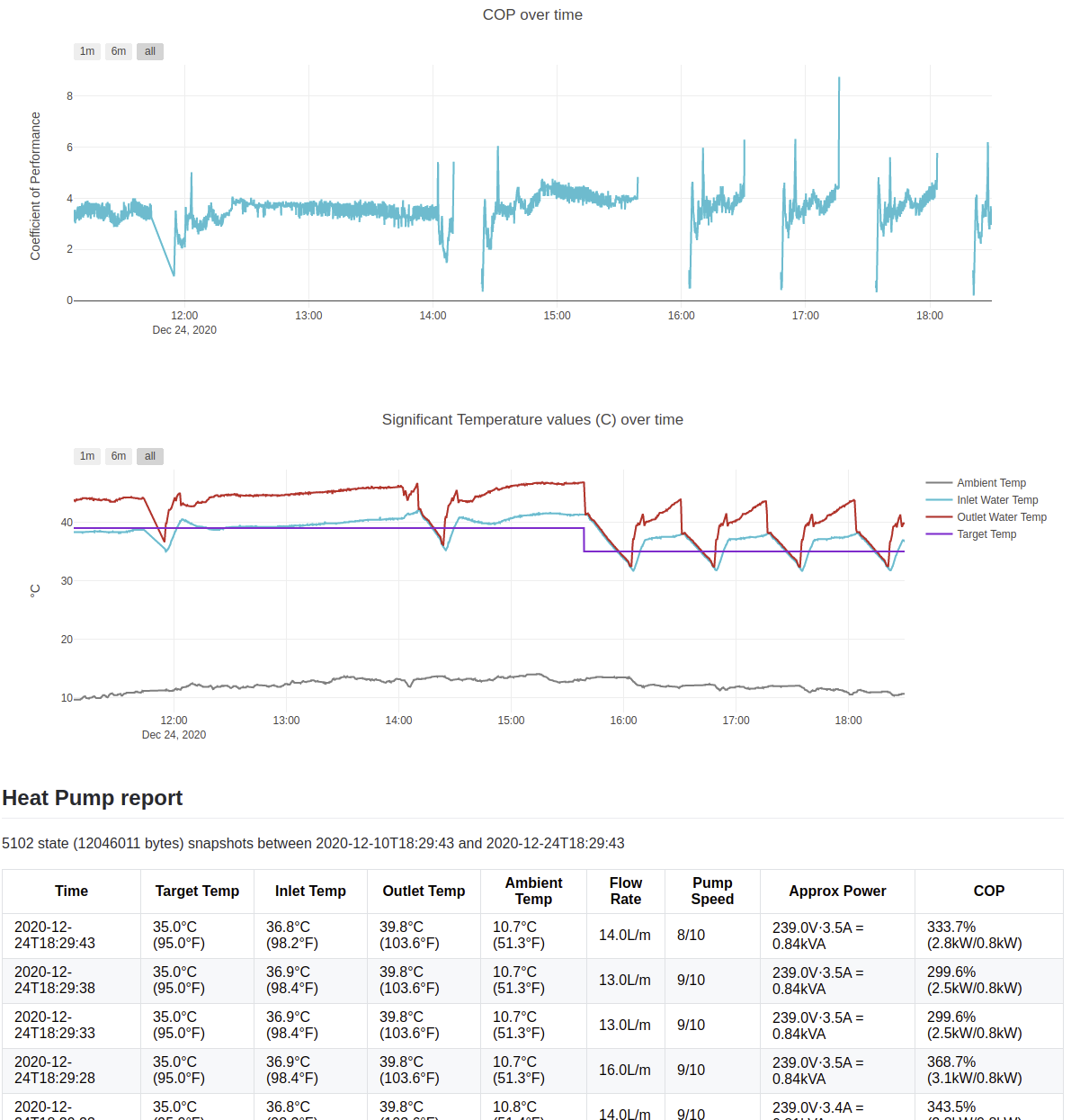
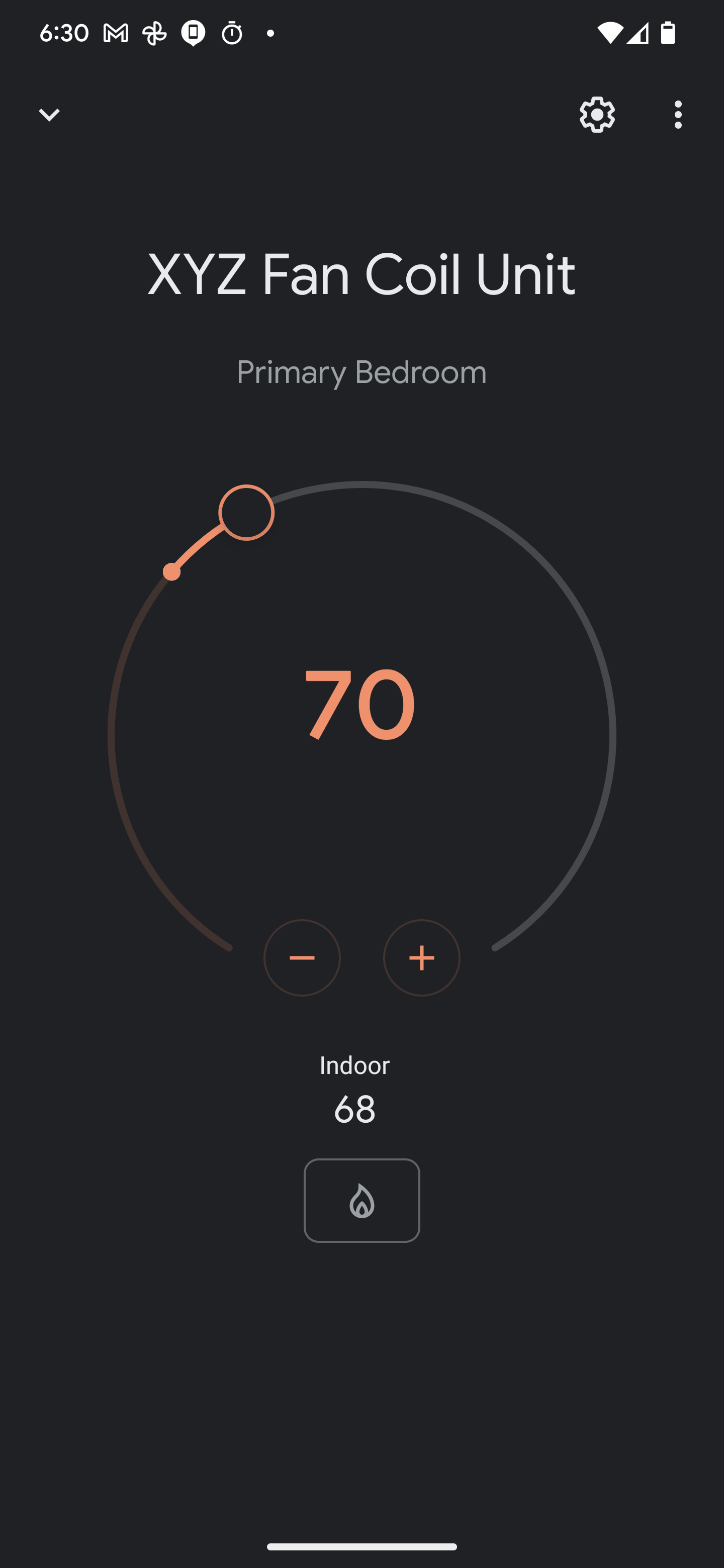
This project is used to communicate with a hydronic heating system that uses the Chiltrix CX34 air-to-water heat pump. The components of the system are as follows:
-
A Raspberry Pi.
-
The Chiltrix CX34 heat pump chiller. The Pi communicates with the chiller using using serial communication, which is used natively by the CX34 to talk with its controller per the wiring diagram and ProtoAir FPA-W44 manual.
-
A USB-to-RS484 dongle that connects the Raspberry Pi to the Chiltrix. This device should show up as
/dev/ttyUSB0. -
Optional DS18B20 temperature sensors, which can now be bought for about $2 each. Several temperature sensors can be connected to single GPIO port on the Pi. I followed this guide to get up and running and then wrote the
github.com/gonzojive/heatpump/tempsensorGo package to read the sensor values.
There is also work in progress Google Home integration, which allows setting the temperature of the fan coil units from the Google Home app. You can also say commands like:
- "Set the temperature to 72 degrees"
- "Set the fan speed to low"
This project is written in Go.
Install go on the Raspberry Pi according to the official instructions.
Install the collector binary as of the latest version:
go install github.com/gonzojive/heatpump/cmd/cx34collector@latest github.com/gonzojive/heatpump/cmd/cx34install@latestInstall the systemd service so the service runs at boot.
sudo `which cx34install`Inspect the logs with
journalctl -u cx34collector.serviceThe Chiltrix uses RS485 to communicate with its controller. I have a USB-to-RS484 with a ch340T chip and pins labelbed "A / D+" and "B / D-".
TODO: more info
My ~/.ssh/config has a section like
Host waterpi
HostName 192.168.86.22
User pi
and the Pi's ~/.ssh/authorized_hosts and /etc/ssh/sshd_config has a section with
# To disable tunneled clear text passwords, change to no here!
PasswordAuthentication no
Mounting the Raspberry Pi's OS can be helpful for developing on a workstation. I followed this guide and ran these commands:
sudo mkdir /mnt/waterpi
sudo chown <YOUR_USERNAME> /mnt/waterpi
sudo sshfs -o "allow_other,default_permissions,IdentityFile=/home/<YOUR_USERNAME>/.ssh/id_rsa" [email protected]:/ /mnt/waterpiThere is a gRPC server that can be started for getting and setting fan coil state. Run this command on the fan coil unit:
go run fancoil/cmd/fancoil_status/fancoil_status.go --alsologtostderr --start-server --grpc-port 8083You can then run the scheduler on the device:
go run fancoil/cmd/fancoil_schedule/fancoil_schedule.go --alsologtostderr --fancoil-service localhost:8083For the Google Home app integration to work, some cloud-hosted services are needed. These can be deployed as follows:
(optional): Build the docker images used to run all of the services. This is
also done automatically by a Cloud Build hook that is triggered by pushes to
main, but it can be useful for pushing local images.
./cloud/deployment/cloudbuild/image-pusher/push-all-images.shTerraform is used to deploy the Cloud Run images based on the contents of
cloud/deployment/terraform/environments/infra-dev/image-versions.json, which
is pulled into the main terraform config
cloud/deployment/terraform/environments/infra-dev/main.tf.
To update the pinned version of the images, run the following:
bazel run --run_under="cd $PWD &&" //cmd/cloud/update-image-versions -- --alsologtostderr --input "cloud/deployment/terraform/environments/infra-dev/image-versions.json" --output "cloud/deployment/terraform/environments/infra-dev/image-versions.json"The following linkes might need to be updated if the Cloud Run deployment changes significantly:
https://console.actions.google.com/u/0/project/hydronics-9f50d/actions/smarthome/ https://console.actions.google.com/u/0/project/hydronics-9f50d/smarthomeaccountlinking/