👉 Live demo here!
Magic Square Dance simulator, as described in the Mathologer video:
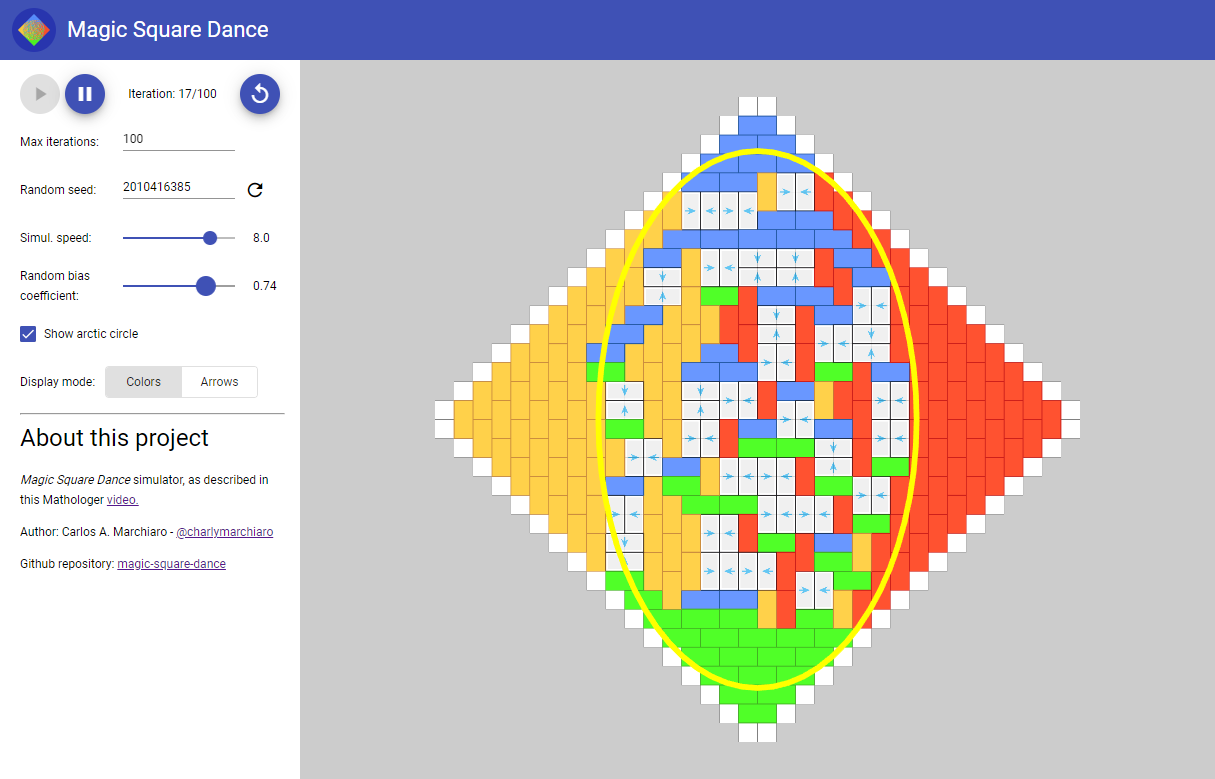
When a random bias coefficient other than 0.5 (fair) is applied, the arctic circle seems to take, in general, the shape of an ellipse tangent to the sides of the diamond. The intersection point on each side is such that the segment is divided in two parts whose lengths have the same ratio as the probabilities of the two random outcomes.
This is not proved but rather observed empirically by myself as a good fit for a large number of iterations. This is a personal hypothesis and haven't yet found any other information to support it.
The width and height of the ellipse can be calculated by following a reasoning such as the one shown here: https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/1971097/what-are-the-axes-of-an-ellipse-within-a-rhombus
Then, the intersection points are calculated as a function of the random bias coefficient, and finally the (normalized) ellipse dimensions are obtained as:
width = 2 * sqrt ( 1 - (random bias coef) )
height = 2 * sqrt (random bias coef)
The matrix size can be calculated quickly as a function of the number of grid cells:
iteration | number of cells (N)
0 | 0
1 | 1*4 = 4
2 | 1*4 + 2*4 = 12
3 | 1*4 + 2*4 + 3*4 = 24
n | (1 + ... + n)*4 = n*(n+1)/2*4 = 2*n*(n+1)
Then, the iteration as a function of N is:
i = 1/2 * (-1 + sqr(1 + 2*N))
We must find all the 2x2 empty spaces (insertion points) into which insert pairs of tiles in order to cover all empty space optimally for current iteration.
Algorithm:
- List all the 2x2 (maybe overlapped) empty spaces.
- Select the ones which are located in at least one corner, next to the diamond edge and/or other tiles. These are clearly valid insertion points, because no other could cover that corner cell.
- Mark the selected 2x2 spaces as occupied by tiles.
- Repeat from step 1 until all space is covered (as mentioned in the Mathologer video, there is always a way to do it).
The whole process takes, at most, M iterations, being:
M = (initial number of empty spaces) / 4
because in each iteration at least one valid insertion point must be found.
This project was generated with Angular CLI version 10.1.4.
Run ng serve for a dev server. Navigate to http://localhost:4200/. The app will automatically reload if you change any of the source files.
Run ng generate component component-name to generate a new component. You can also use ng generate directive|pipe|service|class|guard|interface|enum|module.
Run ng build to build the project. The build artifacts will be stored in the dist/ directory. Use the --prod flag for a production build.
Run ng test to execute the unit tests via Karma.
Run ng e2e to execute the end-to-end tests via Protractor.
To get more help on the Angular CLI use ng help or go check out the Angular CLI README.