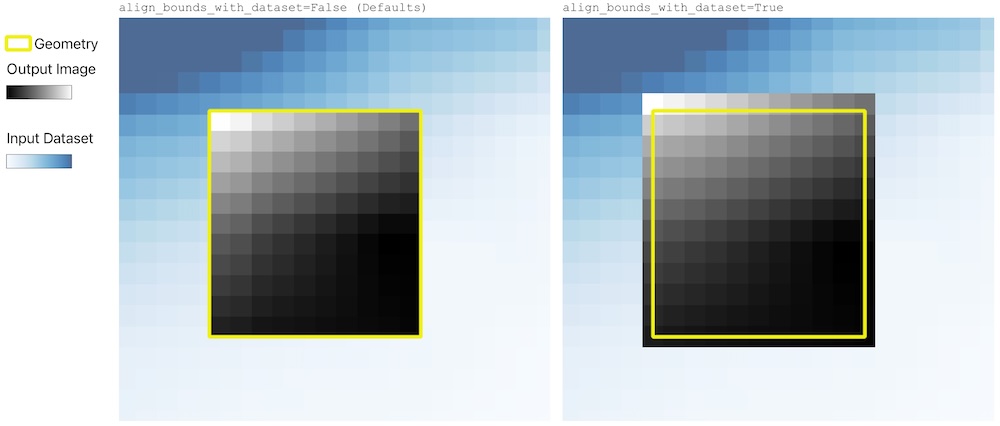
+#### Adjusting geometry `align_bounds_with_dataset=True`
-```python
-from rio_tiler.io import Reader
-from rio_tiler.constants import WGS84_CRS
+In rio-tiler `6.3,0` a new option has been introduced to reduce artifacts and produce more precise zonal statistics. This option is available in the low-level `reader.part()` method used in rio-tiler reader's `.feature()` and `.part()` methods.
-with Reader(path) as src:
- # First get the array for the feature
- data = src_dst.feature(
+```python
+with Reader("cog.tif") as src:
+ data = src.feature(
shape,
shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ align_bounds_with_dataset=True,
)
- # Get the coverage % array, using ImageData.get_coverage_array method
coverage_array = data.get_coverage_array(
- shape, shape_crs=WGS84_CRS
+ shape,
+ shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
)
- # Get statistics (ImageData.statistics is calling `rio_tiler.utils.get_array_statistics`)
stats = data.statistics(coverage=coverage_array)
```
-!!! warnings
- The coverage weights will only have influence on specific statistics:
+When passing `align_bounds_with_dataset=True` to the `reader.part()` method (forwared from `.feature` or `.part` reader's method), rio-tiler will adjust the input geometry bounds to math the input dataset resolution/transform and avoid unnecessary resampling.
- - `mean`
- - `count`
- - `sum`
- - `std`
- - `median`
+
* allow uppercase in `cmap.get` method
diff --git a/docs/src/advanced/statistics.md b/docs/src/advanced/statistics.md
index 8209b50c..f3acc561 100644
--- a/docs/src/advanced/statistics.md
+++ b/docs/src/advanced/statistics.md
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
-### Statistics
+#### Form `Readers`
`rio-tiler`'s Readers provide simple `.statistics` method to retrieve dataset global statistics
@@ -34,83 +34,19 @@ print(stats["1"].model_dump().keys())
]
```
-### Zonal Statistics
+#### ImageData
-You can easily extend the `statistics()` method to create a `.zonal_statistics` one which will accept input features to get statistics from.
+You can get statistics from `ImageData` objects which are returned by all rio-tiler reader methods (e.g. `.tile()`, `.preview()`, `.part()`, ...)
```python
-
-import attr
-from typing import Any, Union, Optional, List, Dict
-
-from rio_tiler import io
-from rio_tiler.models import BandStatistics
-
-from geojson_pydantic.features import Feature, FeatureCollection
-from geojson_pydantic.geometries import Polygon
-
-class Reader(io.Reader):
- """Custom Reader with zonal_statistics method."""
-
- def zonal_statistics(
- self,
- geojson: Union[FeatureCollection, Feature],
- categorical: bool = False,
- categories: Optional[List[float]] = None,
- percentiles: Optional[List[int]] = None,
- hist_options: Optional[Dict] = None,
- max_size: int = None,
- **kwargs: Any,
- ) -> Union[FeatureCollection, Feature]:
- """Return statistics from GeoJSON features.
-
- Args:
- geojson (Feature or FeatureCollection): a GeoJSON Feature or FeatureCollection.
- categorical (bool): treat input data as categorical data. Defaults to False.
- categories (list of numbers, optional): list of categories to return value for.
- percentiles (list of numbers, optional): list of percentile values to calculate. Defaults to `[2, 98]`.
- hist_options (dict, optional): Options to forward to numpy.histogram function.
- max_size (int, optional): Limit the size of the longest dimension of the dataset read, respecting bounds X/Y aspect ratio. Defaults to None.
- kwargs (optional): Options to forward to `self.preview`.
-
- Returns:
- Feature or FeatureCollection
-
- """
- kwargs = {**self.options, **kwargs}
-
- hist_options = hist_options or {}
-
- fc = geojson
- # We transform the input Feature to a FeatureCollection
- if isinstance(fc, Feature):
- fc = FeatureCollection(type="FeatureCollection", features=[geojson])
-
- for feature in fc:
- # Get data overlapping with the feature (using Reader.feature method)
- data = self.feature(
- feature.model_dump(exclude_none=True),
- max_size=max_size,
- **kwargs,
- )
- stats = data.statistics(
- categorical=categorical,
- categories=categories,
- percentiles=percentiles,
- hist_options=hist_options,
- )
-
- # Update input feature properties and add the statistics
- feature.properties = feature.properties or {}
- feature.properties.update({"statistics": stats})
-
- return fc.features[0] if isinstance(geojson, Feature) else fc
+with Reader("cog.tif") as src:
+ image = src.preview()
+ stats = image.statistics()
```
-
### Area Weighted Statistics
-When getting statistics from `feature`, you may want to calculate values from the pixels which intersect with the geometry but also take the pixel intersection percentage into account. Starting with rio-tiler `6.2.0`, we've added a `coverage` option to the `statistics` utility which enable the user to pass an array representing the coverage percentage such as:
+When getting statistics from a `feature`, you may want to calculate values from the pixels which intersect with the geometry but also take the pixel intersection percentage into account. Starting with rio-tiler `6.2.0`, we've added a `coverage` option to the `statistics` utility which enable the user to pass an array representing the coverage percentage such as:
```python
import numpy
@@ -133,34 +69,110 @@ assert stats[0]["mean"] == 1.125 # (1 * 0.5 + 2 * 0.0 + 3 * 1.0 + 4 * 0.25) / 4
assert stats[0]["count"] == 1.75 # (0.5 + 0 + 1 + 0.25) sum of the coverage array
```
-When using with a `feature`, your code might look something like:
+#### Adjusting geometry `align_bounds_with_dataset=True`
-```python
-from rio_tiler.io import Reader
-from rio_tiler.constants import WGS84_CRS
+In rio-tiler `6.3,0` a new option has been introduced to reduce artifacts and produce more precise zonal statistics. This option is available in the low-level `reader.part()` method used in rio-tiler reader's `.feature()` and `.part()` methods.
-with Reader(path) as src:
- # First get the array for the feature
- data = src_dst.feature(
+```python
+with Reader("cog.tif") as src:
+ data = src.feature(
shape,
shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ align_bounds_with_dataset=True,
)
- # Get the coverage % array, using ImageData.get_coverage_array method
coverage_array = data.get_coverage_array(
- shape, shape_crs=WGS84_CRS
+ shape,
+ shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
)
- # Get statistics (ImageData.statistics is calling `rio_tiler.utils.get_array_statistics`)
stats = data.statistics(coverage=coverage_array)
```
-!!! warnings
- The coverage weights will only have influence on specific statistics:
+When passing `align_bounds_with_dataset=True` to the `reader.part()` method (forwared from `.feature` or `.part` reader's method), rio-tiler will adjust the input geometry bounds to math the input dataset resolution/transform and avoid unnecessary resampling.
- - `mean`
- - `count`
- - `sum`
- - `std`
- - `median`
+ +
+### Zonal Statistics method
+
+You can easily extend the rio-tiler's reader to add a `.zonal_statistics()` method as:
+
+```python
+
+import attr
+from typing import Any, Union, Optional, List, Dict
+
+from rio_tiler import io
+from rio_tiler.models import BandStatistics
+
+from geojson_pydantic.features import Feature, FeatureCollection
+from geojson_pydantic.geometries import Polygon
+
+class Reader(io.Reader):
+ """Custom Reader with zonal_statistics method."""
+
+ def zonal_statistics(
+ self,
+ geojson: Union[FeatureCollection, Feature],
+ categorical: bool = False,
+ categories: Optional[List[float]] = None,
+ percentiles: Optional[List[int]] = None,
+ hist_options: Optional[Dict] = None,
+ max_size: int = None,
+ **kwargs: Any,
+ ) -> Union[FeatureCollection, Feature]:
+ """Return statistics from GeoJSON features.
+
+ Args:
+ geojson (Feature or FeatureCollection): a GeoJSON Feature or FeatureCollection.
+ categorical (bool): treat input data as categorical data. Defaults to False.
+ categories (list of numbers, optional): list of categories to return value for.
+ percentiles (list of numbers, optional): list of percentile values to calculate. Defaults to `[2, 98]`.
+ hist_options (dict, optional): Options to forward to numpy.histogram function.
+ max_size (int, optional): Limit the size of the longest dimension of the dataset read, respecting bounds X/Y aspect ratio. Defaults to None.
+ kwargs (optional): Options to forward to `self.preview`.
+
+ Returns:
+ Feature or FeatureCollection
+
+ """
+ kwargs = {**self.options, **kwargs}
+
+ hist_options = hist_options or {}
+
+ fc = geojson
+ # We transform the input Feature to a FeatureCollection
+ if isinstance(fc, Feature):
+ fc = FeatureCollection(type="FeatureCollection", features=[geojson])
+
+ for feature in fc:
+ geom = feature.model_dump(exclude_none=True)
+
+ # Get data overlapping with the feature (using Reader.feature method)
+ data = self.feature(
+ geom,
+ shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ align_bounds_with_dataset=True,
+ max_size=max_size,
+ **kwargs,
+ )
+ coverage_array = data.get_coverage_array(
+ geom,
+ shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ )
+
+ stats = data.statistics(
+ categorical=categorical,
+ categories=categories,
+ percentiles=percentiles,
+ hist_options=hist_options,
+ coverage=coverage_array,
+ )
+
+ # Update input feature properties and add the statistics
+ feature.properties = feature.properties or {}
+ feature.properties.update({"statistics": stats})
+
+ return fc.features[0] if isinstance(geojson, Feature) else fc
+```
diff --git a/rio_tiler/reader.py b/rio_tiler/reader.py
index f3244bc2..8fe18dda 100644
--- a/rio_tiler/reader.py
+++ b/rio_tiler/reader.py
@@ -12,6 +12,7 @@
from rasterio.crs import CRS
from rasterio.enums import ColorInterp, MaskFlags, Resampling
from rasterio.io import DatasetReader, DatasetWriter
+from rasterio.transform import array_bounds
from rasterio.vrt import WarpedVRT
from rasterio.warp import transform as transform_coords
from rasterio.warp import transform_bounds
@@ -289,6 +290,7 @@ def part(
force_binary_mask: bool = True,
nodata: Optional[NoData] = None,
vrt_options: Optional[Dict] = None,
+ align_bounds_with_dataset: bool = False,
resampling_method: RIOResampling = "nearest",
reproject_method: WarpResampling = "nearest",
unscale: bool = False,
@@ -312,6 +314,7 @@ def part(
buffer (float, optional): Buffer to apply to each bbox edge. Defaults to `0.`.
nodata (int or float, optional): Overwrite dataset internal nodata value.
vrt_options (dict, optional): Options to be passed to the rasterio.warp.WarpedVRT class.
+ align_bounds_with_dataset (bool): Align input bounds with dataset transform. Defaults to `False`.
resampling_method (RIOResampling, optional): RasterIO resampling algorithm. Defaults to `nearest`.
reproject_method (WarpResampling, optional): WarpKernel resampling algorithm. Defaults to `nearest`.
unscale (bool, optional): Apply 'scales' and 'offsets' on output data value. Defaults to `False`.
@@ -363,7 +366,9 @@ def part(
src_dst,
bounds,
dst_crs=dst_crs,
+ align_bounds_with_dataset=align_bounds_with_dataset,
)
+ bounds = array_bounds(vrt_height, vrt_width, vrt_transform)
if max_size and not (width and height):
height, width = _get_width_height(max_size, vrt_height, vrt_width)
@@ -379,7 +384,9 @@ def part(
src_dst,
bounds,
dst_crs=dst_crs,
+ align_bounds_with_dataset=align_bounds_with_dataset,
)
+ bounds = array_bounds(vrt_height, vrt_width, vrt_transform)
if padding > 0 and not is_aligned(src_dst, bounds, bounds_crs=dst_crs):
vrt_transform = vrt_transform * Affine.translation(-padding, -padding)
@@ -415,6 +422,18 @@ def part(
# else no re-projection needed
window = windows.from_bounds(*bounds, transform=src_dst.transform)
+ if align_bounds_with_dataset:
+ (row_start, row_stop), (col_start, col_stop) = window.toranges()
+ row_start, row_stop = int(math.floor(row_start)), int(math.ceil(row_stop))
+ col_start, col_stop = int(math.floor(col_start)), int(math.ceil(col_stop))
+ window = windows.Window(
+ col_off=col_start,
+ row_off=row_start,
+ width=max(col_stop - col_start, 0.0),
+ height=max(row_stop - row_start, 0.0),
+ )
+ bounds = windows.bounds(window, src_dst.transform)
+
if max_size and not (width and height):
height, width = _get_width_height(
max_size, round(window.height), round(window.width)
diff --git a/rio_tiler/utils.py b/rio_tiler/utils.py
index 237f2329..19ef25e9 100644
--- a/rio_tiler/utils.py
+++ b/rio_tiler/utils.py
@@ -1,5 +1,6 @@
"""rio_tiler.utils: utility functions."""
+import math
import warnings
from io import BytesIO
from typing import Any, Dict, Generator, List, Optional, Sequence, Tuple, Union
@@ -229,6 +230,7 @@ def get_vrt_transform(
width: Optional[int] = None,
dst_crs: CRS = WEB_MERCATOR_CRS,
window_precision: int = 6,
+ align_bounds_with_dataset: bool = False,
) -> Tuple[Affine, int, int]:
"""Calculate VRT transform.
@@ -238,6 +240,7 @@ def get_vrt_transform(
height (int, optional): Desired output height of the array for the input bounds.
width (int, optional): Desired output width of the array for the input bounds.
dst_crs (rasterio.crs.CRS, optional): Target Coordinate Reference System. Defaults to `epsg:3857`.
+ align_bounds_with_dataset (bool): Align input bounds with dataset transform. Defaults to `False`.
Returns:
tuple: VRT transform (affine.Affine), width (int) and height (int)
@@ -299,6 +302,19 @@ def get_vrt_transform(
# Get Bounds for the rounded window
bounds = src_dst.window_bounds(w)
+ elif align_bounds_with_dataset:
+ window = windows.from_bounds(*bounds, transform=dst_transform)
+ (row_start, row_stop), (col_start, col_stop) = window.toranges()
+ row_start, row_stop = int(math.floor(row_start)), int(math.ceil(row_stop))
+ col_start, col_stop = int(math.floor(col_start)), int(math.ceil(col_stop))
+ window = windows.Window(
+ col_off=col_start,
+ row_off=row_start,
+ width=max(col_stop - col_start, 0.0),
+ height=max(row_stop - row_start, 0.0),
+ )
+ bounds = windows.bounds(window, dst_transform)
+
w, s, e, n = bounds
# TODO: Explain
diff --git a/tests/test_io_rasterio.py b/tests/test_io_rasterio.py
index 98b9c3a3..153c328e 100644
--- a/tests/test_io_rasterio.py
+++ b/tests/test_io_rasterio.py
@@ -1013,3 +1013,101 @@ def test_metadata_img():
img = src.preview()
assert img.dataset_statistics
assert img.metadata
+
+
+def test_feature_statistics():
+ """Test feature statistics method implemented in titiler."""
+ # square
+ square = {
+ "type": "Feature",
+ "properties": {},
+ "geometry": {
+ "coordinates": [
+ [
+ [-56.85853679288809, 73.6870721652219],
+ [-56.85853679288809, 73.18595963998644],
+ [-54.97274279983506, 73.18595963998644],
+ [-54.97274279983506, 73.6870721652219],
+ [-56.85853679288809, 73.6870721652219],
+ ]
+ ],
+ "type": "Polygon",
+ },
+ }
+
+ square_crs = {
+ "type": "Polygon",
+ "coordinates": [
+ [
+ [442337.0, 8175239.0],
+ [517915.0, 8175239.0],
+ [517915.0, 8134628.0],
+ [442337.0, 8134628.0],
+ [442337.0, 8175239.0],
+ ]
+ ],
+ }
+
+ # Case 1 - image should be aligned with the bounds
+ # because we reproject to the shape crs
+ with Reader(COGEO) as src:
+ image = src.feature(
+ square,
+ dst_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ )
+ coverage_array = image.get_coverage_array(
+ square,
+ shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ )
+ stats = image.statistics(coverage=coverage_array)
+ assert numpy.unique(coverage_array).tolist() == [1.0]
+
+ # Case 2 - image not aligned with bounds because we align the
+ # bounds to the reprojected dataset
+ with Reader(COGEO) as src:
+ image = src.feature(
+ square,
+ dst_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ align_bounds_with_dataset=True,
+ )
+ coverage_array = image.get_coverage_array(
+ square,
+ shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ )
+ stats_align = image.statistics(coverage=coverage_array)
+ assert not numpy.unique(coverage_array).tolist() == [1.0]
+
+ assert stats["b1"].mean != stats_align["b1"].mean
+
+ # Case 3 - square geometry in dataset CRS
+ with Reader(COGEO) as src:
+ image = src.feature(
+ square_crs,
+ dst_crs=src.crs,
+ shape_crs=src.crs,
+ )
+ coverage_array = image.get_coverage_array(
+ square_crs,
+ shape_crs=src.crs,
+ )
+ stats = image.statistics(coverage=coverage_array)
+ assert numpy.unique(coverage_array).tolist() == [1.0]
+
+ # Case 4 - square geometry in dataset CRS but aligned with dataset
+ with Reader(COGEO) as src:
+ image = src.feature(
+ square_crs,
+ dst_crs=src.crs,
+ shape_crs=src.crs,
+ align_bounds_with_dataset=True,
+ )
+ coverage_array = image.get_coverage_array(
+ square_crs,
+ shape_crs=src.crs,
+ )
+ stats_align = image.statistics(coverage=coverage_array)
+ assert not numpy.unique(coverage_array).tolist() == [1.0]
+
+ assert stats["b1"].mean != stats_align["b1"].mean
diff --git a/tests/test_reader.py b/tests/test_reader.py
index 7b99614e..ca7204f2 100644
--- a/tests/test_reader.py
+++ b/tests/test_reader.py
@@ -9,6 +9,7 @@
from rasterio.warp import transform_bounds
from rio_tiler import constants, reader
+from rio_tiler.constants import WGS84_CRS
from rio_tiler.errors import PointOutsideBounds, TileOutsideBounds
S3_KEY = "hro_sources/colorado/201404_13SED190110_201404_0x1500m_CL_1.tif"
@@ -669,3 +670,169 @@ def test_part_no_VRT():
assert img_small.height == 1
assert img_small.width == 1
assert_array_almost_equal(img_small.bounds, bounds_small_dst_crs)
+
+
+@pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "bounds,crs",
+ [
+ (
+ (
+ -56.624124590533825,
+ 73.50183615350426,
+ -56.530950796449005,
+ 73.52687881825946,
+ ),
+ "epsg:32621",
+ ), # Case 1 - square bounds within dataset
+ (
+ (
+ -62.841631140841685,
+ 73.15163488990189,
+ -60.36648908847309,
+ 73.97773652099218,
+ ),
+ "epsg:32621",
+ ), # Case 2 - boundless (left)
+ (
+ (
+ -52.927554190740736,
+ 73.3960640725901,
+ -51.96837664926392,
+ 73.77350422465656,
+ ),
+ "epsg:32621",
+ ), # Case 3 - boundless (right)
+ (
+ (
+ -57.15027188947926,
+ 74.56177365126999,
+ -56.37556339673152,
+ 74.75029925196495,
+ ),
+ "epsg:32621",
+ ), # Case 4 - boundless (top)
+ (
+ (
+ -55.86202533996874,
+ 71.8988448629112,
+ -54.6335972683694,
+ 72.28789003457715,
+ ),
+ "epsg:32621",
+ ), # Case 5 - boundless (bottom)
+ (
+ (
+ -62.968685159182414,
+ 71.95907543637196,
+ -51.60091205568341,
+ 74.78461407516858,
+ ),
+ "epsg:32621",
+ ), # Case 6 - boundless whole raster
+ (
+ (
+ -66.79529480522785,
+ 74.22513769476188,
+ -65.89488418613195,
+ 74.48258818252089,
+ ),
+ "epsg:32621",
+ ), # Case 7 - outside bounds
+ # With Reprojection
+ (
+ (
+ -56.624124590533825,
+ 73.50183615350426,
+ -56.530950796449005,
+ 73.52687881825946,
+ ),
+ "epsg:4326",
+ ), # Case 1 - square bounds within dataset
+ (
+ (
+ -62.841631140841685,
+ 73.15163488990189,
+ -60.36648908847309,
+ 73.97773652099218,
+ ),
+ "epsg:4326",
+ ), # Case 2 - boundless (left)
+ (
+ (
+ -52.927554190740736,
+ 73.3960640725901,
+ -51.96837664926392,
+ 73.77350422465656,
+ ),
+ "epsg:4326",
+ ), # Case 3 - boundless (right)
+ (
+ (
+ -57.15027188947926,
+ 74.56177365126999,
+ -56.37556339673152,
+ 74.75029925196495,
+ ),
+ "epsg:4326",
+ ), # Case 4 - boundless (top)
+ (
+ (
+ -55.86202533996874,
+ 71.8988448629112,
+ -54.6335972683694,
+ 72.28789003457715,
+ ),
+ "epsg:4326",
+ ), # Case 5 - boundless (bottom)
+ (
+ (
+ -62.968685159182414,
+ 71.95907543637196,
+ -51.60091205568341,
+ 74.78461407516858,
+ ),
+ "epsg:4326",
+ ), # Case 6 - boundless whole raster
+ (
+ (
+ -66.79529480522785,
+ 74.22513769476188,
+ -65.89488418613195,
+ 74.48258818252089,
+ ),
+ "epsg:4326",
+ ), # Case 7 - outside bounds
+ ],
+)
+def test_part_align_transform(bounds, crs):
+ """test `align_bounds_with_dataset` option."""
+ with rasterio.open(COG) as src_dst:
+ img = reader.part(
+ src_dst,
+ bounds,
+ dst_crs=crs,
+ bounds_crs="epsg:4326",
+ align_bounds_with_dataset=True,
+ )
+ img_default = reader.part(
+ src_dst,
+ bounds,
+ dst_crs=crs,
+ bounds_crs="epsg:4326",
+ align_bounds_with_dataset=False,
+ )
+ assert not img.array.shape == img_default.array.shape
+ assert not img.bounds == img_default.bounds
+
+ # output image aligned with bounds should have the origin
+ # with the bounds UL
+ if crs != WGS84_CRS:
+ bounds = transform_bounds(WGS84_CRS, crs, *bounds, densify_pts=21)
+
+ assert round(img_default.transform.c, 5) == round(bounds[0], 5)
+ assert round(img_default.transform.f, 5) == round(bounds[3], 5)
+
+ # output image bounds aligned to the dataset transform should have the origin
+ # with the bounds greater than UL
+ assert img.transform.c < bounds[0]
+ assert img.transform.f > bounds[3]
+
+### Zonal Statistics method
+
+You can easily extend the rio-tiler's reader to add a `.zonal_statistics()` method as:
+
+```python
+
+import attr
+from typing import Any, Union, Optional, List, Dict
+
+from rio_tiler import io
+from rio_tiler.models import BandStatistics
+
+from geojson_pydantic.features import Feature, FeatureCollection
+from geojson_pydantic.geometries import Polygon
+
+class Reader(io.Reader):
+ """Custom Reader with zonal_statistics method."""
+
+ def zonal_statistics(
+ self,
+ geojson: Union[FeatureCollection, Feature],
+ categorical: bool = False,
+ categories: Optional[List[float]] = None,
+ percentiles: Optional[List[int]] = None,
+ hist_options: Optional[Dict] = None,
+ max_size: int = None,
+ **kwargs: Any,
+ ) -> Union[FeatureCollection, Feature]:
+ """Return statistics from GeoJSON features.
+
+ Args:
+ geojson (Feature or FeatureCollection): a GeoJSON Feature or FeatureCollection.
+ categorical (bool): treat input data as categorical data. Defaults to False.
+ categories (list of numbers, optional): list of categories to return value for.
+ percentiles (list of numbers, optional): list of percentile values to calculate. Defaults to `[2, 98]`.
+ hist_options (dict, optional): Options to forward to numpy.histogram function.
+ max_size (int, optional): Limit the size of the longest dimension of the dataset read, respecting bounds X/Y aspect ratio. Defaults to None.
+ kwargs (optional): Options to forward to `self.preview`.
+
+ Returns:
+ Feature or FeatureCollection
+
+ """
+ kwargs = {**self.options, **kwargs}
+
+ hist_options = hist_options or {}
+
+ fc = geojson
+ # We transform the input Feature to a FeatureCollection
+ if isinstance(fc, Feature):
+ fc = FeatureCollection(type="FeatureCollection", features=[geojson])
+
+ for feature in fc:
+ geom = feature.model_dump(exclude_none=True)
+
+ # Get data overlapping with the feature (using Reader.feature method)
+ data = self.feature(
+ geom,
+ shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ align_bounds_with_dataset=True,
+ max_size=max_size,
+ **kwargs,
+ )
+ coverage_array = data.get_coverage_array(
+ geom,
+ shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ )
+
+ stats = data.statistics(
+ categorical=categorical,
+ categories=categories,
+ percentiles=percentiles,
+ hist_options=hist_options,
+ coverage=coverage_array,
+ )
+
+ # Update input feature properties and add the statistics
+ feature.properties = feature.properties or {}
+ feature.properties.update({"statistics": stats})
+
+ return fc.features[0] if isinstance(geojson, Feature) else fc
+```
diff --git a/rio_tiler/reader.py b/rio_tiler/reader.py
index f3244bc2..8fe18dda 100644
--- a/rio_tiler/reader.py
+++ b/rio_tiler/reader.py
@@ -12,6 +12,7 @@
from rasterio.crs import CRS
from rasterio.enums import ColorInterp, MaskFlags, Resampling
from rasterio.io import DatasetReader, DatasetWriter
+from rasterio.transform import array_bounds
from rasterio.vrt import WarpedVRT
from rasterio.warp import transform as transform_coords
from rasterio.warp import transform_bounds
@@ -289,6 +290,7 @@ def part(
force_binary_mask: bool = True,
nodata: Optional[NoData] = None,
vrt_options: Optional[Dict] = None,
+ align_bounds_with_dataset: bool = False,
resampling_method: RIOResampling = "nearest",
reproject_method: WarpResampling = "nearest",
unscale: bool = False,
@@ -312,6 +314,7 @@ def part(
buffer (float, optional): Buffer to apply to each bbox edge. Defaults to `0.`.
nodata (int or float, optional): Overwrite dataset internal nodata value.
vrt_options (dict, optional): Options to be passed to the rasterio.warp.WarpedVRT class.
+ align_bounds_with_dataset (bool): Align input bounds with dataset transform. Defaults to `False`.
resampling_method (RIOResampling, optional): RasterIO resampling algorithm. Defaults to `nearest`.
reproject_method (WarpResampling, optional): WarpKernel resampling algorithm. Defaults to `nearest`.
unscale (bool, optional): Apply 'scales' and 'offsets' on output data value. Defaults to `False`.
@@ -363,7 +366,9 @@ def part(
src_dst,
bounds,
dst_crs=dst_crs,
+ align_bounds_with_dataset=align_bounds_with_dataset,
)
+ bounds = array_bounds(vrt_height, vrt_width, vrt_transform)
if max_size and not (width and height):
height, width = _get_width_height(max_size, vrt_height, vrt_width)
@@ -379,7 +384,9 @@ def part(
src_dst,
bounds,
dst_crs=dst_crs,
+ align_bounds_with_dataset=align_bounds_with_dataset,
)
+ bounds = array_bounds(vrt_height, vrt_width, vrt_transform)
if padding > 0 and not is_aligned(src_dst, bounds, bounds_crs=dst_crs):
vrt_transform = vrt_transform * Affine.translation(-padding, -padding)
@@ -415,6 +422,18 @@ def part(
# else no re-projection needed
window = windows.from_bounds(*bounds, transform=src_dst.transform)
+ if align_bounds_with_dataset:
+ (row_start, row_stop), (col_start, col_stop) = window.toranges()
+ row_start, row_stop = int(math.floor(row_start)), int(math.ceil(row_stop))
+ col_start, col_stop = int(math.floor(col_start)), int(math.ceil(col_stop))
+ window = windows.Window(
+ col_off=col_start,
+ row_off=row_start,
+ width=max(col_stop - col_start, 0.0),
+ height=max(row_stop - row_start, 0.0),
+ )
+ bounds = windows.bounds(window, src_dst.transform)
+
if max_size and not (width and height):
height, width = _get_width_height(
max_size, round(window.height), round(window.width)
diff --git a/rio_tiler/utils.py b/rio_tiler/utils.py
index 237f2329..19ef25e9 100644
--- a/rio_tiler/utils.py
+++ b/rio_tiler/utils.py
@@ -1,5 +1,6 @@
"""rio_tiler.utils: utility functions."""
+import math
import warnings
from io import BytesIO
from typing import Any, Dict, Generator, List, Optional, Sequence, Tuple, Union
@@ -229,6 +230,7 @@ def get_vrt_transform(
width: Optional[int] = None,
dst_crs: CRS = WEB_MERCATOR_CRS,
window_precision: int = 6,
+ align_bounds_with_dataset: bool = False,
) -> Tuple[Affine, int, int]:
"""Calculate VRT transform.
@@ -238,6 +240,7 @@ def get_vrt_transform(
height (int, optional): Desired output height of the array for the input bounds.
width (int, optional): Desired output width of the array for the input bounds.
dst_crs (rasterio.crs.CRS, optional): Target Coordinate Reference System. Defaults to `epsg:3857`.
+ align_bounds_with_dataset (bool): Align input bounds with dataset transform. Defaults to `False`.
Returns:
tuple: VRT transform (affine.Affine), width (int) and height (int)
@@ -299,6 +302,19 @@ def get_vrt_transform(
# Get Bounds for the rounded window
bounds = src_dst.window_bounds(w)
+ elif align_bounds_with_dataset:
+ window = windows.from_bounds(*bounds, transform=dst_transform)
+ (row_start, row_stop), (col_start, col_stop) = window.toranges()
+ row_start, row_stop = int(math.floor(row_start)), int(math.ceil(row_stop))
+ col_start, col_stop = int(math.floor(col_start)), int(math.ceil(col_stop))
+ window = windows.Window(
+ col_off=col_start,
+ row_off=row_start,
+ width=max(col_stop - col_start, 0.0),
+ height=max(row_stop - row_start, 0.0),
+ )
+ bounds = windows.bounds(window, dst_transform)
+
w, s, e, n = bounds
# TODO: Explain
diff --git a/tests/test_io_rasterio.py b/tests/test_io_rasterio.py
index 98b9c3a3..153c328e 100644
--- a/tests/test_io_rasterio.py
+++ b/tests/test_io_rasterio.py
@@ -1013,3 +1013,101 @@ def test_metadata_img():
img = src.preview()
assert img.dataset_statistics
assert img.metadata
+
+
+def test_feature_statistics():
+ """Test feature statistics method implemented in titiler."""
+ # square
+ square = {
+ "type": "Feature",
+ "properties": {},
+ "geometry": {
+ "coordinates": [
+ [
+ [-56.85853679288809, 73.6870721652219],
+ [-56.85853679288809, 73.18595963998644],
+ [-54.97274279983506, 73.18595963998644],
+ [-54.97274279983506, 73.6870721652219],
+ [-56.85853679288809, 73.6870721652219],
+ ]
+ ],
+ "type": "Polygon",
+ },
+ }
+
+ square_crs = {
+ "type": "Polygon",
+ "coordinates": [
+ [
+ [442337.0, 8175239.0],
+ [517915.0, 8175239.0],
+ [517915.0, 8134628.0],
+ [442337.0, 8134628.0],
+ [442337.0, 8175239.0],
+ ]
+ ],
+ }
+
+ # Case 1 - image should be aligned with the bounds
+ # because we reproject to the shape crs
+ with Reader(COGEO) as src:
+ image = src.feature(
+ square,
+ dst_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ )
+ coverage_array = image.get_coverage_array(
+ square,
+ shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ )
+ stats = image.statistics(coverage=coverage_array)
+ assert numpy.unique(coverage_array).tolist() == [1.0]
+
+ # Case 2 - image not aligned with bounds because we align the
+ # bounds to the reprojected dataset
+ with Reader(COGEO) as src:
+ image = src.feature(
+ square,
+ dst_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ align_bounds_with_dataset=True,
+ )
+ coverage_array = image.get_coverage_array(
+ square,
+ shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ )
+ stats_align = image.statistics(coverage=coverage_array)
+ assert not numpy.unique(coverage_array).tolist() == [1.0]
+
+ assert stats["b1"].mean != stats_align["b1"].mean
+
+ # Case 3 - square geometry in dataset CRS
+ with Reader(COGEO) as src:
+ image = src.feature(
+ square_crs,
+ dst_crs=src.crs,
+ shape_crs=src.crs,
+ )
+ coverage_array = image.get_coverage_array(
+ square_crs,
+ shape_crs=src.crs,
+ )
+ stats = image.statistics(coverage=coverage_array)
+ assert numpy.unique(coverage_array).tolist() == [1.0]
+
+ # Case 4 - square geometry in dataset CRS but aligned with dataset
+ with Reader(COGEO) as src:
+ image = src.feature(
+ square_crs,
+ dst_crs=src.crs,
+ shape_crs=src.crs,
+ align_bounds_with_dataset=True,
+ )
+ coverage_array = image.get_coverage_array(
+ square_crs,
+ shape_crs=src.crs,
+ )
+ stats_align = image.statistics(coverage=coverage_array)
+ assert not numpy.unique(coverage_array).tolist() == [1.0]
+
+ assert stats["b1"].mean != stats_align["b1"].mean
diff --git a/tests/test_reader.py b/tests/test_reader.py
index 7b99614e..ca7204f2 100644
--- a/tests/test_reader.py
+++ b/tests/test_reader.py
@@ -9,6 +9,7 @@
from rasterio.warp import transform_bounds
from rio_tiler import constants, reader
+from rio_tiler.constants import WGS84_CRS
from rio_tiler.errors import PointOutsideBounds, TileOutsideBounds
S3_KEY = "hro_sources/colorado/201404_13SED190110_201404_0x1500m_CL_1.tif"
@@ -669,3 +670,169 @@ def test_part_no_VRT():
assert img_small.height == 1
assert img_small.width == 1
assert_array_almost_equal(img_small.bounds, bounds_small_dst_crs)
+
+
+@pytest.mark.parametrize(
+ "bounds,crs",
+ [
+ (
+ (
+ -56.624124590533825,
+ 73.50183615350426,
+ -56.530950796449005,
+ 73.52687881825946,
+ ),
+ "epsg:32621",
+ ), # Case 1 - square bounds within dataset
+ (
+ (
+ -62.841631140841685,
+ 73.15163488990189,
+ -60.36648908847309,
+ 73.97773652099218,
+ ),
+ "epsg:32621",
+ ), # Case 2 - boundless (left)
+ (
+ (
+ -52.927554190740736,
+ 73.3960640725901,
+ -51.96837664926392,
+ 73.77350422465656,
+ ),
+ "epsg:32621",
+ ), # Case 3 - boundless (right)
+ (
+ (
+ -57.15027188947926,
+ 74.56177365126999,
+ -56.37556339673152,
+ 74.75029925196495,
+ ),
+ "epsg:32621",
+ ), # Case 4 - boundless (top)
+ (
+ (
+ -55.86202533996874,
+ 71.8988448629112,
+ -54.6335972683694,
+ 72.28789003457715,
+ ),
+ "epsg:32621",
+ ), # Case 5 - boundless (bottom)
+ (
+ (
+ -62.968685159182414,
+ 71.95907543637196,
+ -51.60091205568341,
+ 74.78461407516858,
+ ),
+ "epsg:32621",
+ ), # Case 6 - boundless whole raster
+ (
+ (
+ -66.79529480522785,
+ 74.22513769476188,
+ -65.89488418613195,
+ 74.48258818252089,
+ ),
+ "epsg:32621",
+ ), # Case 7 - outside bounds
+ # With Reprojection
+ (
+ (
+ -56.624124590533825,
+ 73.50183615350426,
+ -56.530950796449005,
+ 73.52687881825946,
+ ),
+ "epsg:4326",
+ ), # Case 1 - square bounds within dataset
+ (
+ (
+ -62.841631140841685,
+ 73.15163488990189,
+ -60.36648908847309,
+ 73.97773652099218,
+ ),
+ "epsg:4326",
+ ), # Case 2 - boundless (left)
+ (
+ (
+ -52.927554190740736,
+ 73.3960640725901,
+ -51.96837664926392,
+ 73.77350422465656,
+ ),
+ "epsg:4326",
+ ), # Case 3 - boundless (right)
+ (
+ (
+ -57.15027188947926,
+ 74.56177365126999,
+ -56.37556339673152,
+ 74.75029925196495,
+ ),
+ "epsg:4326",
+ ), # Case 4 - boundless (top)
+ (
+ (
+ -55.86202533996874,
+ 71.8988448629112,
+ -54.6335972683694,
+ 72.28789003457715,
+ ),
+ "epsg:4326",
+ ), # Case 5 - boundless (bottom)
+ (
+ (
+ -62.968685159182414,
+ 71.95907543637196,
+ -51.60091205568341,
+ 74.78461407516858,
+ ),
+ "epsg:4326",
+ ), # Case 6 - boundless whole raster
+ (
+ (
+ -66.79529480522785,
+ 74.22513769476188,
+ -65.89488418613195,
+ 74.48258818252089,
+ ),
+ "epsg:4326",
+ ), # Case 7 - outside bounds
+ ],
+)
+def test_part_align_transform(bounds, crs):
+ """test `align_bounds_with_dataset` option."""
+ with rasterio.open(COG) as src_dst:
+ img = reader.part(
+ src_dst,
+ bounds,
+ dst_crs=crs,
+ bounds_crs="epsg:4326",
+ align_bounds_with_dataset=True,
+ )
+ img_default = reader.part(
+ src_dst,
+ bounds,
+ dst_crs=crs,
+ bounds_crs="epsg:4326",
+ align_bounds_with_dataset=False,
+ )
+ assert not img.array.shape == img_default.array.shape
+ assert not img.bounds == img_default.bounds
+
+ # output image aligned with bounds should have the origin
+ # with the bounds UL
+ if crs != WGS84_CRS:
+ bounds = transform_bounds(WGS84_CRS, crs, *bounds, densify_pts=21)
+
+ assert round(img_default.transform.c, 5) == round(bounds[0], 5)
+ assert round(img_default.transform.f, 5) == round(bounds[3], 5)
+
+ # output image bounds aligned to the dataset transform should have the origin
+ # with the bounds greater than UL
+ assert img.transform.c < bounds[0]
+ assert img.transform.f > bounds[3]
 +
+  * allow uppercase in `cmap.get` method
diff --git a/docs/src/advanced/statistics.md b/docs/src/advanced/statistics.md
index 8209b50c..f3acc561 100644
--- a/docs/src/advanced/statistics.md
+++ b/docs/src/advanced/statistics.md
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
-### Statistics
+#### Form `Readers`
`rio-tiler`'s Readers provide simple `.statistics` method to retrieve dataset global statistics
@@ -34,83 +34,19 @@ print(stats["1"].model_dump().keys())
]
```
-### Zonal Statistics
+#### ImageData
-You can easily extend the `statistics()` method to create a `.zonal_statistics` one which will accept input features to get statistics from.
+You can get statistics from `ImageData` objects which are returned by all rio-tiler reader methods (e.g. `.tile()`, `.preview()`, `.part()`, ...)
```python
-
-import attr
-from typing import Any, Union, Optional, List, Dict
-
-from rio_tiler import io
-from rio_tiler.models import BandStatistics
-
-from geojson_pydantic.features import Feature, FeatureCollection
-from geojson_pydantic.geometries import Polygon
-
-class Reader(io.Reader):
- """Custom Reader with zonal_statistics method."""
-
- def zonal_statistics(
- self,
- geojson: Union[FeatureCollection, Feature],
- categorical: bool = False,
- categories: Optional[List[float]] = None,
- percentiles: Optional[List[int]] = None,
- hist_options: Optional[Dict] = None,
- max_size: int = None,
- **kwargs: Any,
- ) -> Union[FeatureCollection, Feature]:
- """Return statistics from GeoJSON features.
-
- Args:
- geojson (Feature or FeatureCollection): a GeoJSON Feature or FeatureCollection.
- categorical (bool): treat input data as categorical data. Defaults to False.
- categories (list of numbers, optional): list of categories to return value for.
- percentiles (list of numbers, optional): list of percentile values to calculate. Defaults to `[2, 98]`.
- hist_options (dict, optional): Options to forward to numpy.histogram function.
- max_size (int, optional): Limit the size of the longest dimension of the dataset read, respecting bounds X/Y aspect ratio. Defaults to None.
- kwargs (optional): Options to forward to `self.preview`.
-
- Returns:
- Feature or FeatureCollection
-
- """
- kwargs = {**self.options, **kwargs}
-
- hist_options = hist_options or {}
-
- fc = geojson
- # We transform the input Feature to a FeatureCollection
- if isinstance(fc, Feature):
- fc = FeatureCollection(type="FeatureCollection", features=[geojson])
-
- for feature in fc:
- # Get data overlapping with the feature (using Reader.feature method)
- data = self.feature(
- feature.model_dump(exclude_none=True),
- max_size=max_size,
- **kwargs,
- )
- stats = data.statistics(
- categorical=categorical,
- categories=categories,
- percentiles=percentiles,
- hist_options=hist_options,
- )
-
- # Update input feature properties and add the statistics
- feature.properties = feature.properties or {}
- feature.properties.update({"statistics": stats})
-
- return fc.features[0] if isinstance(geojson, Feature) else fc
+with Reader("cog.tif") as src:
+ image = src.preview()
+ stats = image.statistics()
```
-
### Area Weighted Statistics
-When getting statistics from `feature`, you may want to calculate values from the pixels which intersect with the geometry but also take the pixel intersection percentage into account. Starting with rio-tiler `6.2.0`, we've added a `coverage` option to the `statistics` utility which enable the user to pass an array representing the coverage percentage such as:
+When getting statistics from a `feature`, you may want to calculate values from the pixels which intersect with the geometry but also take the pixel intersection percentage into account. Starting with rio-tiler `6.2.0`, we've added a `coverage` option to the `statistics` utility which enable the user to pass an array representing the coverage percentage such as:
```python
import numpy
@@ -133,34 +69,110 @@ assert stats[0]["mean"] == 1.125 # (1 * 0.5 + 2 * 0.0 + 3 * 1.0 + 4 * 0.25) / 4
assert stats[0]["count"] == 1.75 # (0.5 + 0 + 1 + 0.25) sum of the coverage array
```
-When using with a `feature`, your code might look something like:
+#### Adjusting geometry `align_bounds_with_dataset=True`
-```python
-from rio_tiler.io import Reader
-from rio_tiler.constants import WGS84_CRS
+In rio-tiler `6.3,0` a new option has been introduced to reduce artifacts and produce more precise zonal statistics. This option is available in the low-level `reader.part()` method used in rio-tiler reader's `.feature()` and `.part()` methods.
-with Reader(path) as src:
- # First get the array for the feature
- data = src_dst.feature(
+```python
+with Reader("cog.tif") as src:
+ data = src.feature(
shape,
shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ align_bounds_with_dataset=True,
)
- # Get the coverage % array, using ImageData.get_coverage_array method
coverage_array = data.get_coverage_array(
- shape, shape_crs=WGS84_CRS
+ shape,
+ shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
)
- # Get statistics (ImageData.statistics is calling `rio_tiler.utils.get_array_statistics`)
stats = data.statistics(coverage=coverage_array)
```
-!!! warnings
- The coverage weights will only have influence on specific statistics:
+When passing `align_bounds_with_dataset=True` to the `reader.part()` method (forwared from `.feature` or `.part` reader's method), rio-tiler will adjust the input geometry bounds to math the input dataset resolution/transform and avoid unnecessary resampling.
- - `mean`
- - `count`
- - `sum`
- - `std`
- - `median`
+
* allow uppercase in `cmap.get` method
diff --git a/docs/src/advanced/statistics.md b/docs/src/advanced/statistics.md
index 8209b50c..f3acc561 100644
--- a/docs/src/advanced/statistics.md
+++ b/docs/src/advanced/statistics.md
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
-### Statistics
+#### Form `Readers`
`rio-tiler`'s Readers provide simple `.statistics` method to retrieve dataset global statistics
@@ -34,83 +34,19 @@ print(stats["1"].model_dump().keys())
]
```
-### Zonal Statistics
+#### ImageData
-You can easily extend the `statistics()` method to create a `.zonal_statistics` one which will accept input features to get statistics from.
+You can get statistics from `ImageData` objects which are returned by all rio-tiler reader methods (e.g. `.tile()`, `.preview()`, `.part()`, ...)
```python
-
-import attr
-from typing import Any, Union, Optional, List, Dict
-
-from rio_tiler import io
-from rio_tiler.models import BandStatistics
-
-from geojson_pydantic.features import Feature, FeatureCollection
-from geojson_pydantic.geometries import Polygon
-
-class Reader(io.Reader):
- """Custom Reader with zonal_statistics method."""
-
- def zonal_statistics(
- self,
- geojson: Union[FeatureCollection, Feature],
- categorical: bool = False,
- categories: Optional[List[float]] = None,
- percentiles: Optional[List[int]] = None,
- hist_options: Optional[Dict] = None,
- max_size: int = None,
- **kwargs: Any,
- ) -> Union[FeatureCollection, Feature]:
- """Return statistics from GeoJSON features.
-
- Args:
- geojson (Feature or FeatureCollection): a GeoJSON Feature or FeatureCollection.
- categorical (bool): treat input data as categorical data. Defaults to False.
- categories (list of numbers, optional): list of categories to return value for.
- percentiles (list of numbers, optional): list of percentile values to calculate. Defaults to `[2, 98]`.
- hist_options (dict, optional): Options to forward to numpy.histogram function.
- max_size (int, optional): Limit the size of the longest dimension of the dataset read, respecting bounds X/Y aspect ratio. Defaults to None.
- kwargs (optional): Options to forward to `self.preview`.
-
- Returns:
- Feature or FeatureCollection
-
- """
- kwargs = {**self.options, **kwargs}
-
- hist_options = hist_options or {}
-
- fc = geojson
- # We transform the input Feature to a FeatureCollection
- if isinstance(fc, Feature):
- fc = FeatureCollection(type="FeatureCollection", features=[geojson])
-
- for feature in fc:
- # Get data overlapping with the feature (using Reader.feature method)
- data = self.feature(
- feature.model_dump(exclude_none=True),
- max_size=max_size,
- **kwargs,
- )
- stats = data.statistics(
- categorical=categorical,
- categories=categories,
- percentiles=percentiles,
- hist_options=hist_options,
- )
-
- # Update input feature properties and add the statistics
- feature.properties = feature.properties or {}
- feature.properties.update({"statistics": stats})
-
- return fc.features[0] if isinstance(geojson, Feature) else fc
+with Reader("cog.tif") as src:
+ image = src.preview()
+ stats = image.statistics()
```
-
### Area Weighted Statistics
-When getting statistics from `feature`, you may want to calculate values from the pixels which intersect with the geometry but also take the pixel intersection percentage into account. Starting with rio-tiler `6.2.0`, we've added a `coverage` option to the `statistics` utility which enable the user to pass an array representing the coverage percentage such as:
+When getting statistics from a `feature`, you may want to calculate values from the pixels which intersect with the geometry but also take the pixel intersection percentage into account. Starting with rio-tiler `6.2.0`, we've added a `coverage` option to the `statistics` utility which enable the user to pass an array representing the coverage percentage such as:
```python
import numpy
@@ -133,34 +69,110 @@ assert stats[0]["mean"] == 1.125 # (1 * 0.5 + 2 * 0.0 + 3 * 1.0 + 4 * 0.25) / 4
assert stats[0]["count"] == 1.75 # (0.5 + 0 + 1 + 0.25) sum of the coverage array
```
-When using with a `feature`, your code might look something like:
+#### Adjusting geometry `align_bounds_with_dataset=True`
-```python
-from rio_tiler.io import Reader
-from rio_tiler.constants import WGS84_CRS
+In rio-tiler `6.3,0` a new option has been introduced to reduce artifacts and produce more precise zonal statistics. This option is available in the low-level `reader.part()` method used in rio-tiler reader's `.feature()` and `.part()` methods.
-with Reader(path) as src:
- # First get the array for the feature
- data = src_dst.feature(
+```python
+with Reader("cog.tif") as src:
+ data = src.feature(
shape,
shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
+ align_bounds_with_dataset=True,
)
- # Get the coverage % array, using ImageData.get_coverage_array method
coverage_array = data.get_coverage_array(
- shape, shape_crs=WGS84_CRS
+ shape,
+ shape_crs=WGS84_CRS,
)
- # Get statistics (ImageData.statistics is calling `rio_tiler.utils.get_array_statistics`)
stats = data.statistics(coverage=coverage_array)
```
-!!! warnings
- The coverage weights will only have influence on specific statistics:
+When passing `align_bounds_with_dataset=True` to the `reader.part()` method (forwared from `.feature` or `.part` reader's method), rio-tiler will adjust the input geometry bounds to math the input dataset resolution/transform and avoid unnecessary resampling.
- - `mean`
- - `count`
- - `sum`
- - `std`
- - `median`
+