This repository is part of a blog post: https://deepdrive.pl/wykreslanie-plaszczyzn-na-obrazie-dicom-w-pythonie/
To run this project, you will need to add the following packages:
pydicom
matplotlib
numpy
Also download one of datasets with .dcm extension from FUMPE
Program calculates:
- Pixel spacing
- Slices thickness
- Axial Aspect Ratio
- Sagittal Aspect Ratio
- Coronal Aspect Ratio
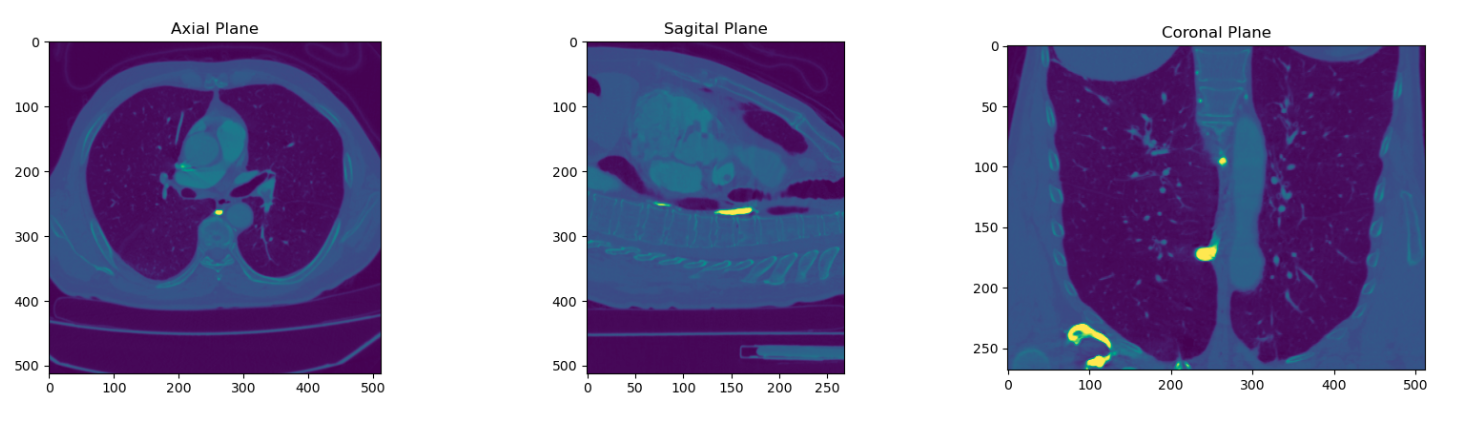
The aspect ratio usually consists of two integers. These values do not represent actual widths and heights, but the ratio between height and width. Axial ratio, for any structure or shape with two, or more, axes, is the ratio of the length (or size) of these axes to each other-the longer axis divided by the shorter. In this case, we divide the retrieved value between pixels: [0.673828, 0.673828], obtaining 1.
The sagittal plane divides a body or organ into two parts: right (dexter) and left (sinister). It is determined by the sagittal axis (axis sagittalis) and the vertical axis (axis verticalis). It is also called the median plane or plane of symmetry because it divides the body into two symmetrical halves: left and right. Further sagittal planes can also be drawn parallel to the sagittal plane. In relation to the sagittal plane, we speak of medial (medialis) and lateral (lateralis) directions. One organ may lie more medially and the other more laterally. It can also have a medial and lateral surface. If the organ is located in the sagittal plane, it will occupy a medial (medianus) position.
The frontal plane (sometimes also called the coronal plane, from the Latin corona, "garland, crown") is any vertical plane that divides the body into ventral and dorsal sections (abdomen and back). The frontal plane is an example of a longitudinal plane, because it is perpendicular to the transverse plane. For humans, the mid-coronal plane would cut the standing body into two halves (front and back or front and back) in an imaginary line that crosses both shoulders. The description of the frontal plane applies to most animals as well as humans, although humans walk upright and the various planes are usually shown in vertical orientation.
Results obtained:
Pixel spacing: [0.673828, 0.673828]
Slice Thickness: 1
Axial Aspect Ratio: 1.0
Sagittal Aspect Ratio: 0.673828
Coronal Aspect Ratio: 1.4840582463180516Implement on base of PyDICOM