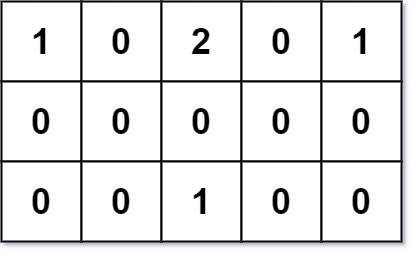
You are given an m x n grid grid of values 0, 1, or 2, where:
- each
0marks an empty land that you can pass by freely, - each
1marks a building that you cannot pass through, and - each
2marks an obstacle that you cannot pass through.
You want to build a house on an empty land that reaches all buildings in the shortest total travel distance. You can only move up, down, left, and right.
Return the shortest travel distance for such a house. If it is not possible to build such a house according to the above rules, return -1.
The total travel distance is the sum of the distances between the houses of the friends and the meeting point.
The distance is calculated using Manhattan Distance, where distance(p1, p2) = |p2.x - p1.x| + |p2.y - p1.y|.
Example 1:
Input: grid = [[1,0,2,0,1],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,1,0,0]] Output: 7 Explanation: Given three buildings at (0,0), (0,4), (2,2), and an obstacle at (0,2). The point (1,2) is an ideal empty land to build a house, as the total travel distance of 3+3+1=7 is minimal. So return 7.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[1,0]] Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[1]] Output: -1
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 50grid[i][j]is either0,1, or2.- There will be at least one building in the
grid.
BFS.
class Solution:
def shortestDistance(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
q = deque()
total = 0
cnt = [[0] * n for _ in range(m)]
dist = [[0] * n for _ in range(m)]
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if grid[i][j] == 1:
total += 1
q.append((i, j))
d = 0
vis = set()
while q:
d += 1
for _ in range(len(q)):
r, c = q.popleft()
for a, b in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
x, y = r + a, c + b
if (
0 <= x < m
and 0 <= y < n
and grid[x][y] == 0
and (x, y) not in vis
):
cnt[x][y] += 1
dist[x][y] += d
q.append((x, y))
vis.add((x, y))
ans = inf
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if grid[i][j] == 0 and cnt[i][j] == total:
ans = min(ans, dist[i][j])
return -1 if ans == inf else ansclass Solution {
public int shortestDistance(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
Deque<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
int total = 0;
int[][] cnt = new int[m][n];
int[][] dist = new int[m][n];
int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
++total;
q.offer(new int[] {i, j});
int d = 0;
boolean[][] vis = new boolean[m][n];
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
++d;
for (int k = q.size(); k > 0; --k) {
int[] p = q.poll();
for (int l = 0; l < 4; ++l) {
int x = p[0] + dirs[l];
int y = p[1] + dirs[l + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 0
&& !vis[x][y]) {
++cnt[x][y];
dist[x][y] += d;
q.offer(new int[] {x, y});
vis[x][y] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0 && cnt[i][j] == total) {
ans = Math.min(ans, dist[i][j]);
}
}
}
return ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int shortestDistance(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size();
int n = grid[0].size();
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
queue<pii> q;
int total = 0;
vector<vector<int>> cnt(m, vector<int>(n));
vector<vector<int>> dist(m, vector<int>(n));
vector<int> dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
++total;
q.push({i, j});
vector<vector<bool>> vis(m, vector<bool>(n));
int d = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
++d;
for (int k = q.size(); k > 0; --k) {
auto p = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int l = 0; l < 4; ++l) {
int x = p.first + dirs[l];
int y = p.second + dirs[l + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 0 && !vis[x][y]) {
++cnt[x][y];
dist[x][y] += d;
q.push({x, y});
vis[x][y] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
int ans = INT_MAX;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if (grid[i][j] == 0 && cnt[i][j] == total)
ans = min(ans, dist[i][j]);
return ans == INT_MAX ? -1 : ans;
}
};func shortestDistance(grid [][]int) int {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
var q [][]int
total := 0
cnt := make([][]int, m)
dist := make([][]int, m)
for i := range cnt {
cnt[i] = make([]int, n)
dist[i] = make([]int, n)
}
dirs := []int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if grid[i][j] == 1 {
total++
q = append(q, []int{i, j})
vis := make([]bool, m*n)
d := 0
for len(q) > 0 {
d++
for k := len(q); k > 0; k-- {
p := q[0]
q = q[1:]
for l := 0; l < 4; l++ {
x, y := p[0]+dirs[l], p[1]+dirs[l+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 0 && !vis[x*n+y] {
cnt[x][y]++
dist[x][y] += d
q = append(q, []int{x, y})
vis[x*n+y] = true
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
ans := math.MaxInt32
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if grid[i][j] == 0 && cnt[i][j] == total {
if ans > dist[i][j] {
ans = dist[i][j]
}
}
}
}
if ans == math.MaxInt32 {
return -1
}
return ans
}