June 2023
tl;dr: Extension of Pix2seq to multiple core vision tasks.
The paper showed that a diverse set of core computer vision tasks can also be unified if formulated in term s of a shared pixel-to-sequence interface. Such tasks includes object detection (the only task supported by pix2seq), instance segmentation, keypoint detection, image captioning.
The formulation of various vision-centric tasks have significant differences in the form of the outputs, customized models with specialized architectures and loss functions are designed for each task. In order to unify them into one single model, a unified interface has to be created.
Pix2seq_v2 expands on pix2seq and defines a new paradigm. Pix2seq is a conditioned sequence generation task (conditioned on heterogeneous features other than this token language). Pix2seq_v2 is a conditioned sequence completion task.
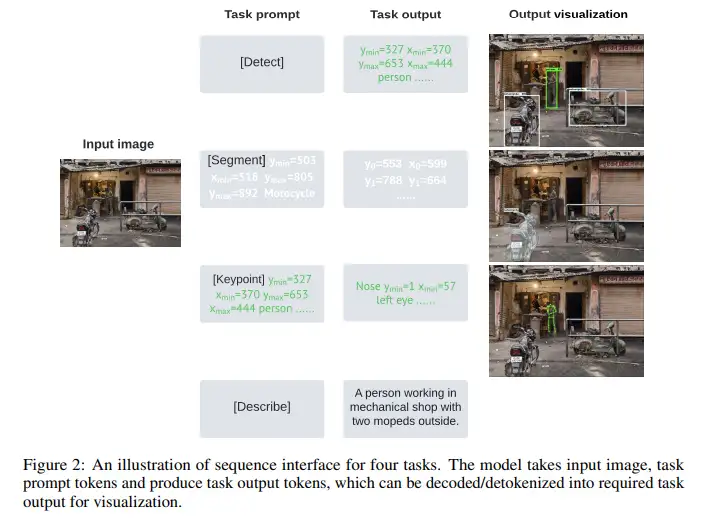
Many vision-centric tasks can be treated as image captioning or visual question answering (VQA) in a specific language dialect, a language spoken in the format of specific json schema, for example.
This work is further extended by Vision LLM which leverages the pretrained LLM.
- Same architecture with pix2seq, but pix2seq_v2 also conditions on a task prompt so that the model can produce outputs adapted to the task of interest. --> Essentially it set a start of the sentence and ask the decoder to finish.
- Unified sequence interface
- Both task description and outputs are expressed as sequences of discrete tokens.
- Task prompt start with special tokens such as
[Detect],[Segment],[Keypoint],[Describe], and[Segment],[Keypoint]tasks are conditioned on a given object instance. The bbox of the object instance is also tokenized and given as part of the prompt, following the practice in pix2seq. - For image captioning directly predict text token. All four tasks share the same vocabulary, so it combines the vision-centric detection language proposed in pix2seq, and the natural language vocab, which should be in the order of 32k or larger. This is much larger than the vocab size for pix2seq.
- Training
- Data mixing: multitask batch. Hard to do data aug in a heterogeneous batch.
- Batch mixing: single-task batch. Adopted by the paper.
- Nucleus sampling is used, similar to pix2seq. Alternatives such as beam search can also be used.
- For instance segmentation, multiple (8) samples are independently drawn and averaged (ensembled) to boost performance.
- For multitask weight tuning is searched greedily by adding one task at a time while keeping the weighting ratio of existing task unchanged.
- For image captioning, BLEU score is used as KPI.
- Interestingly, the region for keypoint detection is twice the bbox size to provide some background for optimal performance.
- Other tasks such as OFA and Flamingo focus on higher level tasks where natural language inherently the desired output. This is different from pix2seq focusing on vision-centric task which requires accurate location.
- Questions and notes on how to improve/revise the current work