A simple android weather application to demonstrate the usage for MVVM design pattern using LiveData, RxJava, View-DataBinding, Retrofit, Moshi, Koin (Dependency Injection), based on Clean Architecture & Gradle Dependency Management (GDM) . The application supports caching using retrofits default caching mechanism.
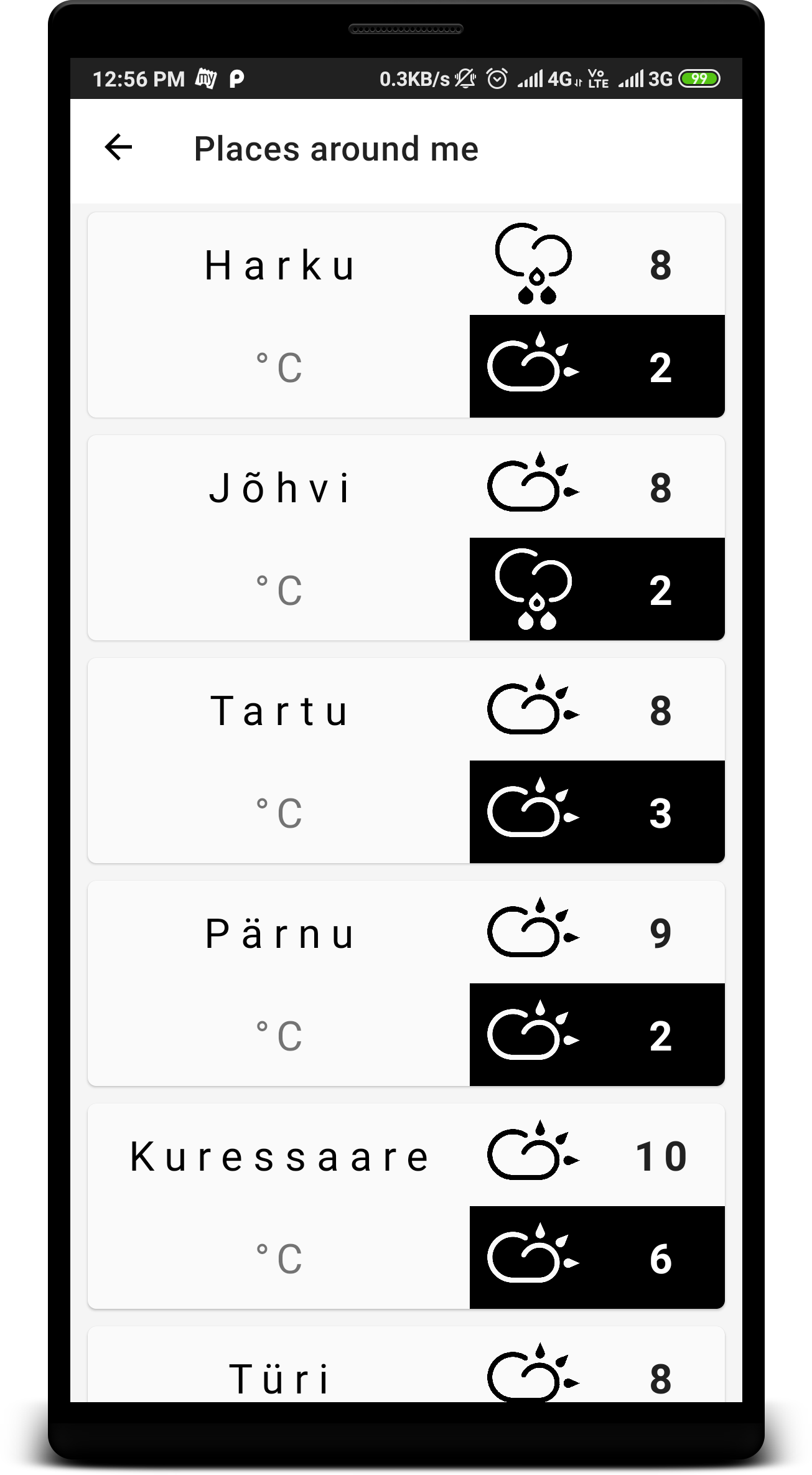
The application uses the Weather API for Estonia and shows weather forecast with respect to 4 day forecast. It presents weather information for day & night with respected to the date selected and also for multiple cities in Estonia.
- MVVM Architecture - Robust, testable, and maintainable app with classes for managing your UI component lifecycle and handling data persistence.
- Clean Architecture - Isolates UI, business logic and data sources' responsibilities creating a Testable system
- KOIN - A pragmatic lightweight dependency injection framework for Kotlin
- AndroidX - AndroidX is a major improvement to the original Android [Support Library]
- Lifecycles - Create a UI that automatically responds to lifecycle events.
- LiveData - Build data objects that notify views when the underlying database changes.
- ViewModel - Store UI-related data that isn't destroyed on app rotations. Easily schedule asynchronous tasks for optimal execution.
- Test - An Android testing framework for unit and runtime UI tests.
Let’s start explaining Data Flow in Clean Architecture as follows,
- UI calls method from ViewModel.
- ViewModel executes Use case.
- Use case combines data from Multiple Repositories.
- Each Repository returns data from a Data Source (Cached or Remote). [ In current scope only Remote ]
- Information flows back to the UI where we display the list of requested information.
In Clean Architecture adopted, relationship that exists between the different layers is very crucial.
Different layers & their boundaries are explained below,
Presentation Layer contains UI (Activities & Fragments)_ that are coordinated by ViewModels which execute one or more Use cases._ Presentation layer depends on Domain Layer.
Domain Layer It contains Entities, Use cases & Repository Interfaces. Use cases combine data from one or more Repository Interfaces.
Data Layer contains Repository Implementations and one or more Data Sources. Repositories are responsible to coordinate data from the different Data Sources. Data Layer depends on Domain Layer.
Clean Architecture helps Isolates UI, business logic and data sources' responsibilities creating a Testable system.
If you've found an error in this sample, please file an issue: https://github.com/faiyyazs/ShiftWeather/issues
Patches are encouraged, and may be submitted by forking this project and submitting a pull request through GitHub.