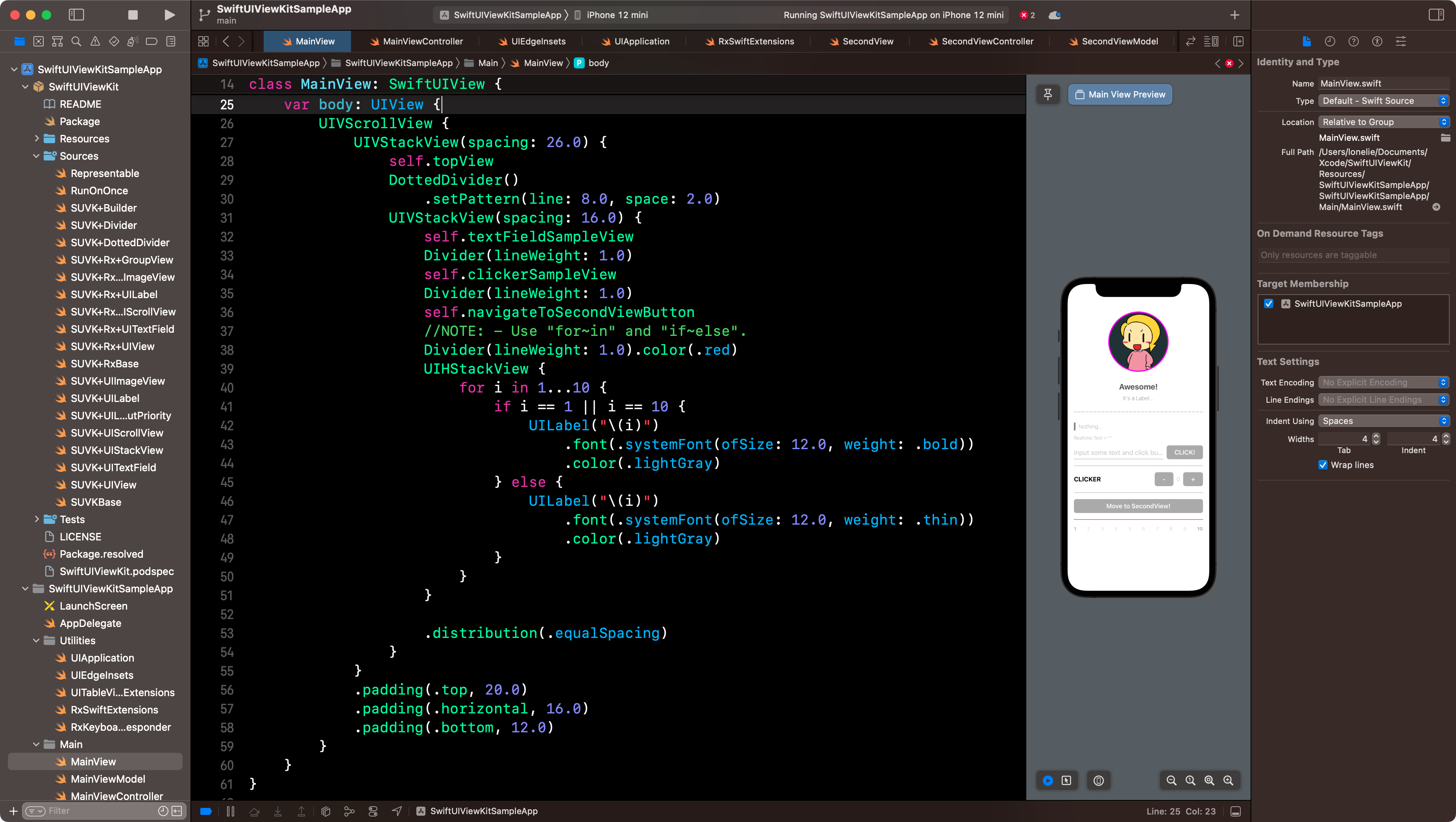
Can more EASILY made UI.
import UIKit
import SwiftUIViewKit
class MyView: SwiftUIView {
func body: UIView {
UIVStackView {
UILabel("blah")
UIHStackView {
UILabel("some title")
.priority(.required)
UILabel("some description")
}
}
}
}
By default, layouts can be configured with Vertical or Horizontal and Linear using UIStackView.
UIVStackView(alignment: .center, spacing: 12.0) {
/* ANYTHING */
}
.distribution(.fillEqually)
At this time, you can obtain the layout you want by utilizing the .spacing, .alignment, and .distribution of UIStrackView.
UIView.spacer()
.frame(maxWidth: .greatestFiniteMagnitude, horizontalAlignment: .right)
.padding(.top, 12.0)
All UIViews (including inherited children) can be sized through .frame, or .padding allows you to specify margins.
UIVScrollView {
/*Any UIView*/
}
UIHScrollView {
/*Any UIView*/
)
UIScrollView is also easy to use.
UILabel(
UILabel(image: "ImageName(String literal) or UIImage object.")
+ UILabel("Big").font(.systemFont(ofSize: 20.0, weight: .regular))
+ UILabel("Small").font(.systemFont(ofSize: 10.0, weight: .regular))
)
The
+operator in UILabel makes it easy to formatted text.
UIVScrollView {
UILabel("some text")
UIImageView(named: "imageName").renderingMode(.alwaysTemplate)
)
.color(.cyan)
.color finds all the UIViews contained within, including the corresponding UIView, and applies the color value.
private let disposeBag = DisposeBag()
private let text = BehaviorRelay<String>(value: "Now loading...")
private let imageName = BehaviorRelay<String>(value: "icn_default_place_holder")
private let color = BehaviorRelay<Color>(value: .red)
var body: UIView {
UIVScrollView {
UILabel(self.text)
UIImageView(named: self.imageName)
)
.color(self.color)
}
Use Rx then You can easily made responsive UI.
someView.subscribe(someObservable) {view, element in
/* blah */
}
Similarly, you can customize the behavior after receiving the Observable.
someView.configure {view in
/* blah */
}
Features not yet supported can be customized using the .configure in UIView.