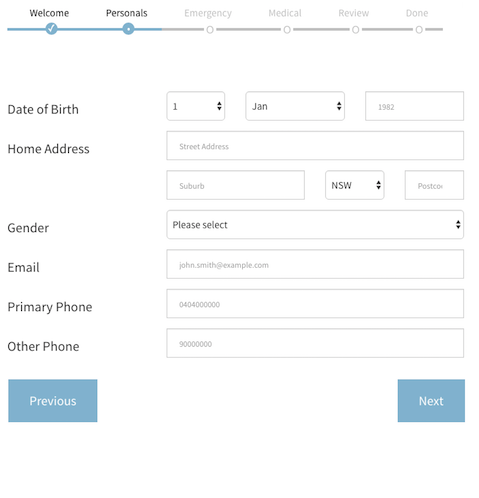
is a multi-step, wizard component for sequential data collection. It basically lets you throw a bunch of react components at it (data forms, text / html components etc) and it will take the user through those components in steps. If it's a data-entry form it can trigger validation and only proceed if the data is valid.
v7.0.0: React hooks support! (finally)
v6.0.0: dev tools updated to latest versions for security and stability (webpack, gulp, babel, node env)
v5.0.0: ported to react and react-dom 16.4.1. Redux demo implementation (finally!)
v4.8.0: multiple examples. includes a cool demo of i18n - Internationalization and localization (tnx @tomtoxx)
v4.7.2: optimised react, react-dom dependency loading (peerDependencies)
v4.3.0: now supporting higher order component based validation via react-validation-mixin!
something like this of course:
🤘🤘🤘🤘🤘🤘🤘
Full example usage code is available in the src/examples directory. Have a look at a live working version here
- run
npm install --save react-stepzilla
- require into your project via
import StepZilla from "react-stepzilla";
- define the list of all the components* you want to step through. The
nameindicates the title of the UI step and component is what loads.
const steps =
[
{name: 'Step 1', component: <Step1 />},
{name: 'Step 2', component: <Step2 />},
{name: 'Step 3', component: <Step3 />},
{name: 'Step 4', component: <Step4 />},
{name: 'Step 5', component: <Step5 />}
]
as of v7.0.0 you can use React Hooks based function components that also support custom state based validation using the isValidated method (see Step5.js in the examples directory). Note that Pure Components (functions without state or refs) can also be used but they wont support validation, see Step2.js in the examples directory for more info.
- and now render it out somewhere in your app
<div className='step-progress'>
<StepZilla steps={steps}/>
</div>
- pass in following options as well if you want to customise it further
// hide or show Next and Previous Buttons at the bottom
showNavigation: true | false
// disable or enable the steps UI navigation on top
showSteps: true | false
// disable or enable onClick step jumping from the UI navigation on top
stepsNavigation: true | false
// show or hide the previous button in the last step (maybe the last step is a thank you message and you don't want them to go back)
prevBtnOnLastStep: true | false
// dev control to disable validation rules called in step components **
dontValidate: true | false
// by default if you hit the Enter key on any element it validates the form and moves to next step if validation passes. Use this to prevent this behaviour
preventEnterSubmission: true | false
// specify what step to start from in the case you need to skip steps (send in a 0 based index for the item in the steps array. e.g. 2 will load <Step3 /> initially)
startAtStep: [stepIndex]
// specify the next button text (if not given it defaults to "Next")
nextButtonText: "Siguiente"
// specify the back button text (if not given it default to "Previous")
backButtonText: "Atrás"
// specify the next button class (if not given it defaults to "btn btn-prev btn-primary btn-lg" which depends on bootstrap)
nextButtonCls: "btn btn-prev btn-primary btn-lg pull-right"
// specify the back button text (if not given it default to "btn btn-next btn-primary btn-lg")
backButtonCls: "btn btn-next btn-primary btn-lg pull-left"
// specify what the next button text should be in the step before the last (This is usually the last "Actionable" step. You can use this option to change the Next button to say Save - if you save the form data collected in previous steps)
nextTextOnFinalActionStep: "Save"
// its recommended that you use basic javascript validation (i.e simple validation implemented inside your step component. But stepzilla steps can also use 'react-validation-mixin' which wraps your steps as higher order components. If you use this then you need to specify those steps indexes that use 'react-validation-mixin' below in this array)
hocValidationAppliedTo: [1, 2]
// function, which is called every time the index of the current step changes (it uses a zero based index)
onStepChange: (step) => console.log(step)
example options usage:
<div className='step-progress'>
<StepZilla steps={steps} stepsNavigation={false} prevBtnOnLastStep={false} startAtStep=2 />
</div>
- stepzilla injects an utility method called
jumpToStepas a prop into all your react step components - this utility methods lets you jump between steps from inside your react component
e.g.
this.props.jumpToStep(2)will jump to your 3rd step (it uses a zero based index) - check out
src/examples/Step2for an actual usage example - important!! this jumpToStep() utility method will not validate data! so use with caution. its only meant to be a utility to break from the standard flow of steps
each component step can expose a local isValidated method that will be invoked during runtime by StepZilla to determine if we can go to next step. This utility is available to Class based component and Hooks components.
- to use this feature, you need to implement a
isValidated()method in your react step component. - this
isValidated()method should return a booltrue/false(true to proceed and false to prevent). It can also return aPromisewhich in turn shouldresolveorreject(which maps to the statictrue/falsebehaviour) - if your step is a from, note that stepzilla also supports advanced form validation via
react-validation-mixin - validation can also be Async and therefore Promise based. This is useful if you do server side validation or you want to save data to a server and only proceed if it was a success. For an e.g. on this have a look at the
src/examples/Step5component. - for class components, check out sample code in the
src/examplesdirectory. (Step3.js and Step4.js show you all this in action) - for hooks components, you will need to use the
forwardRefand theuseImperativeHandleprimitives to make this work, a full example is insrc/examples/Step5.js
-
if you want some default style, copy the source from
src/css/main.csscode into your project (the above look in the picture also requires bootstrap) -
check out
src/examples/for howonStepChangecan be used to persist last known step state across browser reloads (usingstartAtSteppulled from session storage)
- all node source is in src/main.js
- you need to install dependencies first
npm install - make any changes and run
npm run buildto transpile the jsx intodist - the transpilation is run as an auto pre-publish task so it should usually be up to date when consumed via npm
npm run build-examplebuilds and packs the example app into the 'docs' folder so it can be accessed via ghpages
- test driven development has been setup and its recommended you follow these steps when you are developing
- follow steps below in
run and view example in browserto launch the dev server that live reloads - in a seperate terminal run
npm run test:watchto trigger TDD - now all code updates you make are sent through
lintandtestand you can monitor any quality regression in real time
A full example is found in the src/examples directory.
- run
npm install - then run
npm start - then go to
http://localhost:8080/webpack-dev-server/src/examples/index.htmlin your browser - hot reload will work as you dev
- tests are written in the mocha, chai, sinon, enzyme stack
- located in the 'tests' folder and supports es6
- run the
npm run testcommand run tests - run the
npm run test:watchcommand run test in watch mode
test coverage is done via istanbulrun thenpm run test:coveragecommand to generate full coverage report (shown in terminal and as lcov report in coverage directory)all code is run against coverage, not just the unit tested modulestest coverage improvement is currently a work in progress- Note: As of v5.0.1 (the gulp / webpack upgrade) istanbul no longer works. We will replace with a new coverage tool soon.
Current coverage sitting at v5.0.0:
Statements : 86.39% ( 146/169 ), 4 ignored
Branches : 73.1% ( 106/145 ), 13 ignored
Functions : 83.33% ( 35/42 ), 1 ignored
Lines : 82.93% ( 102/123 )
- improve code coverage
- migrate to jest
our brilliant community sometimes solves implementation issues themselves, head over to the Useful Dev Tips page for a curated list of the most useful tips. For e.g. How to persist Step State on "Previous/Back" button click or How to hide navigation buttons in some steps
do you have any ideas for new features or improvements to stepzilla? we would love to hear from you. head over to the issues section here and raise a new thread about what you would like. make sure you include some use cases for your request, or upvote existing community requests here
- open bugs are here
- change log is here