| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
2276 |
Biweekly Contest 120 Q4 |
|
You are given an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, and rooted at node 0. You are given a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
You are also given a 0-indexed integer array cost of length n, where cost[i] is the cost assigned to the ith node.
You need to place some coins on every node of the tree. The number of coins to be placed at node i can be calculated as:
- If size of the subtree of node
iis less than3, place1coin. - Otherwise, place an amount of coins equal to the maximum product of cost values assigned to
3distinct nodes in the subtree of nodei. If this product is negative, place0coins.
Return an array coin of size n such that coin[i] is the number of coins placed at node i.
Example 1:
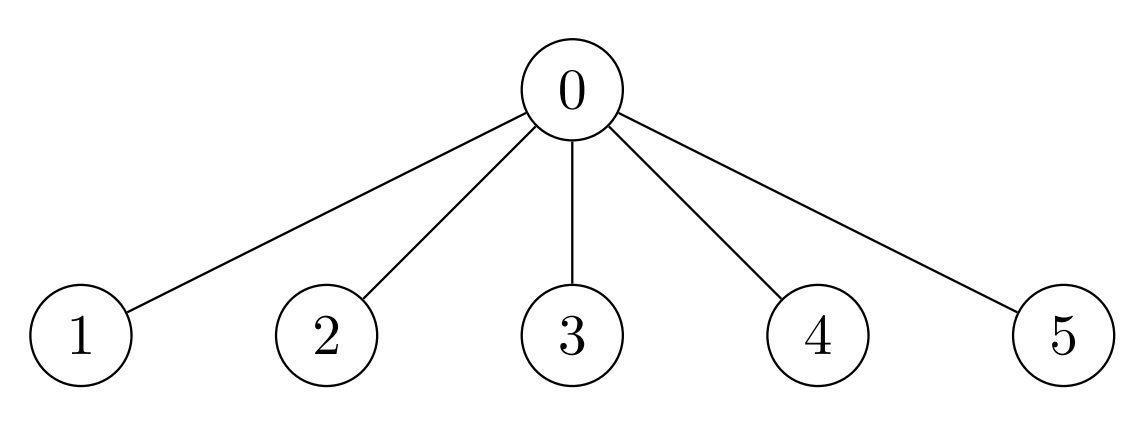
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[0,4],[0,5]], cost = [1,2,3,4,5,6] Output: [120,1,1,1,1,1] Explanation: For node 0 place 6 * 5 * 4 = 120 coins. All other nodes are leaves with subtree of size 1, place 1 coin on each of them.
Example 2:
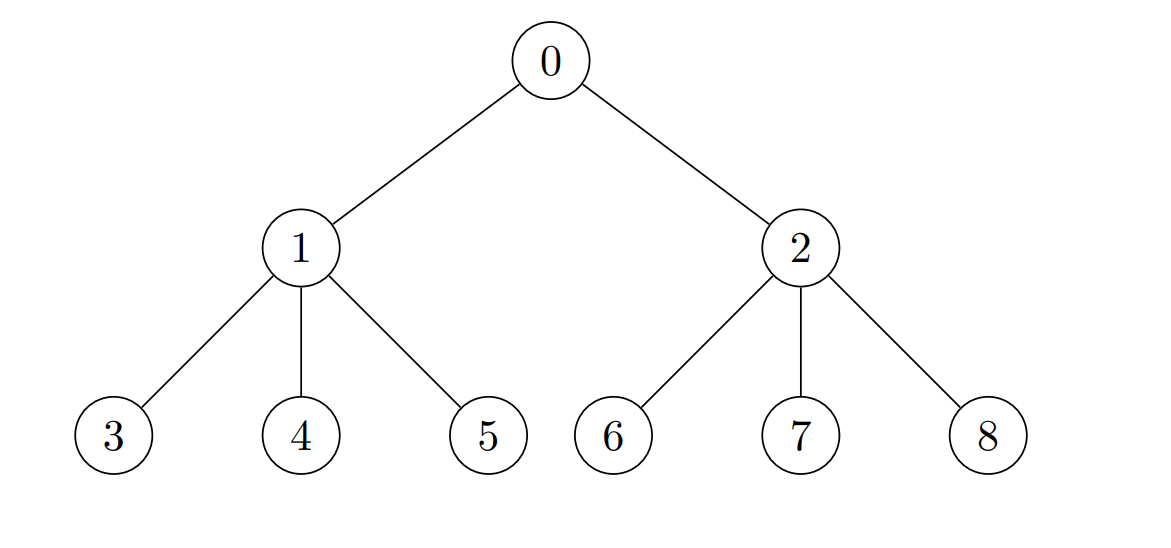
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[1,5],[2,6],[2,7],[2,8]], cost = [1,4,2,3,5,7,8,-4,2] Output: [280,140,32,1,1,1,1,1,1] Explanation: The coins placed on each node are: - Place 8 * 7 * 5 = 280 coins on node 0. - Place 7 * 5 * 4 = 140 coins on node 1. - Place 8 * 2 * 2 = 32 coins on node 2. - All other nodes are leaves with subtree of size 1, place 1 coin on each of them.
Example 3:
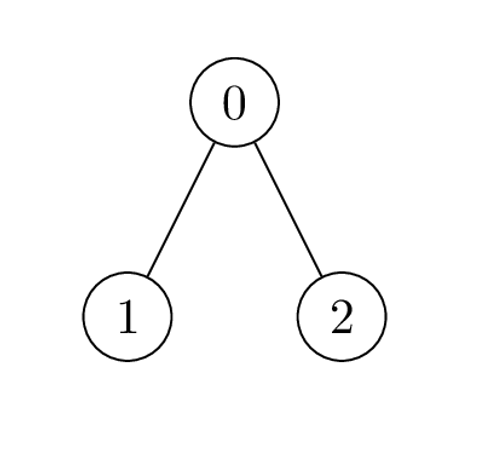
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2]], cost = [1,2,-2] Output: [0,1,1] Explanation: Node 1 and 2 are leaves with subtree of size 1, place 1 coin on each of them. For node 0 the only possible product of cost is 2 * 1 * -2 = -4. Hence place 0 coins on node 0.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 2 * 104edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < ncost.length == n1 <= |cost[i]| <= 104- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree.
According to the problem description, there are two situations for the number of coins placed at each node
- If the number of nodes in the subtree corresponding to node
$a$ is less than$3$ , then place$1$ coin; - If the number of nodes in the subtree corresponding to node
$a$ is greater than or equal to$3$ , then we need to take out$3$ different nodes from the subtree, calculate the maximum value of their cost product, and then place the corresponding number of coins at node$a$ . If the maximum product is negative, place$0$ coins.
The first situation is relatively simple, we just need to count the number of nodes in the subtree of each node during the traversal.
For the second situation, if all costs are positive, we should take the
We first construct the adjacency list
Next, we design a function
In the function
Then, we sort the array
- If
$m \ge 3$ , then the number of coins placed at node$a$ is$\max(0, res[m - 1] \times res[m - 2] \times res[m - 3], res[0] \times res[1] \times res[m - 1])$ , otherwise the number of coins placed at node$a$ is$1$ ; - If
$m > 5$ , then we only need to keep the first$2$ elements and the last$3$ elements of the array$res$ .
Finally, we call the function
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def placedCoins(self, edges: List[List[int]], cost: List[int]) -> List[int]:
def dfs(a: int, fa: int) -> List[int]:
res = [cost[a]]
for b in g[a]:
if b != fa:
res.extend(dfs(b, a))
res.sort()
if len(res) >= 3:
ans[a] = max(res[-3] * res[-2] * res[-1], res[0] * res[1] * res[-1], 0)
if len(res) > 5:
res = res[:2] + res[-3:]
return res
n = len(cost)
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for a, b in edges:
g[a].append(b)
g[b].append(a)
ans = [1] * n
dfs(0, -1)
return ansclass Solution {
private int[] cost;
private List<Integer>[] g;
private long[] ans;
public long[] placedCoins(int[][] edges, int[] cost) {
int n = cost.length;
this.cost = cost;
ans = new long[n];
g = new List[n];
Arrays.fill(ans, 1);
Arrays.setAll(g, i -> new ArrayList<>());
for (int[] e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
g[a].add(b);
g[b].add(a);
}
dfs(0, -1);
return ans;
}
private List<Integer> dfs(int a, int fa) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
res.add(cost[a]);
for (int b : g[a]) {
if (b != fa) {
res.addAll(dfs(b, a));
}
}
Collections.sort(res);
int m = res.size();
if (m >= 3) {
long x = (long) res.get(m - 1) * res.get(m - 2) * res.get(m - 3);
long y = (long) res.get(0) * res.get(1) * res.get(m - 1);
ans[a] = Math.max(0, Math.max(x, y));
}
if (m >= 5) {
res = List.of(res.get(0), res.get(1), res.get(m - 3), res.get(m - 2), res.get(m - 1));
}
return res;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<long long> placedCoins(vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& cost) {
int n = cost.size();
vector<long long> ans(n, 1);
vector<int> g[n];
for (auto& e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
g[a].push_back(b);
g[b].push_back(a);
}
function<vector<int>(int, int)> dfs = [&](int a, int fa) -> vector<int> {
vector<int> res = {cost[a]};
for (int b : g[a]) {
if (b != fa) {
auto t = dfs(b, a);
res.insert(res.end(), t.begin(), t.end());
}
}
sort(res.begin(), res.end());
int m = res.size();
if (m >= 3) {
long long x = 1LL * res[m - 1] * res[m - 2] * res[m - 3];
long long y = 1LL * res[0] * res[1] * res[m - 1];
ans[a] = max({0LL, x, y});
}
if (m >= 5) {
res = {res[0], res[1], res[m - 1], res[m - 2], res[m - 3]};
}
return res;
};
dfs(0, -1);
return ans;
}
};func placedCoins(edges [][]int, cost []int) []int64 {
n := len(cost)
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
a, b := e[0], e[1]
g[a] = append(g[a], b)
g[b] = append(g[b], a)
}
ans := make([]int64, n)
for i := range ans {
ans[i] = int64(1)
}
var dfs func(a, fa int) []int
dfs = func(a, fa int) []int {
res := []int{cost[a]}
for _, b := range g[a] {
if b != fa {
res = append(res, dfs(b, a)...)
}
}
sort.Ints(res)
m := len(res)
if m >= 3 {
x := res[m-1] * res[m-2] * res[m-3]
y := res[0] * res[1] * res[m-1]
ans[a] = max(0, int64(x), int64(y))
}
if m >= 5 {
res = append(res[:2], res[m-3:]...)
}
return res
}
dfs(0, -1)
return ans
}function placedCoins(edges: number[][], cost: number[]): number[] {
const n = cost.length;
const ans: number[] = Array(n).fill(1);
const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
for (const [a, b] of edges) {
g[a].push(b);
g[b].push(a);
}
const dfs = (a: number, fa: number): number[] => {
const res: number[] = [cost[a]];
for (const b of g[a]) {
if (b !== fa) {
res.push(...dfs(b, a));
}
}
res.sort((a, b) => a - b);
const m = res.length;
if (m >= 3) {
const x = res[m - 1] * res[m - 2] * res[m - 3];
const y = res[0] * res[1] * res[m - 1];
ans[a] = Math.max(0, x, y);
}
if (m > 5) {
res.splice(2, m - 5);
}
return res;
};
dfs(0, -1);
return ans;
}