-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 169
Allow New Apps
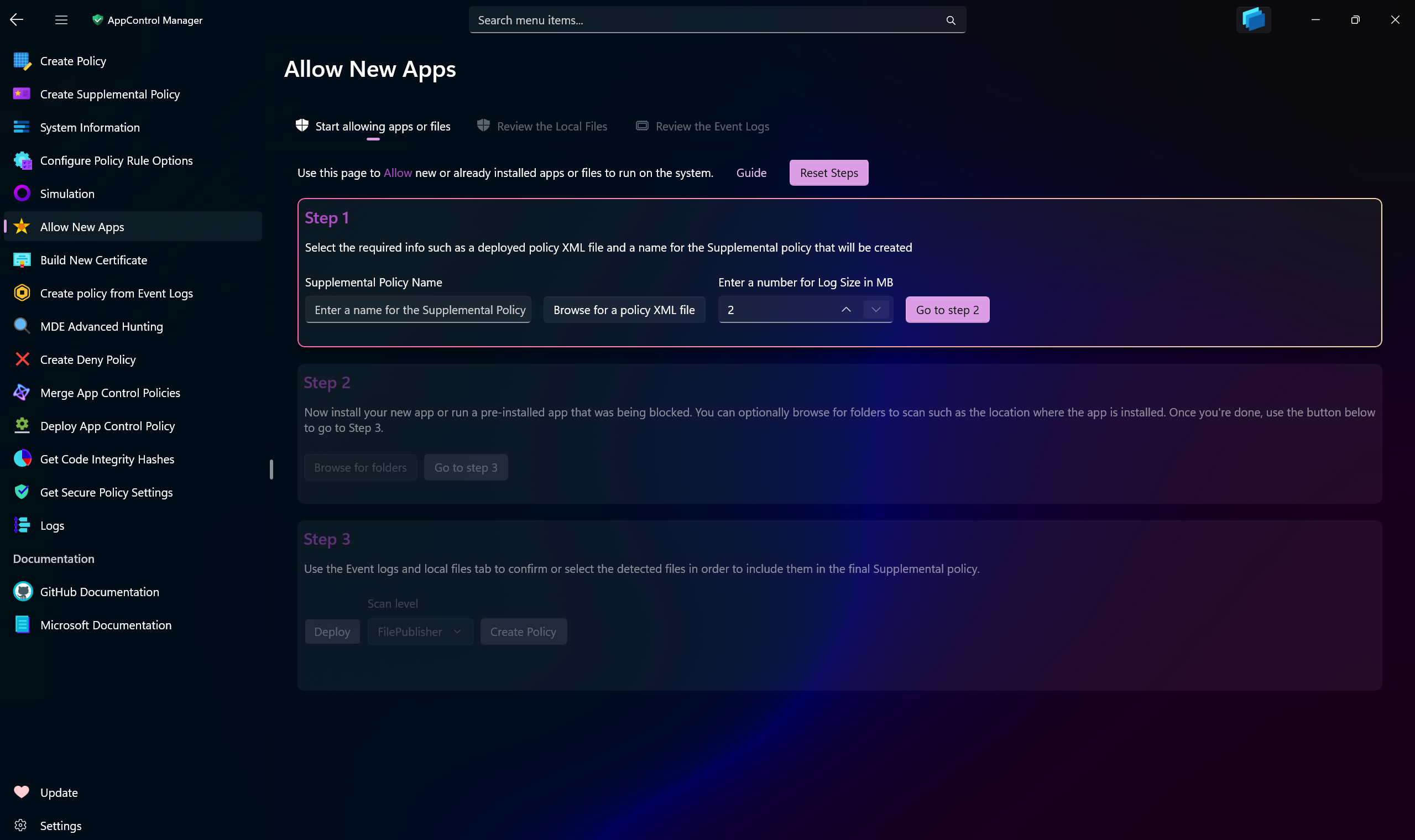
This page in AppControl Manager is designed as a practical hub for managing App Control on your system. Consider it your centralized solution for effortlessly overseeing your app-related policies and allowing new apps.
When you need to install a new application, this page provides an intuitive way to temporarily enable Audit mode in your existing base policy. This allows the installation of the app while ensuring the base policy automatically reverts to Enforced mode immediately afterward.
During Audit mode, AppControl Manager captures all relevant Code Integrity and AppLocker events, analyzes them, and presents detailed insights in an organized view. You can also navigate to the specific folder paths where the application was installed, enabling the tool to scan and display the contents on a separate page.
The compiled data, scanned files and recorded events, are presented for you to review, filter, sort, and manage. Once you're satisfied, you can seamlessly convert these into a single Supplemental policy ready for deployment.
While much of the process is automated, you remain in full control. With just a few clicks, you can fine-tune and manage your App Control policy efficiently.
Rest assured, no unauthorized software or malware can make its way into your Supplemental policy. Every file and event is accompanied by highly detailed information, eliminating any guesswork and ensuring only trusted elements are included.
If something like a power outage occurs during the audit mode phase, on the next reboot, the enforced mode base policy will be automatically deployed using a scheduled task that acts as a "snapback guarantee".
Note
This feature can also detect and create supplemental policy for Kernel protected files, such as the executables of games installed using Xbox app. Make sure you run the game while the base policy is deployed in Audit mode so that it can capture those executables.
Tip
You can use both Signed and Unsigned App Control policies. The app will automatically detect the signing status of the XML policy file that you select and prompt for any additional information required.
-
Supplemental Policy Name: Enter the name for the Supplemental policy that will be created. Preferably use the name of the app you're trying to install so that you will be able to recognize the policy in System Information page easily.
-
Browse for a Policy XML file: Use this button to browse for the path to the base policy file.
-
Log Size: Use this number box to increase or decrease the maximum capacity of the
Code Integrity/Operationallogs. The bigger the number, the more events will be captured without being overwritten. -
Scan Level: You can choose from different scan levels. Refer to this page for all the information about them.
- Create AppControl Policy
- Create Supplemental Policy
- System Information
- Configure Policy Rule Options
- Simulation
- Allow New Apps
- Build New Certificate
- Create Policy From Event Logs
- Create Policy From MDE Advanced Hunting
- Create Deny Policy
- Merge App Control Policies
- Deploy App Control Policy
- Get Code Integrity Hashes
- Get Secure Policy Settings
- Update
- Sidebar
- Validate Policies
- View File Certificates
- Introduction
- How To Generate Audit Logs via App Control Policies
- How To Create an App Control Supplemental Policy
- The Strength of Signed App Control Policies
- How To Upload App Control Policies To Intune Using AppControl Manager
- How To Create and Maintain Strict Kernel‐Mode App Control Policy
- App Control Notes
- How to use Windows Server to Create App Control Code Signing Certificate
- Fast and Automatic Microsoft Recommended Driver Block Rules updates
- App Control policy for BYOVD Kernel mode only protection
- EKUs in App Control for Business Policies
- App Control Rule Levels Comparison and Guide
- Script Enforcement and PowerShell Constrained Language Mode in App Control Policies
- How to Use Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Advanced Hunting With App Control
- App Control Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Create Bootable USB flash drive with no 3rd party tools
- Event Viewer
- Group Policy
- How to compact your OS and free up extra space
- Hyper V
- Overrides for Microsoft Security Baseline
- Git GitHub Desktop and Mandatory ASLR
- Signed and Verified commits with GitHub desktop
- About TLS, DNS, Encryption and OPSEC concepts
- Things to do when clean installing Windows
- Comparison of security benchmarks
- BitLocker, TPM and Pluton | What Are They and How Do They Work
- How to Detect Changes in User and Local Machine Certificate Stores in Real Time Using PowerShell
- Cloning Personal and Enterprise Repositories Using GitHub Desktop
- Only a Small Portion of The Windows OS Security Apparatus
- Rethinking Trust: Advanced Security Measures for High‐Stakes Systems
- Clean Source principle, Azure and Privileged Access Workstations
- How to Securely Connect to Azure VMs and Use RDP
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes Part 2
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes Part 3
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes Part 4
- Basic PowerShell tricks and notes Part 5
- How To Access All Stream Outputs From Thread Jobs In PowerShell In Real Time
- PowerShell Best Practices To Follow When Coding
- How To Asynchronously Access All Stream Outputs From Background Jobs In PowerShell
- Powershell Dynamic Parameters and How to Add Them to the Get‐Help Syntax
- RunSpaces In PowerShell
- How To Use Reflection And Prevent Using Internal & Private C# Methods in PowerShell
