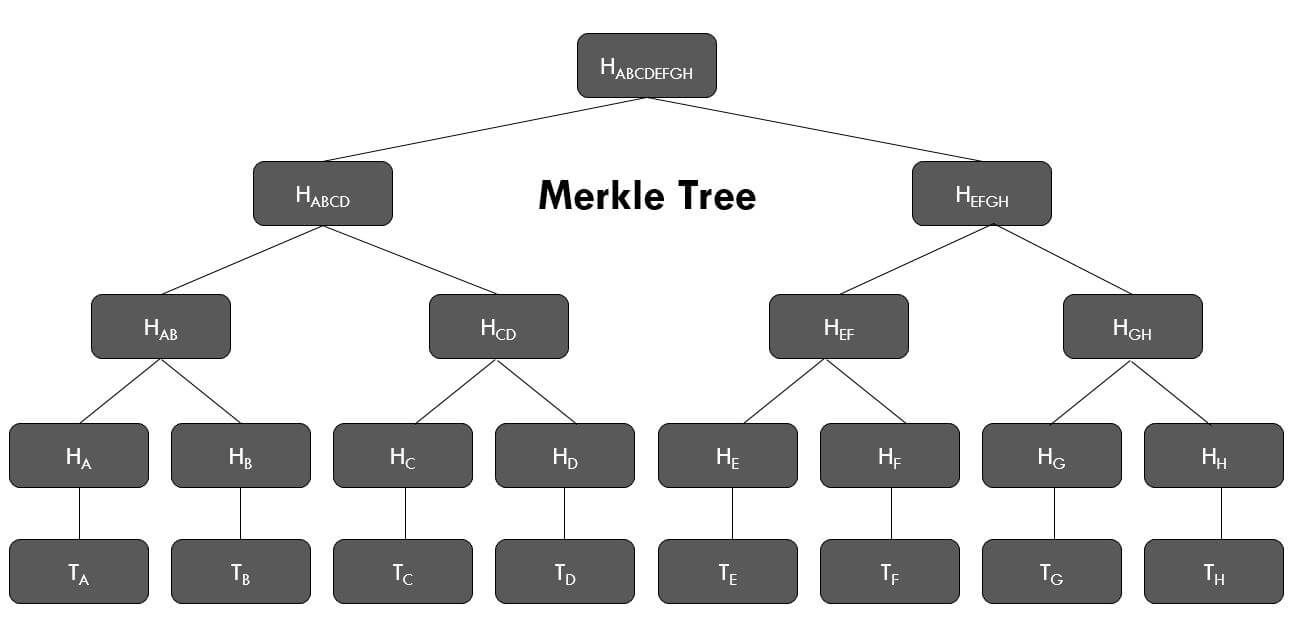
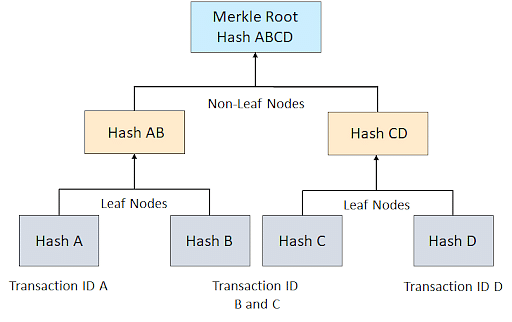
A merkle tree is a data structure that allows you to verify the integrity of a large set of data. It is a binary tree where each leaf node is the hash of a block of data. Each non-leaf node is the hash of the two child nodes. The root node is the hash of the entire tree.
The idea of this project is just to implement a simple version of a merkle tree in Rust. Anyway, if you want to learn more about merkle trees, I highly recommend you to read this Wikipedia article and also Simplilearn Article.
🚀 Or even better, if you want to contribute to this humble implementation, feel free to open a pull request. 🚀
Merkle trees are used in many applications, including blockchains, to verify the integrity of large sets of data. For example, in a blockchain, the merkle tree is used to verify that a transaction is included in a block. The merkle tree is also used to verify that a block is included in a blockchain.
Each item in the set is hashed and stored in a leaf node. The leaf nodes are then paired and hashed together. The resulting hash is stored in a non-leaf node. This process is repeated until there is only one node left, the root node.
A Merkle tree totals all transactions in a block and generates a digital fingerprint of the entire set of operations, allowing the user to verify whether it includes a transaction in the block.
I wrote a suite of unit tests to test the merkle tree.
To run the tests, run the following command:
1 - Clone the project:
git clone https://github.com/nhussein11/merkle-tree.git2 - Run the tests:
cargo test