Before You Begin
Prepare
Start Terraform
To successfully perform this tutorial, you must have the following:
- An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure account. See Signing Up for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- A MacOS, Linux, or Windows environment:
- MacOS
- Linux (Any distribution)
- You can install a Linux VM with an Always Free Compute shape, on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure:
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Cloud Shell:
- Windows 10
- Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
- Git for Windows to access a Linux VM.
Prepare your environment for authenticating and running your Terraform scripts. Also, gather the information your account needs to authenticate the scripts.
Install the latest version of Terraform v1.3.0+:
-
In your environment, check your Terraform version.
terraform -vIf you don't have Terraform v1.3.0+, then install Terraform using the following steps.
-
From a browser, go to Download Latest Terraform Release.
-
Find the link for your environment and then follow the instructions for your environment. Alternatively, you can perform the following steps. Here is an example for installing Terraform v1.3.3 on Linux 64-bit.
-
In your environment, create a temp directory and change to that directory:
mkdir tempcd temp -
Download the Terraform zip file. Example:
wget https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/1.3.3/terraform_1.3.3_linux_amd64.zip -
Unzip the file. Example:
unzip terraform_1.3.3_linux_amd64.zip -
Move the folder to /usr/local/bin or its equivalent in Mac. Example:
sudo mv terraform /usr/local/bin -
Go back to your home directory:
cd -
Check the Terraform version:
terraform -vExample:
Terraform v1.3.3 on linux_amd64.
If you created API keys for the Terraform Set Up Resource Discovery tutorial, then skip this step.
Create RSA keys for API signing into your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure account.
-
Log in to the Oracle Cloud site and access the user portal.
-
Enter the User menu.
-
Choice User Account Name to use.
-
Click api-key in the lower left resource and click add api key
-
Under API Key Pairing, click Download Private Key and Download Public Key, and then click the Add button. If there are more than three API Key, Delete API Key or use another User Account Name.
-
Copy the results from Configuration File Preview onto the notepad.
-
Select Networking from the menu, then select Virtual Cloud Networks
-
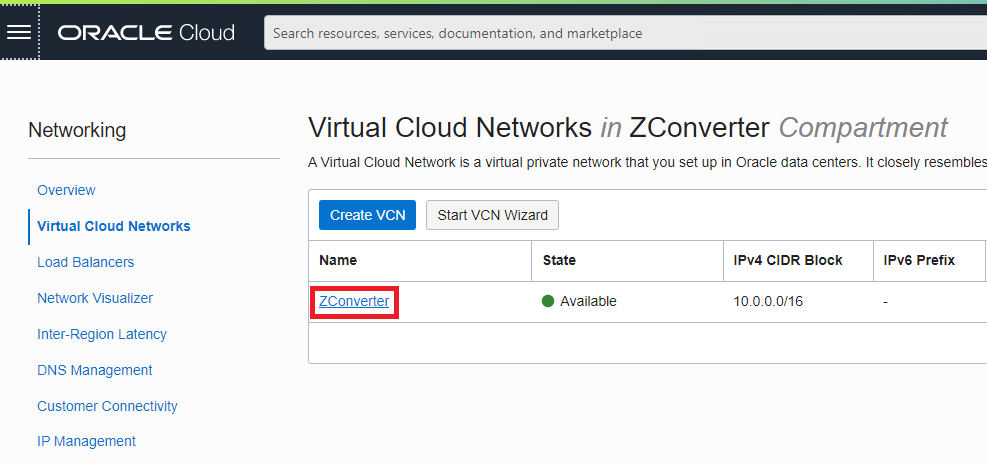
Choice VCN User Account Name to use
-
Choice Subnets Name to use
-
Copy the Subnet OCID onto the notepad
-
Result
- To use terraform, you must have a terraform file of command written and a terraform executable.
- You should create a folder to use terraform, create a terraform.tf file, and enter the contents below.
terraform { required_version = ">= 1.3.0" required_providers { oci = { source = "oracle/oci" version = "4.96.0" } } } provider "oci" { tenancy_ocid = var.terraform_data.provider.tenancy_ocid user_ocid = var.terraform_data.provider.user_ocid fingerprint = var.terraform_data.provider.fingerprint region = var.terraform_data.provider.region private_key_path = var.terraform_data.provider.private_key_path } locals { compartment_ocid = var.terraform_data.vm_info.compartment_ocid == null ? var.terraform_data.provider.tenancy_ocid : var.terraform_data.vm_info.compartment_ocid } variable "terraform_data" { type = object({ provider = object({ tenancy_ocid = string user_ocid = string fingerprint = string private_key_path = string region = string }) vm_info = object({ vm_name = string compartment_ocid = optional(string) user_data_file_path = optional(string) additional_volumes = optional(list(number)) OS = object({ OS_name = string OS_version = string custom_image_name = optional(string) boot_volume_size_in_gbs = optional(number) }) network_interface = object({ subnet_ocid = string create_security_group_rules = optional(list(object({ direction = optional(string) protocol = optional(string) port_range_min = optional(string) port_range_max = optional(string) remote_ip_prefix = optional(string) type = optional(string) code = optional(string) }))) }) shape = object({ shape_name = string shape_cpus = optional(number) shape_memory_in_gbs = optional(number) }) ssh_authorized_keys = optional(object({ ssh_public_key = optional(string) ssh_public_key_file_path = optional(string) })) }) }) default = { provider = { fingerprint = null private_key_path = null region = null tenancy_ocid = null user_ocid = null } vm_info = { additional_volumes = [] compartment_ocid = null network_interface = { create_security_group_rules = [{ code = null direction = null port_range_max = null port_range_min = null protocol = null remote_ip_prefix = null type = null }] subnet_ocid = null } OS = { OS_name = null OS_version = null boot_volume_size_in_gbs = 50 custom_image_name = null } shape = { shape_cpus = 1 shape_memory_in_gbs = 16 shape_name = null } ssh_authorized_keys = { ssh_public_key = null ssh_public_key_file_path = null } user_data_file_path = null vm_name = null } } } module "create_oci_instance" { source = "git::https://github.com/ZConverter-samples/terraform-oci-create-instnace-modules.git" region = var.terraform_data.provider.region vm_name = var.terraform_data.vm_info.vm_name compartment_ocid = local.compartment_ocid user_data_file_path = var.terraform_data.vm_info.user_data_file_path additional_volumes = var.terraform_data.vm_info.additional_volumes OS = var.terraform_data.vm_info.OS.OS_name OS_version = var.terraform_data.vm_info.OS.OS_version custom_image_name = var.terraform_data.vm_info.OS.custom_image_name boot_volume_size_in_gbs = var.terraform_data.vm_info.OS.boot_volume_size_in_gbs subnet_ocid = var.terraform_data.vm_info.network_interface.subnet_ocid create_security_group_rules = var.terraform_data.vm_info.network_interface.create_security_group_rules shape_name = var.terraform_data.vm_info.shape.shape_name shape_cpus = var.terraform_data.vm_info.shape.shape_cpus shape_memory_in_gbs = var.terraform_data.vm_info.shape.shape_memory_in_gbs ssh_public_key = var.terraform_data.vm_info.ssh_authorized_keys.ssh_public_key ssh_public_key_file_path = var.terraform_data.vm_info.ssh_authorized_keys.ssh_public_key_file_path } output "result" { value = module.create_oci_instance.result } - After creating the oci_terraform.json file to enter the user's value, you must enter the contents below.
- The oci_terraform.json below is an example of a required value only. See below the Attributes table for a complete example.
- There is an attribute table for input values under the script, so you must refer to it.
{ "terraform_data" : { "provider" : { "tenancy_ocid" : "ocid1.tenancy.oc1..aaaaaaaa******************", "user_ocid" : "ocid1.user.oc1..aaaaaaaa********************", "fingerprint" : "1a:****************************", "private_key_path" : "C:/Users/opc/terraform/oci_private_key.pem", "region" : "us-ashburn-1" }, "vm_info" : { "vm_name" : "oci_instnace_test", "additional_volumes" : [50], "OS" : { "OS_name" : "CentOS", "OS_version" : "7" }, "shape" : { "shape_name" : "VM.Standard.E4.Flex", "shape_cpus" : 2, "shape_memory_in_gbs" : 4 }, "network_interface" : { "subnet_ocid" : "ocid1.subnet.oc1.us-ashburn-1.aaaaaaaa**************************" }, "ssh_authorized_keys" : { "ssh_public_key" : "ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EA**********************" } } } }
| Attribute | Data Type | Required | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| terraform_data.provider.tenancy_ocid | string | yes | none | The tenancy_ocid you recorded in the memo during the preparation step. |
| terraform_data.provider.user_ocid | string | yes | none | The user_ocid you recorded in the memo during the preparation step. |
| terraform_data.provider.fingerprint | string | yes | none | The fingerprint you recorded in the memo during the preparation step. |
| terraform_data.provider.region | string | yes | none | The region you recorded in the memo during the preparation step. |
| terraform_data.provider.private_key_path | string | yes | none | The absolute path of the private key that you downloaded during the preparation step. |
| terraform_data.vm_info.vm_name | string | yes | none | The name of the instance you want to create. |
| terraform_data.vm_info.compartment_ocid | string | no | terraform_data.provider.tenancy_ocid | Parcel to create an instance (automatically use tenancy_ocid if not entered). |
| terraform_data.vm_info.OS.OS_name | string | yes | none | Enter the OS name you want to create among (Canonical Ubuntu, CentOS, Oracle Autonomous Linux, Oracle Linux, Oracle Linux Cloud Developer, Windows). |
| terraform_data.vm_info.OS.OS_version | string | yes | none | The version of the OS you want to create. |
| terraform_data.vm_info.OS.custom_image_name | string | no | none | Enter the image name when the OS you want to create is a custom user image of the oci. |
| terraform_data.vm_info.OS.boot_volume_size_in_gbs | number | no | 50 | Boot volume size of the instance you want to create. |
| terraform_data.vm_info.shape.shape_name | string | yes | none | Shape types provided by Oracle Cloud. |
| terraform_data.vm_info.shape.shape_cpus | number | conditional | 1 | Number of cpu to use when using instance_type_name as flexible type. |
| terraform_data.vm_info.shape.shape_memory_in_gbs | number | conditional | 16 | Number of memory size to use when using instance_type_name as flexible type. |
| terraform_data.vm_info.network_interface.subnet_ocid | string | yes | none | The subnets in which the instance primary VNICs are created. |
| terraform_data.vm_info.network_interface.create_security_group_rules | list | no | none | When you need to create ingress and egress rules. |
| terraform_data.vm_info.network_interface.create_security_group_rules.[*].direction | stirng | conditional | none | Either "ingress" or "egress" |
| terraform_data.vm_info.network_interface.create_security_group_rules.[*].protocol | string | conditional | none | Enter a supported protocol name |
| terraform_data.vm_info.network_interface.create_security_group_rules.[*].port_range_min | string | conditional | none | Minimum Port Range (Use only when using udp, tcp protocol) |
| terraform_data.vm_info.network_interface.create_security_group_rules.[*].port_range_max | string | conditional | none | Maximum Port Range (Use only when using udp, tcp protocol) |
| terraform_data.vm_info.network_interface.create_security_group_rules.[*].type | string | conditional | none | type number (Use only when using the icmp protocol) |
| terraform_data.vm_info.network_interface.create_security_group_rules.[*].code | string | conditional | none | code number (Use only when using the icmp protocol) |
| terraform_data.vm_info.network_interface.create_security_group_rules.[*].remote_ip_prefix | string | conditional | none | CIDR (ex : 0.0.0.0/0) |
| terraform_data.vm_info.ssh_authorized_keys.ssh_public_key | string | conditional | none | ssh public key to use when using Linux-based OS. (Use only one of the following: ssh_public_key, ssh_public_key_file_path) |
| terraform_data.vm_info.ssh_authorized_keys.ssh_public_key_file_path | string | conditional | none | Absolute path of ssh public key file to use when using Linux-based OS. (Use only one of the following: ssh_public_key, ssh_public_key_file_path) |
| terraform_data.vm_info.user_data_file_path | string | conditional | none | Absolute path of user data file path to use when cloud-init. |
| terraform_data.vm_info.additional_volumes | string | conditional | none | Use to add a block volume. Use numeric arrays. |
-
oci_terraform.json Full Example
{ "terraform_data" : { "provider" : { "tenancy_ocid" : null, "user_ocid" : null, "fingerprint" : null, "private_key_path" : null, "region" : null }, "vm_info" : { "region" : null, "vm_name" : null, "compartment_ocid" : null, "user_data_file_path" : null, "additional_volumes" : null, "OS" : { "OS_name" : null, "OS_version" : null, "custom_image_name" : null, "boot_volume_size_in_gbs" : null }, "shape" : { "shape_name" : null, "shape_cpus" : null, "shape_memory_in_gbs" : null }, "network_interface" : { "subnet_ocid" : null, "create_security_group_rules" : [ { "direction" : null, "protocol" : null, "port_range_min" : null, "port_range_max" : null, "remote_ip_prefix" : null, "type" : null, "code" : null } ] }, "ssh_authorized_keys" : { "ssh_public_key" : null, "ssh_public_key_file_path" : null } } } } -
Go to the file path of Terraform.exe and Initialize the working directory containing the terraform configuration file.
terraform init- Note
-chdir : When you use a chdir the usual way to run Terraform is to first switch to the directory containing the
.tffiles for your root module (for example, using thecdcommand), so that Terraform will find those files automatically without any extra arguments. (ex : terraform -chdir=<terraform data file path> init) - terraform -chdir
- Note
-chdir : When you use a chdir the usual way to run Terraform is to first switch to the directory containing the
-
Creates an execution plan. By default, creating a plan consists of:
- Reading the current state of any already-existing remote objects to make sure that the Terraform state is up-to-date.
- Comparing the current configuration to the prior state and noting any differences.
- Proposing a set of change actions that should, if applied, make the remote objects match the configuration.
terraform plan -var-file=<Absolute path of oci_terraform.json>- Note
- -var-file : When you use a var-file Sets values for potentially many input variables declared in the root module of the configuration, using definitions from a "tfvars" file. Use this option multiple times to include values from more than one file.
- The file name of vars.tfvars can be changed.
-
Executes the actions proposed in a Terraform plan.
terraform apply -var-file=<Absolute path of oci_terraform.json> -auto-approve -
Note
- -auto-approve : Skips interactive approval of plan before applying. This option is ignored when you pass a previously-saved plan file, because Terraform considers you passing the plan file as the approval and so will never prompt in that case.