A confusing number is a number that when rotated 180 degrees becomes a different number with each digit valid.
We can rotate digits of a number by 180 degrees to form new digits.
- When
0,1,6,8, and9are rotated180degrees, they become0,1,9,8, and6respectively. - When
2,3,4,5, and7are rotated180degrees, they become invalid.
Note that after rotating a number, we can ignore leading zeros.
- For example, after rotating
8000, we have0008which is considered as just8.
Given an integer n, return true if it is a confusing number, or false otherwise.
Example 1:
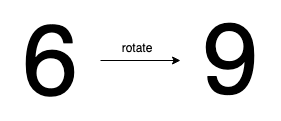
Input: n = 6 Output: true Explanation: We get 9 after rotating 6, 9 is a valid number, and 9 != 6.
Example 2:
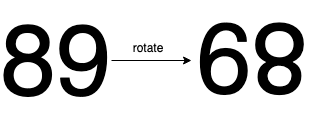
Input: n = 89 Output: true Explanation: We get 68 after rotating 89, 68 is a valid number and 68 != 89.
Example 3:
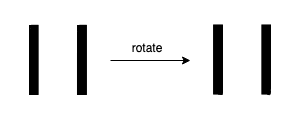
Input: n = 11 Output: false Explanation: We get 11 after rotating 11, 11 is a valid number but the value remains the same, thus 11 is not a confusing number
Constraints:
0 <= n <= 109
class Solution:
def confusingNumber(self, n: int) -> bool:
x, y = n, 0
d = [0, 1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 9, -1, 8, 6]
while x:
x, v = divmod(x, 10)
if d[v] < 0:
return False
y = y * 10 + d[v]
return y != nclass Solution {
public boolean confusingNumber(int n) {
int[] d = new int[] {0, 1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 9, -1, 8, 6};
int x = n, y = 0;
while (x > 0) {
int v = x % 10;
if (d[v] < 0) {
return false;
}
y = y * 10 + d[v];
x /= 10;
}
return y != n;
}
}class Solution {
public:
bool confusingNumber(int n) {
vector<int> d = {0, 1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 9, -1, 8, 6};
int x = n, y = 0;
while (x) {
int v = x % 10;
if (d[v] < 0) {
return false;
}
y = y * 10 + d[v];
x /= 10;
}
return y != n;
}
};func confusingNumber(n int) bool {
d := []int{0, 1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 9, -1, 8, 6}
x, y := n, 0
for x > 0 {
v := x % 10
if d[v] < 0 {
return false
}
y = y*10 + d[v]
x /= 10
}
return y != n
}