| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
Example 1:
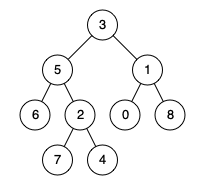
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1 Output: 3 Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 1 is 3.
Example 2:
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4 Output: 5 Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 4 is 5, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2], p = 1, q = 2 Output: 1
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 105]. -109 <= Node.val <= 109- All
Node.valare unique. p != qpandqwill exist in the tree.
We recursively traverse the binary tree:
If the current node is null or equals to
Otherwise, we recursively traverse the left and right subtrees, and record the returned results as
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(
self, root: "TreeNode", p: "TreeNode", q: "TreeNode"
) -> "TreeNode":
if root in (None, p, q):
return root
left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
return root if left and right else (left or right)/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null || root == p || root == q) {
return root;
}
var left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
var right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if (left != null && right != null) {
return root;
}
return left == null ? right : left;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if (root == nullptr || root == p || root == q) {
return root;
}
auto left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
auto right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if (left && right) {
return root;
}
return left ? left : right;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func lowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
if root == nil || root == p || root == q {
return root
}
left := lowestCommonAncestor(root.Left, p, q)
right := lowestCommonAncestor(root.Right, p, q)
if left != nil && right != nil {
return root
}
if left != nil {
return left
}
return right
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function lowestCommonAncestor(
root: TreeNode | null,
p: TreeNode | null,
q: TreeNode | null,
): TreeNode | null {
if (!root || root === p || root === q) {
return root;
}
const left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
const right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
return left && right ? root : left || right;
}// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {
pub fn lowest_common_ancestor(
root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
p: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
q: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
if root.is_none() || root == p || root == q {
return root;
}
let left = Self::lowest_common_ancestor(
root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().left.clone(),
p.clone(),
q.clone(),
);
let right = Self::lowest_common_ancestor(
root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().right.clone(),
p.clone(),
q.clone(),
);
if left.is_some() && right.is_some() {
return root;
}
if left.is_none() {
return right;
}
return left;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {TreeNode} p
* @param {TreeNode} q
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var lowestCommonAncestor = function (root, p, q) {
if (!root || root === p || root === q) {
return root;
}
const left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
const right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
return left && right ? root : left || right;
};