** Bakgrunn:
Substratet for Fettsyresyntese er Acetyl-CoA. Et produkt i sitronsyresyklus der glukose omdannes til energi.
Dette kommer via citrat som passerer mitokondriemembranen.
Citrat tar veien over til cytosol.
- I simpleste form handler FAS om å kombinere Acetyl-CoA (2 C) til Palmitin-Syre (16 C) i en energikrevende sirkelreaksjon. ATP + H20 -> ADP + H+
- Palmitinsyre brukes videre som utgangspunkt for å lage lengre fettsyrer og for å legge til dobbeltbindinger.
Fatty acid synthesis starts with the carboxylation of acetyl CoA to malonyl CoA. This irreversible reaction is the committed step in fatty acid synthesis
- The enzyme system that catalyzes the synthesis of saturated long-chain fatty acids from acetyl CoA, malonyl CoA, and NADPH is called the fatty acid synthase
- Fatty acids are synthesized by the repetition of the following reaction sequence: condensation, reduction, dehydration, and reduction.
- The growing fatty acid chain is elongated by the sequential addition of two-carbon units derived from acetyl CoA. The activated donor of twocarbon units in the elongation step is malonyl ACP.(Acyl carrier protein)
- Fatty acids are synthesized in the cytosol, whereas acetyl CoA is formed from pyruvate in mitochondria. Hence, acetyl CoA must be transferred from mitochondria to the cytosol. The barrier to acetyl CoA is bypassed by citrate, which carries acetyl groups across the inner mitochondrial membrane
- Elongation by the fatty acid synthase complex stops on formation of palmitate (C16). Further elongation and the insertion of double bonds are carried out by other enzyme systems.
Endelig skjebne Fettsyrene blir koblet på glycerol til triaceyl-glyserider og syntetisert til VLDL i leveren og transportert til resten av kroppen
Acetyl-CoA karboksylase Rate limiting enzyme..
- Legger til karboksylgruppe til Acetyl-CoA --> Malonyl-CoA. Pos regulering:
- Alosterisk (molekyl fester seg på anne sted på enzymet) ved Citrat Regulerer oppover/fremover-
- Hormonell: Insulin (Trenger fettsyresyntese etter høy glukose i blodet) Neg Regulering:
- Hormonell:Glukagon (Bryter ned fettsyrer for energi.)
- Alosterisk: Langkjedede fettsyrer. (Neg tilbakekobling)
- Fettsyrer trenger å transporteres fra cytosol til Mitokondriemembran.
- Carnitine Acyl transferase I.
- Aktivere Fettsyren.
- Legge til Carnitin
- Transport inn i mitokondriell matrix.
- Beta-oksidasjon
- Lager NADH og FADH2 til elktrontransportkjeden og prod av ATP.
Hvert andre C fra karbonyl-ende av acyl-CoA bli oksydert til Acetyl CoA og prod Reduksjonsagenter for ATP-prod.
Malonyl-CoA alosteriks hemmer av Carnitine Acyl transferase I
All produksjon av energi skjer i mitokondriet, både Oksidering samt celleånding. Krebs-syklus.
Legg til mer tekst.
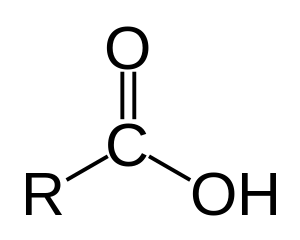
Fettsyre: Karboksylsyre med lang karbonkjede. Karboksylsyre
General Fatty Acid Formula
FA oxidation on Wikpedia In the words of Wikipedia:
"Beta-oxidation is the process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the mitochondria to generate acetyl-coA, which enters the citric acid cycle, and NADH and FADH2, which are used by the electron transport chain."
General chemical structure of an acyl-CoA, where R is a fatty acid side chain -->
NADH
In metabolism, NAD+ is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another.
FADH2
flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is a redox cofactor involved in several important reactions in metabolism.