WAPIml is an OpenAPI round-trip tool that leverages model-driven techniques to create, visualize, manage, and generate OpenAPI definitions. WAPIml embeds an OpenAPI metamodel but also a UML profile to enable working with OpenAPI in any Eclipse UML-compatible modeling tool.
N.B. The legacy tool OpenAPItoUML, which generates UML models from OpenAPI definitions, can be found under the branch openapi-to-uml.
- Eclipse Modeling tools (it can be found here).
- Papyrus to visualize the UML model and manage the profile.
- Open Eclipse IDE
- Click on Help / Install New Software...
- Click on Add... and fill in the form as indicated (the update site is https://opendata-for-all.github.io/wapiml/update/wapiml/) then click on OK.
Note: It's normal to get a 404 page if you open the link in the browser (there is no index.html page in the update site directory).
- Select WAPIlml then click on Next.
- Follow the the rest of the steps (license, etc...) and reboot Eclipse.
- Create a Project or use an existing project in your workspace.
- Import your OpenAPI 2 definition into the project (we support both JSON and YAML).
- Right-click on the definition file and select WAPIml/Generate a class diagram to start. This will initiate a wizard to guide the generation process. The first page of the wizard is shown below.
- Check Apply the OpenAPI profile if you want to enrich your UML model with OpenAPI stereotypes (this mandatory if you want to generate an OpenAPI definition later) and check Discover associations if you want the process to discover implicit associations by analyzing schema properties (note: this only concerns the association that are not explicitly defined. Explicit associations will be included in the model either way).
- Click on Next. This will display the second page of the wizard.
- The first table includes the explicit associations defined using JSON Schema (properties of type object or array of objects). You could change the aggregation kind of an association by clicking on its row (the default one is composite).
- The second table shows the discovered associations which are not explicity defined in the definition. You could change the aggregation kind and the target property. You could also delete the association using a right-click on the row of the association and selecting Delete Selection.
- Click on Finish. The generated model are located under the folder src-gen
From a generated model:
- Open the perspective Papyrus.
- Right-click on the generated UML model and select New -> Papyrus Model.
- Follow the steps in the wizard to initialize a Class diagram (keep everything as predefined except in the Initialization information step where you should check Class Diagram as the Respresentation kind).
- Drag-and-drop the UML elements from the Model Explorer into the editor.
- Align and arrange the layout as you prefer.
- Save.
From scratch:
- Open the perspective Papyrus.
- Click on File then select New -> Papyrus Model.
- Follow the steps in the wizard to initialize a Class diagram (keep everything as predefined except in the Initialization information step where you should check Class Diagram as the Representation kind and click on Browse Registered Profiles and select OpenAPI as shown below).
- Add UML elements to the canvas.
- Use the the Properties view to apply the stereotypes and set the tag values (see an example below).
- Switch to the perspective Java.
- Right-click on the annotated UML model and select WAPIml -> Generate an OpenAPI definition in JSON format to generate the definition in JSON or WAPIml -> Generate an OpenAPI definition in YAML format to generate the definition in YAML.
The generated OpenAPI definition will be located under the folder src-gen.
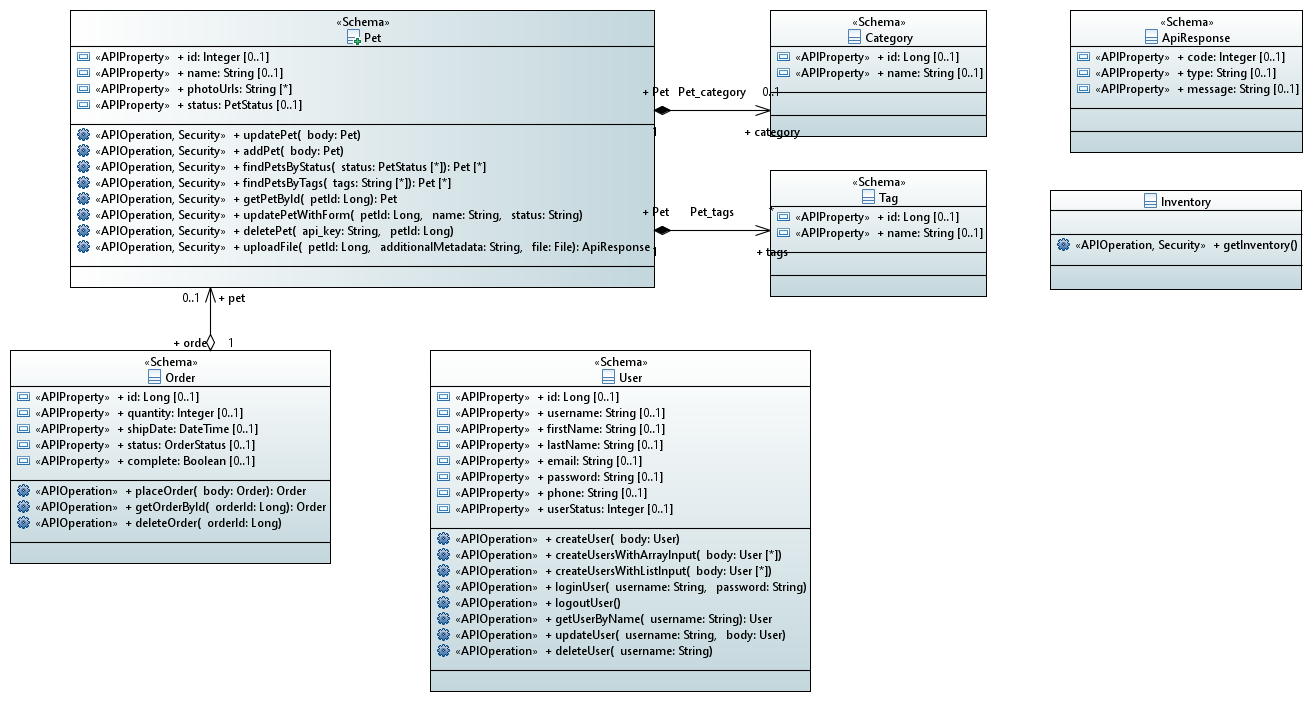
- Each schema definition (#/definitions) of type
objectis represented as a class. - The location of an operation (i.e., in which class it should be) is decided based on the schema this operation produces (response 2xx schema), the schema it consumes (parameter of type body), or the tags properties of the operation. When no class is a good fit for the operation, an artificial class is created to host the operation. The name of such class is inferred from the path of the operation.
- The name of an operation is taken from
operationIdof the operation definition. If such information is not provided the name is created by concatenating the method of the operation (e.g., get, post) plus the name of its class. - The cardinalities of attributes and parameters are inferred from:
- the
typefield (arrayfor multivalued) - the
requiredfield in the OpenAPI definition (note that a required parameter or property of typearraydoesn't not mean that the lower bound should be 1. Empty arrays are still valid). minItemsandmaxItemsforarraytypes.
- the
N.B. This tool relies on the OpenAPI metamodel and the OpenAPI UML profile.