The library helps you build a distributed application with decoupled components using a FIFO queue.
It implements the Redis Reliable queue pattern and supports moving unprocessed or corrupted messages to a dead-letter queue.
All important operations are produced with LUA scripts that guarantee that they are executed in an atomic way.
The library supports the following features (described below in details):
- A FIFO queue for published messages
- Monitoring metrics that allow you to integrate the library with your monitoring system
- A processing timeout that determines the length of time for which a message is invisible for other consumer when the message begins to be processed
- A maximum number of processing attempts before a message is moved to the dead-letter queue
- Create a new "quick-start.js" (or copy the example from the quick-start.js file):
const dmq = require("durable-message-queue"); const queueName = "send-registration-confirmation-email"; const config = { host: "127.0.0.1", port: "6379" }; const producer = dmq.Builder.createProducer(queueName, config); const consumer = dmq.Builder.createConsumer(queueName, config); consumer.subscribe(async (message) => console.log(message)); const message = { userId: "1", messageType: "registrationConfirmation", to: "[email protected]" }; producer.send(JSON.stringify(message)); - Install the package:
npm i durable-message-queue - Start the script:
node quick-start.js - See the output:
{ id: '2', receiveCount: '1', updatedDt: '2020-11-26T21:46:01.870Z', createdDt: '2020-11-26T21:46:01.827Z', payload: '{"userId":"1","messageType":"registrationConfirmation","to":"[email protected]"}', receivedDt: '2020-11-26T21:46:01.870Z' }
One or more producers can send messages to a FIFO queue. Messages are stored in the order that they were successfully received by Redis.
Before being added to the queue each message is updated by metadata. This metadata is used by the queue manager to conduct the message state:
- a message can be available to process by consumers
- the message can be invisible for other consumers because it is processed
- the message is moved to the dead queue because a maximum receive count is exceeded
One or more consumers can subscribe to the queue's updates but only one of them receives the message to process. The message should be processed during a limited period of time, otherwise, the message is marked as available and can be processed again by this or another consumer. See the processing timeout section to get more details.
In case if a message cannot be processed X times, it is moved to the dead queue by the queue manager. See all details about this feature in the maximum receive count section below.
If the consumers are started after messages were added to the queue, they check the queue for available unprocessed messages and start processing them. Your Redis infrastructure is responsible for retaining all messages that are added to the queue and the messages are stored for an unlimited period of time until they are not processed by consumers.
The consumer has access to message metadata and should filter all outdated messages on its own using a value of the "createdDt" or "updatedDt" property (see the output of the quick start section above).
When a message is added to the queue the consumer starts processing the message and the message is become unavailable for other consumers:
If something goes wrong and the message cannot be processed by the consumer due to any reason, a queue manager makes the message visible for processing by another consumer. By default, the processing timeout equals 300 seconds.
You can specify this period by assigning desired value in seconds to the visibilityTimeout value. See the Settings section to get more details.
If a message cannot be processed X times by a consumer, the message is moved to the dead-letter queue by a queue manager. This period of time is called the maximum receive count and equals 3 by default.
You can change the default value by modifying the maxReceiveCount property. See the Settings section to get more details.
The description is under construction.
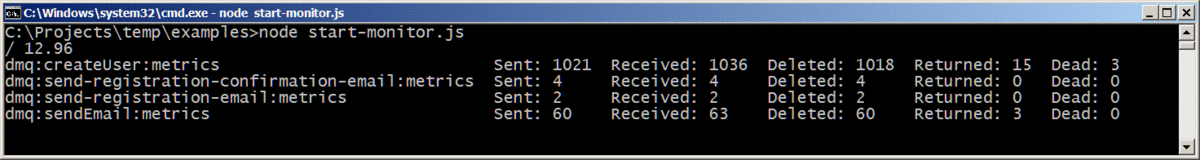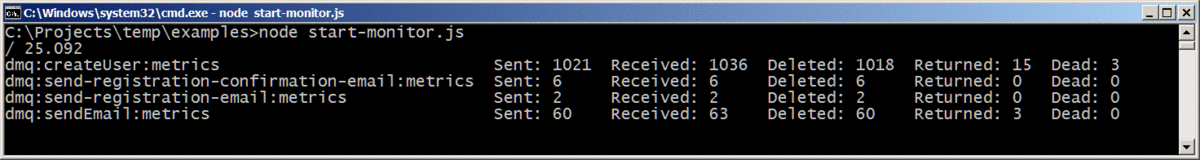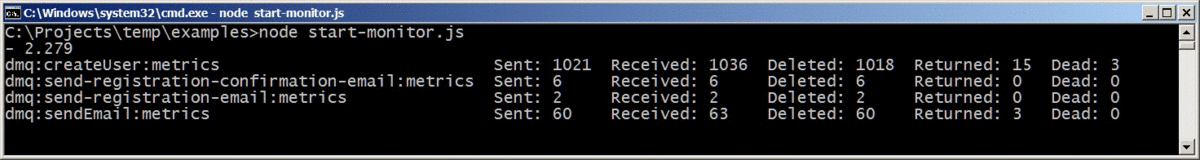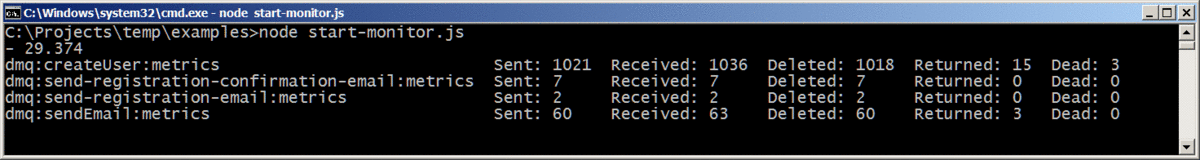
The monitor tool is an additional component that allows us to keep up to date on metrics across all queues.
Please use the start-monitor.js file as an example to start the monitor tool and see the Settings section to get more details about configuration.
There are three settings that you can use with this library:
- visibilityTimeout - the period of time in seconds during which the library prevents other consumers from receiving and processing the message. The default visibility timeout for a message is 300 seconds (5 minutes).
- maxReceiveCount - the maximum number of receives that are allowed before the message is moved to the dead-letter queue. If something goes wrong and the number of receives exceeds the MaxReceiveCount value, the queue manager moves the message to the dead-letter queue (see the picture of the maximum receive count section to get more details). The default value is 3.
- monitorUpdateInterval - the period of time in seconds to update metrics of the queue monitor tool.
As far as the library uses ioredis to access to Redis, all ioredis-related configuration settings are transmitted to ioredis as is. Visit the ioredis main page to get more details about configuration of the connection.
The simplest configuration includes only a host property with the server address:
const config = {
host: "server name or ip address"
};
The library supports a set of monitoring metrics that indicates the number of:
- "numberOfMessagesSent" - messages are sent by producers for processing
- "numberOfMessagesReceived" - messages are received and started processing by consumers
- "numberOfMessagesDead" - corrupted messages are moved to the dead-letter queue by a queue manager
- "numberOfMessagesReturned" - unprocessed messages are moved back to the queue because of crashing a consumer or for an undefined reason
- "numberOfMessagesDeleted" - messages are successfully processed and removed from the queue.
You can set the DEBUG env to ioredis:* to print debug and error info. Here is the example for Windows and the quick-start.js file:
set DEBUG=dmq:* & node quick-start.js