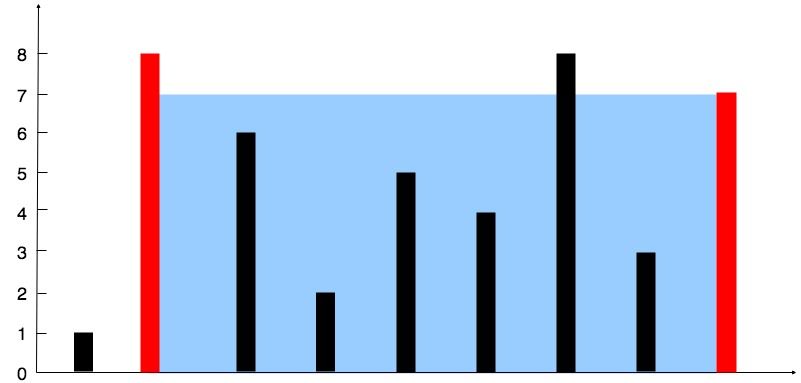
给定一个长度为 n 的整数数组 height 。有 n 条垂线,第 i 条线的两个端点是 (i, 0) 和 (i, height[i]) 。
找出其中的两条线,使得它们与 x 轴共同构成的容器可以容纳最多的水。
返回容器可以储存的最大水量。
说明:你不能倾斜容器。
示例 1:
输入:[1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7] 输出:49 解释:图中垂直线代表输入数组 [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]。在此情况下,容器能够容纳水(表示为蓝色部分)的最大值为 49。
示例 2:
输入:height = [1,1] 输出:1
提示:
n == height.length2 <= n <= 1050 <= height[i] <= 104
双指针解决。
一开始,我们考虑相距最远的两个柱子所能容纳水的面积。水的宽度是两根柱子之间的距离,而水的高度取决于两根柱子之间较短的那个。
- 当前柱子是最两侧的柱子,水的宽度最大,其他的组合,水的宽度都比这个小;
- 当前左侧柱子较短,决定了水的高度。如果移动左侧的柱子,新的水面高度不确定,但一定不会超过右侧的柱子高度;
- 如果移动右侧的柱子,新的水面高度一定不会超过左侧的柱子高度,也就是不会超过当前的水面高度。
可见,如果固定左侧的柱子,向内移动右侧的柱子,水的高度一定不会增加,且宽度一定减少,所以水的面积一定减少。所以左侧的柱子跟右侧其他柱子的组合,都可以排除了。也就是代码中的 i++。
移动左侧的柱子中,重复进行上面的操作。
在此过程中,我们不断排除掉无法成为构成最大值的柱子组合,而每一次都获取到可能为最大值的面积 t。那么遍历结束之后,我们就可以得到最大值。
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
i, j = 0, len(height) - 1
res = 0
while i < j:
t = (j - i) * min(height[i], height[j])
res = max(res, t)
if height[i] < height[j]:
i += 1
else:
j -= 1
return resclass Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int i = 0, j = height.length - 1;
int res = 0;
while (i < j) {
int t = (j - i) * Math.min(height[i], height[j]);
res = Math.max(res, t);
if (height[i] < height[j]) ++i;
else --j;
}
return res;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {
int i = 0, j = height.size() - 1;
int res = 0;
while (i < j) {
int t = (j - i) * min(height[i], height[j]);
res = max(res, t);
if (height[i] < height[j]) ++i;
else --j;
}
return res;
}
};func maxArea(height []int) int {
i, j := 0, len(height) - 1
res := 0
for i != j {
t := (j - i) * min(height[i], height[j])
res = max(res, t)
if height[i] < height[j] {
i++
} else {
j--
}
}
return res
}
func min(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return b
}
return a
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}/**
* @param {number[]} height
* @return {number}
*/
var maxArea = function (height) {
let i = 0,
j = height.length - 1;
let res = 0;
while (i < j) {
const t = (j - i) * Math.min(height[i], height[j]);
res = Math.max(res, t);
if (height[i] < height[j]) ++i;
else --j;
}
return res;
};function maxArea(height: number[]): number {
const n = height.length;
let res = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
for (let j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (height[i] * (j - i) < res) {
break;
}
res = Math.max(res, Math.min(height[i], height[j]) * (j - i));
}
}
return res;
}impl Solution {
pub fn max_area(height: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let mut i = 0;
let mut j = height.len() - 1;
let mut res = 0;
while i < j {
res = res.max(height[i].min(height[j]) * (j - i) as i32);
if height[i] <= height[j] {
i += 1;
} else {
j -= 1;
}
}
res
}
}