- Read/write single data and multi data, large data automatic subcontracting.
- Read/write serialized batch multiple addresses and discontinuous address.
- Read/write DB, I, Q, M, and V.
- Read/write Siemens S1500, S1200, S400, S300, S200Smart, Siemens Machine Tool 828D.
- Support automatic PLC reconnection.
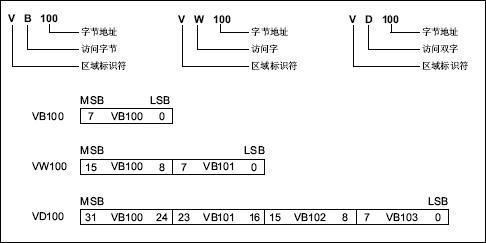
- You can check this address if
you're not familiar with the S7 protocol.
- 200smartPLC, V Area == DB1.X. Example: V1=DB1.1, V100=DB1.100
Tips1: Format and meaning of the address, case compatible.
| Abbr | Area | Byte Index | Bit Index | PLC Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB1.1.2 | DB1 | 1 | 2 | S1200/S1500 |
| DB2 | DB2 | 0 | 0 | S1200/S1500 |
| DB3.3 | DB3 | 3 | 0 | S1200/S1500 |
| D1.1.2 | DB1 | 1 | 2 | S1200/S1500 |
| Q1.6 | Q | 1 | 6 | S1200/S1500 |
| Q1 | Q | 1 | 0 | S1200/S1500 |
| I2.5 | I | 2 | 5 | S1200/S1500 |
| I2 | I | 2 | 0 | S1200/S1500 |
| M3.2 | M | 3 | 2 | S1200/S1500 |
| M3 | M | 3 | 0 | S1200/S1500 |
| V2.1 | V | 2 | 1 | S200Smart |
| V2 | V | 2 | 0 | S200Smart |
Tips2: Access data types mapping to JAVA data types and PLC data types.
| Access Data Type | Data Size in Bit | Data Size in Byte | JAVA Data Type | PLC Data Type | Instance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| boolean | 1 | 1/8 | Boolean | BOOL | true |
| byte | 8 | 1 | Byte | BYTE | 0x11 |
| uint16 | 16 | 2 | Integer | WORD/UINT | 65535 |
| int16 | 16 | 2 | Short | WORD/INT | -32760 |
| uint32 | 32 | 4 | Long | DWORD/UDINT | 70000 |
| int32 | 32 | 4 | Integer | DWORD/DINT | -70000 |
| float32 | 32 | 4 | Float | REAL | 3.14 |
| float64 | 64 | 8 | Double | LREAL | 3.14 |
| string | 8 | 1 | String | String | ABC |
| time | 32 | 4 | Long | Time | 100ms |
| date | 16 | 2 | LocalDate | Date | 2023-04-03 |
| timeOfDay | 32 | 4 | LocalTime | TimeOfDay | 10:22:11 |
| dtl | 96 | 12 | LocalDateTime | DTL | 2023-04-03 10:22:11 |
Tip3: The PLC address mapping to the project address and data type
| PLC Address | Data Size in Bit | Data Size in Byte | Access Address | Access Data Type | PLC Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB100.DBX0.0 | 1 | 1/8 | DB100.0.0 | boolean | S1200/S1500 |
| DB100.DBB5 | 8 | 1 | DB100.5 | byte | S1200/S1500 |
| DB100.DBW6 | 16 | 2 | DB100.6 | uint16/int16 | S1200/S1500 |
| DB100.DBD3 | 32 | 4 | DB100.3 | uint32/int32/float32 | S1200/S1500 |
| VB100 | 8 | 1 | V100 | byte | S200Smart |
| VW100 | 16 | 2 | V100 | uint16/int16 | S200Smart |
| VD100 | 32 | 4 | V100 | uint32/int32/float32 | S200Smart |
| MB1 | 8 | 1 | M1 | byte | - |
| MW1 | 16 | 2 | M1 | uint16/int16 | - |
| MD1 | 32 | 4 | M1 | uint32/int32/float32 | - |
If you want to know the actual input and output of packets during communication, you can print packet information by yourself.
class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200, "127.0.0.1");
// print message
s7PLC.setComCallback((tag, bytes) -> System.out.printf("%s[%d] %s%n", tag, bytes.length, HexUtil.toHexString(bytes)));
s7PLC.readByte("DB2.1");
s7PLC.close();
}
}- By default, the long connection mode is adopted. You need to close connection manually when it is not in use.
- If a short connection is required, you need to set it manually.
class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// long connection mode, persistence = true
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200, "127.0.0.1");
s7PLC.writeByte("DB2.1", (byte) 0x11);
s7PLC.readByte("DB2.1");
// close it manually, if you want to use it all the time, you do not need to close it
s7PLC.close();
}
}class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// short connection mode
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200, "127.0.0.1");
// set short connection mode,persistence = false
s7PLC.setPersistence(false);
s7PLC.writeByte("DB2.1", (byte) 0x11);
s7PLC.readByte("DB2.1");
}
}class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200, "127.0.0.1");
// read boolean
boolean boolData = s7PLC.readBoolean("DB1.2.0");
List<Boolean> boolDatas = s7PLC.readBoolean("DB1.2.0", "DB1.2.1", "DB1.2.7");
List<Boolean> iDatas = s7PLC.readBoolean("I0.0", "I0.1", "I0.2", "I0.3", "I0.4", "I0.5");
List<Boolean> qDatas = s7PLC.readBoolean("Q0.0", "Q0.1", "Q0.2", "Q0.3", "Q0.4", "Q0.5", "Q0.6", "Q0.7");
List<Boolean> mDatas = s7PLC.readBoolean("M1.0", "M1.1", "M1.2", "M1.3", "M1.4", "M1.5", "M1.6", "M1.7");
List<Boolean> vDatas = s7PLC.readBoolean("V1.0", "V1.1", "V1.2", "V1.3", "V1.4", "V1.5", "V1.6", "V1.7"); // 200smart有V区
// read byte
byte byteData = s7PLC.readByte("DB14.0");
byte[] byteDatas = s7PLC.readByte("DB14.0", 4);
byte iByteData = s7PLC.readByte("I0");
byte qByteData = s7PLC.readByte("Q0");
byte mByteData = s7PLC.readByte("M0");
byte vByteData = s7PLC.readByte("V0"); // 200smart有V区
// read UInt16
int intData = s7PLC.readUInt16("DB14.0");
List<Integer> intDatas = s7PLC.readUInt16("DB1.0", "DB1.2");
// read UInt32
long int32Data = s7PLC.readUInt32("DB1.0");
List<Long> int32Datas = s7PLC.readUInt32("DB1.0", "DB1.4");
// read float32
float float32Data = s7PLC.readFloat32("DB1.0");
List<Float> float32Datas = s7PLC.readFloat32("DB1.0", "DB1.4");
// read float64
double float64Data = s7PLC.readFloat64("DB1.0");
List<Double> float64Datas = s7PLC.readFloat64("DB1.0", "DB1.4");
// read String
String strData = s7PLC.readString("DB14.4");
String strData1 = s7PLC.readString("DB14.4", 10);
// read time
long timeData = s7PLC.readTime("DB1.0");
// read date
LocalDate localDateData = s7PLC.readDate("DB1.0");
// read time of day
LocalTime localTimeOfDayData = s7PLC.readTimeOfDay("DB1.0");
// read multi address
MultiAddressRead addressRead = new MultiAddressRead();
addressRead.addData("DB1.0", 1)
.addData("DB1.2", 3)
.addData("DB1.3", 5);
List<byte[]> multiByte = s7PLC.readMultiByte(addressRead);
s7PLC.close();
}
}class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200, "127.0.0.1");
// write boolean
s7PLC.writeBoolean("DB2.0.7", true);
s7PLC.writeBoolean("Q0.7", true);
s7PLC.writeBoolean("M1.4", true);
// write byte
s7PLC.writeByte("DB2.1", (byte) 0x11);
s7PLC.writeByte("M1", (byte) 0x11);
s7PLC.writeByte("V1", (byte) 0x11); // 200smart
// write UInt16
s7PLC.writeUInt16("DB2.0", 0x2222);
// write UInt32
s7PLC.writeUInt32("DB2.0", 0x11111122);
// write float32
s7PLC.writeFloat32("DB2.0", 12);
// write float64
s7PLC.writeFloat64("DB2.0", 12.02);
// write String
s7PLC.writeString("DB14.4", "demo");
// write time
s7PLC.writeTime("DB1.0", 1000);
// write date
s7PLC.writeDate("DB1.0", LocalDate.now());
// write time of day
s7PLC.writeTimeOfDay("DB1.0", LocalTime.now());
// write multi address
MultiAddressWrite addressWrite = new MultiAddressWrite();
addressWrite.addByte("DB2.0", (byte) 0x11)
.addUInt16("DB2.2", 88)
.addBoolean("DB2.1.0", true);
s7PLC.writeMultiData(addressWrite);
s7PLC.close();
}
}class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200, "127.0.0.1");
// hot restart
s7PLC.hotRestart();
// cold restart
s7PLC.coldRestart();
// plc stop
s7PLC.plcStop();
// copy ram to rom
s7PLC.copyRamToRom();
// compress
s7PLC.compress();
s7PLC.close();
}
}class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S200_SMART, "127.0.0.1");
//********************************* upload ***************************************/
// upload file data, PLC -> PC, success in 200Smart
byte[] bytes = s7PLC.uploadFile(EFileBlockType.OB, 1);
//******************************** download **************************************/
// 1. create mc7 file
Mc7File mc7 = Mc7File.fromBytes(bytes);
// 2. plc stop, stop plc before download file
s7PLC.plcStop();
// 3. download file data, PC -> PLC, success in 200Smart
s7PLC.downloadFile(mc7);
// 4. insert new filename
s7PLC.insert(mc7.getBlockType(), mc7.getBlockNumber());
// 5. hot restart, restart plc after download and insert file
s7PLC.hotRestart();
s7PLC.close();
}
}class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200, "127.0.0.1");
// bit data read-write
byte[] expect = new byte[]{(byte) 0x00};
s7PLC.writeRaw(EParamVariableType.BIT, 1, EArea.DATA_BLOCKS, 1, 0, 3,
EDataVariableType.BIT, expect);
byte[] actual = s7PLC.readRaw(EParamVariableType.BIT, 1, EArea.DATA_BLOCKS, 1, 0, 3);
// byte data read-write
expect = new byte[]{(byte) 0x02, (byte) 0x03};
s7PLC.writeRaw(EParamVariableType.BYTE, 2, EArea.DATA_BLOCKS, 1, 1, 0,
EDataVariableType.BYTE_WORD_DWORD, expect);
byte[] actual1 = s7PLC.readRaw(EParamVariableType.BYTE, 2, EArea.DATA_BLOCKS, 1, 1, 0);
// send with object
RequestNckItem item = new RequestNckItem(ENckArea.C_CHANNEL, 1, 23, 1, ENckModule.S, 1);
S7Data s7Data = NckRequestBuilder.creatNckRequest(item);
S7Data ackData = s7PLC.readFromServerByPersistence(s7Data);
// send with raw message
byte[] sendByteArray = new byte[]{
// tpkt
(byte) 0x03, (byte) 0x00, (byte) 0x00, (byte) 0x1D,
// cotp DT Data
(byte) 0x02, (byte) 0xF0, (byte) 0x80,
// header
(byte) 0x32, (byte) 0x01, (byte) 0x00, (byte) 0x00, (byte) 0x00, (byte) 0x13, (byte) 0x00, (byte) 0x0C, (byte) 0x00, (byte) 0x00,
// parameter
(byte) 0x04, (byte) 0x01,
// request item
(byte) 0x12, (byte) 0x08, (byte) 0x82, (byte) 0x41, (byte) 0x00, (byte) 0x03, (byte) 0x00, (byte) 0x01, (byte) 0x7f, (byte) 0x01
};
byte[] recByteArray = s7PLC.readFromServerByPersistence(sendByteArray);
s7PLC.close();
}
}Support BOOL, UINT16, INT16, UINT32, INT32, FLOAT32, FLOAT64, STRING, TIME, DATE, TIME_OF_DAY, DTL read-write.
Create small size data class.
@Data
public class DemoBean {
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.0.1", type = EDataType.BOOL)
private Boolean bitData;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.4", type = EDataType.UINT16)
private Integer uint16Data;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.6", type = EDataType.INT16)
private Short int16Data;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.8", type = EDataType.UINT32)
private Long uint32Data;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.12", type = EDataType.INT32)
private Integer int32Data;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.16", type = EDataType.FLOAT32)
private Float float32Data;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.20", type = EDataType.FLOAT64)
private Double float64Data;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.28", type = EDataType.BYTE, count = 3)
private byte[] byteData;
// Note: The actual total length is 12, not 10, 31 + 12 = 43.
// If there are other fields after the string, you need to reserve 2 more bytes of data
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.31", type = EDataType.STRING, count = 10)
private String stringData;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.43", type = EDataType.TIME)
private Long timeData;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.47", type = EDataType.DATE)
private LocalDate dateData;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.49", type = EDataType.TIME_OF_DAY)
private LocalTime timeOfDayData;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.53", type = EDataType.DTL)
private LocalDateTime dateTimeData;
}For large amounts of data, byte array is recommended.
Create big size data class.
@Data
public class DemoLargeBean {
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.0.1", type = EDataType.BOOL)
private boolean bitData;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.10", type = EDataType.BYTE, count = 50)
private byte[] byteData1;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.60", type = EDataType.BYTE, count = 65)
private byte[] byteData2;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.125", type = EDataType.BYTE, count = 200)
private byte[] byteData3;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.325", type = EDataType.BYTE, count = 322)
private byte[] byteData4;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.647", type = EDataType.BYTE, count = 99)
private byte[] byteData5;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.746", type = EDataType.BYTE, count = 500)
private byte[] byteData6;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.1246", type = EDataType.BYTE, count = 44)
private byte[] byteData7;
}Read and write.
class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create PLC instance
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200, "127.0.0.1");
// create S7Serializer instance
S7Serializer s7Serializer = S7Serializer.newInstance(s7PLC);
// small size data read-write
DemoBean bean = new DemoBean();
bean.setBitData(true);
bean.setUint16Data(42767);
bean.setInt16Data((short) 32767);
bean.setUint32Data(3147483647L);
bean.setInt32Data(2147483647);
bean.setFloat32Data(3.14f);
bean.setFloat64Data(4.15);
bean.setByteData(new byte[]{(byte) 0x01, (byte) 0x02, (byte) 0x03});
bean.setStringData("1234567890");
bean.setTimeData(12L);
bean.setDateData(LocalDate.of(2023, 5, 15));
bean.setTimeOfDayData(LocalTime.of(20, 22, 13));
bean.setDateTimeData(LocalDateTime.of(2023, 5, 27, 12, 11, 22, 333225555));
s7Serializer.write(bean);
bean = s7Serializer.read(DemoBean.class);
// big size data read-write
DemoLargeBean largeBean = s7Serializer.read(DemoLargeBean.class);
largeBean.getByteData2()[0] = (byte) 0x05;
largeBean.getByteData3()[0] = (byte) 0x05;
largeBean.getByteData4()[0] = (byte) 0x05;
largeBean.getByteData5()[0] = (byte) 0x05;
largeBean.getByteData6()[0] = (byte) 0x05;
largeBean.getByteData7()[0] = (byte) 0x05;
largeBean.getByteData2()[64] = (byte) 0x02;
largeBean.getByteData3()[199] = (byte) 0x03;
largeBean.getByteData4()[321] = (byte) 0x04;
largeBean.getByteData5()[98] = (byte) 0x05;
largeBean.getByteData6()[499] = (byte) 0x06;
largeBean.getByteData7()[43] = (byte) 0x07;
s7Serializer.write(bean);
s7PLC.close();
}
}read and write
class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create PLC instance
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200, "127.0.0.1");
// create S7Serializer instance
S7Serializer s7Serializer = S7Serializer.newInstance(s7PLC);
byte[] byteData = new byte[]{(byte) 0x01, (byte) 0x02, (byte) 0x03};
List<S7Parameter> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.0.1", EDataType.BOOL, 1, true));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.4", EDataType.UINT16, 1, 42767));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.6", EDataType.INT16, 1, (short) 32767));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.8", EDataType.UINT32, 1, 3147483647L));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.12", EDataType.INT32, 1, 2147483647));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.16", EDataType.FLOAT32, 1, 3.14f));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.20", EDataType.FLOAT64, 1, 4.15));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.28", EDataType.BYTE, 3, byteData));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.31", EDataType.STRING, 10, "1234567890"));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.43", EDataType.TIME, 1, 12L));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.47", EDataType.DATE, 1, LocalDate.of(2023, 5, 15)));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.49", EDataType.TIME_OF_DAY, 1, LocalTime.of(20, 22, 13)));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.53", EDataType.DTL, 1, LocalDateTime.of(2023, 5, 27, 12, 11, 22, 333225555)));
s7Serializer.write(list);
list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.0.1", EDataType.BOOL));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.4", EDataType.UINT16));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.6", EDataType.INT16));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.8", EDataType.UINT32));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.12", EDataType.INT32));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.16", EDataType.FLOAT32));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.20", EDataType.FLOAT64));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.28", EDataType.BYTE, 3));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.31", EDataType.STRING, 10));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.43", EDataType.TIME));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.47", EDataType.DATE));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.49", EDataType.TIME_OF_DAY));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.53", EDataType.DTL));
List<S7Parameter> actual = s7Serializer.read(list);
s7PLC.close();
}
}- By default, the server supports area I, Q, M, T, C and DB1, each area includes 65536 bytes.
- The server can customize the DB area and add it at will.
- Currently, only read and write operations are supported.
class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create server
S7PLCServer server = new S7PLCServer();
// add DB2,DB3,DB4
server.addDBArea(2, 3, 4);
// server start
server.start();
// server stop
server.stop();
}
}class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create server
S7PLCServer server = new S7PLCServer();
server.addDBArea(2, 3, 4);
server.start();
// create client
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200);
s7PLC.writeByte("DB2.0", (byte) 0x01);
byte b = s7PLC.readByte("DB2.0");
// close
s7PLC.close();
server.stop();
}
}class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.SINUMERIK_828D, "127.0.0.1");
String cncId = s7PLC.readCncId();
String cncVersion = s7PLC.readCncVersion();
String cncType = s7PLC.readCncType();
String cncManufactureDate = s7PLC.readCncManufactureDate();
List<Double> machinePosition = s7PLC.readMachinePosition();
List<Double> readRelativePosition = s7PLC.readRelativePosition();
List<Double> readRemainPosition = s7PLC.readRemainPosition();
List<Double> tWorkPiecePosition = s7PLC.readTWorkPiecePosition();
int toolRadiusCompensationNumber = s7PLC.readToolRadiusCompensationNumber();
int toolNumber = s7PLC.readToolNumber();
double actSpindleSpeed = s7PLC.readActSpindleSpeed();
double feedRate = s7PLC.readFeedRate();
int workMode = s7PLC.readWorkMode();
double runTime = s7PLC.readRunTime();
double remainTime = s7PLC.readRemainTime();
String programName = s7PLC.readProgramName();
int alarmNumber = s7PLC.readAlarmNumber();
s7PLC.close();
}
}The data content is in little-endian mode.
class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.SINUMERIK_828D, "127.0.0.1");
// single request
RequestNckItem requestNckItem = new RequestNckItem(ENckArea.N_NCK, 1, 18040, 4, ENckModule.M, 1);
DataItem dataItem = s7PLC.readS7NckData(requestNckItem);
String cncType = ByteReadBuff.newInstance(dataItem.getData(), true).getString(dataItem.getCount()).trim();
System.out.println(cncType);
// multi request
List<RequestNckItem> requestNckItems = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3, 4)
.mapToObj(x -> new RequestNckItem(ENckArea.C_CHANNEL, 1, 2, x, ENckModule.SMA, 1))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
List<DataItem> dataItems = s7PLC.readS7NckData(requestNckItems);
List<Double> positions = dataItems.stream().map(x -> ByteReadBuff.newInstance(x.getData(), true).getFloat64())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
positions.forEach(System.out::println);
s7PLC.close();
}
}1、Why can PLC write data but checkConnected function return always false?
Communication uses lazy loading. The connection is triggered only when reading or writing. CheckConnected function will return true after reading or writing.
2、What about getting exceptions after PLC shutdown and automatically connecting after PLC restarts?
Disconnection reconnects is supported. If the PLC has been disconnected, the reconnection is triggered in each time of reading and writing operation.
3、When the feedback error message is "This service was not implemented on the module or a frame error was reported", what is the reason?
Message in chinese: 未在模块上实现此服务或报告了帧错误
The PLC does not have the address block data, or the address data does not support access.
4、Maximum read/write data byte size during PLC communication?
Depend on different types of PLC PDULength, S1200 = 240, S1500 = 960. In a word there are 240, 480, 960.
The maximum read byte array size is 222 = 240 - 18, 462 = 480 - 18, 942 = 960 - 18.
The default value of PDULength is 240, which can be adjusted by yourself.
According to the test S1200[CPU 1214C], read multiple bytes in a single time
Send:The maximum byte read length is 216 = 240 - 24, 24(request PDU) = 10(header) + 14(parameter)
Receive:The maximum byte read length is 222 = 240 - 18, 18(response PDU) = 12(header) + 2(parameter) + 4(dataItem)
According to the test S1200[CPU 1214C], write multiple bytes in a single time
Send:The maximum byte write length is 212 = 240 - 28, 28(request PDU) = 10(header) + 14(parameter) + 4(dataItem)
Receive:The maximum byte write length is 225 = 240 - 15, 15(response PDU) = 12(header) + 2(parameter) + 1(dataItem)
5、How much data can I read or write in batches in a single communication?
| PDU length | Data Type | Byte Size | (Write) Maximum Number | (Read) Maximum Number | PLC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 240 | boolean / byte | 1 | 12 | 18 | S1200 / S200Smart |
| 240 | uint16 / int16 | 2 | 12 | 18 | S1200 / S200Smart |
| 240 | uint32 / int32 / float32 | 4 | 11 | 18 | S1200 / S200Smart |
| 240 | float64 | 8 | 9 | 17 | S1200 / S200Smart |
| PDU length | Data Type | Byte Size | (Write) Maximum Number | (Read) Maximum Number | PLC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 480 | boolean / byte | 1 | 26 | 38 | S400 |
| 480 | uint16 / int16 | 2 | 24 | 38 | S400 |
| 480 | uint32 / int32 / float32 | 4 | 22 | 38 | S400 |
| 480 | float64 | 8 | 18 | 35 | S400 |
| PDU length | Data Type | Byte Size | (Write) Maximum Number | (Read) Maximum Number | PLC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 960 | boolean / byte | 1 | 52 | 78 | S1500 |
| 960 | uint16 / int16 | 2 | 49 | 78 | S1500 |
| 960 | uint32 / int32 / float32 | 4 | 45 | 78 | S1500 |
| 960 | float64 | 8 | 38 | 72 | S1500 |
6、PLC initialization parameters
| PLC | Max PDU length | Rack | Slot |
|---|---|---|---|
| S200_SMART | 240 | 0 | 1 |
| S300 | 240 | 0 | 2 |
| S400 | 480 | 0 | 3 |
| S1200 | 240 | 0 | 1 |
| S1500 | 960 | 0 | 1 |
7、General PLC online connection number is limited, do not repeat new S7PLC()!!!