A calculation tool for orbital transfer trajectories in the physics simulator Kerbal Space Program. Enter information about your current orbit and desination, and the program will calculate the necessary transfer trajectories using real life astronomical formulas.
- Clone the repository
- Compile the program by typing make
- Run the program by typing make run
- Follow the instructions in the terminal
Prograde
- Rotational motion that is in the direction of the central body's orbit
Retrograde
- Rotation motion that is in the opposite direction of the central body's orbit
Apoapsis
- Highest point in an orbit where kinetic energy is lowest and potential energy is highest
Periapsis
- Lowest point in an orbit where kinetic energy is highest and potential energy is lowest
Orbital Period
- Time it takes for an object to complete a single orbit around a body
- Longest radius of an orbit
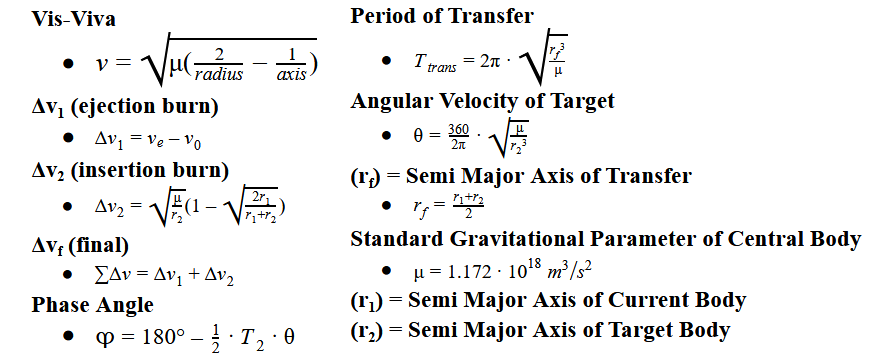
Standard Gravitational Parameter
- Represented by Mu, it is the product of the gravitational constant G and the mass of the body
- Minimum speed needed to escape the gravitational influence of a body
- Angle between the current body, target body, and the central body (sun or planet)
- This tells you how far forward or backward the target body will be relative to you
- The amount of energy you have to perform a maneuver
- Due to the lack of non-conservative forces (like air resistance) in the simulator, you maintain the same speed when performing maneuvers
- This manuever is the most efficent way to perform an interplanetary transfer
- A sandbox space flight simulator that features realistic orbital mechanics and physics
- Values for the body's are taken directly from the Kerbal Space Program Wiki
Each planetary body is organized into a data structure that contains the important information about each planet. Each body is identified with a number from zero to six, with zero being closest to the Sun and six being farthest. Additionally, the length of the Semi-Major Axis and Escape Velocity for each body is also held.