给定两个由一些 闭区间 组成的列表,firstList 和 secondList ,其中 firstList[i] = [starti, endi] 而 secondList[j] = [startj, endj] 。每个区间列表都是成对 不相交 的,并且 已经排序 。
返回这 两个区间列表的交集 。
形式上,闭区间 [a, b](其中 a <= b)表示实数 x 的集合,而 a <= x <= b 。
两个闭区间的 交集 是一组实数,要么为空集,要么为闭区间。例如,[1, 3] 和 [2, 4] 的交集为 [2, 3] 。
示例 1:
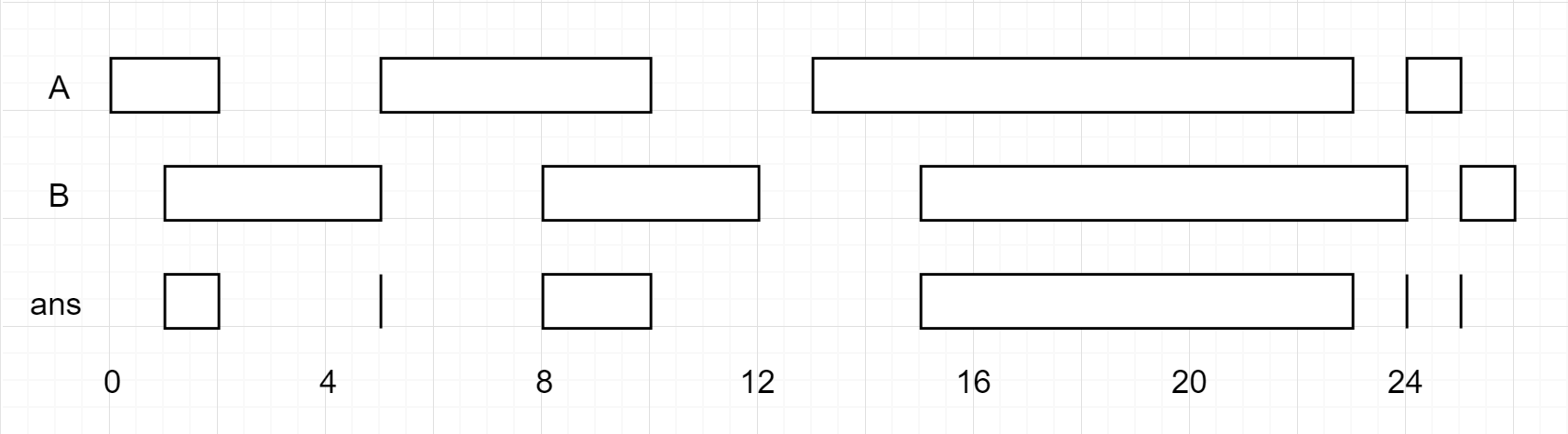
输入:firstList = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], secondList = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]] 输出:[[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]]
示例 2:
输入:firstList = [[1,3],[5,9]], secondList = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:firstList = [], secondList = [[4,8],[10,12]] 输出:[]
示例 4:
输入:firstList = [[1,7]], secondList = [[3,10]] 输出:[[3,7]]
提示:
0 <= firstList.length, secondList.length <= 1000firstList.length + secondList.length >= 10 <= starti < endi <= 109endi < starti+10 <= startj < endj <= 109endj < startj+1
方法一:双指针
class Solution:
def intervalIntersection(self, firstList: List[List[int]], secondList: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
i = j = 0
ans = []
while i < len(firstList) and j < len(secondList):
s1, e1, s2, e2 = *firstList[i], *secondList[j]
l, r = max(s1, s2), min(e1, e2)
if l <= r:
ans.append([l, r])
if e1 < e2:
i += 1
else:
j += 1
return ansclass Solution {
public int[][] intervalIntersection(int[][] firstList, int[][] secondList) {
List<int[]> ans = new ArrayList<>();
int m = firstList.length, n = secondList.length;
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < m && j < n;) {
int l = Math.max(firstList[i][0], secondList[j][0]);
int r = Math.min(firstList[i][1], secondList[j][1]);
if (l <= r) {
ans.add(new int[]{l, r});
}
if (firstList[i][1] < secondList[j][1]) {
++i;
} else {
++j;
}
}
return ans.toArray(new int[ans.size()][]);
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> intervalIntersection(vector<vector<int>>& firstList, vector<vector<int>>& secondList) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
int m = firstList.size(), n = secondList.size();
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < m && j < n;)
{
int l = max(firstList[i][0], secondList[j][0]);
int r = min(firstList[i][1], secondList[j][1]);
if (l <= r) ans.push_back({l, r});
if (firstList[i][1] < secondList[j][1]) ++i;
else ++j;
}
return ans;
}
};func intervalIntersection(firstList [][]int, secondList [][]int) [][]int {
m, n := len(firstList), len(secondList)
var ans [][]int
for i, j := 0, 0; i < m && j < n; {
l := max(firstList[i][0], secondList[j][0])
r := min(firstList[i][1], secondList[j][1])
if l <= r {
ans = append(ans, []int{l, r})
}
if firstList[i][1] < secondList[j][1] {
i++
} else {
j++
}
}
return ans
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
func min(a, b int) int {
if a < b {
return a
}
return b
}