This is an open-source demo related to the eRob product, provided solely for reference by developers. Please note that issues within the open-source project are independent of the quality of eRob products. Users are advised to exercise caution while using the demo. We are not responsible for any damage caused by improper operations. For any project errors, please raise a query in the Issues section. Collaboration and forks to resolve open-source project issues are welcome.
- Introduction
- Prerequisites
- Environment Setup
- Integrating Large Models with Isaac Sim
- Control and Simulation
- Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- Appendix
This development documentation guides developers on integrating locally deployed large-scale machine learning models with the NVIDIA Isaac Sim simulation platform to drive eRob robots in executing autonomous tasks. By following this guide, you will learn how to set up the simulation environment, configure the large model interface using Ollama and Llama3, and implement autonomous control of the robot within the simulation.
Before getting started, ensure you meet the following prerequisites:
- Hardware Requirements:
- Equipped with an NVIDIA GPU, preferably supporting CUDA 11.x or higher.
- At least 16GB of RAM.
- Sufficient storage space (recommended 50GB or more).
- Software Requirements:
- Operating System: Windows 10 or later.
- NVIDIA Isaac Sim: Latest version.
- Ollama: Installed and configured.
- Llama3 Model: Downloaded and ready for deployment.
-
Register for NVIDIA Omniverse:
Visit the NVIDIA Omniverse website to create an account and download the Omniverse Launcher.
-
Install Isaac Sim:
You can refer to the NVIDIA website to install the Isaac Sim platform.
- Verify Installation:
Once you have successfully installed the Isaac Sim platform, navigate to the Isaac Sim directory. For example, my path is D:\Isaac_sim\OMNIVERSE\pkg\isaac-sim-4.1.0.
After entering the Isaac Sim directory, you need to open the terminal and activate the Python development environment provided by Isaac Sim. If you encounter package dependency issues afterward, you can install the dependencies as follows:
python.bat -m pip install pyads
python.bat -m pip install pyQT5-
Install Ollama:
- Follow the Ollama installation guide to set up Ollama on your local machine.
-
Deploy
llama3.1:latestModel with Ollama:
- Deploy the Llama3.1 model using Ollama.
ollama deploy llama3.1:latestWait for the deployment process to complete. This may take several minutes depending on your internet speed and system performance.
- Verify that the model is successfully deployed and running.
ollama listYou should see llama3.1:latest in the list of deployed models.
- Verifying the Installation:
To ensure that the llama3.1:latest model is installed and functioning correctly, perform a simple test.
- Start the Model If not already running, start the model.
ollama run llama3.1:latest- Interact with the Model Use Ollama's interface to send a test prompt to the model.
ollama prompt llama3.1:latest "Hello, how can you assist me today?"Here you can download eRob's usd file and modify the path in your Python code.
# Start Isaac Sim; required for Standalone mode
from omni.isaac.kit import SimulationApp
# Choose whether to run in headless mode
simulation_app = SimulationApp({"headless": False})
# Code execution
print("Simulation started")
# Load an existing scene
from omni.isaac.core.utils.stage import open_stage
#
file_path = "Your usd file path\\eRob_LLM_TC_MIN.usd"
open_stage(usd_path=file_path)
# Add a world
from omni.isaac.core import World
world = World()
# It's recommended by the official documentation to reset the world after adding objects
world.reset()
# Start rendering
while True:
# Retrieve pose and velocity attributes (placeholders)
# position, orientation = my_cube.get_world_pose()
# linear_velocity = my_cube.get_linear_velocity()
# Step the simulation with rendering enabled
world.step(render=True)Below is the key code to launch the local large model:
def get_model_output(prompt, conversation):
print("Interpreting command...")
context = """You are an AI assistant capable of chatting conversationally and controlling eRob based on commands.
For regular conversation, respond naturally.
For robot control commands, interpret and respond with specific parameter values in the exact format:
velocity=X
duration=Y
position=Z
continuous=True/False
angle=A
Only include parameters that are explicitly mentioned or directly inferred from the command.
Do not add any explanation or additional text.
For rotation commands, use the 'angle' parameter.
Example: 'rotate to 30 degrees' should be interpreted as 'angle=30'."""
recent_conversation = conversation[-3:]
for entry in recent_conversation:
context += f"{entry['role']}: {entry['content']}\n"
full_prompt = f"{context}\nHuman: {prompt}\nAssistant:"
try:
process = subprocess.Popen(
['ollama', 'run', 'llama3.1:latest', full_prompt],
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
text=True,
encoding='utf-8',
errors='ignore'
)
stdout, stderr = process.communicate()
clean_output = re.sub(r'failed to get console mode.*\n?', '', stdout).strip()
return clean_output
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error running Ollama: {e}")
return NoneWe provide a sample project that integrates a large model for reference purposes only.
-
Enable eRob Drive with TwinCAT3
- Action: Run TwinCAT3 to enable the eRob robot's drive functionality.
- Reference: For detailed configurations and the driving process, refer to the TwinCAT3 setup within the
eRob_driver. - Sample Code: A sample code repository is provided here for reference.
-
Launch
gui_main.pyUsing Isaac Sim'spython.bat- Action: Use the
python.batscript provided by NVIDIA Isaac Sim to launch thegui_main.pyroutine. - Purpose: This script initializes the GUI and starts the main control loop for interacting with the eRob robot.
- Action: Use the
-
Install Required Dependencies
- Action: Install the necessary Python dependencies required for the project.
- Command:
python.bat -m pip install XXX
- Note: Replace
XXXwith the actual package names needed for your project.
-
Update File Paths in the Code
- Action: After installing dependencies, ensure that all file paths within your code point to the correct locations in your project directory.
- Command:
python.bat your_project_path/gui_main.py
- Purpose: Running this command executes the
gui_main.pyscript with the updated paths, allowing the simulation and control to function correctly.
-
Verify Successful Execution
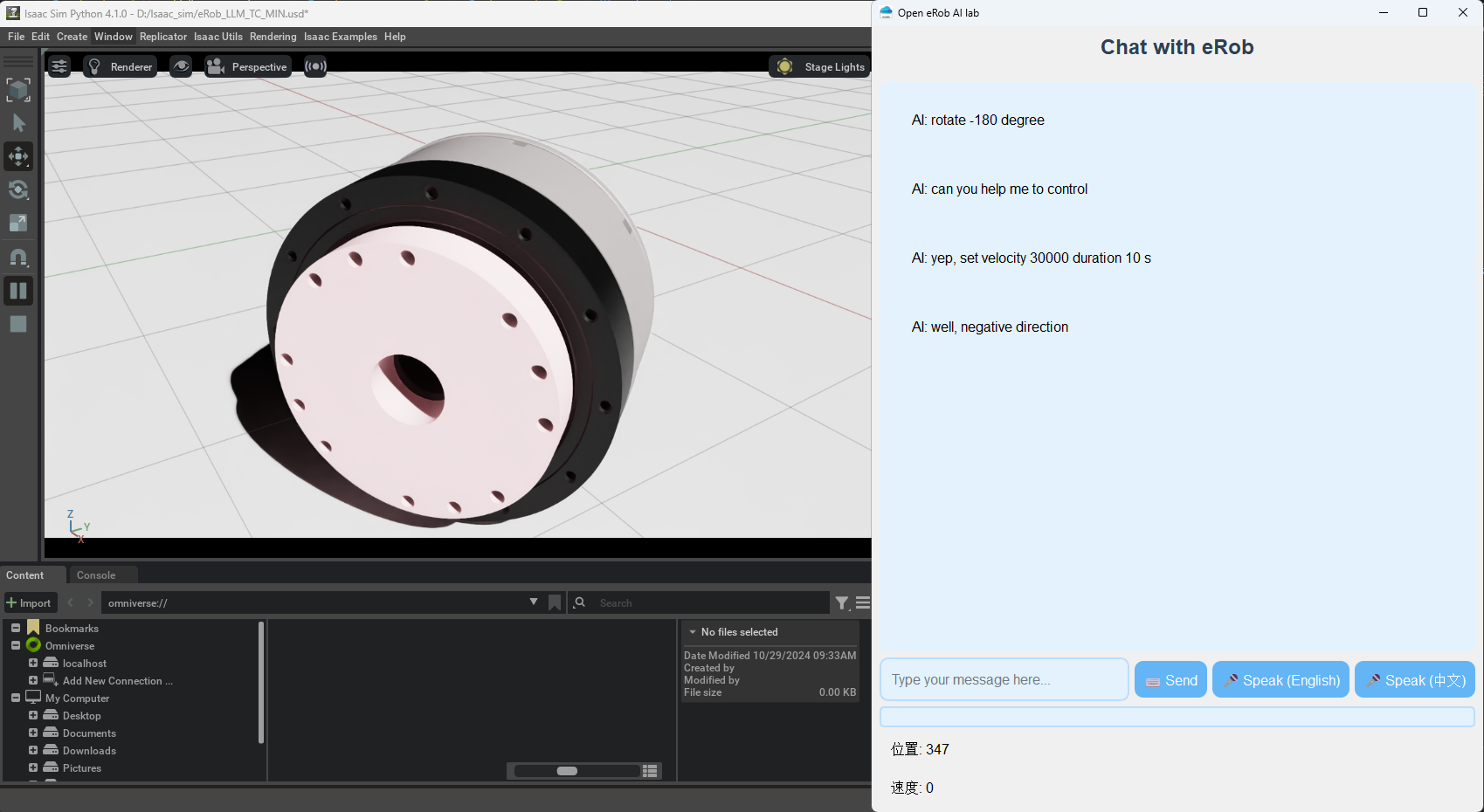
- Outcome: Upon successful execution, an interface will appear (as depicted in the image below).
-
Interaction: You can now interact with the local large model through the dialog box. Utilize the model's understanding capabilities to control the eRob robot.
-
Example Commands:
set velocity = 30000can you return position 0?set velocity = 30000 for 10 sHalf turn
-
Functionality: The large model interprets these commands and automatically outputs corresponding instructions to control the eRob robot.
-
Note: This is a sample project. Additional refinements and details may be necessary for a complete implementation.
-
Testing and Validation: After setting up, thoroughly test each component to ensure seamless integration between TwinCAT3, Isaac Sim, and the Llama3 model hosted by Ollama.
-
Logging and Monitoring: Implement logging within your scripts to monitor the interactions between the model and the robot. This aids in troubleshooting and optimizing performance.
-
Documentation: Keep your documentation updated with any changes in configurations, dependencies, or workflows to maintain clarity for future developments.
-
Security: Ensure that any API endpoints or local services (like Ollama) are secured to prevent unauthorized access, especially if the system will be used in production environments.