You can train your MNIST CNN model by using pytorch (python3), and you can predict a handwritten digit by using libtorch (C++11).
| version | |
|---|---|
| OS | Ubuntu 18.04.2 LTS |
| gcc | 7.4.0 |
| miniconda3 | 4.6.14 |
| python | 3.7.1 |
| opencv | 4.1.0 |
| pytorch & libtorch | 1.1.0 |
-
clone repository
$ cd ${HOME} $ git clone https://github.com/nmatsui/libtorch_pytorch_mnist.git
-
install libraries
$ sudo apt install -y build-essential cmake unzip pkg-config wget $ sudo apt install -y qt5-default libvtk6-dev zlib1g-dev libwebp-dev \ libopenexr-dev libgdal-dev libjpeg-dev libpng-dev \ libtiff-dev libtiff5-dev libv4l-dev libavcodec-dev \ libavformat-dev libswscale-dev libxine2-dev \ libxvidcore-dev libx264-dev libdc1394-22-dev \ libtheora-dev libvorbis-dev libgtk-3-dev libtbb-dev \ libatlas-base-dev libopencore-amrnb-dev \ libopencore-amrwb-dev libeigen3-dev gfortran yasm -
install opencv
$ cd ${HOME} $ wget -O opencv-4.1.0.zip https://github.com/opencv/opencv/archive/4.1.0.zip $ unzip opencv-4.1.0.zip $ cd opencv-4.1.0 $ mkdir build && cd build $ cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RELEASE \ -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local \ -DCMAKE_CXX_FLAGS=-D_GLIBCXX_USE_CXX11_ABI=0 \ -DWITH_QT=ON -DWITH_OPENGL=ON -DFORCE_VTK=ON -DWITH_TBB=ON -DWITH_GDAL=ON \ -DWITH_XINE=ON -DBUILD_EXAMPLES=ON -DENABLE_PRECOMPILED_HEADERS=OFF \ .. $ make -j4 $ sudo make install $ sudo ldconfig -
install libtorch
$ cd ${HOME} $ wget -O libtorch-1.1.zip https://download.pytorch.org/libtorch/cpu/libtorch-shared-with-deps-latest.zip $ unzip libtorch-1.1.zip $ sudo cp -r libtorch/include/* /usr/local/include/ $ sudo cp -r libtorch/lib/* /usr/local/lib/ $ sudo cp -r libtorch/share/* /usr/local/share/ $ sudo ldconfig
-
cd
libtorchdirectory$ cd ${HOME}/libtorch_pytorch_mnist/libtorch -
prepare build directory
$ mkdir build && cd build -
build
$ cmake .. $ make $ cp pimage/predict_image .. $ cp pcamera/predict_camera ..
-
go to the python source directory
$ cd ${HOME}/libtorch_pytorch_mnist/pytorch -
create virtualenv and install required package by using conda
$ conda env create --file conda-linux.yaml $ conda activate pytorch_mnist -
train data
$ ./train.py --epochs 12 ../models/mnist_py.pt ../data-
1st argument: the model weights file to be trained
-
2nd argument: the root directory to be saved MNIST data
-
when training is complete, the loss and accuracy will be displayed like below:
Test set: Average loss: 0.050700, Accuracy: 9847/10000 (98.47%)
-
-
convert the model weights file to be able to use by c++
$ ./convert_model.py ../models/mnist_py.pt ../models/mnist_cpp.pt- 1st argument: trained model weights file
- 2nd argument: the model weights file to be converted for c++
-
go to the python source directory
$ cd ${HOME}/libtorch_pytorch_mnist/pytorch -
predict a handwitten digit like below:
$ ./predict.py ../models/mnist_py.pt ../digit_images/5.png- 1st argument: trained model weights file
- 2nd argument: a handwritten digit image file
-
go to the c++ source directory
$ cd ${HOME}/libtorch_pytorch_mnist/libtorch -
predict a handwitten digit like below:
$ ./predict_image ../models/mnist_cpp.pt ../digit_images/5.png- 1st argument: converted model weights file for c++
- 2nd argument: a handwritten digit image file
-
go to the c++ source directory
$ cd ${HOME}/libtorch_pytorch_mnist/libtorch -
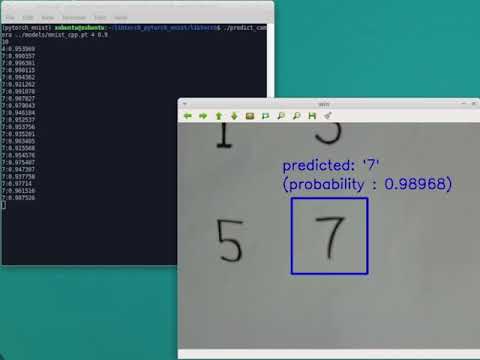
start camera preview like below:
$ ./predict_camera ../models/mnist_cpp.pt 0 0.9- 1st argument: converted model weights file for c++
- 2nd argument: camera device id
- 3rd argument: predict the handwritten digit when the calcurated probability is greater than this float
-
predict the digit when a character is displayed in the green box
Copyright (c) 2019 Nobuyuki Matsui [email protected]