| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
You are given a positive integer n which is the number of nodes of a 0-indexed directed weighted graph and a 0-indexed 2D array edges where edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi] indicates that there is an edge from node ui to node vi with weight wi.
You are also given a node s and a node array marked; your task is to find the minimum distance from s to any of the nodes in marked.
Return an integer denoting the minimum distance from s to any node in marked or -1 if there are no paths from s to any of the marked nodes.
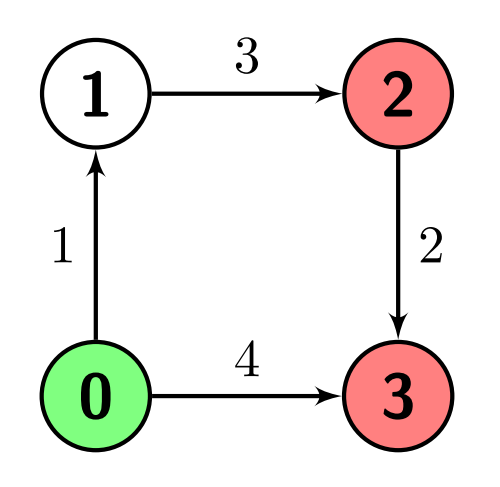
Example 1:
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,3],[2,3,2],[0,3,4]], s = 0, marked = [2,3] Output: 4 Explanation: There is one path from node 0 (the green node) to node 2 (a red node), which is 0->1->2, and has a distance of 1 + 3 = 4. There are two paths from node 0 to node 3 (a red node), which are 0->1->2->3 and 0->3, the first one has a distance of 1 + 3 + 2 = 6 and the second one has a distance of 4. The minimum of them is 4.
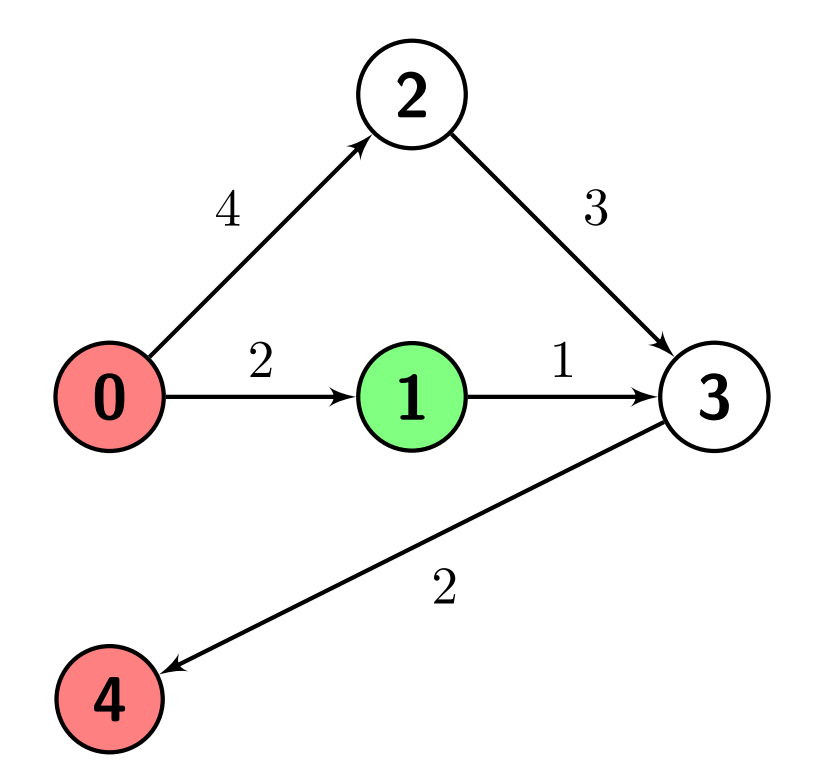
Example 2:
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1,2],[0,2,4],[1,3,1],[2,3,3],[3,4,2]], s = 1, marked = [0,4] Output: 3 Explanation: There are no paths from node 1 (the green node) to node 0 (a red node). There is one path from node 1 to node 4 (a red node), which is 1->3->4, and has a distance of 1 + 2 = 3. So the answer is 3.
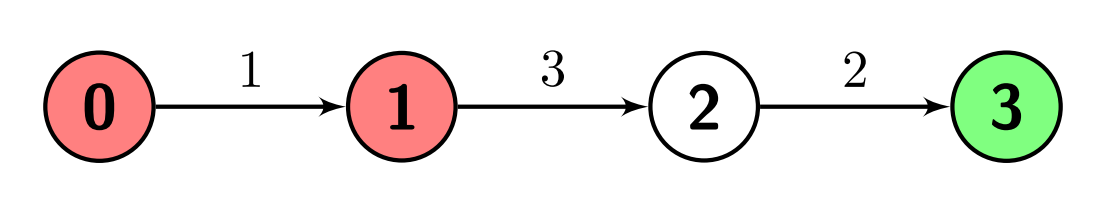
Example 3:
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,3],[2,3,2]], s = 3, marked = [0,1] Output: -1 Explanation: There are no paths from node 3 (the green node) to any of the marked nodes (the red nodes), so the answer is -1.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 5001 <= edges.length <= 104edges[i].length = 30 <= edges[i][0], edges[i][1] <= n - 11 <= edges[i][2] <= 1061 <= marked.length <= n - 10 <= s, marked[i] <= n - 1s != marked[i]marked[i] != marked[j]for everyi != j- The graph might have repeated edges.
- The graph is generated such that it has no self-loops.
First, we construct an adjacency matrix
Then, we can use Dijkstra's algorithm to find the shortest distance from the starting point
Finally, we traverse all the marked nodes and find the marked node with the smallest distance. If the distance is positive infinity, we return
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def minimumDistance(
self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], s: int, marked: List[int]
) -> int:
g = [[inf] * n for _ in range(n)]
for u, v, w in edges:
g[u][v] = min(g[u][v], w)
dist = [inf] * n
vis = [False] * n
dist[s] = 0
for _ in range(n):
t = -1
for j in range(n):
if not vis[j] and (t == -1 or dist[t] > dist[j]):
t = j
vis[t] = True
for j in range(n):
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j])
ans = min(dist[i] for i in marked)
return -1 if ans >= inf else ansclass Solution {
public int minimumDistance(int n, List<List<Integer>> edges, int s, int[] marked) {
final int inf = 1 << 29;
int[][] g = new int[n][n];
for (var e : g) {
Arrays.fill(e, inf);
}
for (var e : edges) {
int u = e.get(0), v = e.get(1), w = e.get(2);
g[u][v] = Math.min(g[u][v], w);
}
int[] dist = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(dist, inf);
dist[s] = 0;
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int t = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (!vis[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j])) {
t = j;
}
}
vis[t] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
dist[j] = Math.min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j]);
}
}
int ans = inf;
for (int i : marked) {
ans = Math.min(ans, dist[i]);
}
return ans >= inf ? -1 : ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int minimumDistance(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int s, vector<int>& marked) {
const int inf = 1 << 29;
vector<vector<int>> g(n, vector<int>(n, inf));
vector<int> dist(n, inf);
dist[s] = 0;
vector<bool> vis(n);
for (auto& e : edges) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1], w = e[2];
g[u][v] = min(g[u][v], w);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int t = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (!vis[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j])) {
t = j;
}
}
vis[t] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j]);
}
}
int ans = inf;
for (int i : marked) {
ans = min(ans, dist[i]);
}
return ans >= inf ? -1 : ans;
}
};func minimumDistance(n int, edges [][]int, s int, marked []int) int {
const inf = 1 << 29
g := make([][]int, n)
dist := make([]int, n)
for i := range g {
g[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := range g[i] {
g[i][j] = inf
}
dist[i] = inf
}
dist[s] = 0
for _, e := range edges {
u, v, w := e[0], e[1], e[2]
g[u][v] = min(g[u][v], w)
}
vis := make([]bool, n)
for _ = range g {
t := -1
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if !vis[j] && (t == -1 || dist[j] < dist[t]) {
t = j
}
}
vis[t] = true
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[t]+g[t][j])
}
}
ans := inf
for _, i := range marked {
ans = min(ans, dist[i])
}
if ans >= inf {
return -1
}
return ans
}function minimumDistance(n: number, edges: number[][], s: number, marked: number[]): number {
const inf = 1 << 29;
const g: number[][] = Array(n)
.fill(0)
.map(() => Array(n).fill(inf));
const dist: number[] = Array(n).fill(inf);
const vis: boolean[] = Array(n).fill(false);
for (const [u, v, w] of edges) {
g[u][v] = Math.min(g[u][v], w);
}
dist[s] = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
let t = -1;
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (!vis[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j])) {
t = j;
}
}
vis[t] = true;
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
dist[j] = Math.min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j]);
}
}
let ans = inf;
for (const i of marked) {
ans = Math.min(ans, dist[i]);
}
return ans >= inf ? -1 : ans;
}