欢迎大家参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
看完本篇可以一起做了如下两道题目:
- 104.二叉树的最大深度
- 559.N叉树的最大深度
题目地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例: 给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
返回它的最大深度 3 。
本题其实也要后序遍历(左右中),依然是因为要通过递归函数的返回值做计算树的高度。
按照递归三部曲,来看看如何来写。
- 确定递归函数的参数和返回值:参数就是传入树的根节点,返回就返回这棵树的深度,所以返回值为int类型。
代码如下:
int getDepth(TreeNode* node)
- 确定终止条件:如果为空节点的话,就返回0,表示高度为0。
代码如下:
if (node == NULL) return 0;
- 确定单层递归的逻辑:先求它的左子树的深度,再求的右子树的深度,最后取左右深度最大的数值 再+1 (加1是因为算上当前中间节点)就是目前节点为根节点的树的深度。
代码如下:
int leftDepth = getDepth(node->left); // 左
int rightDepth = getDepth(node->right); // 右
int depth = 1 + max(leftDepth, rightDepth); // 中
return depth;
所以整体C++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int getDepth(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) return 0;
int leftDepth = getDepth(node->left); // 左
int rightDepth = getDepth(node->right); // 右
int depth = 1 + max(leftDepth, rightDepth); // 中
return depth;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getDepth(root);
}
};代码精简之后C++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
return 1 + max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right));
}
};
精简之后的代码根本看不出是哪种遍历方式,也看不出递归三部曲的步骤,所以如果对二叉树的操作还不熟练,尽量不要直接照着精简代码来学。
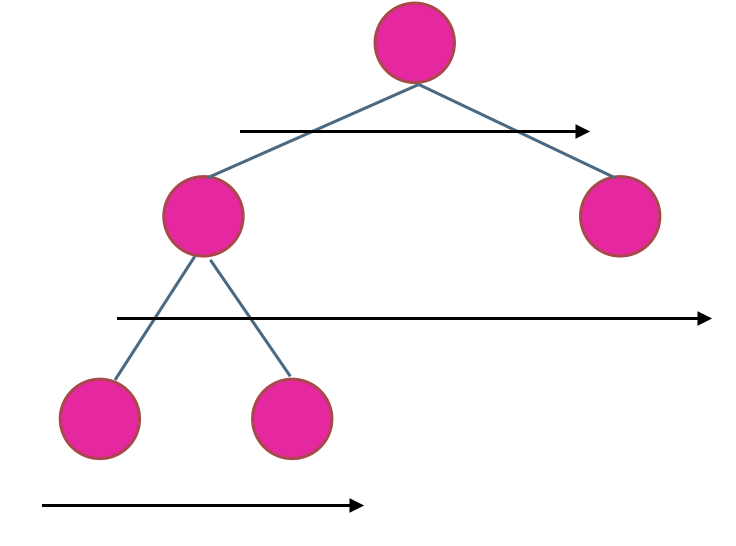
使用迭代法的话,使用层序遍历是最为合适的,因为最大的深度就是二叉树的层数,和层序遍历的方式极其吻合。
在二叉树中,一层一层的来遍历二叉树,记录一下遍历的层数就是二叉树的深度,如图所示:
所以这道题的迭代法就是一道模板题,可以使用二叉树层序遍历的模板来解决的。
如果对层序遍历还不清楚的话,可以看这篇:二叉树:层序遍历登场!
C++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int depth = 0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
depth++; // 记录深度
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return depth;
}
};那么我们可以顺便解决一下N叉树的最大深度问题
题目地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-n-ary-tree/
给定一个 N 叉树,找到其最大深度。
最大深度是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点总数。
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :
我们应返回其最大深度,3。
思路:
依然可以提供递归法和迭代法,来解决这个问题,思路是和二叉树思路一样的,直接给出代码如下:
C++代码:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if (root == 0) return 0;
int depth = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < root->children.size(); i++) {
depth = max (depth, maxDepth(root->children[i]));
}
return depth + 1;
}
};依然是层序遍历,代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
depth++; // 记录深度
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node* node = que.front();
que.pop();
for (int j = 0; j < node->children.size(); j++) {
if (node->children[j]) que.push(node->children[j]);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
};使用栈来模拟后序遍历依然可以
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> st;
if (root != NULL) st.push(root);
int depth = 0;
int result = 0;
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top();
if (node != NULL) {
st.pop();
st.push(node); // 中
st.push(NULL);
depth++;
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左
} else {
st.pop();
node = st.top();
st.pop();
depth--;
}
result = result > depth ? result : depth;
}
return result;
}
};Java:
class Solution {
/**
* 递归法
*/
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
}class Solution {
/**
* 迭代法,使用层序遍历
*/
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList<>();
deque.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
int size = deque.size();
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode poll = deque.poll();
if (poll.left != null) {
deque.offer(poll.left);
}
if (poll.right != null) {
deque.offer(poll.right);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
}Python:
Go:
JavaScript
var maxDepth = function(root) {
if (!root) return root
return 1 + Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right))
};