| stage | group | info | type |
|---|---|---|---|
Create |
Editor |
To determine the technical writer assigned to the Stage/Group associated with this page, see https://about.gitlab.com/handbook/engineering/ux/technical-writing/#designated-technical-writers |
index, reference, howto |
To search through issues and merge requests in multiple projects, you can use the Issues or Merge Requests links in the top-right part of your screen.
Both of them work in the same way, therefore, the following notes are valid for both.
The number displayed on their right represents the number of issues and merge requests assigned to you.
When you click Issues, you'll see the opened issues assigned to you straight away:
You can search through Open, Closed, or All issues.
You can also filter the results using the search and filter field, as described below in Filtering issue and merge request lists.
You'll also find shortcuts to issues and merge requests created by you or assigned to you on the search field on the top-right of your screen:
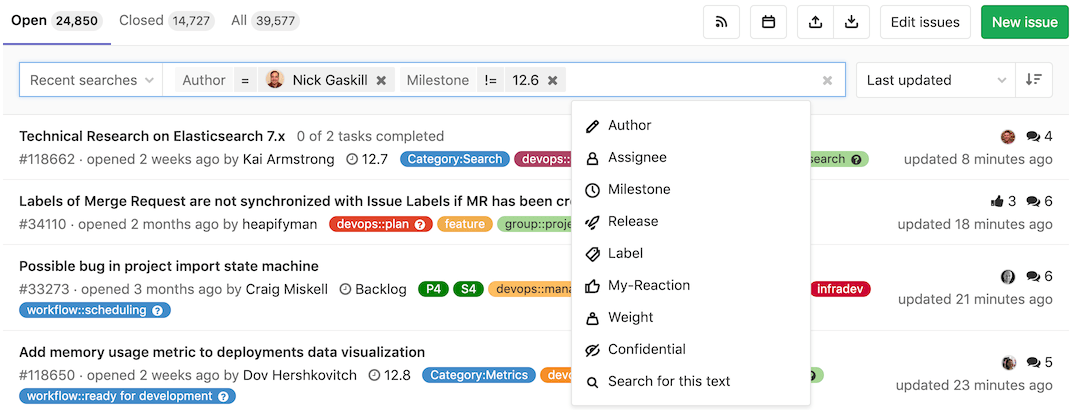
Follow these steps to filter the Issues and Merge Requests list pages within projects and groups:
- Click in the field Search or filter results....
- In the dropdown menu that appears, select the attribute you wish to filter by:
- Author
- Assignee
- Milestone
- Release
- Label
- My-reaction
- Confidential
- Epic (introduced in GitLab 12.9), including child epic (introduced in GitLab Ultimate 13.0)
- Search for this text
- Select or type the operator to use for filtering the attribute. The following operators are
available:
=: Is!=: Is not (Introduced in GitLab 12.7)
- Enter the text to filter the attribute by.
- Repeat this process to filter by multiple attributes. Multiple attributes are joined by a logical
AND.
For example, filtering by Author = Jane and Milestone != 12.6 filters for the issues where Jane
is the author and the milestone is not 12.6.
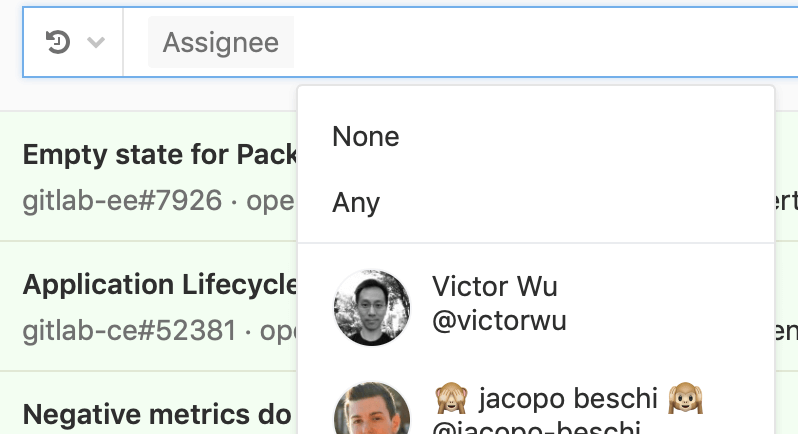
Some filter fields like milestone and assignee, allow you to filter by None or Any.
Selecting None returns results that have an empty value for that field. E.g.: no milestone, no assignee.
Selecting Any does the opposite. It returns results that have a non-empty value for that field.
You can filter issues and merge requests by specific terms included in titles or descriptions.
- Syntax
- Searches look for all the words in a query, in any order. E.g.: searching
issues for
display bugwill return all issues matching both those words, in any order. - To find the exact term, use double quotes:
"display bug"
- Searches look for all the words in a query, in any order. E.g.: searching
issues for
- Limitation
- For performance reasons, terms shorter than 3 chars are ignored. E.g.: searching
issues for
included in titlesis same asincluded titles - Search is limited to 4096 characters and 64 terms per query.
- For performance reasons, terms shorter than 3 chars are ignored. E.g.: searching
issues for
Introduced in GitLab 12.1.
You can filter the Issues list to individual instances by their ID. For example, enter filter #10 to return only issue 10. The same applies to the Merge Requests list. Enter filter #30 to return only merge request 30.
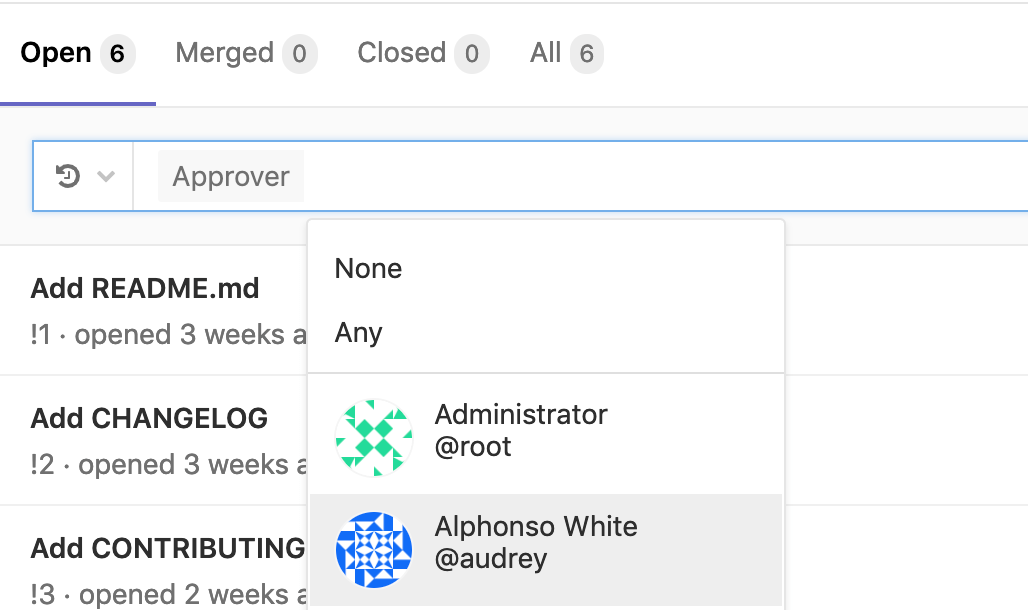
Introduced in GitLab Starter 11.9.
To filter merge requests by an individual approver, you can type (or select from the dropdown) Approver and select the user.
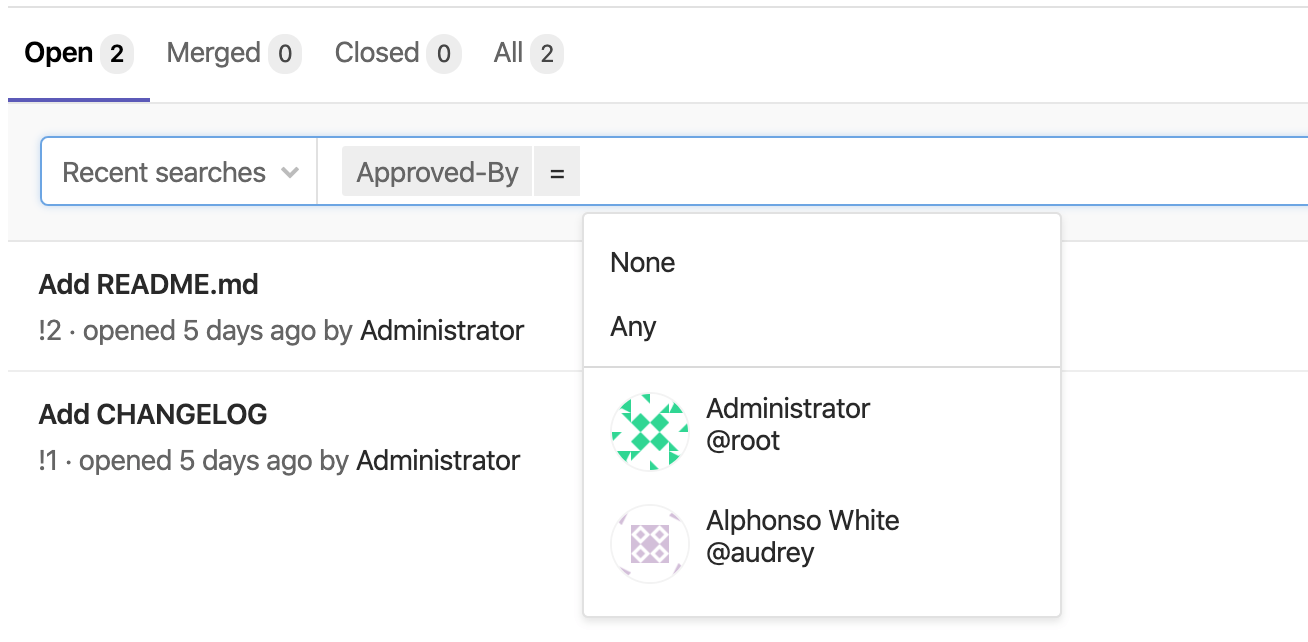
Introduced in GitLab Starter 13.0.
To filter merge requests already approved by a specific individual, you can type (or select from the dropdown) Approved-By and select the user.
GitLab provides many filters across many pages (issues, merge requests, epics, and pipelines among others) which you can use to narrow down your search. When using the filter functionality, you can start typing characters to bring up relevant users or other attributes.
For performance optimization, there is a requirement of a minimum of three characters to begin your search. For example, if you want to search for issues that have the assignee "Simone Presley", you'll need to type at least "Sim" before autocomplete gives any relevant results.
To search through code or other documents in a single project, you can use the search field on the top-right of your screen while the project page is open.
You can view recent searches by clicking on the little arrow-clock icon, which is to the left of the search input. Click the search entry to run that search again. This feature is available for issues and merge requests. Searches are stored locally in your browser.
Individual filters can be removed by clicking on the filter's (x) button or backspacing. The entire search filter can be cleared by clicking on the search box's (x) button or via ⌘ (Mac) + ⌫.
To delete filter tokens one at a time, the ⌥ (Mac) / Ctrl + ⌫ keyboard combination can be used.
Some filters can be added multiple times. These include but are not limited to assignees and labels. When you filter with these multiple filters of the same type, the AND logic is applied. For example, if you were filtering assignee:@sam assignee:@sarah, your results will only include entries whereby the assignees are assigned to both Sam and Sarah are returned.
You'll also find a shortcut on the search field on the top-right of the project's dashboard to quickly access issues and merge requests created or assigned to you within that project:
You can also type in this search bar to see autocomplete suggestions for:
- Projects and groups
- Various help pages (try and type API help)
- Project feature pages (try and type milestones)
- Various settings pages (try and type user settings)
Your To-Do List can be searched by "to do" and "done". You can filter them per project, author, type, and action. Also, you can sort them by Label priority, Last created, and Oldest created.
You can search through your projects from the left menu, by clicking the menu bar, then Projects. On the field Filter by name, type the project or group name you want to find, and GitLab will filter them for you as you type.
You can also look for the projects you starred (Starred projects), and Explore all public and internal projects available in GitLab.com, from which you can filter by visibility, through Trending, best rated with Most stars, or All of them.
You can also sort them by Name, Last created, Oldest created, Last updated, Oldest updated, Owner, and choose to hide or show archived projects:
Similarly to projects search, you can search through your groups from the left menu, by clicking the menu bar, then Groups.
On the field Filter by name, type the group name you want to find, and GitLab will filter them for you as you type.
You can also Explore all public and internal groups available in GitLab.com, and sort them by Last created, Oldest created, Last updated, or Oldest updated.
From an Issue Board, you can filter issues by Author, Assignee, Milestone, and Labels. You can also filter them by name (issue title), from the field Filter by name, which is loaded as you type.
When you want to search for issues to add to lists present in your Issue Board, click the button Add issues on the top-right of your screen, opening a modal window from which you'll be able to, besides filtering them by Name, Author, Assignee, Milestone, and Labels, select multiple issues to add to a list of your choice:
Leverage Elasticsearch for faster, more advanced code search across your entire GitLab instance.
Learn how to use the Advanced Search.
Use advanced queries for more targeted search results.