Adapted from University of Colorado at Boulder CSCI3753 Assignment
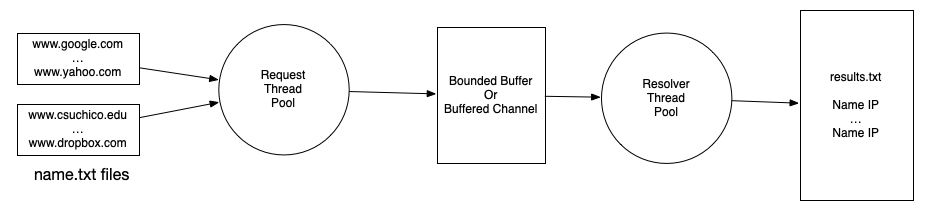
In this assignment you will develop a multi-threaded application that resolves domain names to IP addresses, similar to the operation preformed each time you access a new website in your web browser. The application is composed of two sub-systems, each with one thread pool: requesters and resolvers. The sub-systems communicate with each other using a bounded queue.
This type of system architecture is referred to as a Producer-Consumer architecture. It is also used in search engine systems, like Google. In these systems, a set of crawler threads place URLs onto a queue. This queue is then serviced by a set of indexer threads which connect to the websites, parse the content, and then add an entry to a search index. Refer to Figure 1 for a visual description.
Your application will take as input a set of name files. Names files contain one hostname per line. Each name file should be serviced by a single requester thread from the requester thread pool.
The requester thread pool services a set of name files, each of which contains a list of domain names. Each name that is read from each of the files and shared either through a bounded buffer or channels.
The second thread pool is comprised of a set of THREAD_MAX resolver threads. The resolver thread pool takes a name from either the bounded buffer or channel mechanism and querying its IP address. After the name has been mapped to an IP address, the output is written to a line in the results.txt file in the following format:
www.google.com,74.125.224.81
Your application should synchronize access to shared resources and avoid deadlock. You should use mutexes and channels to meet this requirement. There are at least two shared resources that must be protected: bounded buffer or channel, and the output file. Only the channels are thread-safe by default.
Your program must end after all the names in each file have been serviced by the application. This means that all the hostnames in all the input files have received a corresponding line in the output file.
Some files are included with this assignment for your benefit. You are not required to use these files, but they may prove helpful.
- input/names.txt* This is a set of sample name files. They follow the same format as mentioned earlier. Use them to test your program.
- results-ref.txt This result file is a sample output of the IPs for the hostnames from all the names.txt* files used as input.
- lookup.go This program represents an un-threaded solution to this assignment. Feel free to use it as a starting point for your program, or as a reference for using the utility functions and performing file i/o in Go.
Many of the specifications for your program are embedded in the descriptions above. This section details additional specifications to which you must adhere.
Your executable program should be named "multi-lookup". When called, it should interpret the last argument as the file path for the file to which results will be written. All proceeding arguments should be interpreted as input files containing hostnames in the aforementioned format.
An example call involving five input files might look like:
go run multi-lookup.go input/names1.txt input/names2.txt input/names3.txt input/names4.txt input/names5.txt results.txt
If necessary, you may impose the following limits on your program. If the user specifies input that would require the violation of an imposed limit, your program should gracefully alert the user to the limit and exit with an error.
- MAX_INPUT_FILES: 10 Files (This is an optional upper-limit. Your program may also handle more files, or an unbounded number of files, but may not be limited to less than 10 input files.)
- MAX_RESOLVER_THREADS: 10 Threads (This is an optional upper-limit. Your program may also handle more threads, or match the number of threads to the number of processor cores.)
- MIN_RESOLVER_THREADS: 2 Threads (This is a mandatory lower-limit. Your program may handle more threads, or match the number of threads to the number of processor cores, but must always provide at least 2 resolver threads.)
You must handle the following errors in the following manners:
- Bogus Hostname: Given a hostname that can not be resolved, your program should output a blank string for the IP address, such that the output file contains the hostname, followed by a comma, followed by a line return. You should also print a message to stderr alerting the user to the bogus hostname.
- Bogus Output File Path: Given a bad output file path, your program should exit and print an appropriate error to stderr.
- Bogus Input File Path: Given a bad input file path, your program should print an appropriate error to stderr and move on to the next file.
All system and library calls should be checked for errors. If you encounter errors not listed above, you should print an appropriate message to stderr, and then either exit or continue, depending upon whether or not you can recover from the error gracefully.
You may use the following libraries and code to complete this assignment, as well as anything you have written for this assignment:
- bufio
- fmt
- log
- net
- os
- sync
- runtime
If you would like to use additional external libraries, you must clear it with me first. You will not be allowed to use pre-existing thread-safe queue or file i/o libraries since the point of this assignment is to teach you how to make non-thread-safe resources thread-safe.
To receive full credit, you must submit the following items to Turnin by the due date.
- multi-lookup.go: Your program, conforming to the above requirements
There are a few options for receiving extra credit on this assignment. Completion of each of the following items will gain you 5 points of extra credit per item. If you alter any files other than multi-lookup.go to accomplish the extra credit make sure you submit them as part of your assignment by taring up your whole project directory as a tar.gz file and submit to the extra credit option on Turnin. Make sure you turn in your original function project prior to attempting any of the extra credit.
You should submit all the code in one file with a readme.md that lists off which extra credit you solved in the tar.gz or alternatively you should have one folder for each extra credit with the folder name representing the extra credit solved.
- Multiple IP Addresses: Many hostnames return more than a single IP address. Add support for listing an arbitrary number of addresses to your program. These addresses should be printed to the output file as additional comma-separated strings after the hostname. For example:
www.google.com,74.125.224.81,76.125.232.80,75.125.211.70
- IPv6 Support and Testing: Add support for IPv6 IP addresses and find an IPv6 aware environment where you can test this support. Since IPv6 is relatively new, finding an environment for testing this support is probably harder than adding it.
- Matching Number of Threads to Number of Cores: Make your program dynamically detect the number of cores available on a system and set the number of resolver threads to take into account the number of cores. I would recommend starting with this in trying to get extra credit on this assignment.
To received full credit your program must:
- Meet all requirements elicited in this document
- Document any resources you use to solve your assignment in the header comment of your file
- Include your name in the header comment of your file
This includes adhering to good coding style practices.
You can write your code in any environment you like. But you have to make sure that your programs can be compiled and executed on Ubuntu 18.04.
Refer to your textbook and class notes for descriptions of producer/consumer and reader/writer problems and the different strategies used to solve them. The Internet is also a good resource for finding information related to solving this assignment.