https://github.com/nyanginator/wrtbwmon-remixed
- Adapted from https://code.google.com/p/wrtbwmon
- Uses Chart.js and the chartjs-zoom-plugin, which requires Hammer.js
- Uses SortTable by Stuart Langridge
- Uses Tabbed Content by menucool.com
- What This Is
- Setup
- Viewing the Usage
- Config File
- Users File
- Usage File
- Freeing Up Space
- Resetting Usage
- Notes
- Contact
wrtbwmon is a popular bandwidth monitoring tool for WRT-based routers. This variant is a more featured version:
- Changed columns to:
- User Name + MAC Address
- Total Used
- Total Dowloaded
- Total Uploaded
- Average Daily Total
- Average Daily Download
- Average Daily Upload
- Today Total
- Today Downloaded
- Today Uploaded
- Last Update (Last Seen)
- Added colors and formatting
- Added sortable table columns
- Added a table search filter
- Added clickable rows for viewing detailed usage
- Animated charts (using Chart.js) are viewable on tabs for daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly usage
- Added a Grand Total row
- Added Watch Lists to manage user quotas, which will automatically turn on/off Internet for devices
- Added a config file for easier setting of variables
The original wrtbwmon included the possibility of tracking peak and offpeak usage separately. wrtbwmon-remixed does not make use of this feature.
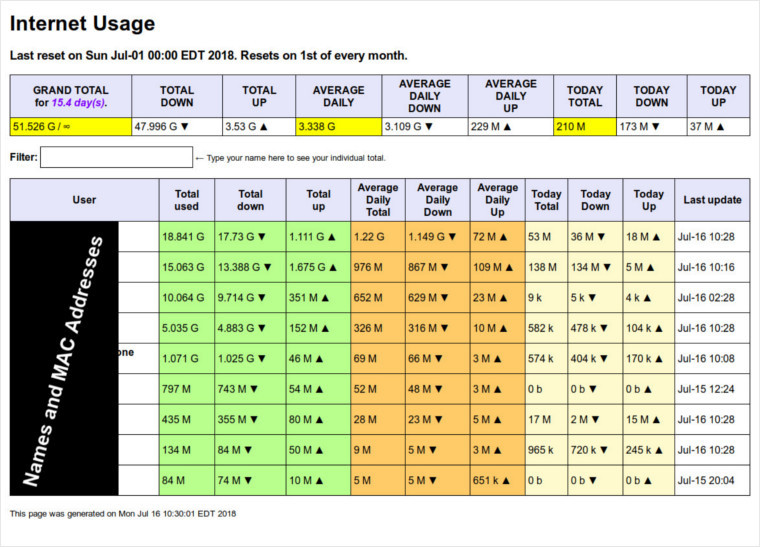
Here is the revised main page:
Watch Lists appear at the top of the page and indicate whether anybody is close to or over a list's set quota:
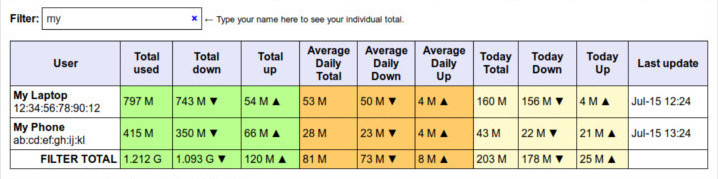
The search filter adjusts the totals row based on the current search results:
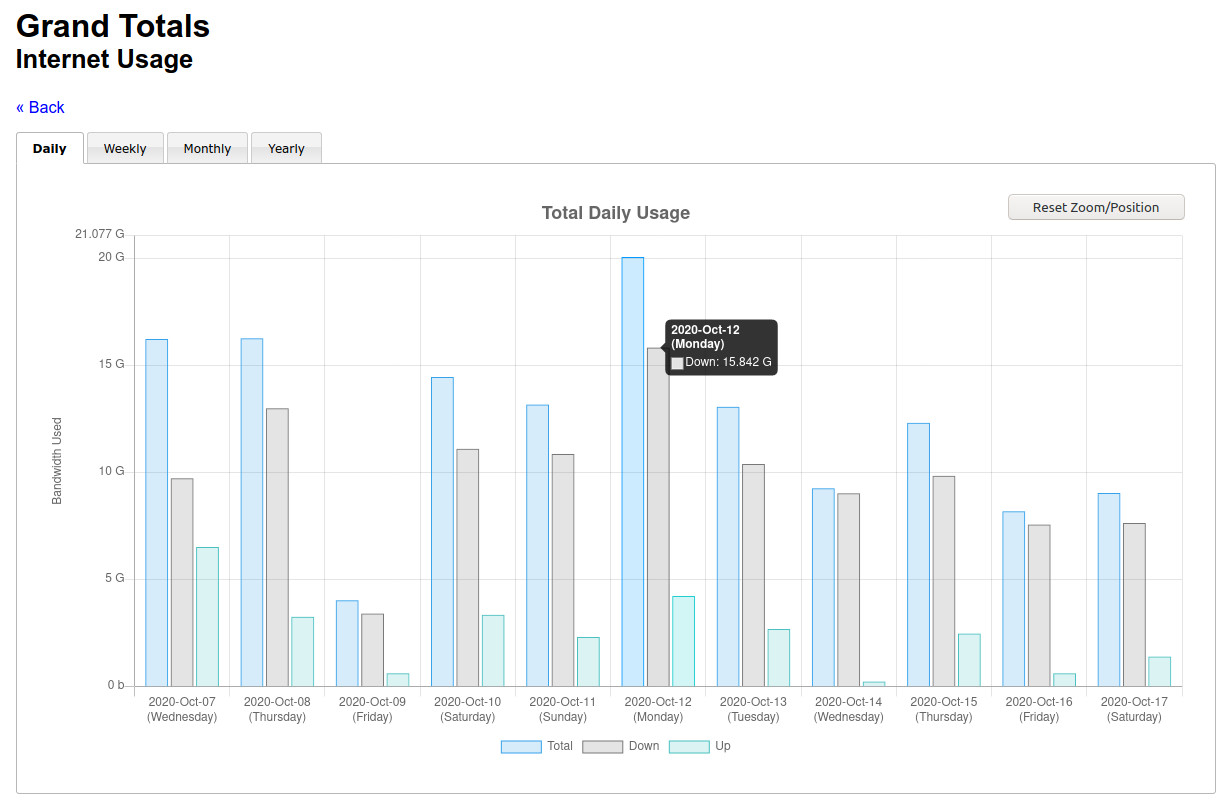
Clicking on any row will bring up the details page:
Use the mouse-wheel (or pinch) to zoom in/out of the chart. Click-and-drag (or touch-drag) to pan.
It's easiest to simply run the script off a USB drive plugged into the router. While this means your router needs to have a USB port, I find this option more convenient than trying to modify the hardware or setup a network location for the script.
First go to the DD-WRT control panel and check that Services > USB are as follows:
- Core USB Support: Enable
- USB Storage Support: Enable
- Automatic Drive Mount: Enable
Format a USB drive and copy all of the wrtbwmon-remixed files onto it. Plug it into the router. You should see it show up under Services > USB with a path (e.g. /dev/sda1). Make note of the device (sda1) for setting up cron next.
Go to Administration > Management and find the cron section. At minimum, you should have 3 lines:
* * * * * root /tmp/mnt/sda1/setup
*/30 * * * * root /tmp/mnt/sda1/update
45 * * * * root /tmp/mnt/sda1/publish
This will keep monitoring the traffic every minute (setup), update the usage numbers every 30 minutes (update), and publish to the router's webpage every hour (publish) when the minute is 45. You can SSH into the router to manually update and publish using the command:
$ /tmp/mnt/sda1/unp
If the router is rebooted, you can use the restore script to try restoring usage.db, users.txt, and the reports directory from the USB drive, assuming backupmin or backupkeep was used at some point to create a backup. To automate this, add these lines to cron:
* * * * * root /tmp/mnt/sda1/restore
15 */2 * * * root /tmp/mnt/sda1/backupmin
0 0 * * * root /tmp/mnt/sda1/backupkeep
The first line runs restore every minute to check whether usage.db is missing (which it would be if the router was rebooted) and restores based on that. File and folder permissions are refreshed as well. The backupmin line copies usage.db, users.txt, and the reports directory to the USB drive every 2 hours. The backupkeep line makes a daily backup to the backups directory on the USB drive. If you look at the backupkeep script, you will see that keep is specified, which means not to reset counters. If you did want to backup and reset everybody's counters at the same time, then forget should be specified instead of keep.
If there is a set day to reset everybody's counters, you can add a line for that as well. This performs a reset on the first of every month:
0 0 1 * * root /tmp/mnt/sda1/reset
After the script has run through at least one cycle of setup, update, and publish, you can view the table and charts at:
http://192.168.1.1/user/usage.htm
If you specify WWWSUBDIR in the config file, then adjust the path accordingly. For example:
http://192.168.1.1/user/WWWSUBDIR/usage.htm
The config file allows you to tweak the output according to your needs and liking.
AXISSTARTDATE- Unix time for what the earliest date on the bar chart's X-axis should bePAGETITLE- The page title appears at the very top of the pageHEADING- The page subtitle/heading appears in a slightly smaller font below the titleDESCRIPTION- You can include any additional text to appear below the heading hereMBTOTALQUOTA- The total quota for everybody altogether in MB, which is just for display purposes, to be shown as the denominator in Grand TotalROUTERNAME- Not really essential, but if you plan on ever merging the HTML output from multiple routers onto the same page, you will need a unique name for each routerWWWSUBDIR- Optional subdirectory for the web directoryDEVICEFILTER- Typically will bebr0, unless you want to track a specific set of devices with a different identifier. You can see the available device types by runningcat /proc/net/arp.
Range size (total X-axis length) for each chart:
RANGE_DAILY(# of days)RANGE_WEEKLY(# of weeks)RANGE_MONTHLY(# of months)RANGE_YEARLY(# of years)
Number of ticks visible (on the X-axis) before having to zoom/pan/drag the chart:
AXISRANGE_DAILY(# of days)AXISRANGE_WEEKLY(# of weeks)AXISRANGE_MONTHLY(# of months)AXISRANGE_YEARLY(# of years)
UNIT="KB" # or "MB"Valid settings are KB and MB. This essentially determines the maximum value for any given number, whether it be for a download, upload, or total. Integer variables in the script are limited to a range of [0, 2147483647], so the maximum value would be either 2147483647 KB (2 TB) or 2147483647 MB (2 PB).
If you expect high usage, then you should set this to MB. Otherwise, when a number exceeds 2147483647, integer overflow will occur, resulting in a nonsensical negative number. Plan to accommodate the highest yearly grand total that you expect to have.
There are some things to keep in mind:
- When changing from MB to KB or vice versa, any previously saved numbers (i.e. in the
.dbfiles) are not adjusted, so you may want to do ahardresetwhen changing. For example, 5 MB becomes 5 KB if you change this setting from MB to KB. This setting merely tells the script how to treat the numbers it finds in the.dbfiles. It does not do any conversions. - In order for bandwidth to be counted for a certain device, its
iptablescounter must have recorded as least 1 unit of data (i.e. either 1 KB or 1 MB, depending on theUNITsetting) since it was last zeroed out. This is because numbers are always rounded down to the nearest unit. For example, sayUNIT="MB"and you call/tmp/mnt/sda1/updatevery frequently, every 5 minutes. If a device never exceeds 1 MB within each of those 5-minute intervals, its usage will always be rounded down to 0 and thus never be counted. The greater the interval, the more likely you will avoid this problem of rounding to zero, because there is a better chance that a user will use more than 1 unit of data in a longer time period. Of course, this means you would also have to wait longer for updates to happen. - Wherever there is a partial unit (i.e. < 1 KB or < 1 MB), the number is always rounded down because floating point numbers are not possible in shell scripts. For example, if
UNIT="KB", 0.5 KB would be considered 0 KB. IfUNIT="MB", 4.8 MB would be considered 4 MB. The counter only records the number of full units used.
The Watch List is a feature that automatically turns on/off Internet access for devices matching a certain search string (i.e. a user's name). Devices that should be turned on/off together must all be set in /tmp/users.txt with this search string. For example, say Calvin has 3 devices. In users.txt, they might be identified as Calvin Phone, Calvin iPad, and Calvin Laptop. In config, Calvin should be in the Watch List array.
STUDENTWATCHLISTARRAY="Calvin Phoebe Justin"If the total usage of Calvin's devices is over the set quota, then all 3 devices will have their connection shut off. If you want to grant access or restore access to a user regardless of the quota, prefix their name with SKIP_.
STUDENTWATCHLISTARRAY="SKIP_Calvin Phoebe _Justin SKIP_admin"Remember that this is a space-separated array (ash is limited), so naturally the names themselves cannot have spaces. Names are case-insensitive. Also note that removing a name from the array will not automatically restore access. You must explicitly restore access by either:
- Adding
SKIP_to the name in the array and then running/tmp/mnt/sda1/publish. - Delete the name from the array, run
iptables -F(restores access for everybody) and then/tmp/mnt/sda1/publish(reimposes Watch List restrictions).
Watch Lists will show up at the top of the usage page when users are either close to or have exceeded their quota. The config file has two sample Watch Lists ("Students" and "Guests") for your reference. Note how all data numbers specified in the config file are in MB. You can define as many Watch Lists as you want, but be sure to update the wrtbwmon script to include any new ones you add. Specifically, look for this line:
# Publish individual watch lists
publishWatchList "${TOTALSDB}" "${TMPUSAGEHTM}" "${STUDENTWATCHLISTARRAY}" "${MBQUOTAPERSTUDENT}" "${STUDENTWATCHLISTTITLE}"Just copy-and-paste this line and update the last 3 variables to whatever you set in config. In this example:
MBQUOTAPERSTUDENT="10000" # 10G limit per student
STUDENTWATCHLISTTITLE="Students" # Title to display
STUDENTWATCHLISTARRAY="Calvin Phoebe Justin" # Who to watchAlso in config, you can set a "step" value, which defines when to show users who are close to the quota limit:
WATCHLISTSTEP="1000" # When users are within 2 increments of this value (MB), they will show up in the listTo define a display name for each MAC address, you should create/edit the file /tmp/users.txt. The given users.txt file will be copied to /tmp/ if you run restore. Like the original wrtbwmon, the format for each line is a MAC address followed by a comma and name. For example:
12:ab:34:cd:56:ef, Dad's Laptop
34:cd:56:ef:78:gh, Dad's Desktop
usage.db is a text file that stores the data of the current cycle (usage since the last reset, or since the script was first run). As with users.txt, devices are identified by MAC address. The format is as follows:
[MAC address],[kB downloaded],[kB uploaded],[not in use],[not in use],[Unix time of Last Update]
The [not in use] numbers were originally used to specify peak/offpeak data in the old wrtbwmon and are not used by wrtbwmon-remixed.
If you need to modify numbers for daily/weekly/monthly/yearly usage, you will need to look in the /tmp/reports/ directory. Grand total numbers are stored in daily.db, weekly.db, monthly.db, and yearly.db. Individual devices' numbers are stored in similarly named files prefixed with [MAC address]_. The format is:
[Unix time of Last Update],[kB downloaded],[kB uploaded],[not in use],[not in use]
If you are trying to synchronize the Grand Total to the usage reported by your ISP, you can manually offset it by adding a line with:
00:00:00:00:00:00,0,<OFFSET>,0,0,0
where OFFSET is the amount of kilobytes to offset (e.g. 11G = 11000000).
I recommend a USB drive with 2G of space, depending on how often you clean out old files. On the USB, old backups can be safely removed from:
/tmp/mnt/sda1/bkup//tmp/mnt/sda1/monthlybkup/
The backupmin and backupkeep commands copy the reports directory to the USB drive. The reports directory stores daily/weekly/monthly/yearly data on all devices that have ever connected to the router, so it may not be ideal to save everything, especially for temporary devices. Report files are named by MAC address, so you can identify the files by name and edit/delete them as needed.
You will probably want to delete the backup copy at /tmp/mnt/sda1/reports/ and then make changes in the live copy /tmp/reports/. Otherwise, if the backup commands are running on cron, the next backup may copy /tmp/reports/ over any changes you make to /tmp/mnt/sda1/reports/.
You can delete lines from the usage.db file as you see fit (i.e. devices that you no longer want to track).
As with the reports directory, make sure to edit the live copy /tmp/usage.db and let the cron backup update /tmp/mnt/sda1/usage.db for you.
HTML files for reports are stored in /tmp/www/reports/. Each device has a directory named according to its MAC address. You can delete report pages of whatever devices you want, but they will be recreated on the next publish if any usage informtion is found in /tmp/reports/.
The command to reset everybody's usage data back to zero is:
$ /tmp/mnt/sda1/reset
This clears out the usage.db file except for one line, which looks something like:
COUNTERSTART,0,0,0,0,1530417601
The COUNTERSTART keyword specifies that the last value on this line is the Unix date denoting the start of this usage cycle. It will show up on the usage page as "Last reset on Sun Jul-01 00:00 EDT 2018".
After resetting, all devices whose access was shut off by the Watch List will have their connections restored.
You can also do a hard reset, which will permanently delete all usage data, reports, HTML/JS/CSS files, and backups:
$ /tmp/mnt/sda1/hardreset
- Touch events may or may not work depending on the specific browser and/or OS that you use.
- Weeks are counted in ISO weeks, so each week begins on a Monday.
- Make sure your USB drive is functioning properly. Failed read/writes to the drive will result in the script not working correctly.
- The code is not very optimized because the
ashshell can be quite limiting. - I have only tested the script on NETGEAR routers running DD-WRT on a network having about 15-25 connected devices. You may need to tweak settings according to your setup.
Nicholas Yang
https://nyanginator.com