This project is an extension that adds MLflow automatic tracing for txtai.
The easiest way to install is via pip and PyPI
pip install mlflow-txtai
The following is a list of examples showing how this plugin works. This notebook also has all of these examples.
The following code initializes the environment. It assumes a mlflow server is running locally. That can be started as follows.
mlflow server --host 127.0.0.1 --port 8000
import mlflow
mlflow.set_tracking_uri(uri="http://localhost:8000")
mlflow.set_experiment("txtai")
# Enable txtai automatic tracing
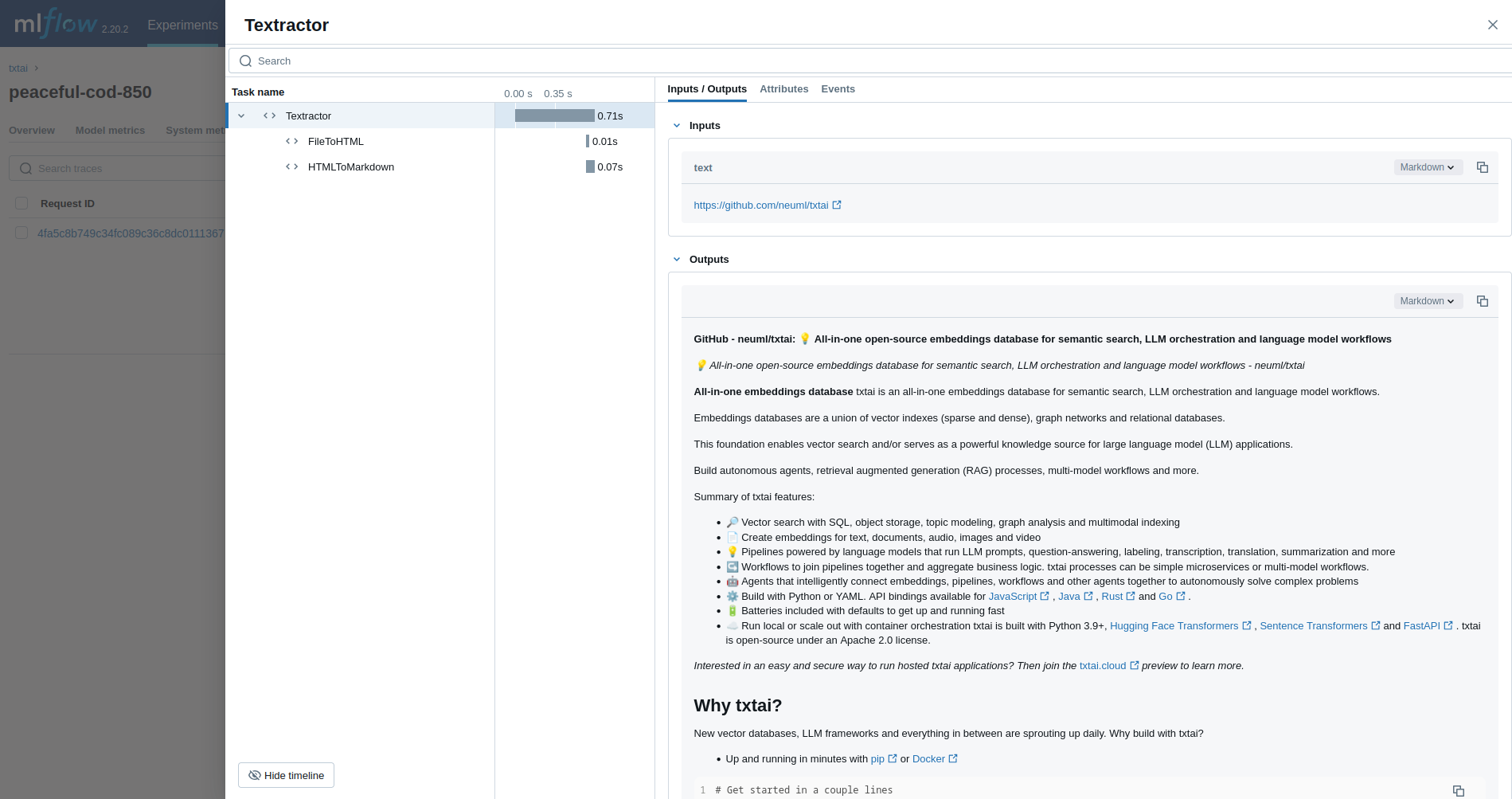
mlflow.txtai.autolog()The first example traces a Textractor pipeline.
from txtai.pipeline import Textractor
with mlflow.start_run():
textractor = Textractor()
textractor("https://github.com/neuml/txtai")Next, we'll trace an Embeddings query.
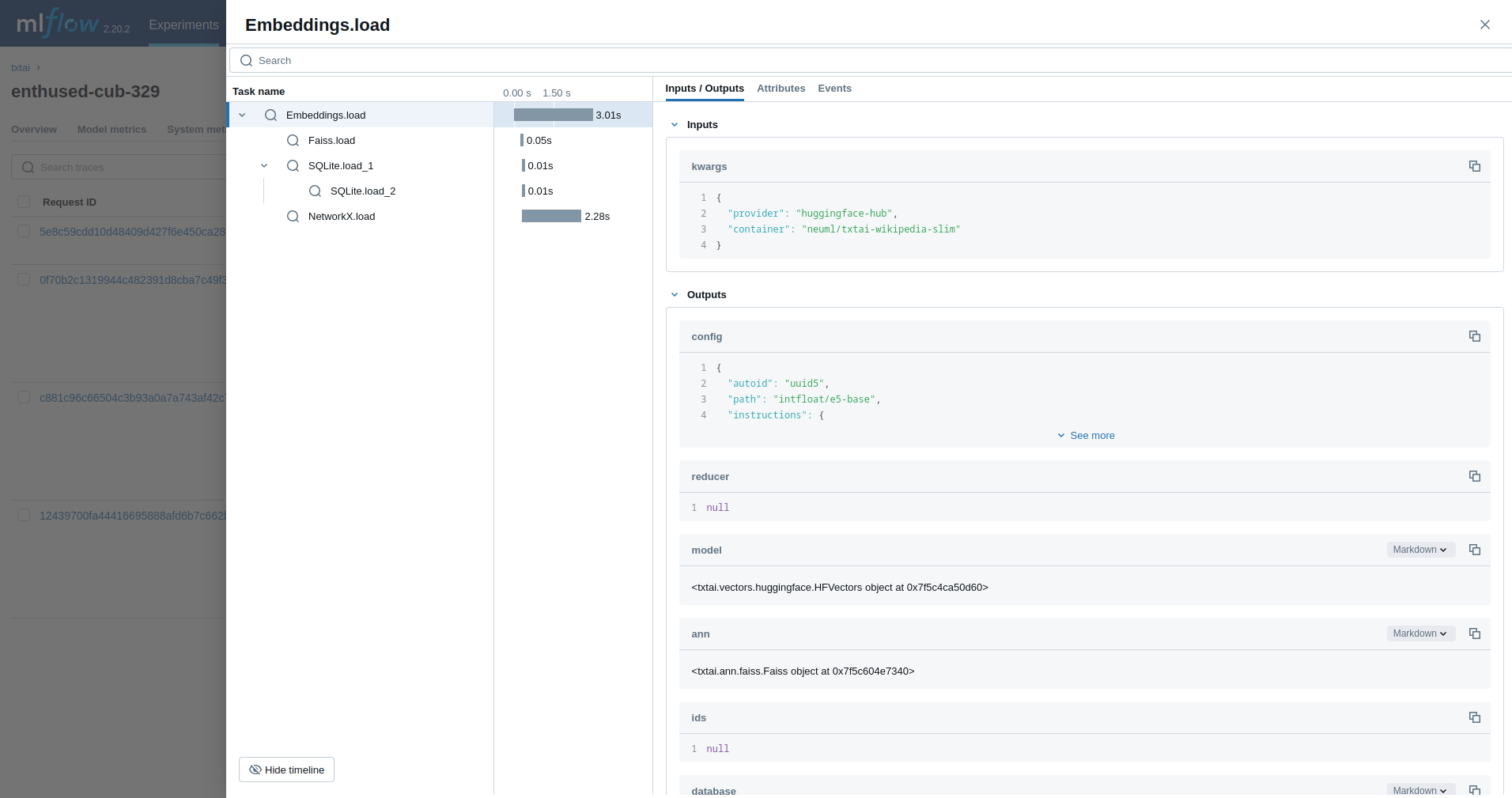
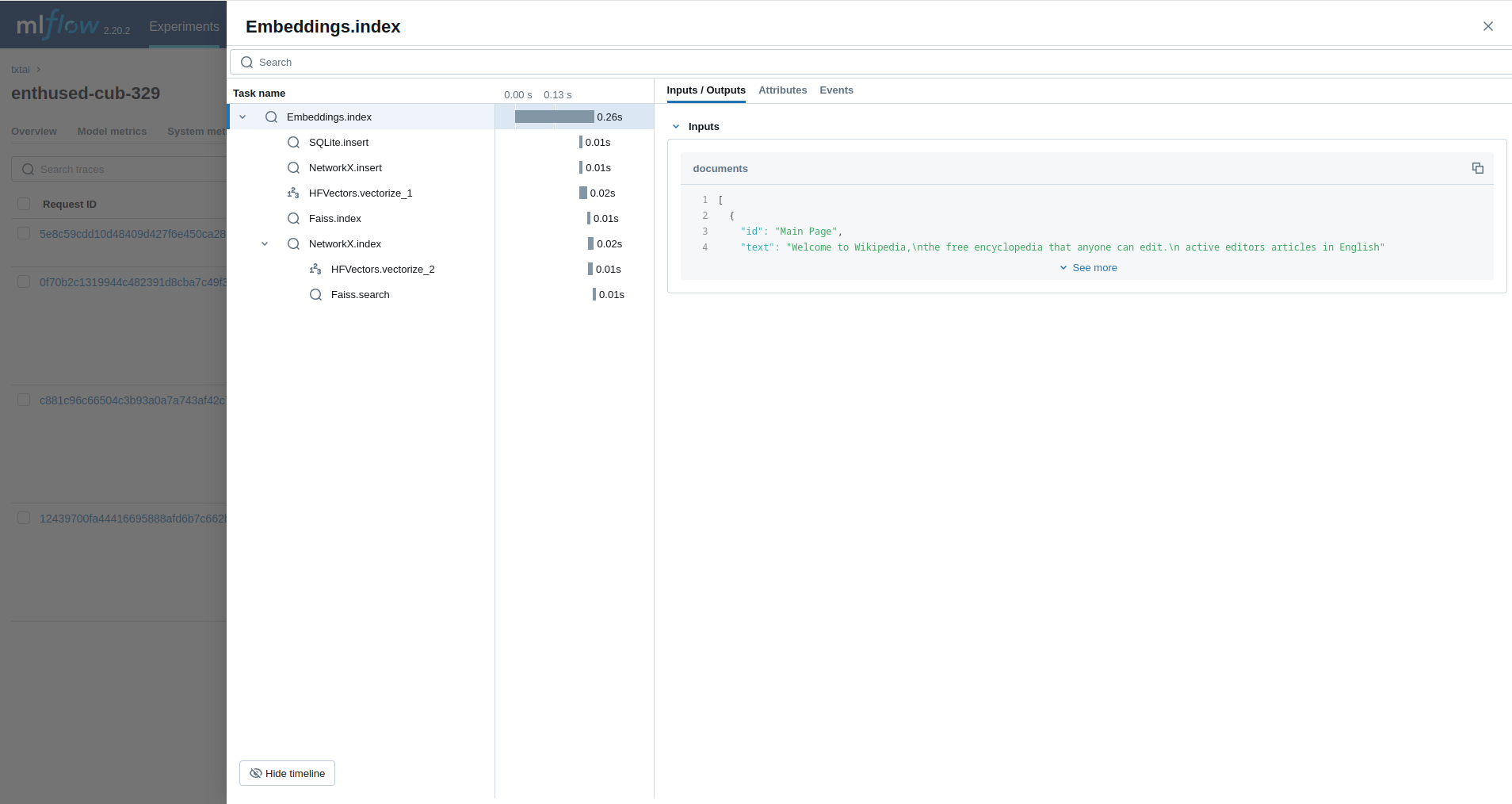
from txtai import Embeddings
with mlflow.start_run():
wiki = Embeddings()
wiki.load(provider="huggingface-hub", container="neuml/txtai-wikipedia-slim")
embeddings = Embeddings(content=True, graph=True)
embeddings.index(wiki.search("SELECT id, text FROM txtai LIMIT 25"))
embeddings.search("MATCH (A)-[]->(B) RETURN A")The next example traces a RAG pipeline.
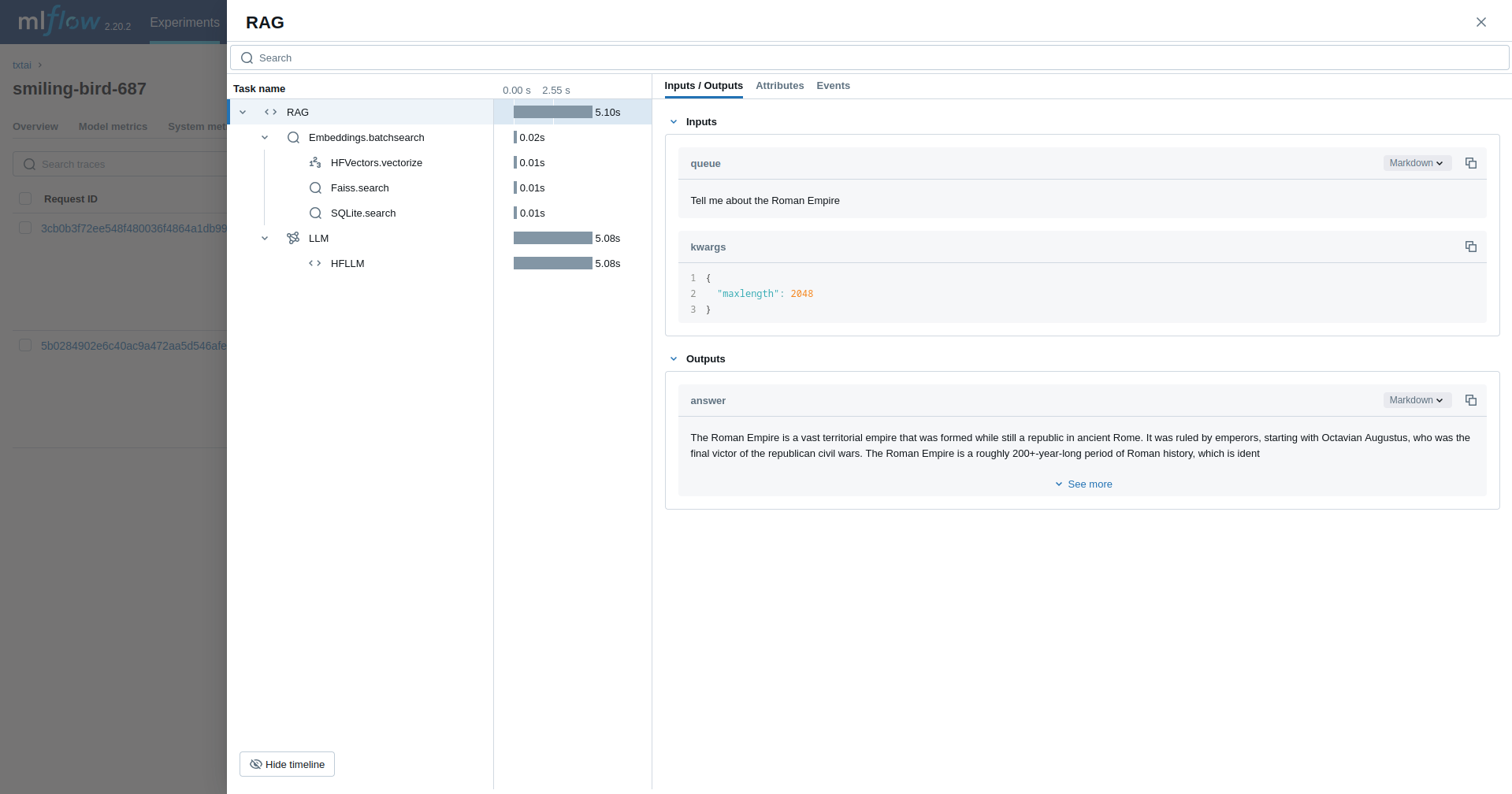
from txtai import Embeddings, RAG
with mlflow.start_run():
wiki = Embeddings()
wiki.load(provider="huggingface-hub", container="neuml/txtai-wikipedia-slim")
# Define prompt template
template = """
Answer the following question using only the context below. Only include information
specifically discussed.
question: {question}
context: {context} """
# Create RAG pipeline
rag = RAG(
wiki,
"hugging-quants/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-AWQ-INT4",
system="You are a friendly assistant. You answer questions from users.",
template=template,
context=10
)
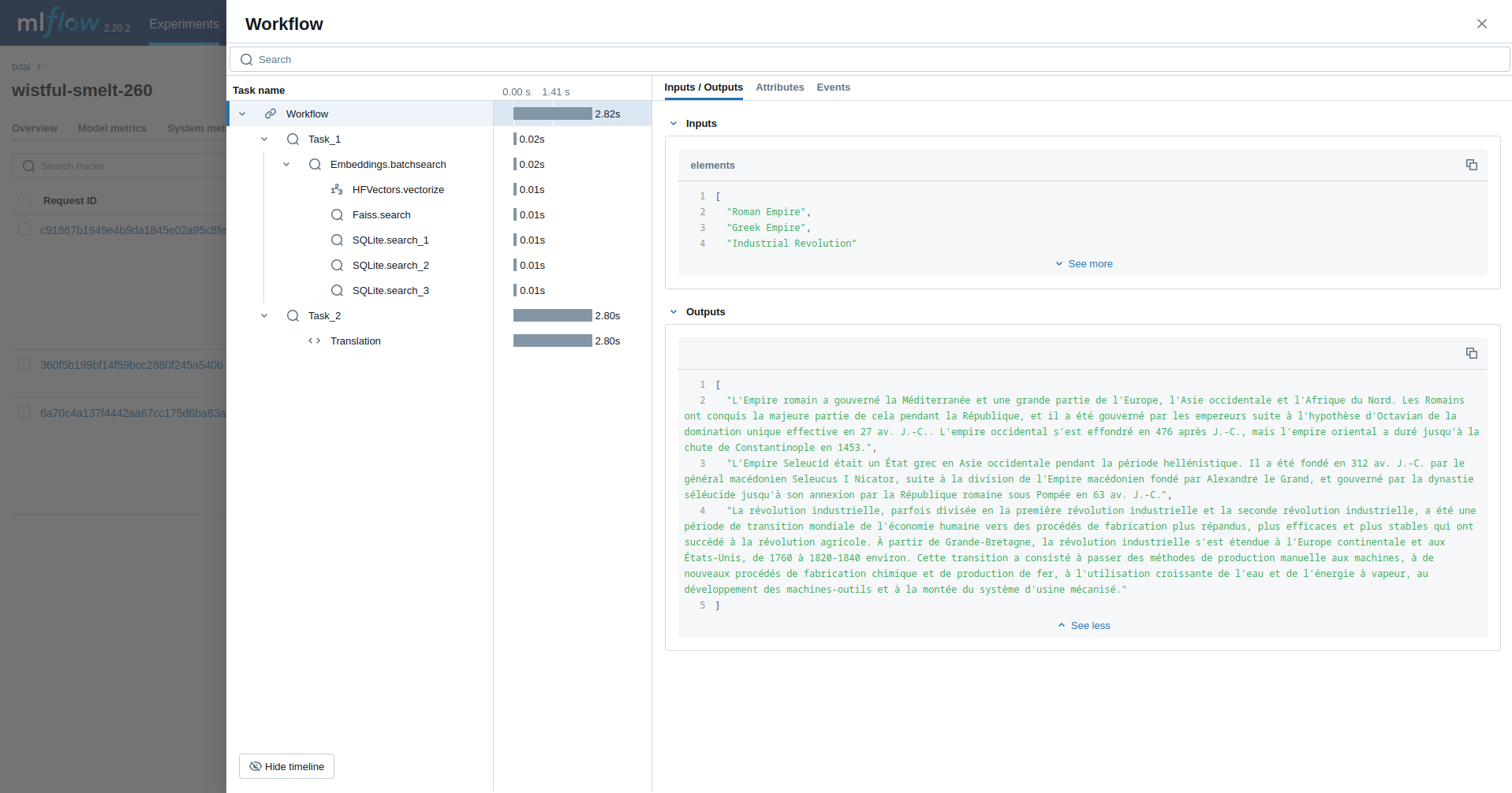
rag("Tell me about the Roman Empire", maxlength=2048)This example runs a workflow. This workflow runs an embeddings query and then translates each result to French.
from txtai import Embeddings, Workflow
from txtai.pipeline import Translation
from txtai.workflow import Task
with mlflow.start_run():
wiki = Embeddings()
wiki.load(provider="huggingface-hub", container="neuml/txtai-wikipedia-slim")
# Translation instance
translate = Translation()
workflow = Workflow([
Task(lambda x: [y[0]["text"] for y in wiki.batchsearch(x, 1)]),
Task(lambda x: translate(x, "fr"))
])
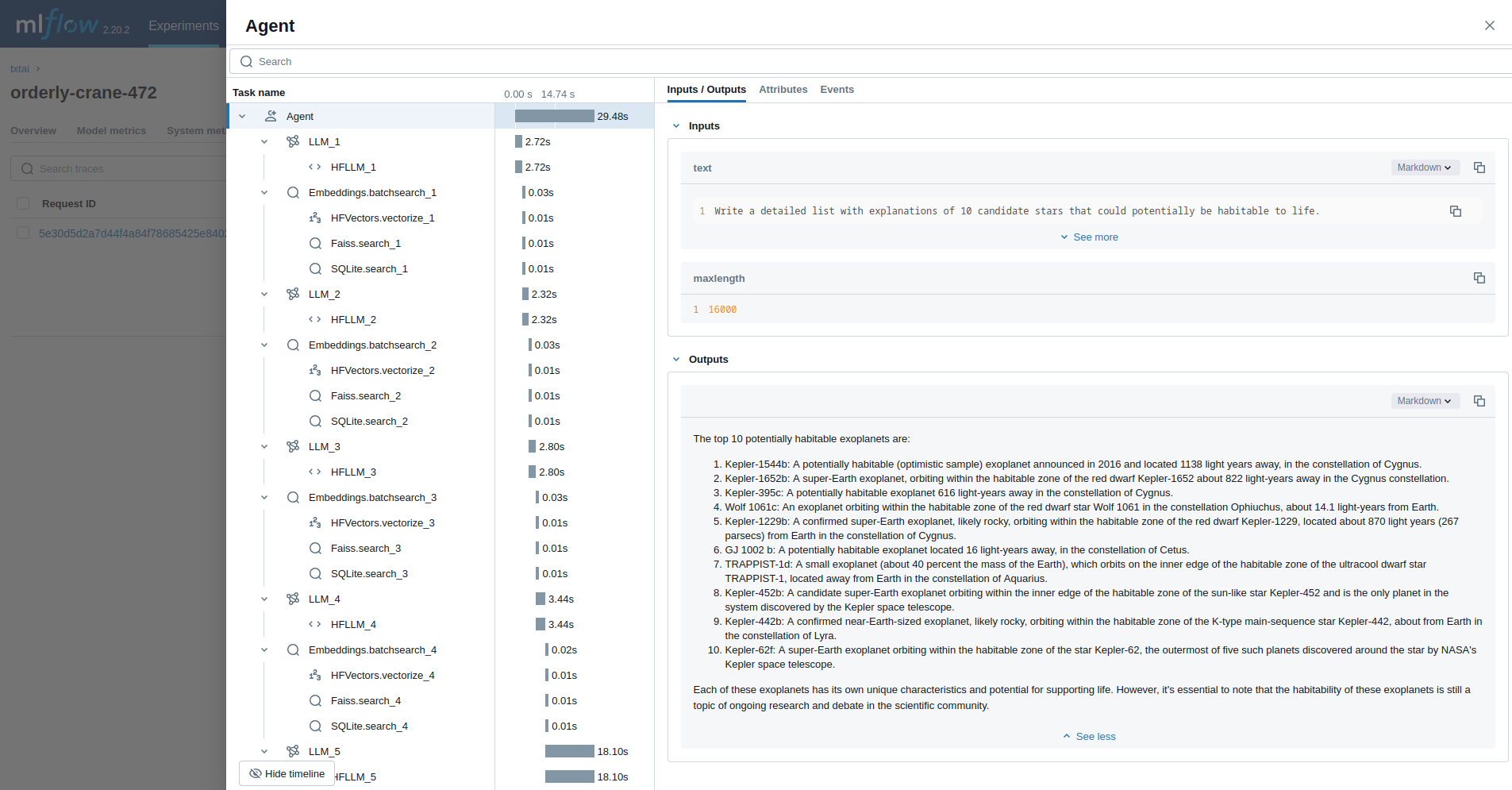
print(list(workflow(["Roman Empire", "Greek Empire", "Industrial Revolution"])))The last example runs a txtai agent designed to research questions on astronomy.
from txtai import Agent, Embeddings
def search(query):
"""
Searches a database of astronomy data.
Make sure to call this tool only with a string input, never use JSON.
Args:
query: concepts to search for using similarity search
Returns:
list of search results with for each match
"""
return embeddings.search(
"SELECT id, text, distance FROM txtai WHERE similar(:query)",
10, parameters={"query": query}
)
embeddings = Embeddings()
embeddings.load(provider="huggingface-hub", container="neuml/txtai-astronomy")
agent = Agent(
tools=[search],
llm="hugging-quants/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-AWQ-INT4",
max_iterations=10,
)
researcher = """
{command}
Do the following.
- Search for results related to the topic.
- Analyze the results
- Continue querying until conclusive answers are found
- Write a Markdown report
"""
with mlflow.start_run():
agent(researcher.format(command="""
Write a detailed list with explanations of 10 candidate stars that could potentially be habitable to life.
"""), maxlength=16000)