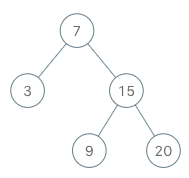
实现一个二叉搜索树迭代器。你将使用二叉搜索树的根节点初始化迭代器。
调用
next()将返回二叉搜索树中的下一个最小的数。
示例:
BSTIterator iterator = new BSTIterator(root); iterator.next(); // 返回 3 iterator.next(); // 返回 7 iterator.hasNext(); // 返回 true iterator.next(); // 返回 9 iterator.hasNext(); // 返回 true iterator.next(); // 返回 15 iterator.hasNext(); // 返回 true iterator.next(); // 返回 20 iterator.hasNext(); // 返回 false
提示:
next()和hasNext()操作的时间复杂度是 O(1),并使用 O(h) 内存,其中 h 是树的高度。- 你可以假设
next()调用总是有效的,也就是说,当调用next()时,BST 中至少存在一个下一个最小的数。
解法一:
//时间复杂度O(logn), 空间复杂度O(1)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class BSTIterator {
public:
BSTIterator(TreeNode* root) : root(nullptr) {//O(logn)
if(!root) return;
while(root->left) {
TreeNode* temp = root;
root = root->left;
temp->left = root->right;
root->right = temp;
}
this->root = root;
}
/** @return the next smallest number */
int next() {//O(logn)
//if(!root) return 0;
while(root->left) {
TreeNode* temp = root;
root = root->left;
temp->left = root->right;
root->right = temp;
}
int res = root->val;
root = root->right;
return res;
}
/** @return whether we have a next smallest number */
bool hasNext() {//O(1)
return root;
}
private:
TreeNode* root;
};
/**
* Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* BSTIterator* obj = new BSTIterator(root);
* int param_1 = obj->next();
* bool param_2 = obj->hasNext();
*/解法二:
//时间复杂度O(1), 空间复杂度O(logn)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class BSTIterator {
public:
BSTIterator(TreeNode* root) {//O(logn)
p = root;
while(p) {
st.push(p);
p = p->left;
}
}
/** @return the next smallest number */
int next() {//O(logn)
while(p) {
st.push(p);
p = p->left;
}
TreeNode* temp = st.top();
st.pop();
p = temp->right;
return temp->val;
}
/** @return whether we have a next smallest number */
bool hasNext() {
return !st.empty() || p;
}
private:
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* p;
};
/**
* Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* BSTIterator* obj = new BSTIterator(root);
* int param_1 = obj->next();
* bool param_2 = obj->hasNext();
*/解法一:
反复将根结点旋转,直到其没有左子结点,此时最小的就是根结点。时间不满足要求,会破坏树的结构。
解法二:
中序遍历的迭代实现,此题并不是一次性完成的,而是随着next()的调用一步一步向下进行。
2020/01/03 14:47