-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 41
/
README.md.orig
678 lines (456 loc) · 48.8 KB
/
README.md.orig
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
391
392
393
394
395
396
397
398
399
400
401
402
403
404
405
406
407
408
409
410
411
412
413
414
415
416
417
418
419
420
421
422
423
424
425
426
427
428
429
430
431
432
433
434
435
436
437
438
439
440
441
442
443
444
445
446
447
448
449
450
451
452
453
454
455
456
457
458
459
460
461
462
463
464
465
466
467
468
469
470
471
472
473
474
475
476
477
478
479
480
481
482
483
484
485
486
487
488
489
490
491
492
493
494
495
496
497
498
499
500
501
502
503
504
505
506
507
508
509
510
511
512
513
514
515
516
517
518
519
520
521
522
523
524
525
526
527
528
529
530
531
532
533
534
535
536
537
538
539
540
541
542
543
544
545
546
547
548
549
550
551
552
553
554
555
556
557
558
559
560
561
562
563
564
565
566
567
568
569
570
571
572
573
574
575
576
577
578
579
580
581
582
583
584
585
586
587
588
589
590
591
592
593
594
595
596
597
598
599
600
601
602
603
604
605
606
607
608
609
610
611
612
613
614
615
616
617
618
619
620
621
622
623
624
625
626
627
628
629
630
631
632
633
634
635
636
637
638
639
640
641
642
643
644
645
646
647
648
649
650
651
652
653
654
655
656
657
658
659
660
661
662
663
664
665
666
667
668
669
670
671
672
673
674
675
676
677
678
# Convenient functions for YOLO v4 based on AlexeyAB Darknet Yolo.
[](https://996.icu)
[](https://github.com/996icu/996.ICU/blob/master/LICENSE)
<<<<<<< HEAD
=======
0. [Improvements in this repository](#improvements-in-this-repository)
1. [How to use](#how-to-use-on-the-command-line)
2. How to compile on Linux
* [Using cmake](#how-to-compile-on-linux-using-cmake)
* [Using make](#how-to-compile-on-linux-using-make)
3. How to compile on Windows
* [Using CMake-GUI](#how-to-compile-on-windows-using-cmake)
* [Using vcpkg](#how-to-compile-on-windows-using-vcpkg)
* [Legacy way](#how-to-compile-on-windows-legacy-way)
4. [Training and Evaluation of speed and accuracy on MS COCO](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/wiki#training-and-evaluation-of-speed-and-accuracy-on-ms-coco)
5. [How to train with multi-GPU:](#how-to-train-with-multi-gpu)
6. [How to train (to detect your custom objects)](#how-to-train-to-detect-your-custom-objects)
7. [How to train tiny-yolo (to detect your custom objects)](#how-to-train-tiny-yolo-to-detect-your-custom-objects)
8. [When should I stop training](#when-should-i-stop-training)
9. [How to improve object detection](#how-to-improve-object-detection)
10. [How to mark bounded boxes of objects and create annotation files](#how-to-mark-bounded-boxes-of-objects-and-create-annotation-files)
11. [How to use Yolo as DLL and SO libraries](#how-to-use-yolo-as-dll-and-so-libraries)
>>>>>>> e6469eb071521a4ff5be8c0e9cceb524d0a65a95
**You only look once (YOLO)** is a state-of-the-art, real-time object detection system. It is implemented based on the Darknet, an Open Source Neural Networks in C. In this project, I improved the YOLO by adding several convenient functions for detecting objects for research and the development community.
<<<<<<< HEAD
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/vincentgong7/VG_AlexeyAB_darknet/master/output/1.jpg" alt="" width="600"/> <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/vincentgong7/VG_AlexeyAB_darknet/master/output/2.jpg" alt="" width="600"/>
Figure 1. Example of Object Detection using Yolo based on the Darknet.
=======
|  | 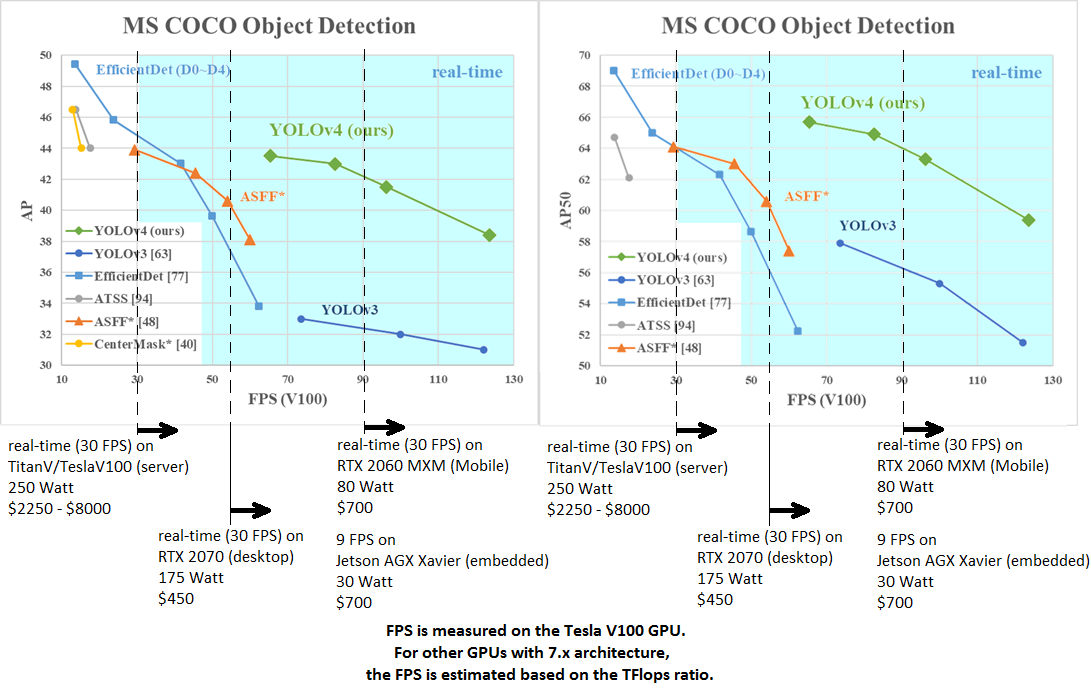 AP50:95 / AP50 - FPS (Tesla V100) Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.10934 |
|---|---|
tkDNN-TensorRT accelerates YOLOv4 **~2x** times for batch=1 and **3x-4x** times for batch=4.
OpenCV-dnn is ~10% slower than tkDNN-TensorRT.
* tkDNN: https://github.com/ceccocats/tkDNN
* OpenCV: https://gist.github.com/YashasSamaga/48bdb167303e10f4d07b754888ddbdcf
**GeForce RTX 2080 Ti:**
| Network Size | Darknet, FPS (avg)| tkDNN TensorRT FP32, FPS | tkDNN TensorRT FP16, FPS | OpenCV FP16, FPS | tkDNN TensorRT FP16 batch=4, FPS | OpenCV FP16 batch=4, FPS | tkDNN Speedup |
|:-----:|:--------:|--------:|--------:|--------:|--------:|--------:|------:|
|320 | 100 | 116 | **202** | 171 | **423** | 384 | **4.2x** |
|416 | 82 | 103 | **162** | 146 | **284** | 260 | **3.5x** |
|512 | 69 | 91 | **134** | 125 | **206** | 190 | **2.9x** |
|608 | 53 | 62 | **103** | 100 | **150** | 133 | **2.8x** |
* Yolo v4 Full comparison: [map_fps](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/4096485/80283279-0e303e00-871f-11ea-814c-870967d77fd1.png)
* CSPNet: [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.11929) and [map_fps](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/4096485/71702416-6645dc00-2de0-11ea-8d65-de7d4b604021.png) comparison: https://github.com/WongKinYiu/CrossStagePartialNetworks
* Yolo v3 on MS COCO: [Speed / Accuracy ([email protected]) chart](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/4096485/52151356-e5d4a380-2683-11e9-9d7d-ac7bc192c477.jpg)
* Yolo v3 on MS COCO (Yolo v3 vs RetinaNet) - Figure 3: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1804.02767v1.pdf
* Yolo v2 on Pascal VOC 2007: https://hsto.org/files/a24/21e/068/a2421e0689fb43f08584de9d44c2215f.jpg
* Yolo v2 on Pascal VOC 2012 (comp4): https://hsto.org/files/3a6/fdf/b53/3a6fdfb533f34cee9b52bdd9bb0b19d9.jpg
#### Youtube video of results
[](https://youtu.be/1_SiUOYUoOI "Yolo v4")
Others: https://www.youtube.com/user/pjreddie/videos
#### How to evaluate AP of YOLOv4 on the MS COCO evaluation server
>>>>>>> e6469eb071521a4ff5be8c0e9cceb524d0a65a95
The added functions are implemented based on **AlexeyAB** version of **Darknet**. As it is updated frequently, hereby I publish a stable version of AlexeyAB Darknet Yolo with those convenient functions. This repo will also be updated regularly.
## Batch images detector
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/vincentgong7/VG_AlexeyAB_darknet/yolo_v3/exp/example/vg_darknet_batch_detector.png" alt="" width="60%" />
Figure. The process of batch detecting images in a folder using Yolo based on the Darknet.
The **detector** function in AlexeyAB Darknet only supports a single image at a time. Therefore I added the batch function into this forked repo, which supports detecting images in a folder in one time. In the meantime, it exports information including the name of the image, the detected classes, the confidence and the <span style="color:blue"> **bounding box coordinates** </span> in **JSON** and **TXT** files.
Hope you like it.
### Github link: [https://github.com/vincentgong7/VG_AlexeyAB_darknet](https://github.com/vincentgong7/VG_AlexeyAB_darknet)
Please also refer to the post for more information:
[https://github.com/pjreddie/darknet/issues/723](https://github.com/pjreddie/darknet/issues/723)
## Update May 07, 2020
1. The new version based on AlexeyAB Yolo v4.
2. Compile without change anything on Linux and Windows. Both are tested.
3. Export the bounding box of detected objects in images to JSON.
4. Export the bounding box of detected objects in images to TXT.
## Usage
### Command
>./darknet detector batch cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg weights/yolov4.weights io_folder sample_imgs/ output/ -out output/result.json -ext_output > output/result.txt
Parameter explain:
1. The input images are: **sample_imgs/**
2. The output images are: **output/**
3. The image name, detected classes, the confidence and the **bounding box coordinates** is saved in: **output/result.txt** and in **output/result.json**
### Installation
1. Clone this project.
2. Download pre-trained weights file into folder **./weights/**. Such as:
[https://bit.ly/yolo_v4](https://bit.ly/yolo_v4)
It is a ZIP file. Unzip it using the password: **jj113.io**
<<<<<<< HEAD
=======
* **TensorFlow:** YOLOv4 on TensorFlow 2.0 / TFlite / Andriod: https://github.com/hunglc007/tensorflow-yolov4-tflite
For YOLOv3 - convert `yolov3.weights`/`cfg` files to `yolov3.ckpt`/`pb/meta`: by using [mystic123](https://github.com/mystic123/tensorflow-yolo-v3) project, and [TensorFlow-lite](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite/guide/get_started#2_convert_the_model_format)
* **OpenCV-dnn** the fastest implementation for CPU (x86/ARM-Android), OpenCV can be compiled with [OpenVINO-backend](https://github.com/opencv/opencv/wiki/Intel's-Deep-Learning-Inference-Engine-backend) for running on (Myriad X / USB Neural Compute Stick / Arria FPGA), use `yolov3.weights`/`cfg` with: [C++ example](https://github.com/opencv/opencv/blob/8c25a8eb7b10fb50cda323ee6bec68aa1a9ce43c/samples/dnn/object_detection.cpp#L192-L221) or [Python example](https://github.com/opencv/opencv/blob/8c25a8eb7b10fb50cda323ee6bec68aa1a9ce43c/samples/dnn/object_detection.py#L129-L150)
* **Intel OpenVINO 2019 R1:** (Myriad X / USB Neural Compute Stick / Arria FPGA): read this [manual](https://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/OpenVINO-Using-TensorFlow#converting-a-darknet-yolo-model)
* **PyTorch > ONNX > CoreML > iOS** how to convert cfg/weights-files to pt-file: [ultralytics/yolov3](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3#darknet-conversion) and [iOS App](https://itunes.apple.com/app/id1452689527)
* **TensorRT** YOLOv4 on TensorRT+tkDNN: https://github.com/ceccocats/tkDNN
For YOLOv3 (-70% faster inference): [Yolo is natively supported in DeepStream 4.0](https://news.developer.nvidia.com/deepstream-sdk-4-now-available/) read [PDF](https://docs.nvidia.com/metropolis/deepstream/Custom_YOLO_Model_in_the_DeepStream_YOLO_App.pdf). [wang-xinyu/tensorrtx](https://github.com/wang-xinyu/tensorrtx) implemented yolov3-spp, yolov4, etc.
* **TVM** - compilation of deep learning models (Keras, MXNet, PyTorch, Tensorflow, CoreML, DarkNet) into minimum deployable modules on diverse hardware backends (CPUs, GPUs, FPGA, and specialized accelerators): https://tvm.ai/about
* **OpenDataCam** - It detects, tracks and counts moving objects by using Yolo: https://github.com/opendatacam/opendatacam#-hardware-pre-requisite
* **Netron** - Visualizer for neural networks: https://github.com/lutzroeder/netron
>>>>>>> e6469eb071521a4ff5be8c0e9cceb524d0a65a95
3. Build the project. No need to modify the code either in Linux or in Windows.
3.1 For linux: Make the project with command in darknet/ folder:
>make
3.2 For windows.
It can be successfully built on Visual Studio.
5. Use the command described above to batch process images.
## Contact
Any questions please let me know.
<<<<<<< HEAD
If you like it, please also let me know.
vincent.gong7[at]gmail.com
=======
>>>>>>> e6469eb071521a4ff5be8c0e9cceb524d0a65a95
<!-- <img src="https://github.com/vincentgong7/VG_AlexeyAB_darknet/blob/master/exp/example/icon_link.png?raw=true" alt="" width="15" valign = "middle"/> [Gong.im](http://gong.im) -->
[*Gong.im*](http://gong.im)
[Guestbook](https://github.com/vincentgong7/VG_AlexeyAB_darknet/issues/7)
<<<<<<< HEAD
<script type="text/javascript" src="//counter.websiteout.net/js/5/4/69/0"></script>
<br>
<div style="float: left;"><script type="text/javascript" id="clustrmaps" src="//cdn.clustrmaps.com/map_v2.js?cl=ffffff&w=600&t=m&d=hUfpL0e-tBg_zcx45xNWS0tq1zo_Jj5POALETOYreCY&co=2d78ad&cmo=3acc3a&cmn=ff5353&ct=ffffff"></script></div>
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>
=======
#### How to use on the command line
On Linux use `./darknet` instead of `darknet.exe`, like this:`./darknet detector test ./cfg/coco.data ./cfg/yolov4.cfg ./yolov4.weights`
On Linux find executable file `./darknet` in the root directory, while on Windows find it in the directory `\build\darknet\x64`
* Yolo v4 COCO - **image**: `darknet.exe detector test cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights -thresh 0.25`
* **Output coordinates** of objects: `darknet.exe detector test cfg/coco.data yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights -ext_output dog.jpg`
* Yolo v4 COCO - **video**: `darknet.exe detector demo cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights -ext_output test.mp4`
* Yolo v4 COCO - **WebCam 0**: `darknet.exe detector demo cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights -c 0`
* Yolo v4 COCO for **net-videocam** - Smart WebCam: `darknet.exe detector demo cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights http://192.168.0.80:8080/video?dummy=param.mjpg`
* Yolo v4 - **save result videofile res.avi**: `darknet.exe detector demo cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights test.mp4 -out_filename res.avi`
* Yolo v3 **Tiny** COCO - video: `darknet.exe detector demo cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov3-tiny.cfg yolov3-tiny.weights test.mp4`
* **JSON and MJPEG server** that allows multiple connections from your soft or Web-browser `ip-address:8070` and 8090: `./darknet detector demo ./cfg/coco.data ./cfg/yolov3.cfg ./yolov3.weights test50.mp4 -json_port 8070 -mjpeg_port 8090 -ext_output`
* Yolo v3 Tiny **on GPU #1**: `darknet.exe detector demo cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov3-tiny.cfg yolov3-tiny.weights -i 1 test.mp4`
* Alternative method Yolo v3 COCO - image: `darknet.exe detect cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights -i 0 -thresh 0.25`
* Train on **Amazon EC2**, to see mAP & Loss-chart using URL like: `http://ec2-35-160-228-91.us-west-2.compute.amazonaws.com:8090` in the Chrome/Firefox (**Darknet should be compiled with OpenCV**):
`./darknet detector train cfg/coco.data yolov4.cfg yolov4.conv.137 -dont_show -mjpeg_port 8090 -map`
* 186 MB Yolo9000 - image: `darknet.exe detector test cfg/combine9k.data cfg/yolo9000.cfg yolo9000.weights`
* Remeber to put data/9k.tree and data/coco9k.map under the same folder of your app if you use the cpp api to build an app
* To process a list of images `data/train.txt` and save results of detection to `result.json` file use:
`darknet.exe detector test cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights -ext_output -dont_show -out result.json < data/train.txt`
* To process a list of images `data/train.txt` and save results of detection to `result.txt` use:
`darknet.exe detector test cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights -dont_show -ext_output < data/train.txt > result.txt`
* Pseudo-lableing - to process a list of images `data/new_train.txt` and save results of detection in Yolo training format for each image as label `<image_name>.txt` (in this way you can increase the amount of training data) use:
`darknet.exe detector test cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights -thresh 0.25 -dont_show -save_labels < data/new_train.txt`
* To calculate anchors: `darknet.exe detector calc_anchors data/obj.data -num_of_clusters 9 -width 416 -height 416`
* To check accuracy mAP@IoU=50: `darknet.exe detector map data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg backup\yolo-obj_7000.weights`
* To check accuracy mAP@IoU=75: `darknet.exe detector map data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg backup\yolo-obj_7000.weights -iou_thresh 0.75`
##### For using network video-camera mjpeg-stream with any Android smartphone
1. Download for Android phone mjpeg-stream soft: IP Webcam / Smart WebCam
* Smart WebCam - preferably: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.acontech.android.SmartWebCam2
* IP Webcam: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.pas.webcam
2. Connect your Android phone to computer by WiFi (through a WiFi-router) or USB
3. Start Smart WebCam on your phone
4. Replace the address below, on shown in the phone application (Smart WebCam) and launch:
* Yolo v4 COCO-model: `darknet.exe detector demo data/coco.data yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights http://192.168.0.80:8080/video?dummy=param.mjpg -i 0`
### How to compile on Linux (using `cmake`)
The `CMakeLists.txt` will attempt to find installed optional dependencies like
CUDA, cudnn, ZED and build against those. It will also create a shared object
library file to use `darknet` for code development.
Open a bash terminal inside the cloned repository and launch:
```bash
./build.sh
```
### How to compile on Linux (using `make`)
Just do `make` in the darknet directory. (You can try to compile and run it on Google Colab in cloud [link](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/12QusaaRj_lUwCGDvQNfICpa7kA7_a2dE) (press «Open in Playground» button at the top-left corner) and watch the video [link](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mKAEGSxwOAY) )
Before make, you can set such options in the `Makefile`: [link](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/9c1b9a2cf6363546c152251be578a21f3c3caec6/Makefile#L1)
* `GPU=1` to build with CUDA to accelerate by using GPU (CUDA should be in `/usr/local/cuda`)
* `CUDNN=1` to build with cuDNN v5-v7 to accelerate training by using GPU (cuDNN should be in `/usr/local/cudnn`)
* `CUDNN_HALF=1` to build for Tensor Cores (on Titan V / Tesla V100 / DGX-2 and later) speedup Detection 3x, Training 2x
* `OPENCV=1` to build with OpenCV 4.x/3.x/2.4.x - allows to detect on video files and video streams from network cameras or web-cams
* `DEBUG=1` to bould debug version of Yolo
* `OPENMP=1` to build with OpenMP support to accelerate Yolo by using multi-core CPU
* `LIBSO=1` to build a library `darknet.so` and binary runable file `uselib` that uses this library. Or you can try to run so `LD_LIBRARY_PATH=./:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH ./uselib test.mp4` How to use this SO-library from your own code - you can look at C++ example: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/src/yolo_console_dll.cpp
or use in such a way: `LD_LIBRARY_PATH=./:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH ./uselib data/coco.names cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights test.mp4`
* `ZED_CAMERA=1` to build a library with ZED-3D-camera support (should be ZED SDK installed), then run
`LD_LIBRARY_PATH=./:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH ./uselib data/coco.names cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights zed_camera`
To run Darknet on Linux use examples from this article, just use `./darknet` instead of `darknet.exe`, i.e. use this command: `./darknet detector test ./cfg/coco.data ./cfg/yolov4.cfg ./yolov4.weights`
### How to compile on Windows (using `CMake`)
This is the recommended approach to build Darknet on Windows if you have already
installed Visual Studio 2015/2017/2019, CUDA >= 10.0, cuDNN >= 7.0, and
OpenCV >= 2.4.
Open a Powershell terminal inside the cloned repository and launch:
```PowerShell
.\build.ps1
```
### How to compile on Windows (using `vcpkg`)
1. Install or update Visual Studio to at least version 2017, making sure to have it fully patched (run again the installer if not sure to automatically update to latest version). If you need to install from scratch, download VS from here: [Visual Studio Community](http://visualstudio.com)
2. Install CUDA
3. Install [vcpkg](https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg) and try to install a test library to make sure everything is working, for example `vcpkg install opengl`
4. Open Powershell and type these commands:
```PowerShell
PS \> cd vcpkg
PS Code\vcpkg> .\vcpkg install darknet[full]:x64-windows #replace with darknet[opencv-base,weights]:x64-windows for a quicker install; use --head if you want to build latest commit on master branch and not latest release
```
5. You will find darknet inside the vcpkg\installed\x64-windows\tools\darknet folder, together with all the necessary weight and cfg files
### How to compile on Windows (legacy way)
1. If you have **CUDA 10.0, cuDNN 7.4 and OpenCV 3.x** (with paths: `C:\opencv_3.0\opencv\build\include` & `C:\opencv_3.0\opencv\build\x64\vc14\lib`), then open `build\darknet\darknet.sln`, set **x64** and **Release** https://hsto.org/webt/uh/fk/-e/uhfk-eb0q-hwd9hsxhrikbokd6u.jpeg and do the: Build -> Build darknet. Also add Windows system variable `CUDNN` with path to CUDNN: https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/4096485/53249764-019ef880-36ca-11e9-8ffe-d9cf47e7e462.jpg
1.1. Find files `opencv_world320.dll` and `opencv_ffmpeg320_64.dll` (or `opencv_world340.dll` and `opencv_ffmpeg340_64.dll`) in `C:\opencv_3.0\opencv\build\x64\vc14\bin` and put it near with `darknet.exe`
1.2 Check that there are `bin` and `include` folders in the `C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v10.0` if aren't, then copy them to this folder from the path where is CUDA installed
1.3. To install CUDNN (speedup neural network), do the following:
* download and install **cuDNN v7.4.1 for CUDA 10.0**: https://developer.nvidia.com/rdp/cudnn-archive
* add Windows system variable `CUDNN` with path to CUDNN: https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/4096485/53249764-019ef880-36ca-11e9-8ffe-d9cf47e7e462.jpg
* copy file `cudnn64_7.dll` to the folder `\build\darknet\x64` near with `darknet.exe`
1.4. If you want to build **without CUDNN** then: open `\darknet.sln` -> (right click on project) -> properties -> C/C++ -> Preprocessor -> Preprocessor Definitions, and remove this: `CUDNN;`
2. If you have other version of **CUDA (not 10.0)** then open `build\darknet\darknet.vcxproj` by using Notepad, find 2 places with "CUDA 10.0" and change it to your CUDA-version. Then open `\darknet.sln` -> (right click on project) -> properties -> CUDA C/C++ -> Device and remove there `;compute_75,sm_75`. Then do step 1
3. If you **don't have GPU**, but have **OpenCV 3.0** (with paths: `C:\opencv_3.0\opencv\build\include` & `C:\opencv_3.0\opencv\build\x64\vc14\lib`), then open `build\darknet\darknet_no_gpu.sln`, set **x64** and **Release**, and do the: Build -> Build darknet_no_gpu
4. If you have **OpenCV 2.4.13** instead of 3.0 then you should change paths after `\darknet.sln` is opened
4.1 (right click on project) -> properties -> C/C++ -> General -> Additional Include Directories: `C:\opencv_2.4.13\opencv\build\include`
4.2 (right click on project) -> properties -> Linker -> General -> Additional Library Directories: `C:\opencv_2.4.13\opencv\build\x64\vc14\lib`
5. If you have GPU with Tensor Cores (nVidia Titan V / Tesla V100 / DGX-2 and later) speedup Detection 3x, Training 2x:
`\darknet.sln` -> (right click on project) -> properties -> C/C++ -> Preprocessor -> Preprocessor Definitions, and add here: `CUDNN_HALF;`
**Note:** CUDA must be installed only after Visual Studio has been installed.
### How to compile (custom):
Also, you can to create your own `darknet.sln` & `darknet.vcxproj`, this example for CUDA 9.1 and OpenCV 3.0
Then add to your created project:
- (right click on project) -> properties -> C/C++ -> General -> Additional Include Directories, put here:
`C:\opencv_3.0\opencv\build\include;..\..\3rdparty\include;%(AdditionalIncludeDirectories);$(CudaToolkitIncludeDir);$(CUDNN)\include`
- (right click on project) -> Build dependecies -> Build Customizations -> set check on CUDA 9.1 or what version you have - for example as here: http://devblogs.nvidia.com/parallelforall/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/VS2013-R-5.jpg
- add to project:
* all `.c` files
* all `.cu` files
* file `http_stream.cpp` from `\src` directory
* file `darknet.h` from `\include` directory
- (right click on project) -> properties -> Linker -> General -> Additional Library Directories, put here:
`C:\opencv_3.0\opencv\build\x64\vc14\lib;$(CUDA_PATH)\lib\$(PlatformName);$(CUDNN)\lib\x64;%(AdditionalLibraryDirectories)`
- (right click on project) -> properties -> Linker -> Input -> Additional dependecies, put here:
`..\..\3rdparty\lib\x64\pthreadVC2.lib;cublas.lib;curand.lib;cudart.lib;cudnn.lib;%(AdditionalDependencies)`
- (right click on project) -> properties -> C/C++ -> Preprocessor -> Preprocessor Definitions
`OPENCV;_TIMESPEC_DEFINED;_CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS;_CRT_RAND_S;WIN32;NDEBUG;_CONSOLE;_LIB;%(PreprocessorDefinitions)`
- compile to .exe (X64 & Release) and put .dll-s near with .exe: https://hsto.org/webt/uh/fk/-e/uhfk-eb0q-hwd9hsxhrikbokd6u.jpeg
* `pthreadVC2.dll, pthreadGC2.dll` from \3rdparty\dll\x64
* `cusolver64_91.dll, curand64_91.dll, cudart64_91.dll, cublas64_91.dll` - 91 for CUDA 9.1 or your version, from C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v9.1\bin
* For OpenCV 3.2: `opencv_world320.dll` and `opencv_ffmpeg320_64.dll` from `C:\opencv_3.0\opencv\build\x64\vc14\bin`
* For OpenCV 2.4.13: `opencv_core2413.dll`, `opencv_highgui2413.dll` and `opencv_ffmpeg2413_64.dll` from `C:\opencv_2.4.13\opencv\build\x64\vc14\bin`
## How to train with multi-GPU:
1. Train it first on 1 GPU for like 1000 iterations: `darknet.exe detector train cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg yolov4.conv.137`
2. Then stop and by using partially-trained model `/backup/yolov4_1000.weights` run training with multigpu (up to 4 GPUs): `darknet.exe detector train cfg/coco.data cfg/yolov4.cfg /backup/yolov4_1000.weights -gpus 0,1,2,3`
If you get a Nan, then for some datasets better to decrease learning rate, for 4 GPUs set `learning_rate = 0,00065` (i.e. learning_rate = 0.00261 / GPUs). In this case also increase 4x times `burn_in =` in your cfg-file. I.e. use `burn_in = 4000` instead of `1000`.
https://groups.google.com/d/msg/darknet/NbJqonJBTSY/Te5PfIpuCAAJ
## How to train (to detect your custom objects):
(to train old Yolo v2 `yolov2-voc.cfg`, `yolov2-tiny-voc.cfg`, `yolo-voc.cfg`, `yolo-voc.2.0.cfg`, ... [click by the link](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/tree/47c7af1cea5bbdedf1184963355e6418cb8b1b4f#how-to-train-pascal-voc-data))
Training Yolo v4 (and v3):
0. For training `cfg/yolov4-custom.cfg` download the pre-trained weights-file (162 MB): [yolov4.conv.137](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/releases/download/darknet_yolo_v3_optimal/yolov4.conv.137) (Google drive mirror [yolov4.conv.137](https://drive.google.com/open?id=1JKF-bdIklxOOVy-2Cr5qdvjgGpmGfcbp) )
1. Create file `yolo-obj.cfg` with the same content as in `yolov4-custom.cfg` (or copy `yolov4-custom.cfg` to `yolo-obj.cfg)` and:
* change line batch to [`batch=64`](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L3)
* change line subdivisions to [`subdivisions=16`](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L4)
* change line max_batches to (`classes*2000` but not less than number of training images, and not less than `6000`), f.e. [`max_batches=6000`](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L20) if you train for 3 classes
* change line steps to 80% and 90% of max_batches, f.e. [`steps=4800,5400`](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L22)
* set network size `width=416 height=416` or any value multiple of 32: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L8-L9
* change line `classes=80` to your number of objects in each of 3 `[yolo]`-layers:
* https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L610
* https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L696
* https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L783
* change [`filters=255`] to filters=(classes + 5)x3 in the 3 `[convolutional]` before each `[yolo]` layer, keep in mind that it only has to be the last `[convolutional]` before each of the `[yolo]` layers.
* https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L603
* https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L689
* https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L776
* when using [`[Gaussian_yolo]`](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/6e5bdf1282ad6b06ed0e962c3f5be67cf63d96dc/cfg/Gaussian_yolov3_BDD.cfg#L608) layers, change [`filters=57`] filters=(classes + 9)x3 in the 3 `[convolutional]` before each `[Gaussian_yolo]` layer
* https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/6e5bdf1282ad6b06ed0e962c3f5be67cf63d96dc/cfg/Gaussian_yolov3_BDD.cfg#L604
* https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/6e5bdf1282ad6b06ed0e962c3f5be67cf63d96dc/cfg/Gaussian_yolov3_BDD.cfg#L696
* https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/6e5bdf1282ad6b06ed0e962c3f5be67cf63d96dc/cfg/Gaussian_yolov3_BDD.cfg#L789
So if `classes=1` then should be `filters=18`. If `classes=2` then write `filters=21`.
**(Do not write in the cfg-file: filters=(classes + 5)x3)**
(Generally `filters` depends on the `classes`, `coords` and number of `mask`s, i.e. filters=`(classes + coords + 1)*<number of mask>`, where `mask` is indices of anchors. If `mask` is absence, then filters=`(classes + coords + 1)*num`)
So for example, for 2 objects, your file `yolo-obj.cfg` should differ from `yolov4-custom.cfg` in such lines in each of **3** [yolo]-layers:
```
[convolutional]
filters=21
[region]
classes=2
```
2. Create file `obj.names` in the directory `build\darknet\x64\data\`, with objects names - each in new line
3. Create file `obj.data` in the directory `build\darknet\x64\data\`, containing (where **classes = number of objects**):
```
classes= 2
train = data/train.txt
valid = data/test.txt
names = data/obj.names
backup = backup/
```
4. Put image-files (.jpg) of your objects in the directory `build\darknet\x64\data\obj\`
5. You should label each object on images from your dataset. Use this visual GUI-software for marking bounded boxes of objects and generating annotation files for Yolo v2 & v3: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/Yolo_mark
It will create `.txt`-file for each `.jpg`-image-file - in the same directory and with the same name, but with `.txt`-extension, and put to file: object number and object coordinates on this image, for each object in new line:
`<object-class> <x_center> <y_center> <width> <height>`
Where:
* `<object-class>` - integer object number from `0` to `(classes-1)`
* `<x_center> <y_center> <width> <height>` - float values **relative** to width and height of image, it can be equal from `(0.0 to 1.0]`
* for example: `<x> = <absolute_x> / <image_width>` or `<height> = <absolute_height> / <image_height>`
* atention: `<x_center> <y_center>` - are center of rectangle (are not top-left corner)
For example for `img1.jpg` you will be created `img1.txt` containing:
```
1 0.716797 0.395833 0.216406 0.147222
0 0.687109 0.379167 0.255469 0.158333
1 0.420312 0.395833 0.140625 0.166667
```
6. Create file `train.txt` in directory `build\darknet\x64\data\`, with filenames of your images, each filename in new line, with path relative to `darknet.exe`, for example containing:
```
data/obj/img1.jpg
data/obj/img2.jpg
data/obj/img3.jpg
```
7. Download pre-trained weights for the convolutional layers and put to the directory `build\darknet\x64`
* for `yolov4.cfg`, `yolov4-custom.cfg` (162 MB): [yolov4.conv.137](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/releases/download/darknet_yolo_v3_optimal/yolov4.conv.137) (Google drive mirror [yolov4.conv.137](https://drive.google.com/open?id=1JKF-bdIklxOOVy-2Cr5qdvjgGpmGfcbp) )
* for `csresnext50-panet-spp.cfg` (133 MB): [csresnext50-panet-spp.conv.112](https://drive.google.com/file/d/16yMYCLQTY_oDlCIZPfn_sab6KD3zgzGq/view?usp=sharing)
* for `yolov3.cfg, yolov3-spp.cfg` (154 MB): [darknet53.conv.74](https://pjreddie.com/media/files/darknet53.conv.74)
* for `yolov3-tiny-prn.cfg , yolov3-tiny.cfg` (6 MB): [yolov3-tiny.conv.11](https://drive.google.com/file/d/18v36esoXCh-PsOKwyP2GWrpYDptDY8Zf/view?usp=sharing)
* for `enet-coco.cfg (EfficientNetB0-Yolov3)` (14 MB): [enetb0-coco.conv.132](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1uhh3D6RSn0ekgmsaTcl-ZW53WBaUDo6j/view?usp=sharing)
8. Start training by using the command line: `darknet.exe detector train data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg yolov4.conv.137`
To train on Linux use command: `./darknet detector train data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg yolov4.conv.137` (just use `./darknet` instead of `darknet.exe`)
* (file `yolo-obj_last.weights` will be saved to the `build\darknet\x64\backup\` for each 100 iterations)
* (file `yolo-obj_xxxx.weights` will be saved to the `build\darknet\x64\backup\` for each 1000 iterations)
* (to disable Loss-Window use `darknet.exe detector train data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg yolov4.conv.137 -dont_show`, if you train on computer without monitor like a cloud Amazon EC2)
* (to see the mAP & Loss-chart during training on remote server without GUI, use command `darknet.exe detector train data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg yolov4.conv.137 -dont_show -mjpeg_port 8090 -map` then open URL `http://ip-address:8090` in Chrome/Firefox browser)
8.1. For training with mAP (mean average precisions) calculation for each 4 Epochs (set `valid=valid.txt` or `train.txt` in `obj.data` file) and run: `darknet.exe detector train data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg yolov4.conv.137 -map`
9. After training is complete - get result `yolo-obj_final.weights` from path `build\darknet\x64\backup\`
* After each 100 iterations you can stop and later start training from this point. For example, after 2000 iterations you can stop training, and later just start training using: `darknet.exe detector train data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg backup\yolo-obj_2000.weights`
(in the original repository https://github.com/pjreddie/darknet the weights-file is saved only once every 10 000 iterations `if(iterations > 1000)`)
* Also you can get result earlier than all 45000 iterations.
**Note:** If during training you see `nan` values for `avg` (loss) field - then training goes wrong, but if `nan` is in some other lines - then training goes well.
**Note:** If you changed width= or height= in your cfg-file, then new width and height must be divisible by 32.
**Note:** After training use such command for detection: `darknet.exe detector test data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg yolo-obj_8000.weights`
**Note:** if error `Out of memory` occurs then in `.cfg`-file you should increase `subdivisions=16`, 32 or 64: [link](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L4)
### How to train tiny-yolo (to detect your custom objects):
Do all the same steps as for the full yolo model as described above. With the exception of:
* Download default weights file for yolov3-tiny: https://pjreddie.com/media/files/yolov3-tiny.weights
* Get pre-trained weights `yolov3-tiny.conv.15` using command: `darknet.exe partial cfg/yolov3-tiny.cfg yolov3-tiny.weights yolov3-tiny.conv.15 15`
* Make your custom model `yolov3-tiny-obj.cfg` based on `cfg/yolov3-tiny_obj.cfg` instead of `yolov3.cfg`
* Start training: `darknet.exe detector train data/obj.data yolov3-tiny-obj.cfg yolov3-tiny.conv.15`
For training Yolo based on other models ([DenseNet201-Yolo](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/build/darknet/x64/densenet201_yolo.cfg) or [ResNet50-Yolo](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/build/darknet/x64/resnet50_yolo.cfg)), you can download and get pre-trained weights as showed in this file: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/build/darknet/x64/partial.cmd
If you made you custom model that isn't based on other models, then you can train it without pre-trained weights, then will be used random initial weights.
## When should I stop training:
Usually sufficient 2000 iterations for each class(object), but not less than number of training images and not less than 6000 iterations in total. But for a more precise definition when you should stop training, use the following manual:
1. During training, you will see varying indicators of error, and you should stop when no longer decreases **0.XXXXXXX avg**:
> Region Avg IOU: 0.798363, Class: 0.893232, Obj: 0.700808, No Obj: 0.004567, Avg Recall: 1.000000, count: 8
> Region Avg IOU: 0.800677, Class: 0.892181, Obj: 0.701590, No Obj: 0.004574, Avg Recall: 1.000000, count: 8
>
> **9002**: 0.211667, **0.60730 avg**, 0.001000 rate, 3.868000 seconds, 576128 images
> Loaded: 0.000000 seconds
* **9002** - iteration number (number of batch)
* **0.60730 avg** - average loss (error) - **the lower, the better**
When you see that average loss **0.xxxxxx avg** no longer decreases at many iterations then you should stop training. The final avgerage loss can be from `0.05` (for a small model and easy dataset) to `3.0` (for a big model and a difficult dataset).
Or if you train with flag `-map` then you will see mAP indicator `Last accuracy [email protected] = 18.50%` in the console - this indicator is better than Loss, so train while mAP increases.
2. Once training is stopped, you should take some of last `.weights`-files from `darknet\build\darknet\x64\backup` and choose the best of them:
For example, you stopped training after 9000 iterations, but the best result can give one of previous weights (7000, 8000, 9000). It can happen due to overfitting. **Overfitting** - is case when you can detect objects on images from training-dataset, but can't detect objects on any others images. You should get weights from **Early Stopping Point**:

To get weights from Early Stopping Point:
2.1. At first, in your file `obj.data` you must specify the path to the validation dataset `valid = valid.txt` (format of `valid.txt` as in `train.txt`), and if you haven't validation images, just copy `data\train.txt` to `data\valid.txt`.
2.2 If training is stopped after 9000 iterations, to validate some of previous weights use this commands:
(If you use another GitHub repository, then use `darknet.exe detector recall`... instead of `darknet.exe detector map`...)
* `darknet.exe detector map data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg backup\yolo-obj_7000.weights`
* `darknet.exe detector map data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg backup\yolo-obj_8000.weights`
* `darknet.exe detector map data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg backup\yolo-obj_9000.weights`
And comapre last output lines for each weights (7000, 8000, 9000):
Choose weights-file **with the highest mAP (mean average precision)** or IoU (intersect over union)
For example, **bigger mAP** gives weights `yolo-obj_8000.weights` - then **use this weights for detection**.
Or just train with `-map` flag:
`darknet.exe detector train data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg yolov4.conv.137 -map`
So you will see mAP-chart (red-line) in the Loss-chart Window. mAP will be calculated for each 4 Epochs using `valid=valid.txt` file that is specified in `obj.data` file (`1 Epoch = images_in_train_txt / batch` iterations)
(to change the max x-axis value - change [`max_batches=`](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L20) parameter to `2000*classes`, f.e. `max_batches=6000` for 3 classes)

Example of custom object detection: `darknet.exe detector test data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg yolo-obj_8000.weights`
* **IoU** (intersect over union) - average instersect over union of objects and detections for a certain threshold = 0.24
* **mAP** (mean average precision) - mean value of `average precisions` for each class, where `average precision` is average value of 11 points on PR-curve for each possible threshold (each probability of detection) for the same class (Precision-Recall in terms of PascalVOC, where Precision=TP/(TP+FP) and Recall=TP/(TP+FN) ), page-11: http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/ckiw/postscript/ijcv_voc09.pdf
**mAP** is default metric of precision in the PascalVOC competition, **this is the same as AP50** metric in the MS COCO competition.
In terms of Wiki, indicators Precision and Recall have a slightly different meaning than in the PascalVOC competition, but **IoU always has the same meaning**.

### Custom object detection:
Example of custom object detection: `darknet.exe detector test data/obj.data yolo-obj.cfg yolo-obj_8000.weights`
|  |  |
|---|---|
## How to improve object detection:
1. Before training:
* set flag `random=1` in your `.cfg`-file - it will increase precision by training Yolo for different resolutions: [link](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L788)
* increase network resolution in your `.cfg`-file (`height=608`, `width=608` or any value multiple of 32) - it will increase precision
* check that each object that you want to detect is mandatory labeled in your dataset - no one object in your data set should not be without label. In the most training issues - there are wrong labels in your dataset (got labels by using some conversion script, marked with a third-party tool, ...). Always check your dataset by using: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/Yolo_mark
* my Loss is very high and mAP is very low, is training wrong? Run training with ` -show_imgs` flag at the end of training command, do you see correct bounded boxes of objects (in windows or in files `aug_...jpg`)? If no - your training dataset is wrong.
* for each object which you want to detect - there must be at least 1 similar object in the Training dataset with about the same: shape, side of object, relative size, angle of rotation, tilt, illumination. So desirable that your training dataset include images with objects at diffrent: scales, rotations, lightings, from different sides, on different backgrounds - you should preferably have 2000 different images for each class or more, and you should train `2000*classes` iterations or more
* desirable that your training dataset include images with non-labeled objects that you do not want to detect - negative samples without bounded box (empty `.txt` files) - use as many images of negative samples as there are images with objects
* What is the best way to mark objects: label only the visible part of the object, or label the visible and overlapped part of the object, or label a little more than the entire object (with a little gap)? Mark as you like - how would you like it to be detected.
* for training with a large number of objects in each image, add the parameter `max=200` or higher value in the last `[yolo]`-layer or `[region]`-layer in your cfg-file (the global maximum number of objects that can be detected by YoloV3 is `0,0615234375*(width*height)` where are width and height are parameters from `[net]` section in cfg-file)
* for training for small objects (smaller than 16x16 after the image is resized to 416x416) - set `layers = 23` instead of https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/6f718c257815a984253346bba8fb7aa756c55090/cfg/yolov4.cfg#L895
set `stride=4` instead of https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/6f718c257815a984253346bba8fb7aa756c55090/cfg/yolov4.cfg#L892
and set `stride=4` instead of https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/6f718c257815a984253346bba8fb7aa756c55090/cfg/yolov4.cfg#L989
* for training for both small and large objects use modified models:
* Full-model: 5 yolo layers: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/master/cfg/yolov3_5l.cfg
* Tiny-model: 3 yolo layers: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/master/cfg/yolov3-tiny_3l.cfg
* YOLOv4: 3 yolo layers: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/master/cfg/yolov4-custom.cfg
* If you train the model to distinguish Left and Right objects as separate classes (left/right hand, left/right-turn on road signs, ...) then for disabling flip data augmentation - add `flip=0` here: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/3d2d0a7c98dbc8923d9ff705b81ff4f7940ea6ff/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L17
* General rule - your training dataset should include such a set of relative sizes of objects that you want to detect:
* `train_network_width * train_obj_width / train_image_width ~= detection_network_width * detection_obj_width / detection_image_width`
* `train_network_height * train_obj_height / train_image_height ~= detection_network_height * detection_obj_height / detection_image_height`
I.e. for each object from Test dataset there must be at least 1 object in the Training dataset with the same class_id and about the same relative size:
`object width in percent from Training dataset` ~= `object width in percent from Test dataset`
That is, if only objects that occupied 80-90% of the image were present in the training set, then the trained network will not be able to detect objects that occupy 1-10% of the image.
* to speedup training (with decreasing detection accuracy) set param `stopbackward=1` for layer-136 in cfg-file
* each: `model of object, side, illimination, scale, each 30 grad` of the turn and inclination angles - these are *different objects* from an internal perspective of the neural network. So the more *different objects* you want to detect, the more complex network model should be used.
* to make the detected bounded boxes more accurate, you can add 3 parameters `ignore_thresh = .9 iou_normalizer=0.5 iou_loss=giou` to each `[yolo]` layer and train, it will increase [email protected], but decrease [email protected].
* Only if you are an **expert** in neural detection networks - recalculate anchors for your dataset for `width` and `height` from cfg-file:
`darknet.exe detector calc_anchors data/obj.data -num_of_clusters 9 -width 416 -height 416`
then set the same 9 `anchors` in each of 3 `[yolo]`-layers in your cfg-file. But you should change indexes of anchors `masks=` for each [yolo]-layer, so that 1st-[yolo]-layer has anchors larger than 60x60, 2nd larger than 30x30, 3rd remaining. Also you should change the `filters=(classes + 5)*<number of mask>` before each [yolo]-layer. If many of the calculated anchors do not fit under the appropriate layers - then just try using all the default anchors.
2. After training - for detection:
* Increase network-resolution by set in your `.cfg`-file (`height=608` and `width=608`) or (`height=832` and `width=832`) or (any value multiple of 32) - this increases the precision and makes it possible to detect small objects: [link](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L8-L9)
* it is not necessary to train the network again, just use `.weights`-file already trained for 416x416 resolution
* but to get even greater accuracy you should train with higher resolution 608x608 or 832x832, note: if error `Out of memory` occurs then in `.cfg`-file you should increase `subdivisions=16`, 32 or 64: [link](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/0039fd26786ab5f71d5af725fc18b3f521e7acfd/cfg/yolov3.cfg#L4)
## How to mark bounded boxes of objects and create annotation files:
Here you can find repository with GUI-software for marking bounded boxes of objects and generating annotation files for Yolo v2 - v4: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/Yolo_mark
With example of: `train.txt`, `obj.names`, `obj.data`, `yolo-obj.cfg`, `air`1-6`.txt`, `bird`1-4`.txt` for 2 classes of objects (air, bird) and `train_obj.cmd` with example how to train this image-set with Yolo v2 - v4
Different tools for marking objects in images:
1. in C++: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/Yolo_mark
2. in Python: https://github.com/tzutalin/labelImg
3. in Python: https://github.com/Cartucho/OpenLabeling
4. in C++: https://www.ccoderun.ca/darkmark/
5. in JavaScript: https://github.com/opencv/cvat
## How to use Yolo as DLL and SO libraries
* on Linux
* using `build.sh` or
* build `darknet` using `cmake` or
* set `LIBSO=1` in the `Makefile` and do `make`
* on Windows
* using `build.ps1` or
* build `darknet` using `cmake` or
* compile `build\darknet\yolo_cpp_dll.sln` solution or `build\darknet\yolo_cpp_dll_no_gpu.sln` solution
There are 2 APIs:
* C API: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/include/darknet.h
* Python examples using the C API::
* https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/darknet.py
* https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/darknet_video.py
* C++ API: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/include/yolo_v2_class.hpp
* C++ example that uses C++ API: https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/src/yolo_console_dll.cpp
----
1. To compile Yolo as C++ DLL-file `yolo_cpp_dll.dll` - open the solution `build\darknet\yolo_cpp_dll.sln`, set **x64** and **Release**, and do the: Build -> Build yolo_cpp_dll
* You should have installed **CUDA 10.0**
* To use cuDNN do: (right click on project) -> properties -> C/C++ -> Preprocessor -> Preprocessor Definitions, and add at the beginning of line: `CUDNN;`
2. To use Yolo as DLL-file in your C++ console application - open the solution `build\darknet\yolo_console_dll.sln`, set **x64** and **Release**, and do the: Build -> Build yolo_console_dll
* you can run your console application from Windows Explorer `build\darknet\x64\yolo_console_dll.exe`
**use this command**: `yolo_console_dll.exe data/coco.names yolov4.cfg yolov4.weights test.mp4`
* after launching your console application and entering the image file name - you will see info for each object:
`<obj_id> <left_x> <top_y> <width> <height> <probability>`
* to use simple OpenCV-GUI you should uncomment line `//#define OPENCV` in `yolo_console_dll.cpp`-file: [link](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/a6cbaeecde40f91ddc3ea09aa26a03ab5bbf8ba8/src/yolo_console_dll.cpp#L5)
* you can see source code of simple example for detection on the video file: [link](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/ab1c5f9e57b4175f29a6ef39e7e68987d3e98704/src/yolo_console_dll.cpp#L75)
`yolo_cpp_dll.dll`-API: [link](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet/blob/master/src/yolo_v2_class.hpp#L42)
```
struct bbox_t {
unsigned int x, y, w, h; // (x,y) - top-left corner, (w, h) - width & height of bounded box
float prob; // confidence - probability that the object was found correctly
unsigned int obj_id; // class of object - from range [0, classes-1]
unsigned int track_id; // tracking id for video (0 - untracked, 1 - inf - tracked object)
unsigned int frames_counter;// counter of frames on which the object was detected
};
class Detector {
public:
Detector(std::string cfg_filename, std::string weight_filename, int gpu_id = 0);
~Detector();
std::vector<bbox_t> detect(std::string image_filename, float thresh = 0.2, bool use_mean = false);
std::vector<bbox_t> detect(image_t img, float thresh = 0.2, bool use_mean = false);
static image_t load_image(std::string image_filename);
static void free_image(image_t m);
#ifdef OPENCV
std::vector<bbox_t> detect(cv::Mat mat, float thresh = 0.2, bool use_mean = false);
std::shared_ptr<image_t> mat_to_image_resize(cv::Mat mat) const;
#endif
};
```
>>>>>>> e6469eb071521a4ff5be8c0e9cceb524d0a65a95