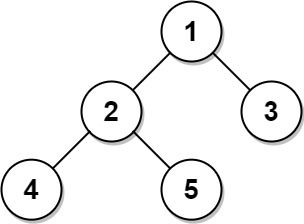
Table: Tree
+-------------+------+ | Column Name | Type | +-------------+------+ | id | int | | p_id | int | +-------------+------+ id is the primary key column for this table. Each row of this table contains information about the id of a node and the id of its parent node in a tree. The given structure is always a valid tree.
Each node in the tree can be one of three types:
- "Leaf": if the node is a leaf node.
- "Root": if the node is the root of the tree.
- "Inner": If the node is neither a leaf node nor a root node.
Write an SQL query to report the type of each node in the tree.
Return the result table in any order.
The query result format is in the following example.
Example 1:
Input: Tree table: +----+------+ | id | p_id | +----+------+ | 1 | null | | 2 | 1 | | 3 | 1 | | 4 | 2 | | 5 | 2 | +----+------+ Output: +----+-------+ | id | type | +----+-------+ | 1 | Root | | 2 | Inner | | 3 | Leaf | | 4 | Leaf | | 5 | Leaf | +----+-------+ Explanation: Node 1 is the root node because its parent node is null and it has child nodes 2 and 3. Node 2 is an inner node because it has parent node 1 and child node 4 and 5. Nodes 3, 4, and 5 are leaf nodes because they have parent nodes and they do not have child nodes.
Example 2:
Input: Tree table: +----+------+ | id | p_id | +----+------+ | 1 | null | +----+------+ Output: +----+-------+ | id | type | +----+-------+ | 1 | Root | +----+-------+ Explanation: If there is only one node on the tree, you only need to output its root attributes.
SELECT id,
(
CASE
WHEN p_id IS NULL THEN 'Root'
WHEN id IN (
SELECT p_id
FROM tree
) THEN 'Inner'
ELSE 'Leaf'
END
) AS type
FROM tree;