| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
1294 |
第 329 场周赛 Q2 |
|
班里有 m 位学生,共计划组织 n 场考试。给你一个下标从 0 开始、大小为 m x n 的整数矩阵 score ,其中每一行对应一位学生,而 score[i][j] 表示第 i 位学生在第 j 场考试取得的分数。矩阵 score 包含的整数 互不相同 。
另给你一个整数 k 。请你按第 k 场考试分数从高到低完成对这些学生(矩阵中的行)的排序。
返回排序后的矩阵。
示例 1:
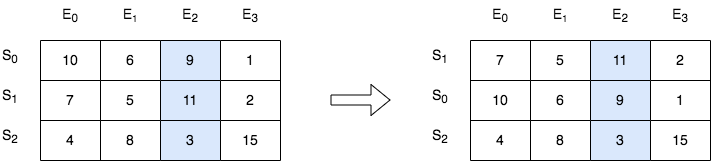
输入:score = [[10,6,9,1],[7,5,11,2],[4,8,3,15]], k = 2 输出:[[7,5,11,2],[10,6,9,1],[4,8,3,15]] 解释:在上图中,S 表示学生,E 表示考试。 - 下标为 1 的学生在第 2 场考试取得的分数为 11 ,这是考试的最高分,所以 TA 需要排在第一。 - 下标为 0 的学生在第 2 场考试取得的分数为 9 ,这是考试的第二高分,所以 TA 需要排在第二。 - 下标为 2 的学生在第 2 场考试取得的分数为 3 ,这是考试的最低分,所以 TA 需要排在第三。
示例 2:
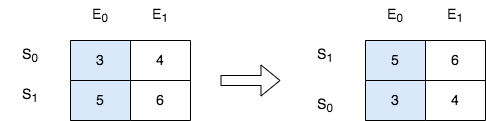
输入:score = [[3,4],[5,6]], k = 0 输出:[[5,6],[3,4]] 解释:在上图中,S 表示学生,E 表示考试。 - 下标为 1 的学生在第 0 场考试取得的分数为 5 ,这是考试的最高分,所以 TA 需要排在第一。 - 下标为 0 的学生在第 0 场考试取得的分数为 3 ,这是考试的最低分,所以 TA 需要排在第二。
提示:
m == score.lengthn == score[i].length1 <= m, n <= 2501 <= score[i][j] <= 105score由 不同 的整数组成0 <= k < n
我们直接将
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def sortTheStudents(self, score: List[List[int]], k: int) -> List[List[int]]:
return sorted(score, key=lambda x: -x[k])class Solution {
public int[][] sortTheStudents(int[][] score, int k) {
Arrays.sort(score, (a, b) -> b[k] - a[k]);
return score;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> sortTheStudents(vector<vector<int>>& score, int k) {
ranges::sort(score, [k](const auto& a, const auto& b) { return a[k] > b[k]; });
return score;
}
};func sortTheStudents(score [][]int, k int) [][]int {
sort.Slice(score, func(i, j int) bool { return score[i][k] > score[j][k] })
return score
}function sortTheStudents(score: number[][], k: number): number[][] {
return score.sort((a, b) => b[k] - a[k]);
}impl Solution {
pub fn sort_the_students(mut score: Vec<Vec<i32>>, k: i32) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let k = k as usize;
score.sort_by(|a, b| b[k].cmp(&a[k]));
score
}
}