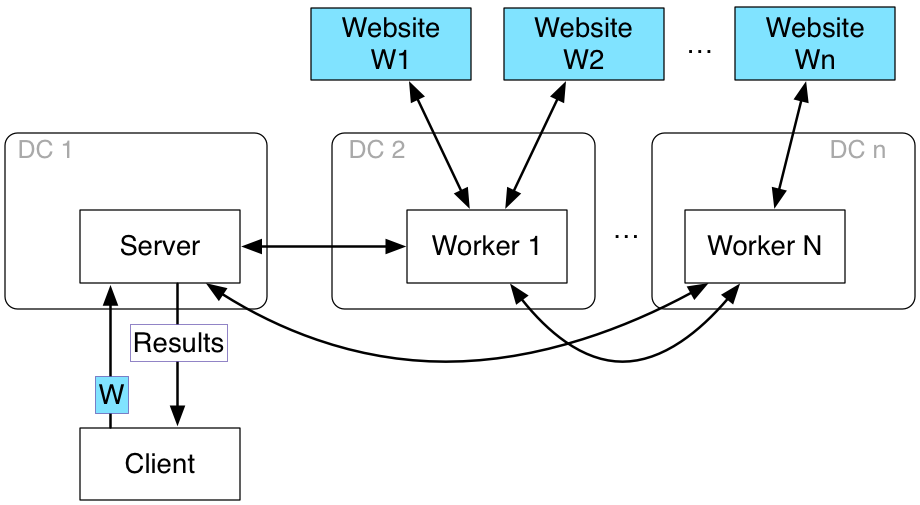
This distributed web crawler uses multithreading to construct the web graph of linking relationships between websites starting at certain root site provided by the user. The crawler will store this graph in a distributed manner and will be able to respond to several kinds of queries about this graph.
Page rank is also calculated which is a value assigned to a web page as a measure of its popularity or importance, used to determine the order in which search engine results are presented.
Code link: https://github.com/dhruvarya/distributed-web-crawler-pagerank Download the crawler from the link
Go to webcrawlermain.go and update siteToCrawl and depth variable
siteToCrawl := "https://www.linkedin.com"
depth := 5
Use commands
=> go build
=> go run .
- It creates multiple threads as workers that send requests to root website
- Find each website is created as a node, with page rank, incoming nodes and outgoing nodes as attributes
// Node is a node in the graph
type Node struct {
Id NodeID
Rank float64
Outgoing map[EdgeID]*Edge
Incoming map[EdgeID]*Edge
}
- extractLinksFromToken function is called from linksextractor.go file that take out the links from a website and return them.
- Clients can initiate the crawling, specifying an initial web page, and can also query the crawled dataset.
- Page rank is calculated using the graph of websites created.
In the algorithm, we used the formula
Calculate the new rank based on the current rank and the out-degree, out-degree is the number of neighbors of pr node
pr := PageRank{
Alpha: 0.85,
MaxIter: 1000,
Tolerance: 1e-12,
}
Here, Alpha is the damping parameter for PageRank, default=0.85. MaxIter is the max amount of iterations Tolerance, (i.e., if you get a new page-rank value that differs from the prior iteration by less than this amount, then stop).