The simple, stupid random Java™ beans generator
Active
- 10/23/2024 7.1.0 Minor release, added support for sealed classes, Thanks @Marian Jureczko . Some minor 3PP updates.
- 1/15/2024 7.0.0 Major release, default Java version bumped to 17 and other 3PP version bump. [Breaking changes].
- 9/1/2023 6.2.1 Minor release to initialize leaf nodes for Records [Breaking change].
- 8/10/2023 6.2.0 Minor release to add custom radomizer support for protobuf, 3PP and code refactoring.
- 5/23/2023 6.1.8 Patch release to fix #26 and #28, thanks @carborgar.
- 5/12/2023 6.1.7 Patch release to improve record support, thanks @mjureczko and minor 3PP fixes.
- 3/19/2023 6.1.5 Patch release to bump protobuf-java and snakeyaml and fix bug preventing custom randomizers on Record Types. Thanks carborgar
- 3/12/2023 6.1.3 Patch release to fix bug preventing Collections field population
- 10/29/2022 6.1.2 Patch release to bump protobuf version to vulnerability
- 9/23/2022 6.1.1 Added support to generate random protobuf data, this is based on murdos/easy-random-protobuf
- 8/10/2022 Added a fork with JDK 11 support easy-random-jdk11 package is available in maven centeral.
- 8/3/2022: Added support to JDK 16 and Java Record and minor bug fixes
- 15/11/2020: Easy Random v5.0.0 is out and is now based on Java 11. Feature wise, this release is the same as v4.3.0. Please check the release notes for more details.
- 07/11/2020: Easy Random v4.3.0 is now released with support for generic types and fluent setters! You can find all details in the change log.
Easy Random is a library that generates random Java beans. You can think of it as an ObjectMother for the JVM. Let's say you have a class Person and you want to generate a random instance of it, here we go:
EasyRandom easyRandom = new EasyRandom();
Person person = easyRandom.nextObject(Person.class);The method EasyRandom#nextObject is able to generate random instances of any given type.
The java.util.Random API provides 7 methods to generate random data: nextInt(), nextLong(), nextDouble(), nextFloat(), nextBytes(), nextBoolean() and nextGaussian().
What if you need to generate a random String? Or say a random instance of your domain object?
Easy Random provides the EasyRandom API that extends java.util.Random with a method called nextObject(Class type).
This method is able to generate a random instance of any arbitrary Java bean.
The EasyRandomParameters class is the main entry point to configure EasyRandom instances. It allows you to set all
parameters to control how random data is generated:
EasyRandomParameters parameters = new EasyRandomParameters()
.seed(123L)
.objectPoolSize(100)
.randomizationDepth(3)
.charset(forName("UTF-8"))
.timeRange(nine, five)
.dateRange(today, tomorrow)
.stringLengthRange(5, 50)
.collectionSizeRange(1, 10)
.scanClasspathForConcreteTypes(true)
.overrideDefaultInitialization(false)
.ignoreRandomizationErrors(true);
EasyRandom easyRandom = new EasyRandom(parameters);For more details about these parameters, please refer to the configuration parameters section.
In most cases, default options are enough and you can use the default constructor of EasyRandom.
Easy Random allows you to control how to generate random data through the org.jeasy.random.api.Randomizer interface and makes it easy to exclude some fields from the object graph using a java.util.function.Predicate:
EasyRandomParameters parameters = new EasyRandomParameters()
.randomize(String.class, () -> "foo")
.excludeField(named("age").and(ofType(Integer.class)).and(inClass(Person.class)));
EasyRandom easyRandom = new EasyRandom(parameters);
Person person = easyRandom.nextObject(Person.class);In the previous example, Easy Random will:
- Set all fields of type
Stringtofoo(using theRandomizerdefined as a lambda expression) - Exclude the field named
ageof typeIntegerin classPerson.
The static methods named, ofType and inClass are defined in org.jeasy.random.FieldPredicates
which provides common predicates you can use in combination to define exactly which fields to exclude.
A similar class called TypePredicates can be used to define which types to exclude from the object graph.
You can of course use your own java.util.function.Predicate in combination with those predefined predicates.
#Easy Random for Protobuf easy-random-protobuf module provides support for generating random data for protobuf message objects. For full support for easy-random capabilities it is advised to rely on
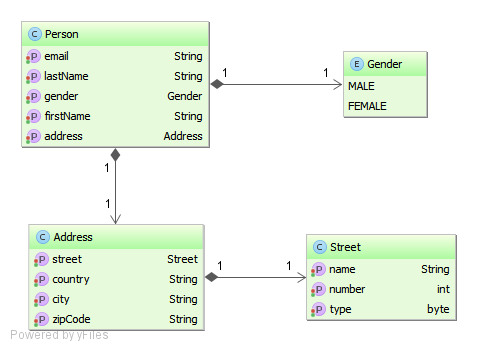
ProtoEasyRandom easyRanom = new ProtoEasyRandom();Populating a Java object with random data can look easy at first glance, unless your domain model involves many related classes. In the previous example, let's suppose the Person type is defined as follows:
Without Easy Random, you would write the following code in order to create an instance of the Person class:
Street street = new Street(12, (byte) 1, "Oxford street");
Address address = new Address(street, "123456", "London", "United Kingdom");
Person person = new Person("Foo", "Bar", "[email protected]", Gender.MALE, address);And if these classes do not provide constructors with parameters (may be some legacy beans you can't change), you would write:
Street street = new Street();
street.setNumber(12);
street.setType((byte) 1);
street.setName("Oxford street");
Address address = new Address();
address.setStreet(street);
address.setZipCode("123456");
address.setCity("London");
address.setCountry("United Kingdom");
Person person = new Person();
person.setFirstName("Foo");
person.setLastName("Bar");
person.setEmail("[email protected]");
person.setGender(Gender.MALE);
person.setAddress(address);With Easy Random, generating a random Person object is done with new EasyRandom().nextObject(Person.class).
The library will recursively populate all the object graph. That's a big difference!
Sometimes, the test fixture does not really matter to the test logic. For example, if we want to test the result of a new sorting algorithm, we can generate random input data and assert the output is sorted, regardless of the data itself:
@org.junit.Test
public void testSortAlgorithm() {
// Given
int[] ints = easyRandom.nextObject(int[].class);
// When
int[] sortedInts = myAwesomeSortAlgo.sort(ints);
// Then
assertThat(sortedInts).isSorted(); // fake assertion
}Another example is testing the persistence of a domain object, we can generate a random domain object, persist it and assert the database contains the same values:
@org.junit.Test
public void testPersistPerson() throws Exception {
// Given
Person person = easyRandom.nextObject(Person.class);
// When
personDao.persist(person);
// Then
assertThat("person_table").column("name").value().isEqualTo(person.getName()); // assretj db
}There are many other uses cases where Easy Random can be useful, you can find a non exhaustive list in the wiki.
- JUnit extension: Use Easy Random to generate random data in JUnit tests (courtesy of glytching)
- Vavr extension: This extension adds support to randomize Vavr types (courtesy of xShadov)
- Protocol Buffers extension: This extension adds support to randomize Protocol Buffers generated types (courtesy of murdos)
- Easy testing with ObjectMothers and EasyRandom
- Quick Guide to EasyRandom in Java
- Top secrets of the efficient test data preparation
- Random Data Generators for API Testing in Java
- EasyRandom 4.0 Released
- Type Erasure Revisited
- Generate Random Test Data With jPopulator
You are welcome to contribute to the project with pull requests on GitHub. Please note that Easy Random is in maintenance mode, which means only pull requests for bug fixes will be considered.
If you believe you found a bug or have any question, please use the issue tracker.
- Adriano Machado
- Alberto Lagna
- Andrew Neal
- Aurélien Mino
- Arne Zelasko
- dadiyang
- Dovid Kopel
- Eric Taix
- euZebe
- Fred Eckertson
- huningd
- Johan Kindgren
- Joren Inghelbrecht
- Jose Manuel Prieto
- kermit-the-frog
- Lucas Andersson
- Michael Düsterhus
- Nikola Milivojevic
- nrenzoni
- Oleksandr Shcherbyna
- Petromir Dzhunev
- Rebecca McQuary
- Rémi Alvergnat
- Rodrigue Alcazar
- Ryan Dunckel
- Sam Van Overmeire
- Valters Vingolds
- Vincent Potucek
- Weronika Redlarska
- Konstantin Lutovich
- Steven_Van_Ophem
- Jean-Michel Leclercq
- Marian Jureczko
- Unconditional One
- JJ1216
- Sergey Chernov
Thank you all for your contributions!
The MIT License. See LICENSE.txt.